International Relations
US-China Tariff Escalation 2025
For Prelims: International Monetary Fund, World Trade Organisation, Semiconductors, Rare Earth Metals,India - US COMPACT Initiative,
For Mains: Global trade conflicts and their impact on emerging economies, India’s trade policy and external sector reforms
Why in News?
China raised tariffs on US goods from 84% to 125% in retaliation for US President Donald Trump’s hike on Chinese imports to 145%. Earlier, President Trump had announced a 90-day suspension of reciprocal tariffs for most countries, including India, but notably excluded China.
- These retaliatory measures between the US and China have heightened concerns over global economic stability.
What Factors Led to the Intensifying Tariffs Between the US and China?
- US: A USD 295 billion US trade deficit with China in 2024 remains a major trigger behind US tariff hikes.
- The US sees such deficits as a sign of losing in global trade, viewing China’s surplus as both unfair and strategically risky.
- The US accuses China of intellectual property theft and forced technology transfers that distort fair competition, and has raised tariffs to protect its domestic industries.
- China: China responded after the US tariffs on Chinese imports had increased to 145%. This measure is part of an ongoing trade dispute between the two countries.
- Supply Chain Security: Both nations aim to reduce mutual dependence, especially in critical goods like Semiconductors, Rare Earth Metals, and Electric vehicles (EVs) components.
- The US is reducing reliance on China, moves like the CHIPS Act and partnerships with India (India-US COMPACT Initiative) and Vietnam aim to de-risk and diversify supply chains.
- Geopolitical Rivalry: US-China tensions go beyond trade, rooted in strategic conflicts over Taiwan, the South China Sea, and tech dominance (Artificial Intelligence, Quantum).
- Tariff Evasion via Third Countries: Chinese firms reroute goods through nations like Vietnam and Malaysia to bypass US tariffs.
- This has led to broader trade tensions beyond China, as the US seeks to prevent backdoor access to its markets through regional intermediaries.
What are the Risks of Full-Scale Trade War Between the US and China?
- Recession Risks: The US and China jointly account for about 43% of global GDP (International Monetary Fund (IMF) 2024 estimate).
- Simultaneous slowdowns or recessions would drag down global growth. The World Trade Organisation (WTO) warns the US-China trade war could slash global GDP by up to 7%.
- Uncertainty around tariffs is also dampening investment and causing market volatility.
- A tariff-heavy regime risks pushing up the prices of everyday goods, fuelling inflation and potentially curbing consumer spending, raising the threat of a global recession.
- Product Dumping Risks: With diminished access to the US market, China may redirect surplus goods like steel and solar panels to other markets at subsidized prices.
- This could undercut local industries in regions like the EU, UK, and India, affecting employment and wages, increasing trade litigation and protectionism.
- Weaponization of Strategic Tools: China’s control over rare earths like gallium, germanium, and lithium could escalate the US-China conflict into a tech cold war, threatening global supply chains.
- For India, this risks disrupting the Make in India push, especially in electronics and renewables.
- Disruption to Global Supply Chains: Countries dependent on Chinese manufacturing (e.g., ASEAN, EU ) or US-designed technologies (e.g., software, chips) would face cross-border economic shocks.
- Reshoring and near-shoring efforts are expensive and time-consuming.
- Geopolitical Polarization: Decoupling may force countries to choose sides, undermining multilateralism and fragmenting global economic governance.
What are the Implications of the US-China Trade War on India?
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Electronics, auto parts, and pharmaceuticals in India heavily rely on Chinese components.
- Rising costs or delayed shipments due to tariffs may make gadgets, vehicles, costlier or harder to source in India.
- Pharmaceutical Sector at Risk: Around 70% of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) used in Indian medicines are imported from China.
- Tariff-linked cost hikes or supply bottlenecks could raise drug prices and impact India’s healthcare and pharma exports.
