Governance
Bills to Include PVTGs to ST List in Odisha and AP
For Prelims: Parliament, Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), PM-JANMAN
For Mains: Government Policies & Interventions, Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population
Why in News?
Recently, Parliament passed two bills that aim to modify the lists of Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) in Andhra Pradesh and Odisha. The bills were passed by voice vote in the Lok Sabha.
- The bills seek to include certain tribes to Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) and certain communities of the SC list to ST list, based on the recommendations of the state governments, after consultation with the Registrar General of India and the National Commissions for Scheduled Castes & Scheduled Tribes.
Voice Vote
- It involves the speaker putting a question to the house and then asking the house to put forward its opinion in the forms of ayes (yes) or noes. Based on a rough measure of which side was louder, the speaker decides if the motion was passed or fell through.
What are the Bills and What do they Propose?
- Andhra Pradesh: The Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2024 seeks to amend the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950, in relation to Andhra Pradesh.
- The Order lists the tribes deemed to be Scheduled Tribes in states and union territories.
- The Bill adds the following Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) to the list of STs in Andhra Pradesh: (i) Bondo Porja, (ii) Khond Porja, and (iii) Konda Savaras.
- Odisha: The Constitution (Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) Orders (Amendment) Bill, 2024 amends the Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1950 and the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950 to modify the list of SCs and STs in Odisha.
- PVTGs added to the Scheduled Tribes list in Odisha:
- Pauri Bhuyan and Paudi Bhuyan (included as synonyms of Bhuyan Tribe).
- Chuktia Bhunjia (recognized as Bhunjia tribe).
- Bondo community (sub-tribe of Bondo Poraja).
- Mankidia community (synonym of Mankirdia tribe).
- Odisha's ST list expanded with two new entries: Muka Dora (also Mooka Dora, Nuka Dora and Nooka Dora) and Konda Reddy (also Konda Reddi) tribes.
- The Bill removes Tamadia and Tamudia communities from the list of SCs in Odisha and adds them to the list of STs.
- PVTGs added to the Scheduled Tribes list in Odisha:
Note
- The bills only added synonyms, phonetic variations, and sub-tribes of existing STs in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh; the count of PVTGs in India remains unchanged at 75.
What is the Importance of these Bills?
- The amendment addresses discrepancies in the treatment of certain tribes across different regions.
- Communities like Konda Reddy and Muka Dora were recognized as ST in Andhra Pradesh but faced discrimination in Odisha.
- The inclusion of these groups in the ST list rectifies long-standing disparities, ensuring equitable access to government provisions and services.
- PVTGS listed as STs gain access to reservation quotas in education, employment, and political representation.
- ST status ensures affirmative action in educational institutions, allowing PVTG students to compete on a level playing field.
What is a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group?
- About:
- A PVTG is a sub-classification of a Scheduled Tribe or section of a Scheduled Tribe that is considered more vulnerable than a regular Scheduled Tribe. The Indian Government created the PVTG list to improve their living.
- There are 75 PVTGs in India, the maximum 13 are in Odisha, followed by 12 in Andhra Pradesh.
- Article 342(1): The President with respect to any State/UT (after consultation with the Governor in case of state) may specify the tribes/tribal communities/part of or groups within tribes/ tribal communities as a Scheduled Tribe in that State/UT.
- Parliament may by law include in or exclude from the list of STs specified in a notification issued under article 342(1) any tribe or tribal community or part of or group within any tribe or tribal community, but save as aforesaid a notification issued under the said clause shall not be varied by any subsequent notification.
- A PVTG is a sub-classification of a Scheduled Tribe or section of a Scheduled Tribe that is considered more vulnerable than a regular Scheduled Tribe. The Indian Government created the PVTG list to improve their living.
- Initiatives:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.1 Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (2019)
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)? (2017)
Q. Why are the tribals in India referred to as ‘the Scheduled Tribes’? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. (2016)
Social Issues
Building An Inclusive Society Through SMILE
For Prelims: Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019, NALSA Judgement 2014, Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Rules, 2020, Garima Greh.
For Mains: Indian Society and the Challenges faced by Transgenders, Reforms for Transgender Persons, Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act - Provisions and Associated Concerns
Why in News?
In 2021, the Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE) scheme, aimed at advancing the vision of Viksit Bharat was initiated. This included the launch of the Central Sector Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation for the Welfare of Transgender Persons.
Who is a Transgender?
- According to the Transgenders Persons Act, 2019, transgender means a person whose gender does not match with the gender assigned to that person at birth.
- It includes trans-person with intersex variations, gender-queer and person having such socio-cultural identities as kinnar, hijra, aaravani and jogta.
- India’s 2011 Census was the first census in its history to incorporate the number of ‘trans’ population of the country. The report estimated that 4.8 million Indians identified as transgender.
What is a SMILE Scheme?
- About:
- It is a new Scheme after the merger of existing Schemes for Beggars and Transgenders.
- The two sub-schemes of SMILE - ‘Central Sector Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation for Welfare of Transgender Persons’ and ‘Central Sector Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of engaged in the act of Begging’ – provide comprehensive welfare and rehabilitation measures to the Transgender community and the people engaged in the act of begging.
- Scheme provides for the use of the existing shelter homes available with the State/UT Governments and Urban local bodies for rehabilitation of the transgender persons.
- In case of non-availability of existing shelter homes, new dedicated shelter homes are to be set up by the implementing agencies.
- The two sub-schemes of SMILE - ‘Central Sector Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation for Welfare of Transgender Persons’ and ‘Central Sector Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of engaged in the act of Begging’ – provide comprehensive welfare and rehabilitation measures to the Transgender community and the people engaged in the act of begging.
- It is a new Scheme after the merger of existing Schemes for Beggars and Transgenders.
- Focus:
- The focus of the scheme is extensively on rehabilitation, provision of medical facilities, counselling, basic documentation, education, skill development, economic linkages and so on.
- It is estimated that an approximate 60,000 poorest persons would be benefited under this scheme for leading a life of dignity.
- It provides Scholarships for Transgender Students studying in Class 9th and above till post-graduation to enable them to complete their education.
- It has provisions for Skill Development and Livelihood under the PM-DAKSH scheme.
- Through Composite Medical Health it provides a comprehensive package in convergence with Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PM-JAY) supporting Gender-Reaffirmation surgeries through selected hospitals.
- The Housing facility in the form of ‘Garima Greh’ ensures food, clothing, recreational facilities, skill development opportunities, recreational activities and medical support etc. to the Transgender community and the people engaged in the act of begging.
- Implementation:
- It will be implemented with the support of State/UT Governments/Local Urban Bodies, Voluntary Organizations, Community Based Organizations (CBOs) , institutions and others.
- The Provision of Transgender Protection Cell in each state will monitor cases of offences and to ensure timely registration, investigation and prosecution of offences.
