Social Justice
India Ageing Report 2023
For Prelims: Poverty, India Ageing Report 2023, UNFPA (United Nations Population Fund), International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS),
For Mains: India Ageing Report 2023 and its Recommendations.
Why in News?
Recently, the UNFPA (United Nations Population Fund) India, in collaboration with the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) has unveiled the India Ageing Report 2023, highlighting the rapidly growing elderly population in India.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Demographic Trends:
- India's elderly population is growing rapidly, with a decadal growth rate of 41%.
- By 2050, over 20% of India's population will be elderly.
- The elderly population in India will surpass the population of children (0 to 15 years old) by 2046.
- The population of people aged 80+ years is expected to increase by around 279% between 2022 and 2050.
- Higher Life Expectancy of Women:
- Women have a higher life expectancy at ages 60 and 80 compared to men, with variations across states and territories.
- For instance, in Himachal Pradesh and Kerala, women at 60 years have a life expectancy of 23 and 22 years, respectively, which is four years greater than men at 60 years in these States — as compared to the national average differential of only 1.5 years.
- Women have a higher life expectancy at ages 60 and 80 compared to men, with variations across states and territories.
- Poverty and Well-being:
- More than 40% of the elderly in India are in the poorest wealth quintile.
- Poverty among the elderly is a concern, affecting their quality of life and healthcare utilization.
- A substantial proportion of elderly individuals, especially women, are living without any income, affecting their quality of life and healthcare utilization.
- More than 40% of the elderly in India are in the poorest wealth quintile.
- Regional Variations:
- There are significant inter-State variations in the elderly population and their growth rates.
- Most States in the southern region and select northern States such as Himachal Pradesh and Punjab reported a higher share of the elderly population than the national average in 2021, a gap that is expected to widen by 2036.
- Sex Ratio of the Elderly Population:
- The sex ratio among the elderly has been climbing steadily since 1991, with the ratio in the general population stagnating.
- Between 2011 and 2021, the ratio increased in India as a whole and across all regions, barring the Union Territories and western India.
- In the northeast and the east, while the sex ratio of the elderly increased, it remained below 1,000 in both years, indicating that men still outnumber the women in these regions even at 60-plus years.
- However in central India, where the sex ratio went from 973 in 2011 to 1,053 in 2021, implying that the women caught up with and outperformed the men in survival after 60 years over the decade.
- The sex ratio among the elderly has been climbing steadily since 1991, with the ratio in the general population stagnating.
- Low Awareness of Social Security Schemes:
- The elderly in India have low awareness about the various social security schemes designed for them.
- A little more than half of the elderly (55%) are aware of the old-age pension scheme (IGNOAPS); 44% about the widow pension scheme (IGNWPS); and 12% about the Annapurna Scheme.
- Concern and Challenges:
- Poverty is inherently gendered in old age when older women are more likely to be widowed, living alone, with no income and with fewer assets of their own, and fully dependent on family for support.
- The major challenges facing India’s aging population are the feminisation and ruralisation of this older population.
What are the Recommendations of the Report?
- Address the lack of credible data on various issues related to the elderly by including relevant questions in data collection exercises such as the National Sample Survey, the National Family Health Survey, and the Census of India. This will help in informed policymaking.
- Increase awareness about existing schemes for older persons and bring all Old Age Homes under regulatory purview. Encourage the creation and running of elderly self-help groups.
- Emphasize the importance of elderly people living in multigenerational households. Encourage policies that facilitate and support this living arrangement.
- Encourage in situ (at home) ageing as much as possible by creating short-term care facilities like creches or day-care facilities. The report suggests that elderly people receive better care when living with their respective families.
What is the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA)?
- About:
- It is a subsidiary organ of the UN General Assembly and works as a sexual and reproductive health agency.
- The UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) establishes its mandate.
- Establishment:
- It was established as a trust fund in 1967 and began operations in 1969.
- In 1987, it was officially renamed the United Nations Population Fund but the original abbreviation, ‘UNFPA’ for the United Nations Fund for Population Activities was retained.