- GDP and Inflation Effects: Weaker global demand could slow India’s GDP growth, as seen earlier when it fell from 8.3% in 2017–18 to 4.2% in 2019–20, with the US-China trade war in 2018 being a major cause
- Inflation could rise due to costlier imports, affecting household spending and business costs.
- Export Opportunities: As the US imposes steep tariffs on China, Indian sectors such as textiles, and leather have an opportunity to become more competitive and capture a larger share of the US market.
What Can be Done to Reduce the Impact of US-China Trade Conflict?
- Global Actions: The WTO’s Appellate Body has been paralyzed since 2019. Reviving it through consensus-building among G20 and Quad countries is vital to mediate large-scale tariff disputes legally.
- South countries must reduce overdependence on the US-China axis by investing in South-South trade corridors (e.g., India- Africa - ASEAN)
- If Europe strengthens ties with Asia, global trade could decentralize from US dominance in the long term.
- Forums like Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation and BRICS must prioritize economic de-escalation and cooperation over unilateralism.
- National Actions: India should fast-track India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA), India-UK FTA, and India-GCC FTA to ensure India’s exports are shielded from US- China trade war linked supply shocks.
- Strengthen Production Linked Incentive Schemes and Make in India in semiconductors, electronics, APIs, and solar modules to curb overdependence on Chinese imports.
- Position India as a preferred China+1 destination to attract supply chains looking to exit China by easing land, labor, logistics, and compliance under PM Gati Shakti and Invest India platforms.
- Use platforms like Quad, BRICS, G20, and Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) to push for non-politicization of supply chains and protect developing country trade rights.
- Establish a National Trade Watchdog to monitor tariff shifts, rerouted goods, and early warning systems for Indian exporters.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the implications of the 2025 US-China tariff escalation on India’s economy and global trade. What steps can India take to mitigate these risks? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q1. The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is viewed as a cardinal subset of China’s larger ‘One Belt One Road’ initiative. Give a brief description of CPEC and enumerate the reasons why India has distanced itself from the same. (2018)
Q2. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)
Q3. ‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (2019)


Governance
Custodial Torture and Need for Police Reforms
For Prelims: Custodial Torture, Human Rights, Custodial Deaths, Article 21, IPC, CrPC.
For Mains: Custodial torture and Custodial Deaths, Technology and Interrogation, Measures to avoid custodial deaths, Policing and Police Reforms in India
Why in News?
The Status of Policing in India Report, 2025 by Lokniti-CSDS and Common Cause (an NGO), based on inputs from 8,276 police personnel across 17 States/UTs, reveals the continued acceptance of custodial torture and coercive methods within the police.
- These insights highlight the urgent need for institutional police reforms to curb abuse and uphold constitutional rights.
What are the Key Findings of CSDS Survey on Custodial Treatment by Police?
- High Acceptance of Custodial Violence: 63% of police personnel justified violence against suspects of serious crimes like rape and murder.
- Even for minor offences such as theft, 30% supported third-degree methods.
- Institutional Endorsement of Torture: 42% of police personnel strongly supported torture in terror cases, and 28% for history-sheeters.
- 25% of police personnel justified mob justice in cases like sexual assault or child abduction, while 22% supported extra-judicial killings of "dangerous criminals".
- While 74% believed that legal procedures should be followed even when dealing with dangerous criminals, only 41% reported consistent adherence to arrest protocols.
- Kerala recorded the highest compliance, with 94% affirming that legal norms are always observed during arrests.
- Ambivalence Towards Mandatory Reporting: 39% of police personnel supported mandatory reporting of custodial torture, while 41% favoured it only in select cases, reflecting conditional accountability.
- Station-level officers were more supportive of reporting than seniors.
- Reform Readiness: 79% of police personnel support human rights training and anti-torture mechanisms, with over 75% willing to report custodial violence if protected legally, and 79% supported evidence-based interrogation techniques indicating strong internal demand for reform and accountability.
- Legal Safeguards vs Ground Reality: Despite legal safeguards under Article 21 and the SC guidelines in D.K. Basu vs State of West Bengal, 1997 case, custodial norms are routinely violated.