- The National Portal & Helpline will provide necessary information and solutions to the Transgender community and the people engaged in the act of begging when needed.
- Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of Trangenders:
- The scheme has been implemented in the selected cities on pilot basis having large concentrations of the Beggar and Transgender community.
- During the year 2019-20, this Ministry had released an amount of Rs. 1 Crore to National Institute of Social Defence (NISD) and Rs. 70 Lakh to National Backward Classes Finance & Development Corporation (NBCFDC) for skill development programmes for beggars.
What are the Problems Faced by Transgenders?
- Societal Stigma:
- Social Exclusion: Transgender individuals often face isolation and marginalization, leading to mental health issues, substance abuse, and a reduced quality of life.
- Stereotyping and Misrepresentation: Society tends to stereotype transgender people, limiting their opportunities for employment, education, and healthcare.
- Family Rejection: Many transgender individuals are disowned by their families, leaving them without familial support and economic stability.
- Discrimination:
- Violence and Hate Crimes: Hate crimes, physical and verbal abuse, and sexual assault are significant threats to the safety and well-being of transgender individuals.
- Educational Barriers: Discrimination in educational institutions hampers access to quality education and future career opportunities.
- Employment Discrimination: Transgender individuals frequently experience job discrimination, which leads to unemployment or underemployment, perpetuating their economic vulnerability.
- Healthcare Disparities: Discrimination by healthcare providers often deters transgender individuals from seeking necessary medical care, including gender-affirming procedures.
- Absence of Legal Recognition:
- Legal Ambiguity: While India has made progress with the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019, there are still legal ambiguities and gaps that need to be addressed.
- Transgender persons are not defined properly and the Act does not have any provision for self-determination of gender.
- Lack of Comprehensive Policies: The absence of comprehensive policies on gender identity, non-binary genders, and a clear legal framework for transgender rights remains a challenge.
- Implementation Gaps: The implementation of existing laws is often ineffective due to a lack of awareness, prejudice, and reluctance on the part of authorities.
- Legal Ambiguity: While India has made progress with the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019, there are still legal ambiguities and gaps that need to be addressed.
What are the Different Initiatives for Transgender Persons?
- An MoU has been signed with National Health Authority for a specialized Ayushman Bharat TG Plus card for providing more than 50 health benefit services to transgender persons and for first-time gender re-assignment as well as cosmetic treatments have been included under the Ayushman Bharat scheme for transgender persons.
- Swachh Bharat Mission(Urban) has included dedicated toilets for transgender persons in their policy guidelines.
- National Portal for Transgender Persons
- Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Rules, 2020
- National Council for Transgender Persons
- Certificate of Identity
- Equal Opportunity Policy
What Can be Done More to Uplift the Transgender Persons?
- Transgender-Inclusive Policies: Legal and the law enforcement systems need to be empowered and sensitized on the issues of Transgender community.
- Inclusive approach for Transgender must be planned and adopted by the Government and society.
- Their grievance of being not included in policies formulation or decision making needs to be allayed and chances for their public participation should increase.
- Addressing Social Concerns: Provision of free legal aid, supportive education, and social entitlement must be ensured for the Transgender community at ground level as suggested by NALSA Judgement.
- Separate policies related to health care must be framed and communicated in all private and public hospitals and clinics.
- There is a need to increase awareness and inculcate sense of respect and acceptance for transgender community.
- Financial Security: Liberal credit facilities and financial assistance must be ensured to start up their career as an entrepreneur or businessman along the lines of SHG-Bank Linkage Programs.
- Transgender in Prisons: Awareness and documentation are two important tools to address the reforms in reference to sexual minorities, especially trans prisoners.
- As the Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative (CHRI) advocates, there is a need for a gender-fluid approach for the treatment of transgender prisoners.
- The CHRI’s recommendations should be considered by the Union government to bring a ‘model policy’ on the special needs of trans prisoners, through a consultative process with the members of the trans community, to honour the mandate of the NALSA judgement.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. In India, Legal Services Authorities provide free legal services to which of the following type of citizens? (2020)
- Person with an annual income of less than Rs. 1,00,000
- Transgender with an annual income of less than Rs. 2,00,000
- Member of Other Backward Classes (OBC) with an annual income of less than Rs. 3,00,000
- All Senior Citizens
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Governance
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana and FIDF
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada, Fisheries Sector, Kisan Credit Card, Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund.
For Mains: Fisheries Sector in India, Steps Taken to Improve the Fisheries Sector in India
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the "Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY) and has granted an extension to the Fisheries Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF) for an additional 3 years until 2025-26.
- The extension aims to cater to the infrastructure needs of the fisheries sector, ensuring sustained development and growth.
What is Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana?
- About:
- PM-MKSSY, a Central Sector Sub-scheme under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada (PMMSY) for formalisation of the fisheries sector and supporting fisheries micro and small enterprises with an investment of over Rs. 6,000 crores over a period of next four years from FY 2023-24 to FY 2026-27 in all States/Union Territories.
- Objectives:
- Gradual Formalisation of the unorganised fisheries sector through self-registration of fishers, fish farmers and supportive workers under a National Fisheries Sector Digital Platform (NFDP).
- Facilitating access to institutional financing for fisheries sector micro and small enterprises.
- Providing a one-time incentive to beneficiaries for purchasing aquaculture insurance.
- Incentivising adoption and expansion of safety and quality assurance systems for fish, and fishery products and maintenance of jobs.
- Intended Beneficiaries:
- Fishers, Fish (Aquaculture) Farmers, fish workers, vendors, and other stakeholders in the fisheries value chain.
- Micro and Small enterprises - proprietary firms, partnership firms, cooperatives, federations, startups, Fish FPOs (FFPOs) and more engaged in fisheries and aquaculture.
- FFPOs also include Farmers Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Any other beneficiaries that may be included by the Department of Fisheries as targeted beneficiaries.
- Implementation Strategy:
- Component 1-A: Formalisation of Fisheries Sector:
- NFDP to be established to formalise the unorganised fisheries sector by creating a national registry of stakeholders.
- Functions of NFDP: Training, financial literacy improvement, project preparation assistance, and strengthening of fisheries cooperative societies.
- Component 1-B: Facilitating Adoption of Aquaculture Insurance:
- Establishing insurance products for aquaculture, covering at least 1 lakh hectares, with a maximum incentive of Rs. 1,00,000 per farmer (farm size for the incentive is 4 hectares) and a 40% incentive for intensive aquaculture methods.
- Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Women beneficiaries receive an additional 10% incentive.
- Component 2: Supporting Microenterprises to Improve Fisheries Sector Value Chain Efficiencies:
- Improving value chain efficiencies through the provision of performance grants. Scale and Criteria for Performance Grants:
- Microenterprises:
- General Category: Grant capped at 25% of total investment or Rs. 35 lakhs.