- Objective:
- UNFPA works directly to tackle Sustainable Development Goals on health (SDG3), education (SDG4) and gender equality (SDG5).
- Fund:
- UNFPA is not supported by the UN budget, instead, it is entirely supported by voluntary contributions of donor governments, intergovernmental organizations, the private sector, foundations and individuals.


International Relations
Significance of Indo-Pacific
For Prelims: South China Sea, Comprehensive Strategic Partnerships, Paris Peace Accords
For Mains: The impact of USA’s venture into Asia Pacific on Asian Giants and South-East Asian countries vis-a-vis China
Why in News?
The General Secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam and the U.S. President met in Vietnam during the visit of the US President, marking a new phase in the bilateral relationship between the two countries.
- Both nations elevated their cooperation to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership from a Comprehensive Partnership forged in 2013.
How were the US-Vietnam Relations in the Past?
- The United States and Vietnam have a complex history marked by the Vietnam War, which lasted from 1955 to 1975. The conflict arose during the Cold War when North Vietnam, backed by the Soviet Union and China, sought to reunify with South Vietnam, supported by the United States and other Western allies.
- The war resulted in significant loss of life and widespread destruction in Vietnam and had a profound impact on U.S. society.
- In 1975, the war ended with the fall of Saigon to North Vietnamese forces, leading to the reunification of Vietnam under communist control. This marked a low point in U.S.-Vietnam relations.
- In 1995, the United States normalized diplomatic ties with Vietnam, and the two countries have since engaged in economic cooperation and increased people-to-people exchanges.
- Today, while the Vietnam War remains a part of their history, the United States and Vietnam have developed a more positive and constructive relationship, focusing on trade, security cooperation, and addressing common regional challenges.
What is the Indo-Pacific?
- About:
- Indo-Pacific is a recent concept. It was about a decade ago that the world started talking about the Indo-Pacific; its rise has been quite significant.
- One of the reasons behind the popularity of this term is an understanding that the Indian and the Pacific Oceans are a linked strategic theater.
- Each and every nation perceives the concept of the Indo-Pacific with its own benefits and concerns and there are no absolute concepts and geographical boundaries of the Indo-Pacific.
- Present Context:
- The Indo-Pacific region is one of the most populous and economically active regions of the world which includes four continents: Asia, Africa, Australia and America.
- The dynamism and vitality of the region are self-evident, 60% of the world's population and 2/3rd of the global economic output makes this region a global economic center.
- India’s Perspective of the Indo-Pacific:
- Cooperate with Others for Security Architecture: A lot of India’s special partners, the US, Australia, Japan and Indonesia want India’s presence in the South China Sea, and East China Sea, basically to counter China.
- India, however, seeks to cooperate for an architecture for peace and security in the region. The common prosperity and security require the countries to evolve, through dialogue, a common rules-based order for the region.
- Equal Share in Trade and Investment: India supports a rule-based, open, balanced and stable trade environment in the Indo-Pacific Region, which lifts up all nations on the tide of trade and investment.
- This is the same as what the country expects from the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
- Cooperate with Others for Security Architecture: A lot of India’s special partners, the US, Australia, Japan and Indonesia want India’s presence in the South China Sea, and East China Sea, basically to counter China.
- Importance of Indo-Pacific for ASEAN countries Like Vietnam:
- Unified ASEAN: Unlike China, India seeks a unified ASEAN, not a divided one. China tries to play off some ASEAN members against others, thereby in a way executing a ‘divide and rule’ conquest strategy.
- Work in Collaboration with China: ASEAN does not comply with the US version of Indo-Pacific, which seeks to contain Chinese dominance. ASEAN is rather looking for ways through which it can work together with China.
What is the Significance of the Indo-Pacific?
- Indo-Pacific Extends from Africa to America:
- For America, Indo-Pacific stands for a free, open, inclusive region. It includes all nations in the geography and also others who have a stake in it.
- In its geographical dimension, the US considers the area from the shores of Africa to the shores of the US.