- Magistrates' inaction, unqualified medical checks, and NHRC’s limited powers highlight institutional gaps, while zero convictions in custodial death cases (2018–2022) reveal deep impunity.
What is Custodial Torture?Click Here to Read: Custodial Torture What are the International Conventions Against Custodial Torture?Click Here to Read: International Conventions Against Custodial Torture |
Why is There a Need for Police Reforms in India?
- Overburden & Manpower Shortage: India has only 155.78 police personnel per 100,000 people, well below the UN norm of 222. High vacancy rates at West Bengal (39.42%), Mizoram (35.06%), Haryana (32%) worsen the burden.
- Officers work 16–18 hours a day, with 83.8% reporting high stress, affecting efficiency, response time, and case quality.
- They also handle multiple roles like VIP security and election duties, often with low pay and little rest, increasing burnout and chances of corruption.
- Politicization & Weak Accountability: Police autonomy is often compromised by political interference with 72% of Delhi police officers reported facing political pressure in investigations (Status of Policing in India Report).
- Misuse of laws like sedition against journalists, activists, and minorities weakens the rule of law and public trust.
- Excessive force during protests (e.g., CAA-NRC, farmers’ protests, 2023 wrestlers’ protest) and 669 custodial deaths (2017–2022) reflect growing militarization and raise serious human rights concerns.
- Inadequate Training: Most states lack proper training infrastructure, with a low proportion of trained personnel as highlighted by the CAG. Weapon training is outdated, and police are rarely trained in modern techniques like cybercrime investigation or forensic science.
- India has only 0.33 forensic experts per 0.1 million people, compared to 20–50 in developed countries, hampering scientific investigations.
- Limited gender sensitivity training further weakens justice delivery in cases of domestic violence, sexual assault, and trafficking.
- Outdated Infrastructure: Many police stations lack modern surveillance tools and digital case management systems. As of 2022, there was only one computer per 11 police personnel, with some states having just one per 30 officers.
- Police forces still rely on outdated weapons and manual record-keeping, making it difficult to address cybercrime, terrorism, and other emerging threats effectively.
- Public Trust Deficit and Gender Imbalance: Community policing initiatives like Janamaithri (Kerala) and Mohalla Committees (Maharashtra) are exceptions rather than the norm, limiting grassroots engagement.
- Marginalized communities like dalits and minorities often view the police as discriminatory and unapproachable, reducing trust and cooperation.
- Women constitute only 11.75% of the police force (MHA), despite rising crimes against women, discouraging reporting and affecting the sensitivity and effectiveness of responses to gender-based violence.
What Steps Should be Taken to Reform the Police System?
- Reducing Workload: Address police shortage through fast-track recruitment and increased funding.
- A fixed 2-year minimum tenure, as per the SC directives in Prakash Singh Case, 2006, will improve efficiency and reduce political interference.
- Ensuring Autonomy and Depoliticization: Implement the State Security Commission (SSC) to protect police from political interference, as recommended by the National Police Commission.
- Empower the Police Establishment Board (PEB), per the Ribeiro Committee, to manage transfers and promotions independently.
- Replace the outdated Police Act, 1861 with the Model Police Act (2006) to ensure legal backing for reforms.
- Infrastructure Modernization: Adopt AI-driven policing, big data analytics, and drone surveillance for smarter crime control.
- Expand the Modernization of Police Forces (MPF) scheme to invest in CCTV networks, forensic labs, GPS-enabled vehicles, and body cameras.
- Strengthen cybercrime units as per the Padmanabhaiah Committee, and implement the NHRC’s 2021 directive on night-vision CCTV in police stations to boost accountability.
- Specialization and Functional Division: As per the Malimath Committee, investigation and law-and-order duties should be separated and a specialized crime investigation cadre for complex cases should be formed.
- It also recommended that confessions made before a senior police officer be admissible as evidence, with safeguards against coercion.