- SC, ST, Women-owned: Grant capped at 35% of total investment or Rs. 45 lakhs.
- Village Level Organizations and Federations: Grant not to exceed 35% of total investment or Rs. 200 lakhs (whichever is lower).
- Microenterprises:
- Improving value chain efficiencies through the provision of performance grants. Scale and Criteria for Performance Grants:
- Component 3: Fish and Fishery Product Safety and Quality Assurance Systems:
- Incentivize fishery enterprises for safety and quality, fostering market expansion and job creation, particularly for women.
- Grants:
- Microenterprises: Same as the one in Value Chain Efficiencies.
- Small enterprises: 25% of total investment or Rs. 75 lakhs (General Category), 35% of total investment or Rs.100 lakhs for (SC/ST/Women-owned).
- Village-level orgs & Federations: Same as the one in Value Chain Efficiencies.
- Component 4: Project Management, Monitoring, and Reporting:
- Establishment of Project Management Units (PMUs) for managing, implementing, monitoring, and evaluating project activities.
- Component 1-A: Formalisation of Fisheries Sector:
Fisheries Sector in India:
- India's total fish output stood at 174 lakh tonnes in 2022-23. India is the third largest fish producer in the world, contributing 8% to total global fish production.
- Over a period of 10 years (2013-2023-24):
- Fish production increased by 79.66 lakh tonnes.
- Coastal aquaculture experienced robust growth during the period.
- Shrimp production surged by 270%.
- Shrimp exports more than doubled reflecting a 123% growth.
- Employment and livelihood opportunities created for ~63 lakh fishers and fish farmers.
- Coverage per fisherman under the Group Accident Insurance Scheme (GAIS) rose from Rs. 1.00 lakh to Rs. 5.00 lakh, benefiting a cumulative total of 267.76 lakh fishers.
- The extension of the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) to fisheries in 2019 led to the issuance of 1.8 lakh cards.
- Despite significant achievements, challenges persist in the sector, including its informal nature, lack of crop risk mitigation, absence of work-based identities, poor access to institutional credit, and sub-optimal safety and quality standards of fish sold by micro and small enterprises.
What is the Fisheries Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF)?
- About:
- It has been established by the Department of Fisheries (Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying). FIDF complements schemes like PMMSY and KCC.
- FIDF envisages the creation of fisheries infrastructure facilities both in marine and inland fisheries sectors.
- Implementation Mechanism
- Concessional Finance: FIDF provides concessional finance to Eligible Entities (EEs) through Nodal Loaning Entities (NLEs) namely the NABARD, National Cooperatives Development Corporation (NCDC) and all scheduled Banks.
- EEs under FIDF include state governments, cooperatives, fisheries cooperative federations, NGOs, women entrepreneurs, private companies, and more.
- Interest Subvention:
- Indian Government offers up to 3% per annum interest subvention.
- Repayment period spans 12 years, including a 2-year moratorium for providing the concessional finance by the NLEs at the minimum interest rate of 5% per annum.
- Concessional Finance: FIDF provides concessional finance to Eligible Entities (EEs) through Nodal Loaning Entities (NLEs) namely the NABARD, National Cooperatives Development Corporation (NCDC) and all scheduled Banks.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Other than poaching, what are the possible reasons for the decline in the population of Ganges River Dolphins? (2014)
- Construction of dams and barrages on rivers
- Increase in the population of crocodiles in rivers
- Getting trapped in fishing nets accidentally
- Use of synthetic fertilisers and other agricultural chemicals in crop-fields in the vicinity of rivers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Q. Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes? (2020)
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Defining blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)
Geography
Atmospheric River
For Prelims: Atmospheric River, Pineapple Express, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
For Mains: Atmospheric River, Geographical features and their location, Impacts of Climate Change.
Why in News?
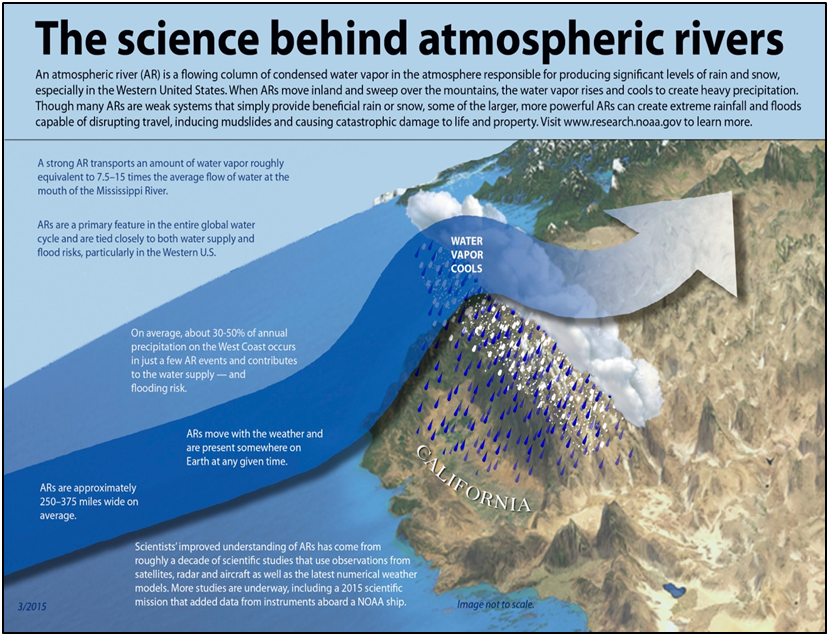
California, US is currently grappling with an extraordinary weather phenomenon known as an Atmospheric River also called Pineapple Express Storm, which has the potential to unleash up to 8 trillion gallons of rain over the state.
What is an Atmospheric River?
- About:
- The atmospheric river is a long, narrow band of moisture-filled air that transports significant amounts of water vapor from the tropics to higher latitudes.
- The Atmospheric River is often associated with mT (Maritime Tropical) air mass.
- When these rivers make landfall, they release this moisture as intense precipitation, which can manifest as either rain or snow depending on the altitude and temperature.
- According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the water vapor they carry is roughly equivalent to the average flow of water at the mouth of the Mississippi River.
- So, when they make landfall and release all that water, they can cause extreme flooding.
- The atmospheric river is a long, narrow band of moisture-filled air that transports significant amounts of water vapor from the tropics to higher latitudes.
- Pineapple Express:
- The "Pineapple Express" is a well-known example of atmospheric river storms that bring heavy rainfall to the US West Coast, particularly California.
- This name originates from the fact that these storms draw moisture from the tropical waters near the Hawaiian Islands, resembling a "express" train of moisture originating from the vicinity of Hawaii, which is often associated with pineapples.