- Against Dominance of a Single Player:
- India is looking to democratise the region. Earlier, the region used to be almost like an American lake. However, there exists a fear that the region will become a Chinese lake. The US, like India, doesn't want the hegemony of any player in the region.
- Geopolitical Importance:
- The Indo-Pacific region is home to some of the world's most populous and economically dynamic countries, including India, China, Japan, Australia, and Indonesia.
- This concentration of economic and political power makes it a critical center of global geopolitics.
- The Indo-Pacific region is home to some of the world's most populous and economically dynamic countries, including India, China, Japan, Australia, and Indonesia.
- Economic Significance:
- The region is a major driver of the global economy. It contains key maritime trade routes, such as the Strait of Malacca, through which a significant portion of the world's trade flows.
- Many of the world's busiest and most important ports are located in the Indo-Pacific, facilitating trade between Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- The region is a major driver of the global economy. It contains key maritime trade routes, such as the Strait of Malacca, through which a significant portion of the world's trade flows.
- Security and Strategic Concerns:
- The Indo-Pacific is a region of increasing strategic competition among major powers, notably the United States, China, India, and Russia. The presence of nuclear-armed states and unresolved territorial disputes, such as the South China Sea disputes, add to its strategic complexity.
- Balancing China's Rise:
- The rise of China as a global economic and military power is a central factor in the Indo-Pacific's significance.
- Many countries in the region are seeking to balance China's influence and ensure their own security by strengthening alliances and partnerships with like-minded nations.
- Maritime Security:
- Ensuring the security of maritime trade routes is a major concern for countries in the Indo-Pacific.
- Issues such as piracy, territorial disputes, and the need to protect sea lanes make maritime security a top priority.
- Regional Organizations and Forums:
- Various regional organizations and forums, such as ASEAN, QUAD, and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), are actively engaged in addressing regional issues, promoting economic cooperation, and enhancing security.
- Connectivity and Infrastructure Development:
- There is a growing focus on infrastructure development, connectivity projects, and economic integration in the Indo-Pacific.
- Initiatives like China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the U.S. "Free and Open Indo-Pacific" strategy aim to shape the economic and political landscape of the region.
- Environmental and Ecological Significance:
- The Indo-Pacific is home to diverse ecosystems, including coral reefs and marine biodiversity.
- Climate change and environmental issues, such as plastic pollution and overfishing, are of global concern, as they affect not only the region's nations but also the entire planet.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.With reference to “Look East Policy” of India, consider the following statements: (2011)
- India wants to establish itself as an important regional player in East Asian affairs.
- India wants to plug the vacuum created by the termination of the Cold War.
- India wants to restore the historical and cultural ties with its neighbors in Southeast and East Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q1. The new tri-nation partnership AUKUS is aimed at countering China’s ambitions in the Indo-Pacific region. Is it going to supersede the existing partnerships in the region? Discuss the strength and impact of AUKUS in the present scenario. (2021)


Economy
Palm-Oil Production
For Prelims: European Union, EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR), Palm oil, China, National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm
For Mains: Impact of European Union’s initiatives to control Palm-Oil production on India’s Palm-Oil Policy.
Why in News?
The European Union (EU) has taken significant steps in recent years to address deforestation and environmental concerns through the EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) related to palm oil production and made massive efforts to phase out palm oil-based biofuels by 2030.
- Malaysia's signing of a deal to double palm oil exports to China annually is a move to offset potential revenue losses from the EU’s ban on commodities that are linked to deforestation.
What is the EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) and Malaysia and Indonesia’s Reactions?
- EUDR:
- This aims at removing deforestation from supply chains of everyday items in the EU. Legislation adopted in Brussels in 2023 with 2030 as the target and Imposes administrative burdens on palm oil exporters wanting to sell in the EU.
- Apart from this, Biofuels, palm oil, and deforestation are the core focus areas of Palm Oil Policy and Deforestation Legislation.
- The regulation requires firms to ensure that the product exported to the EU has been grown on land which has not been deforested after December 31, 2020.
- The regulation is not WTO (World Trade Organization) compatible and a non-tariff barrier.
- Malaysia and Indonesia’s Response:
- Widespread opposition to perceived European protectionism through this legislation.