- Community Policing and Trust Building: Adopt community policing models as per the Model Police Act (2006) and NHRC guidelines. Scale up successful initiatives like Janamaithri Suraksha (Kerala) and Mohalla Committees (Maharashtra).
- Appoint social workers and psychologists in police stations to handle sensitive cases. Promote regular public-police interactions to build trust, especially in marginalized communities.
- Gender Sensitization: Implement 33% reservation for women in police, all-women police stations in each district, and female presence in all stations.
- Mandate gender sensitization training and provide supportive facilities to improve retention.
- Judicial Coordination and Reform: Digitize FIRs, link police records with e-courts, and fast-track undertrial cases as recommended by the Malimath Committee.
- Appoint liaison officers and expand plea bargaining to cut delays and ensure timely justice.
- Capacity Building: Set up a Police Training Advisory Council (PTAC) to modernize training with focus on forensics, human rights, and technology. Include soft skills and citizen interface modules.
- Encourage higher education through scholarships and enable cross-agency training with CBI, NIA, and IB for professional growth.
Conclusion
Police reforms are crucial for building a responsive, professional, and people-centric policing system in India. Implementing long-pending recommendations, ensuring autonomy, leveraging technology can transform law enforcement. A reformed police force is essential for safeguarding democratic values, ensuring justice, and upholding the rule of law.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Why are police reforms necessary in India? Suggest key measures to improve policing. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 Instances of the President’s delay in commuting death sentences have come under public debate as a denial of justice. Should there be a time specified for the President to accept/reject such petitions? Analyse. (2014)
Q.2 The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in India can be most effective when its tasks are adequately supported by other mechanisms that ensure the accountability of a government. In light of the above observation assess the role of NHRC as an effective complement to the judiciary and other institutions in promoting and protecting human rights standards. (2014)


Facts for UPSC Mains
India Ends Trans-Shipment Facility for Bangladesh
Why in News?
India has ended the 2020 transshipment facility that allowed Bangladeshi exports to pass through its ports and airports. This decision comes after Bangladesh's remarks in China, where it described Northeast India as 'landlocked' and positioned itself as the 'guardian of the ocean' for the region, as well as a strategic gateway for China's influence in Northeast India.
Note: The transshipment facility for Bangladesh, introduced by India in 2020, allowed Bangladeshi exporters to use Indian Land Customs Stations (LCSs) to transport goods to third countries like Bhutan, Nepal, and Myanmar.
- This arrangement aimed to streamline trade flows, reduce logistical costs, and benefit Bangladesh's readymade garment (RMG) sector by cutting transit costs and time.
Why did India Withdraw Transshipment Facility for Bangladesh?
- Industry Pushback: The Apparel Export Promotion Council (AEPC) lobbied for the facility’s removal.
- India and Bangladesh are direct competitors in global textile markets, especially in the RMG sector (China ranks 1st, Bangladesh 2nd, and India 6th in global garment exports).
- Indian exporters argued that the facility favored Bangladesh, hurting India’s market share and logistics infrastructure.
- Rising Air Freight Costs: Sharp increases in freight rates to destinations like the US and Europe prompted calls to reduce external cargo burden on Indian facilities.