- This atmospheric river is driven by a strong southern branch of the polar jet stream and transports humid, warm mT air from as far away as the Hawaiian Islands .
Satellite image of clouds over the Pacific Ocean illustrating the “Pineapple Express,” a phenomenon in which a strong jet stream carries mT air from as far away as Hawaii to the West Coast.
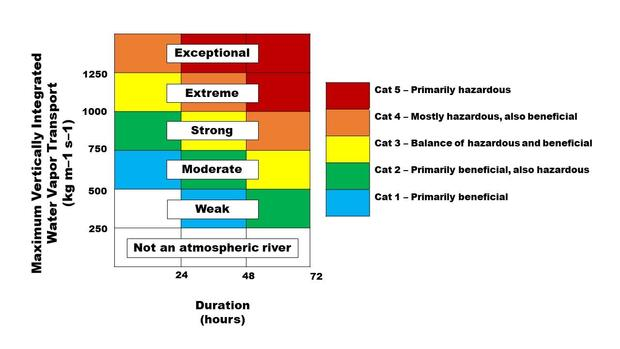
- Categories:
- Category 1 (Weak): A Category 1 atmospheric river would be a milder and briefer weather event with primarily beneficial effects, like 24 hours of modest rainfall.
- Category 2 (Moderate): A Category 2 atmospheric river is a moderate storm with mostly beneficial effects, but also somewhat hazardous.
- Category 3 (Strong): A Category 3 atmospheric river is more powerful and longer lasting, with a balance of beneficial and hazardous impacts. For example, a storm in this category could bring 5-10 inches of rain over 36 hours, enough to help replenish reservoirs but also pushing some rivers close to flood stage.
- Category 4 (Extreme): A Category 4 atmospheric river is mostly hazardous, though also with some beneficial aspects. A storm of this rating could dump enough heavy rain over several days to bring many rivers to flood stage.
- Category 5 (Exceptional): A Category 5 atmospheric river is primarily hazardous.
- An atmospheric river that lasted over 100 hours over the Central California coast during the 1996-97 New Year's holiday period. The heavy rain and runoff caused over USD 100 billion in damage.
- Significance:
- They play a crucial role in replenishing water supplies, particularly in regions like the western United States. The heavy precipitation they bring can contribute significantly to reservoir levels, helping to alleviate drought conditions and ensuring water availability for agricultural, industrial, and domestic use.
- Given their importance for water supply, understanding atmospheric rivers is essential for effective water resource management and planning. This includes strategies for water storage, flood control, and allocation of water resources to meet various demands.
- Atmospheric rivers contribute to maintaining a balance in the hydrological cycle by transporting large amounts of water vapor from the tropics to higher latitudes. This helps to redistribute moisture across different regions, supporting ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Note
An atmospheric river should not be confused with a traditional river found on the Earth's surface. Unlike a visible water body, an atmospheric river is an invisible, elongated corridor in the sky that carries large amounts of water vapor, influencing weather patterns and precipitation.
How Common are Atmospheric Rivers, and Where do They Occur?
- They're not limited to the US West Coast; they can occur worldwide. These rivers of moisture can stretch thousands of miles and affect regions like the UK, Ireland, Norway, and China.
- Atmospheric rivers often make the rainy season in China, known as Mei-Yu season, even worse.
- While they only account for 17% of storms on the US West Coast, atmospheric rivers contribute significantly to California's precipitation, snowpack, and major floods. They're predictable and can be forecasted up to a week in advance.
What is Air Mass?
- About:
- An air mass is a large body of air with relatively uniform temperature, humidity, and pressure characteristics. These masses of air form over source regions, where they take on the characteristics of the surface below due to low wind speeds.
- When air masses move, they can influence weather patterns in the regions they move into, potentially leading to the formation of storms when they interact with other air masses.
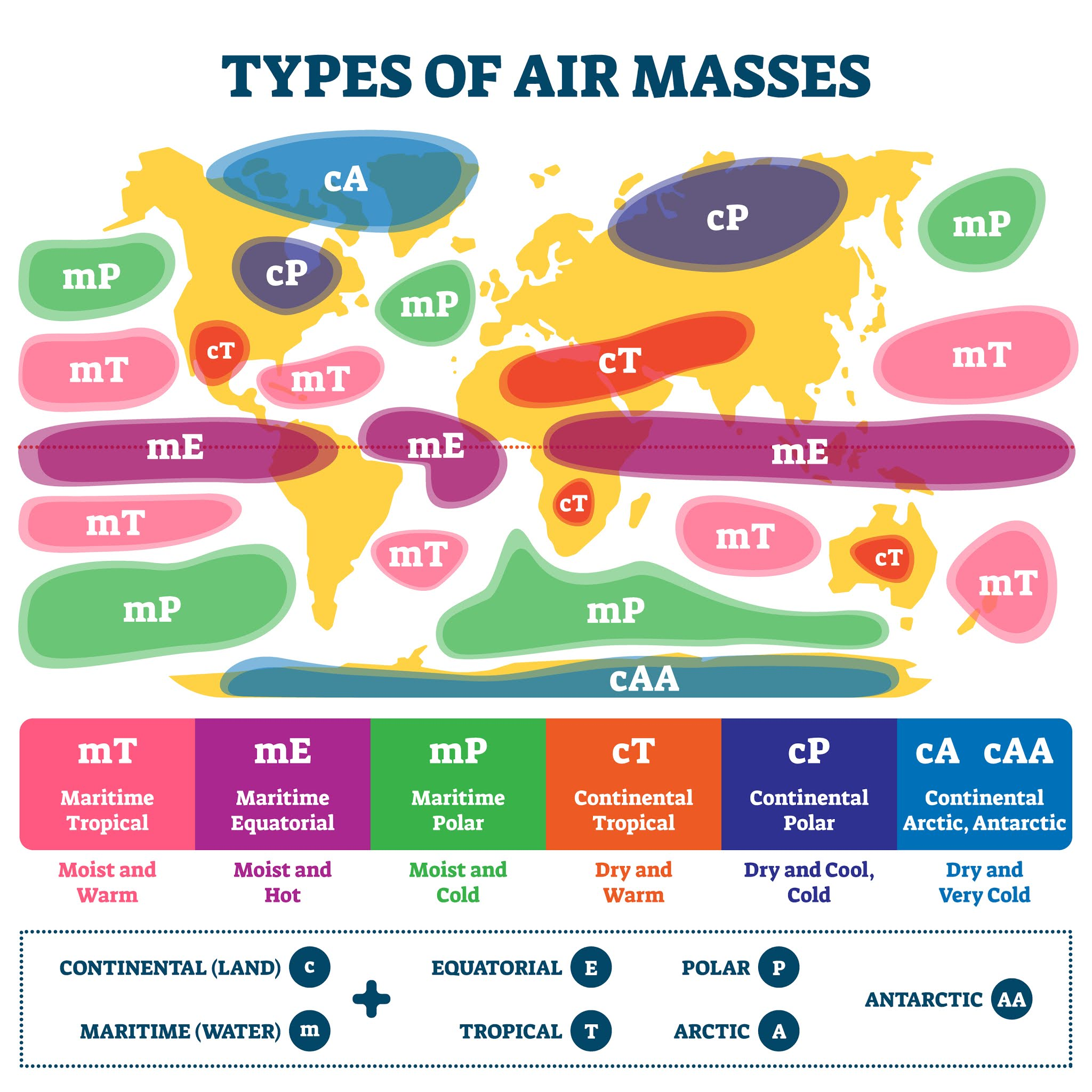
- Types of Air Masses:
- Continental Tropical (cT): These air masses originate over hot and dry continental regions. They are characterized by high temperatures and low humidity.