- It would promote dependency on China for exports, which could nullify environmental benefits.
- Implications for the EU are immense and Chinese markets can benefit from it tremendously.
What is Palm Oil & Its Use?
- About:
- Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms.
- It is used as cooking oil, and in everything from cosmetics, processed foods, cakes, chocolates, spreads, soaps, shampoo, and cleaning products to biofuel.
- The use of crude palm oil in making biodiesel is being branded as ‘green diesel’.
- Production:
- Indonesia and Malaysia together account for almost 90% of the global palm oil production, with Indonesia producing the largest quantity at over 45 million tonnes in 2021.
- Issues with Oil Palm Industry:
- The oil palm industry has come under criticism for what are reportedly unsustainable production practices leading to deforestation, and exploitative labor practices carried forward from the colonial era.
- However, palm oil is preferred by many as it is inexpensive, oil palms produce more oil per hectare than some other vegetable oil plants like soybean.
How Important is Palm Oil for Global Supply Chains?
- Global Supply Chain:
- Palm oil is the world’s most widely used vegetable oil with its global production in the year 2020 being over 73 Million Tones (MT), according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
- It is estimated to be 77 MT for the current year FY 2022-23.
- According to Reuters, palm oil makes up 40% of the global supply of the four most widely used edible oils: palm, soybean, rapeseed (canola), and sunflower oil.
- Indonesia is responsible for 60% of the global supply of palm oil.
- Palm oil is the world’s most widely used vegetable oil with its global production in the year 2020 being over 73 Million Tones (MT), according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
- Status of India in Palm Oil Import:
- India is the biggest importer of palm oil, which makes up 40% of its vegetable oil consumption. India meets half of its annual need for 8.3 MT of palm oil from Indonesia.
- In 2021, India unveiled the National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm to boost India’s domestic palm oil production.
- Given advantages pertaining to Palm oil for India’s cooking requirements, the Indian farmers should be incentivized to intensify efforts for area expansion under oil palm to enhance palm oil production in the country.
- India should also diversify its procurement as well as requirements.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The quantity of imported edible oils is more than the domestic production of edible oils in the last five years.
- The Government does not impose any customs duty on all the imported edible oils as a special case.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q2. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? (2012)
- To enable them to withstand drought
- To increase the nutritive value of the produce
- To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations
- To increase their shelf life
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)


Governance
ECI Clarifies Aadhaar Linkage with Electoral Roll is Voluntary
For Prelims: Aadhaar, Election Commission of India (ECI)
For Mains: Impacts of Linking Electoral Roll with Aadhaar.
Why in News?
In a recent plea before the Supreme Court of India, the Election Commission of India (ECI) clarified that the linking of Aadhaar numbers with the Electoral roll is not mandatory.
Note:
- An electoral roll is a list of eligible voters in a specific jurisdiction, prepared and updated by the ECI.
What are the Concerns Regarding Aadhaar Linkage with the Electoral Roll?
- The Plea:
- Background:
- A petitioner, filed a plea urging the court to direct the Centre and the ECI to amend the application forms for enrolment and update electoral rolls on amended provisions/ rules notified by the Union of India for the authentication of Aadhaar number with the electoral rolls on or before 1st April 2023.
- Concerns Raised:
- The Petitioner expressed concerns about voter privacy and alleged that the Centre and EC were compelling voters to submit their Aadhaar numbers without providing an alternative option.
- Legal Stand:
- This practice violated Articles 14 and 21 of the Constitution and could lead to the misuse of voters' personal data.
- Background:
- Supreme Court's Decision:
- The Supreme Court recorded that the submission of Aadhaar numbers is not mandatory according to Rule 26-B of the Registration of Electors (Amendment) Rules 2022.
- Rule 26B, dealing with “special provision for providing Aadhaar number by existing electors”, states that “every person whose name is listed in the roll may intimate his Aadhaar number to the registration officer in Form 6B in accordance with sub-section (5) of Section 23 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950.
- Form 6B is a letter of information that contains a person's Aadhaar number for the purpose of electoral roll authentication.