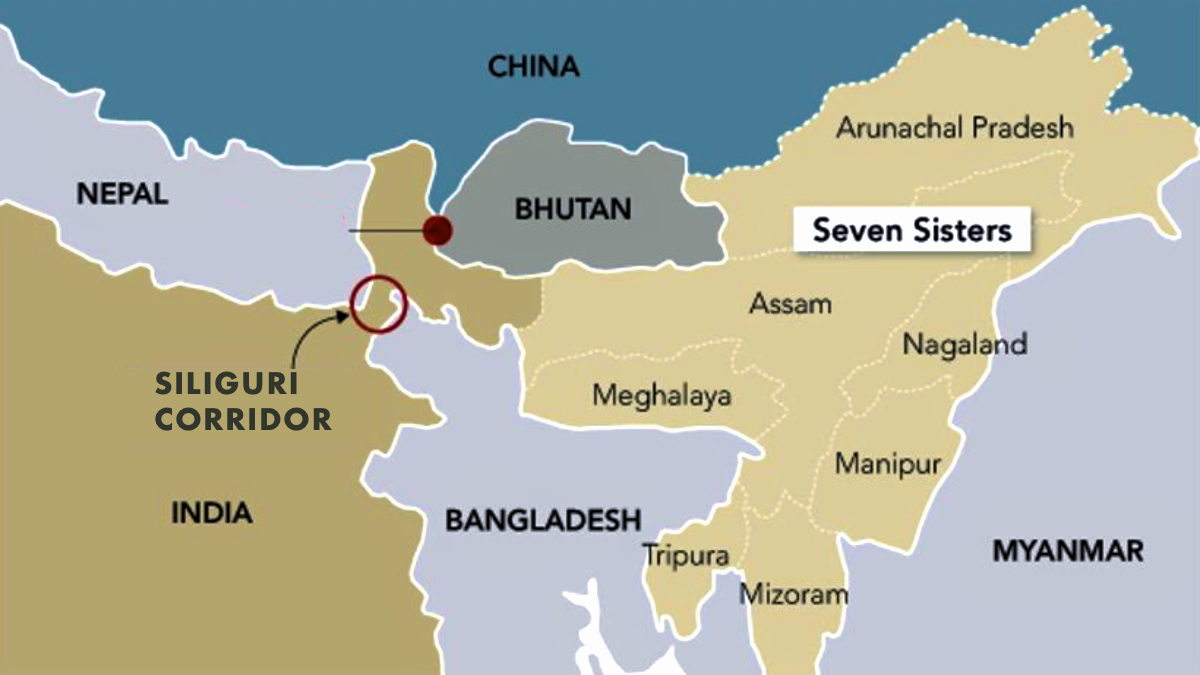
- China Factor: India's move reflects its strategic unease over China’s growing presence near the Siliguri Corridor (Chicken Neck corridor), where Bangladesh has invited Chinese investment in the Lalmonirhat Airbase, close to India’s northeastern frontier.
- The Northeast region, known as the "Seven Sisters," is connected to mainland India through the narrow Siliguri Corridor. It shares international borders with Bangladesh, Bhutan, Myanmar, China and Nepal, making it highly geopolitically sensitive.
- Implications:
- Bangladesh: In 2024, Bangladesh’s USD 50 billion export sector, led by RMG, faces higher costs and delays after India’s move, impacting its global competitiveness in textiles.
- India: The decision signals growing strain in India-Bangladesh relations, particularly as Bangladesh moves closer to China.
- Experts also warn the move may conflict with World Trade Organization (WTO) General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) Article V and Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) Article 11, which ensure freedom of transit for landlocked nations.
| Read more: India-Bangladesh Relations |
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the reasons for India’s withdrawal of the transshipment facility to Bangladesh. What are its implications for regional trade and connectivity? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements: (2017)
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
- River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Analyze internal security threats and transborder crimes along Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan borders including Line of Control (LoC). Also discuss the role played by various security forces in this regard. (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
Japan Created 3D-Printed Train Station
Why in News?
Japan has constructed the world’s first 3D-printed railway station (Hatsushima Station), completed in just 6 hours using additive manufacturing (3D printing) technology.
- The station’s 3D-printed parts, made with special mortar reinforced with concrete, were transported by separate trucks to the construction site, reducing labor needs and on-site construction time, which was then assembled in short time.