- Continental Polar (cP): Originating over cold and dry continental regions, cP air masses are characterized by cold temperatures and low humidity.
- Maritime Tropical (mT): These air masses form over warm and moist oceanic regions. They are characterized by warm temperatures and high humidity.
- Maritime Polar (mP): Originating over cold oceanic regions, mP air masses are characterized by cool temperatures and high humidity.
- Continental Arctic (cA): cA air masses originate over extremely cold Arctic regions. They are characterized by frigid temperatures and very low humidity.
- Characteristics of Air Masses:
- Air masses originate over vast flat surfaces having uniform temperature and humidity.
- Air masses travel slowly over hundreds of kilometers from their source regions.
- As the air masses move away from source regions their chief characteristics of temperature and humidity undergo large-scale changes.
- They affect the weather conditions of the areas visited by them.
- When two air masses of different temperature and humidity approach each other, they do not intermingle but a front is formed between them.
- Weather conditions change abruptly at the front.
- The front keeps two approaching air masses separate from each other.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The formation of ozone hole in the Antarctic region has been a cause of concern. What could be the reason for the formation of this hole? (2011)
(a) Presence of prominent tropospheric turbulence; and inflow of chlorofluorocarbons
(b) Presence of prominent polar front and stratospheric clouds; and inflow of chlorofluorocarbons
(c) Absence of polar front and stratospheric clouds; and inflow of methane and chlorofluorocarbons
(d) Increased temperature at polar region due to global warming
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q.1 How do the melting of the Arctic ice and glaciers of the Antarctic differently affect the weather patterns and human activities on the Earth? Explain. (2021)
Q.2 Why is India taking keen interest in resources of Arctic region? (2018)
Q.3 How does the cryosphere affect global climate? (2017)
Important Facts For Prelims
CAR-T Cell Therapy
Why in News?
Following India’s approval of CAR-T cell therapy, a pioneering treatment for cancer, a patient recently underwent the procedure, achieving freedom from cancer cells, marking a significant advancement in cancer treatment accessibility in the country.
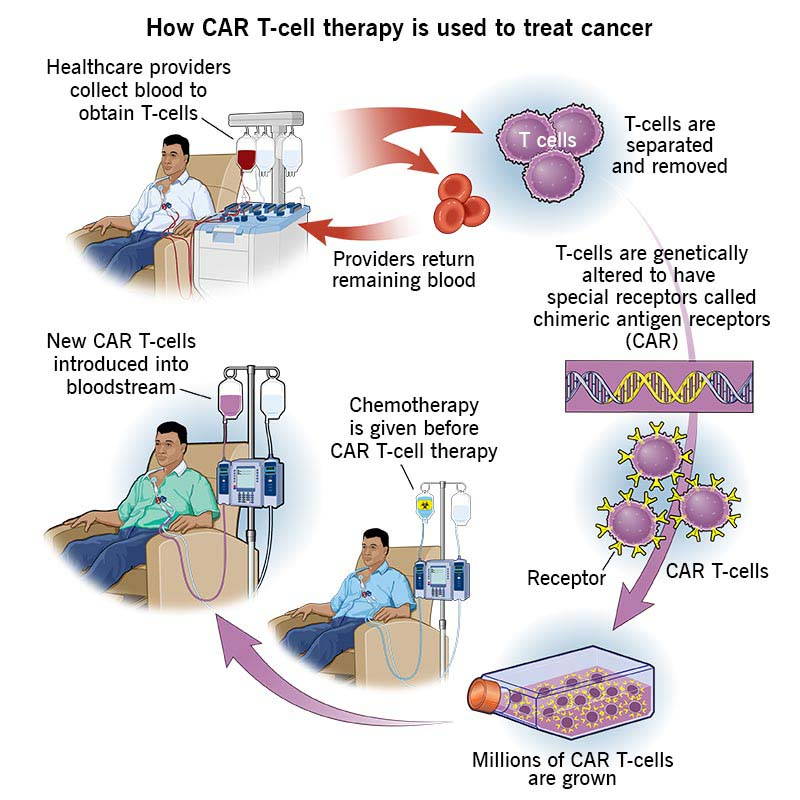
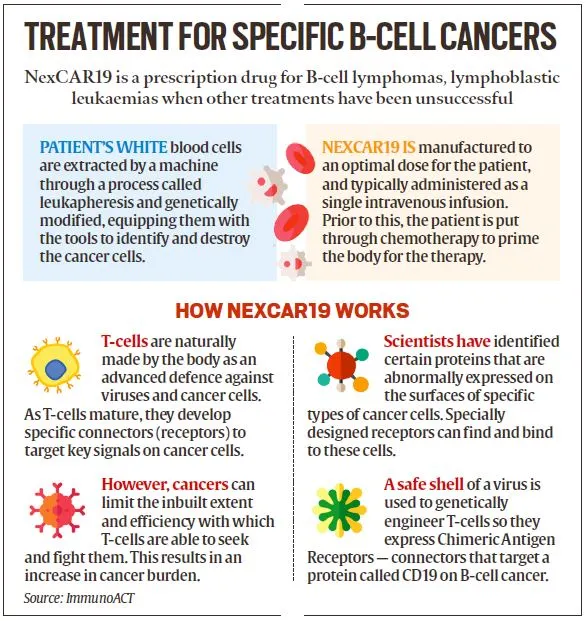
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy?
- About: CAR-T cell therapy, also known as chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, is a type of immunotherapy that uses a patient's own immune system to fight cancer.
- CAR T-cell therapy has been approved for leukaemias (cancers arising from the cells that produce white blood cells) and lymphomas (arising from the lymphatic system).
- CAR-T cell therapies, often referred to as 'living drugs’.