- Rule 26B, dealing with “special provision for providing Aadhaar number by existing electors”, states that “every person whose name is listed in the roll may intimate his Aadhaar number to the registration officer in Form 6B in accordance with sub-section (5) of Section 23 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950.
- The Supreme Court recorded that the submission of Aadhaar numbers is not mandatory according to Rule 26-B of the Registration of Electors (Amendment) Rules 2022.
- ECI's Response:
- The ECI's response was that the submission of Aadhaar numbers is voluntary. The EC is considering making appropriate clarificatory changes to the forms related to the Aadhaar linkage, indicating its intent to clarify the voluntary nature of the Aadhaar submission.
- The poll body informed the Bench that “nearly 66.23 crore Aadhaar numbers have already been uploaded in the process of finalizing electoral rolls”.
The Election Commission of India (ECI)
- Establishment and Role:
- The ECI was established on January 25, 1950, in accordance with the Indian Constitution.
- It is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for overseeing and managing both Union and State election processes in India.
- The commission's secretariat is based in New Delhi.
- The ECI administers elections for the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, and State Legislative Assemblies in India. It also oversees the elections for the offices of the President and Vice President of India.
- It is not concerned with the elections to panchayats and municipalities in the states. For this, the Constitution of India provides for a separate State Election Commission.
- Structure of the ECI:
- Originally, the commission had one election commissioner, but it became a multi-member body after the Election Commissioner Amendment Act 1989.
- The Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and two Election Commissioners (ECs) make up the Election Commission of India.
- The CEC and ECs have the same powers and salaries as a Supreme Court judge.
- At the state level, the Chief Electoral Officer, typically an IAS rank officer, supports the election commission in its duties.
- Originally, the commission had one election commissioner, but it became a multi-member body after the Election Commissioner Amendment Act 1989.
- Appointment and Tenure of Commissioners:
- The President of India appoints the CEC and Election Commissioners.
- They serve fixed terms of 6 years or until the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- Removal of Commissioners:
- Commissioners can resign voluntarily or be removed before their term expires.
- The CEC can be removed from office only through a process of removal similar to that of a SC judge by Parliament.
- Limitations:
- The Constitution has not prescribed the qualifications (legal, educational, administrative or judicial) of the members of the Election Commission.
- The Constitution has not specified the term of the members of the Election Commission.
- The Constitution has not debarred the retiring election commissioners from any further appointment by the government.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
- Once issued, Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2024
Why in News?
Recently, 20th Edition of the Times Higher Education (THE) World University Rankings 2024 have been released, in which as many as 91 Indian institutes have secured a place.
- The 2024 rankings include 1,904 universities from 108 countries and regions.
Note:
- THE, formerly known as The Times Higher Education Supplement (THES), is a magazine reporting specifically on news and issues related to higher education.
What are the Key Highlights of THE World University Rankings 2024?
- Parameters:
- The 2024 Rankings comprehensively assess research-intensive universities worldwide based on 18 key indicators across five areas: teaching (29.5%), research environment (29%), research quality (30%), industry (4%), and international outlook (7.5%).
- Indian Universities' Performance:
- Ranking Details:
- The top university in India, the Indian Institute of Science (IISC), has returned to the global top 250, coming in the 201-250 band, for the first time since 2017.
- The second highest ranked universities in India are Anna University, Jamia Millia Islamia, Mahatma Gandhi University, Shoolini University of Biotechnology and Management Sciences, which are all in the 501-600 band.
- Indian universities made significant gains this year, including five of the countries’ top universities.