- Procedure: It is a complex and personalised treatment process that involves:
- Collecting T cells: T cells, a type of white blood cell that helps fight infection, are extracted from the patient's blood through a process known as Apheresis.
- Genetic Engineering: In the laboratory, the T cells are genetically modified to express a special protein called a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) on their surface.
- This CAR is designed to recognize and bind to a specific antigen (marker) found on cancer cells.
- Expansion: The engineered T cells are multiplied in large numbers in the lab.
- Infusion: The expanded CAR-T cells are then infused back into the patient's bloodstream, where they can identify and attack cancer cells that express the targeted antigen.
- Development in India: NexCAR19, an indigenously developed therapy for B-cell cancers, has been collaboratively developed by ImmunoACT, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT-B), and Tata Memorial Hospital.
- The commercial use of this therapy to treat certain blood cancers was approved by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) in October 2023.
- NexCAR19 is the first CAR-T cell therapy to get CDSCO approval.
- Potential Benefits of CAR-T therapy
- High Remission Rates: For some patients with advanced cancers who have not responded to other treatments, CAR-T therapy can lead to high rates of complete remission.
- Personalised Approach: The therapy is tailored to each individual patient's cancer, making it a highly targeted treatment.
- Potential Risks:
- Severe Side Effects: CAR-T therapy can cause serious side effects, including cytokine release syndrome (a widespread activation of the immune system and collateral damage to the body’s normal cells) and neurological symptoms (severe confusion, seizures, and speech impairment).
- High Cost: CAR-T therapy is a very expensive treatment.
What are the Indian Government’s Initiatives Related to Cancer?
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke
- National Cancer Grid
- Encouraging Cervical Cancer Vaccination for girls (9-14 years) (Interim Budget 2024-25)
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body?(2022)
(a) They protect the environmental allergens. body
(b) They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
(c) They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
(d) They protect the body from diseases caused by pathogens.
Ans: (d)
Important Facts For Prelims
Kyasanur Forest Disease
Why in News?
Since the beginning of 2024, two individuals have lost their lives due to Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), a viral infection prevalent in Karnataka.
- The number of deaths reported due to the disease since 1956, when it was noticed in the forests of Shivamogga district, is above 560.
What is Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD)?
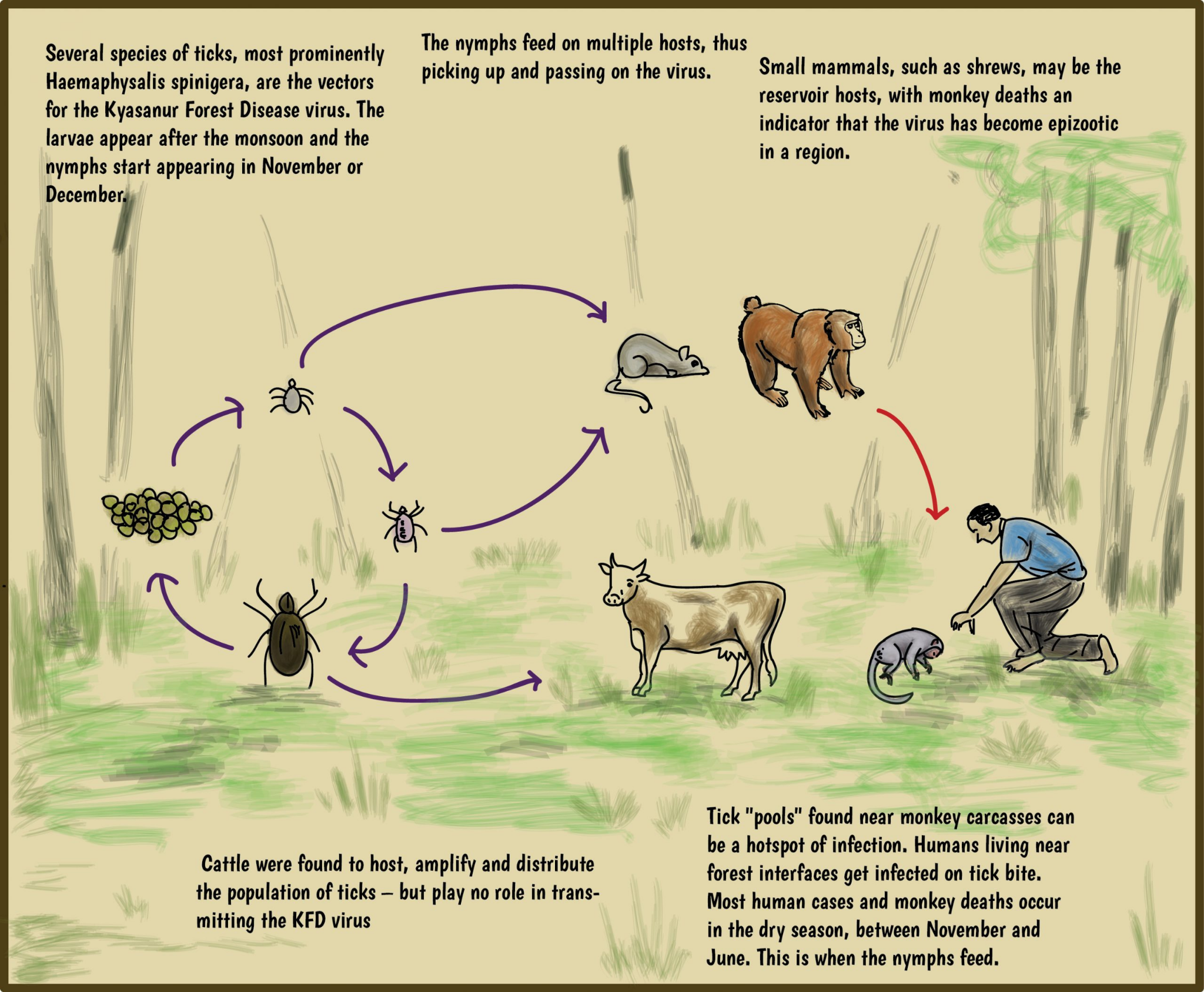
- About:
- Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), a zoonotic illness, is colloquially referred to as “monkey disease” due to its link with monkey fatalities.
- It is caused by the Kyasanur Forest disease Virus (KFDV), which primarily affects humans and monkeys.
- It was first identified in 1957 in a sick monkey from the Kyasanur Forest in Karnataka. Since then, between 400-500 human cases per year have been reported.
- Eventually, KFD emerged as a grave public health problem spreading through the entire Western Ghats.
- Transmission:
- In nature, the virus is maintained mainly in hard ticks (Haemaphysalis spinigera), monkeys, rodents, and birds.
- To humans, it may occur after a tick bite or contact with an infected animal (a sick or recently dead monkey).
- Occurrence:
- Normally, the transmission begins from late November to June and peaks between December and March.