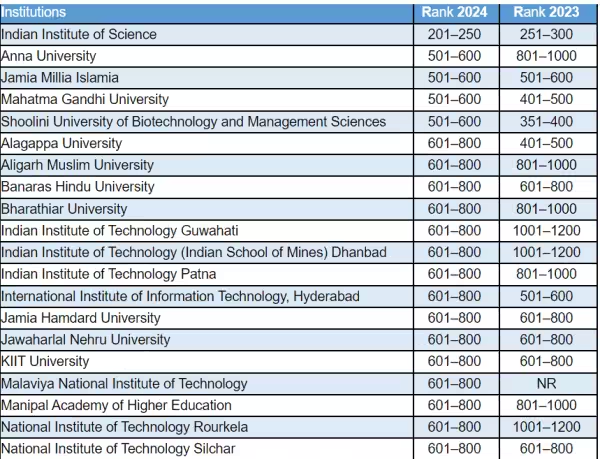
- Fourth Best-Represented Nation:
- India is now the fourth best-represented nation in the THE World University Rankings, with a record-breaking 91 Indian institutions included in the list.
- Ranking Details:
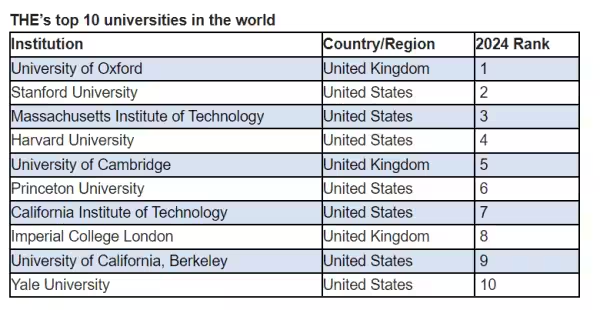
- Global Universities:
- Top Universities:
- Asian Universities' Representation:
- Asia is the most represented continent in the rankings, with 737 universities participating. China and Japan have notably improved their rankings, contributing to the increase in Asian universities in the top 200.
What are the Indian Initiatives Related to Education?


Important Facts For Prelims
Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana
Why in News?
In a significant initiative to empower senior citizens and persons with disabilities across India, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India, organized 'Samajik Adhikarita Shivirs' camps at 72 locations simultaneously.
- These camps aim to distribute various types of aid and assistive devices to over 12000 persons with disabilities and senior citizens under the Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana.
What is the Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana?
- About:
- It was launched in 2017 by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It is a central sector scheme funded from the Senior Citizens’ Welfare Fund.
- The Scheme is being implemented by the Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation (ALIMCO), a PSU (Public Sector Undertaking) under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- Features:
- The eligibility criteria for the scheme are: Senior Citizens, belonging to Below Poverty Line(BPL) category and suffering from any of the age related disability or infirmity.
- The scheme works by distributing free of cost devices, commensurate with the extent of disability or infirmity that is manifested among the eligible senior citizens.
- The devices supported under the scheme are: Walking sticks, Elbow crutches, Walkers/Crutches, Hearing Aids, Wheelchair, Artificial Dentures and Spectacles.
- The scheme is expected to benefit over 5 lakh Senior Citizens across the country.
What are the Other Initiatives Related to Elderly in India?
- National Policy on Older Persons (NPOP).
- National Social Assistance Programme.
- Pradhan Mantri Vaya Vandana Yojana (PMVVY).
- SAMPANN Project.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
2018 - Everyone is a Hero
- 2018- Everyone is a Hero is a Malayalam survival drama that is India's official entry for the 96th Academy Awards. The film is based on the devastating Kerala floods of 2018.
- In August 2018, Kerala experienced its worst floods since 1924 due to torrential rainfall environmental factors like encroachment, sand mining, and deforestation in the Western Ghats contributed to the disaster.
- The Academy Awards, also known as the Oscars, are given annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS).
- The awards recognize and celebrate all aspects of the film industry and the diverse, talented people who make movies.
- India won two Oscars at the 95th Academy Awards in 2023. "Naatu Naatu" from RRR won Best Original Song, and "The Elephant Whisperers" secured Best Documentary Short.
Read more: Flood Situation in Kerala
Gujarat Bans Conocarpus Plants
- The Gujarat government has banned the planting of Conocarpus trees, a non-indigenous species, in both forested and non-forested areas. The government cited the trees' adverse impacts on the environment and human health. Earlier, Telangana too had banned the plant species.
- Conocarpus trees, a fast-growing mangrove shrub found in tropical and subtropical coastal areas globally, have been planted to boost green cover in certain regions.