- Symptoms:
- Characterized by chills, frontal headache, body ache, and high fever for five to 12 days with a case fatality rate of 3 to 5%.
- Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis can be made in the early stage of illness by molecular detection by polymerase chain reaction(PCR) or virus isolation from blood.
- Later, serologic testing using Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Serologic Assay (ELISA) can be performed.
- Treatment and Prevention:
- Doctors manage symptoms and monitor vitals daily, in the absence of any specific treatment.
- Patients are receiving free treatment as per the State Government's decision.
- A vaccine (Formalin inactivated KFDV vaccine) does exist for KFD and is used in endemic areas of India.
- However, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is said to be in consultation with Indian Immunologicals for the development of a vaccine.
- The forest department is distributing (N, N-diethyl phenylacetamide) DEPA oil, to be applied to exposed skin which acts as a tick repellent.
- Doctors manage symptoms and monitor vitals daily, in the absence of any specific treatment.
Kyasanur Forest
- The Kyasanur Forest is a protected area located in the Shimoga district of Karnataka.
- It is part of the Western Ghats mountain range and is known for its rich biodiversity.
- The forest is home to a variety of plants and animals, including tigers, leopards, elephants, and gaur.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following: (2018)
- Birds
- Dust blowing
- Rain
- Wind blowing
Which of the above spreads plant diseases?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: D
Rapid Fire
Focus on Inflation Control
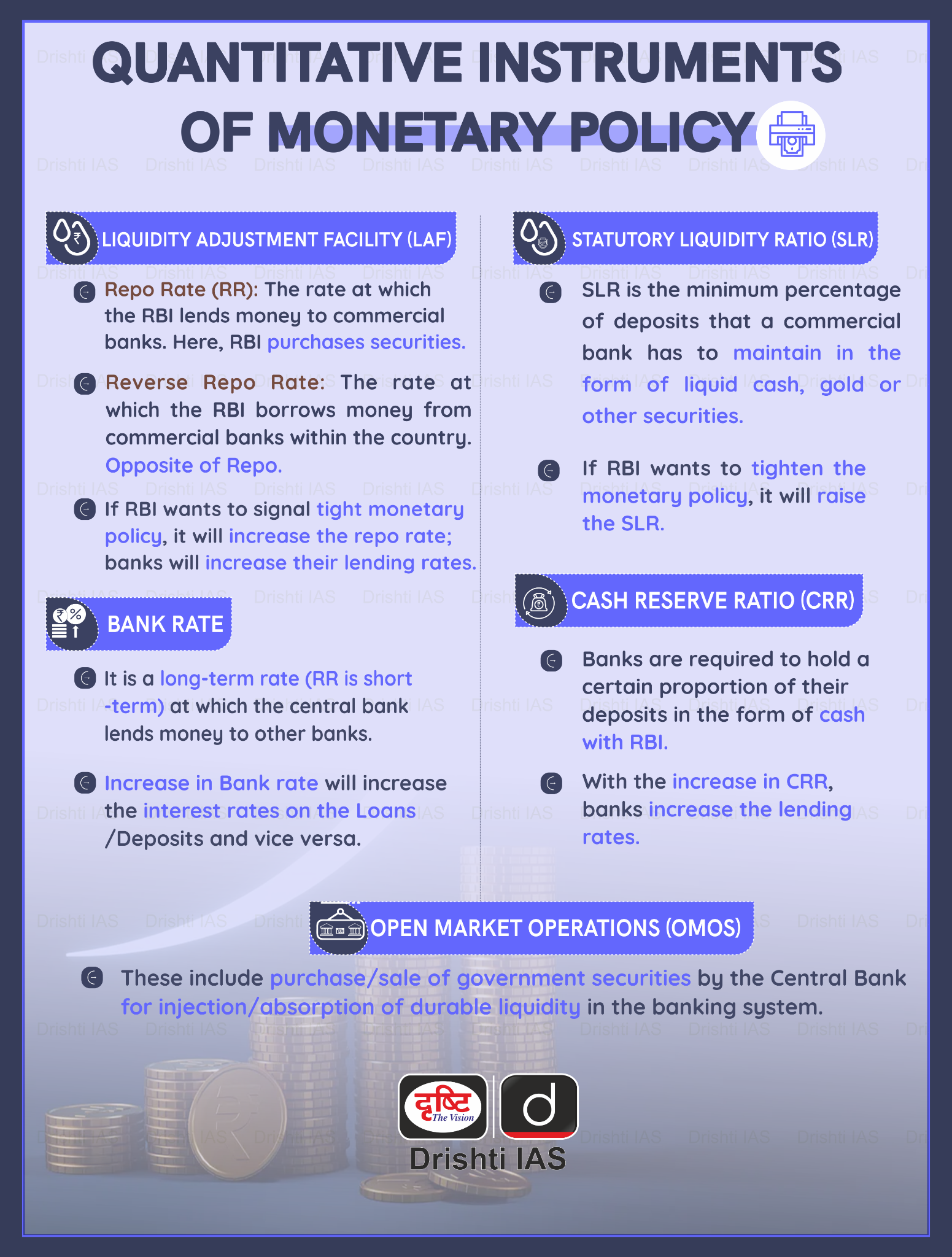
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) maintains its focus on curbing inflation by keeping the repo rate unchanged at 6.5% in February 2024 to align inflation with the 4% target.
- The MPC aims to achieve a medium-term target of 4% inflation within a band of +/- 2%.
- The MPC aims to withdraw accommodation gradually to align inflation with the target while supporting growth.
- An accommodative stance means the central bank is prepared to expand the money supply to boost economic growth.
- Withdrawal of accommodation will mean reducing the money supply in the system which will rein in inflation further.
- A recent RBI Bulletin states that Headline inflation rose to 5.7% in December 2023, primarily driven by food inflation, emphasising the need for continued vigilance.