- However, their small winter flowers produce pollen that can cause health issues like colds, coughs, asthma, and allergies. Moreover, their deep root systems can harm infrastructure, particularly drainage systems.
UrbanShift Asia Forum
Recently, the first UrbanShift Forum (Asia) was held in New Delhi.
- The primary objective was to provide training and capacity-building to regional cities for integrated and sustainable urban development.
- UrbanShift is a Global Environment Facility(GEF)-funded program within Urban Development and the WRI Ross Center for Sustainable Cities. It is led by United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and implemented in partnership with C40 Cities, International Council for Local Environmental Initiatives (ICLEI), UNDP, Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the World Bank.
Read more: National Institute of Urban Affairs
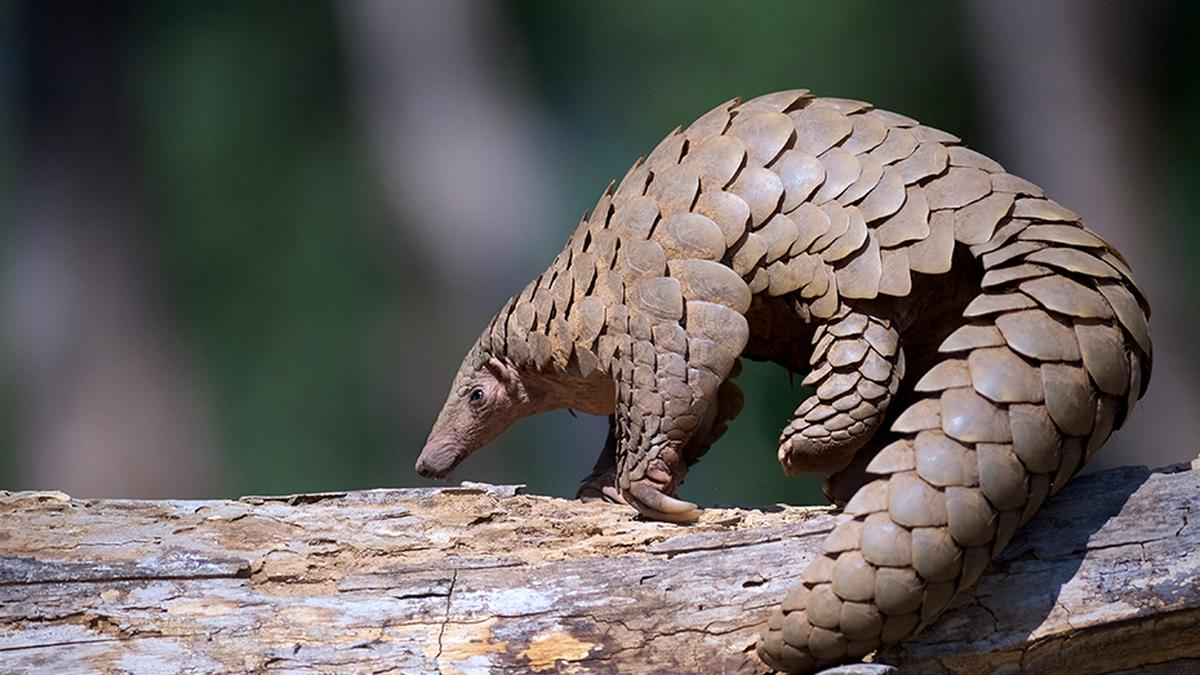
Pangolin's Hidden Diversity
The Pangolin, an elusive and highly endangered creature often touted as the world's most trafficked mammal, has unveiled a hidden secret.
- Previously thought to consist of eight species—four Asian and four African varieties—research has revealed the existence of a ninth pangolin species, provisionally named Manis mysteria.
- This discovery was made through the analysis of scales confiscated from traffickers in China's Yunnan province in 2015 and 2019.
- Despite a ban on international trade since 2016, the newly discovered pangolin species is already under pressure, showing signs of declining population, low genetic diversity, inbreeding, and genetic load.
Read more: Pangolin