- The MPC determines the policy interest rate required to achieve the inflation target. The RBI controls inflation and deflation by employing a variety of monetary policy tools such as:
Read more: RBI Keeps Policy Rates Unchanged
Rapid Fire
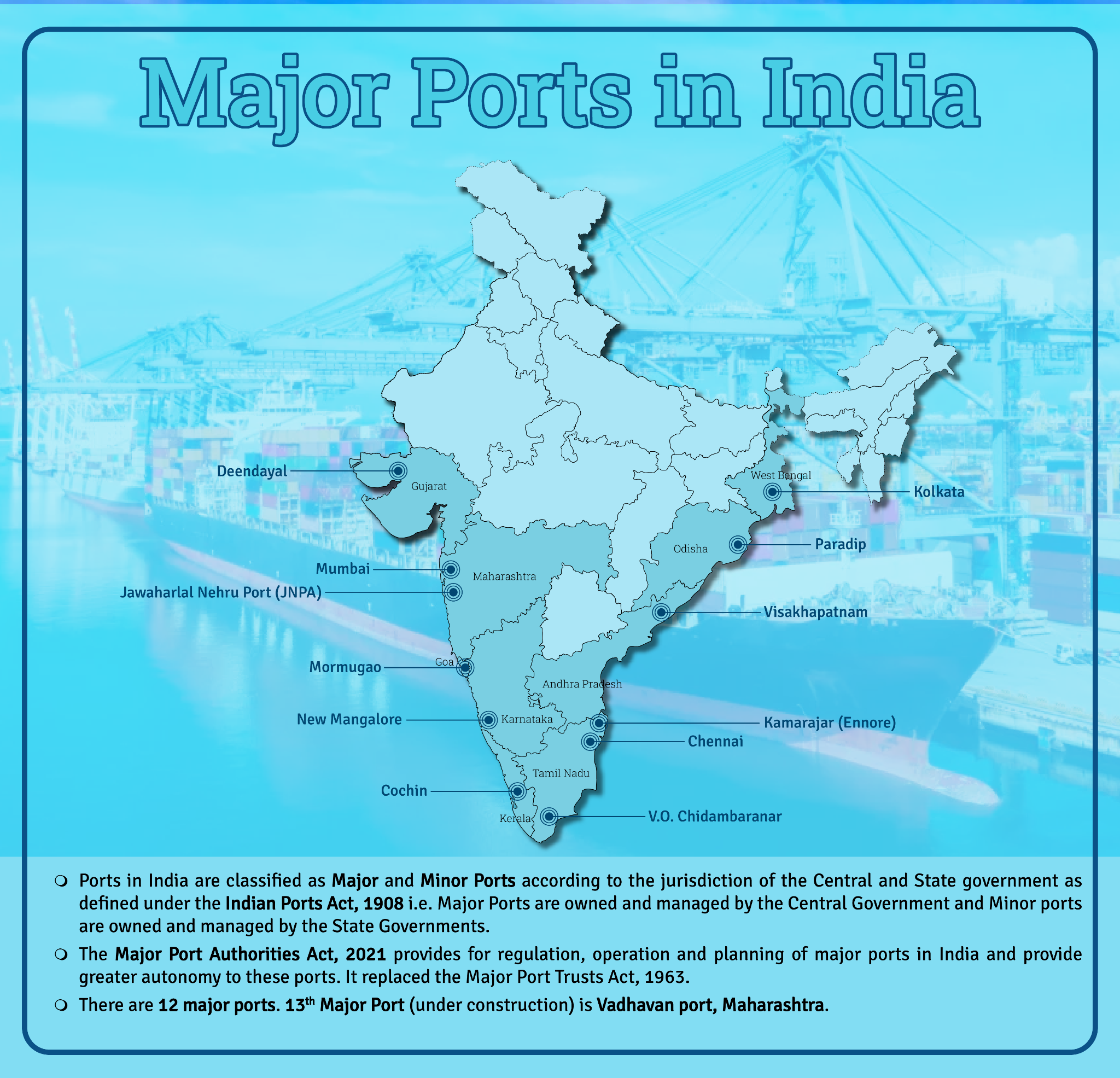
India to Develop Six Mega Ports by 2047
In a recent update by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, significant plans have been outlined for the development of Mega Ports in India by 2047.
- Six port clusters identified for development as Mega Ports by 2047.
- Four port clusters with a capacity exceeding 300 Million Tonnes Per Annum (MTPA):
- Cochin –Vizhinjam Port cluster, Galathea South Bay Port, Chennai – Kamarajar– Cuddalore Port cluster, Paradip and Other Non-Major Ports Cluster.
- Two port clusters with Capacity Exceeding 500 MTPA:
- (i) Deendayal and Tuna Tekra and (ii) Jawaharlal Nehru – Vadhavan.
- Four port clusters with a capacity exceeding 300 Million Tonnes Per Annum (MTPA):
- Major Ports are enhancing capacity and infrastructure as part of the Maritime AmritKaal Vision, 2047.
- Infrastructure projects are underway via Public-Private Partnership (PPP) and internal resources, focusing on port development.
Read more: Vizhinjam International Seaport Project
Rapid Fire
Freestyle Chess
Recently, Chess World No 1 Magnus Carlsen faced off against world champion Ding Liren across the chess board in a new, innovative tournament, called Freestyle Chess.
- More recently, Grandmaster D Gukesh of India defeated World No. 1 Magnus Carlsen of Norway, Levon Aronia of Armenia and ultimately the reigning world champion Ding Liren of China on the opening day of the Weissenhaus Chess Challenge.
- Freestyle chess goes by multiple names: Fischer Random Chess, Chess 9LX, and Chess 960 where 960 is the number of possible starting positions on the board when you shuffle your pieces on the last ranks of the board.
- This form of chess differs from the other forms is in the placement of the pieces on the board at the start of the game. All the eight pawns of each colour remain in the second and the seventh ranks on the board like in regular chess.
- The position of the rest of the pieces - the rooks, the bishops, the knights, the queen, and the king -on the first and the last rank changes randomly at the start of the game.
- It must be noted that the pieces still retain their regular characteristics in action: rooks travel in straight lines, bishops saunter diagonally, and so on.
Read More: FIDE Grand Swiss Open 2023, Olympics
Rapid Fire
Digitalising Fair Price Shops in Himachal Pradesh
The Department of Food and Public Distribution, Government of India, launched a pilot program to onboard Fair Price Shops (FPSs) onto the Open Network Digital Commerce (ONDC) platform in Una and Hamirpur districts of Himachal Pradesh.
- It is the first time that Fair Price Shops are on-boarded on ONDC and aims at providing additional avenues of income generation for FPS dealers along with enhancing beneficiary satisfaction.
- FPS means a shop which has been licensed to distribute essential commodities to the ration card holders under the Public Distribution System.
- The term is defined in Section 2(4) of National Food Security Act, 2013.
- It offers daily food products like rice, oil, sugar, wheat, and other daily useful commodities at a much lower price than the market price.
- ONDC is a freely accessible government-backed platform that aims to democratise e-commerce by moving it from a platform-centric model to an open network for buying and selling of goods and services.
- It was launched by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (Ministry of Commerce and Industry) in 2021.
Read more: Public Distribution System, ONDC
Rapid Fire
Extending the Ban on SIMI
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) extended the ban on the Students Islamic Movement of India (SIMI) for five more years.
- MHA cited involvement in terrorism, disturbing peace, and threatening sovereignty as reasons for the ban extension.
- SIMI was labeled an "unlawful association" under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA) in 2001.
Read more: Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act






-min.jpg)