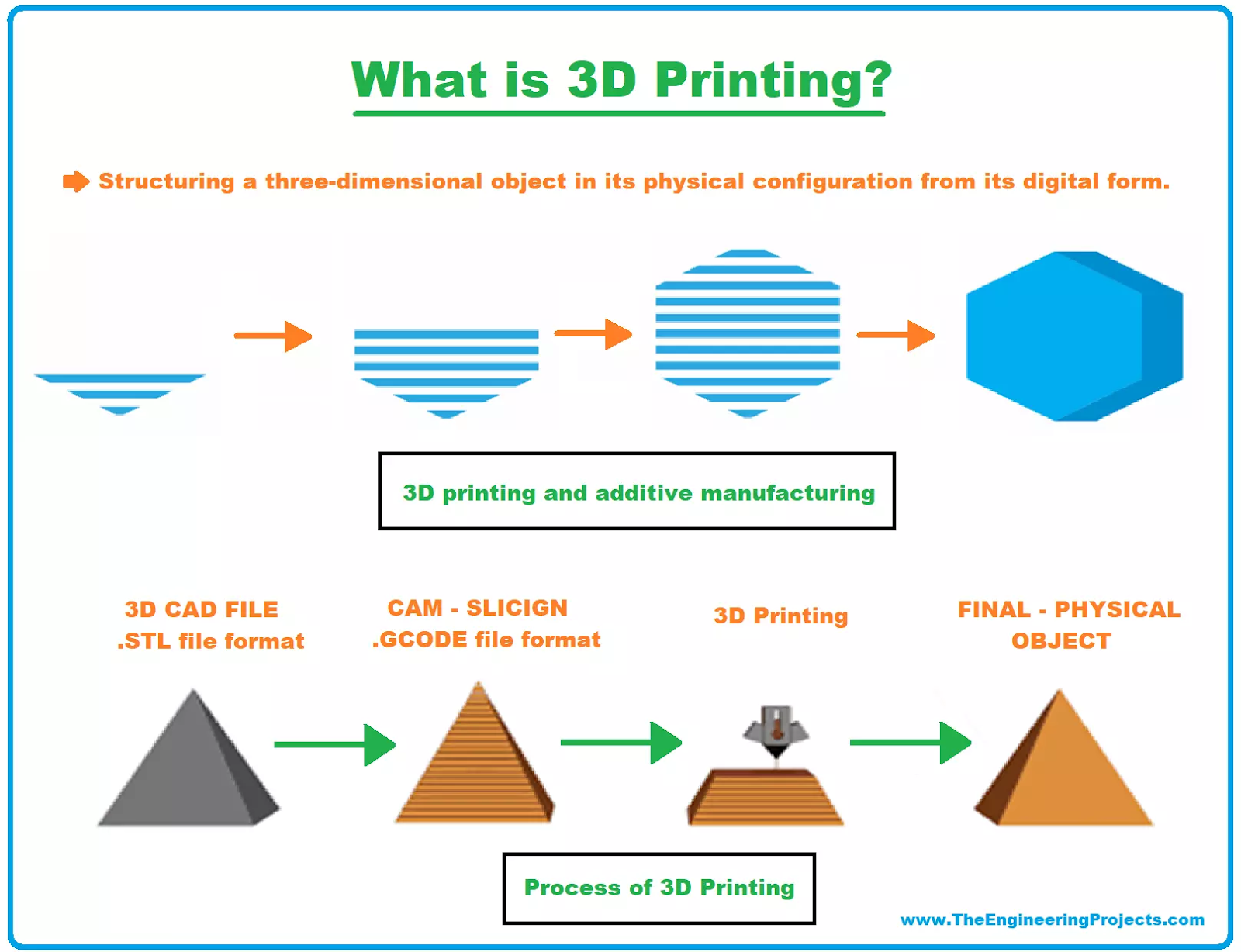
What is 3-D Printing Technology?
- About: 3D printing or Additive Manufacturing (AM), is a process that creates 3-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer based on a digital design.
- It is the opposite of traditional (subtractive) manufacturing, which involves removing material from a solid block through cutting or drilling.
- Working Mechanism:
- Design & Conversion: A digital 3D model is developed using computer-aided design (CAD) software or 3D scanning. This model is then sliced into thin layers and converted into machine-readable G-code instructions.
- Printing & Post-Processing: Material (plastic, metal, etc.) is deposited layer by layer by the 3D printer to build the object as per the design. Post-printing, the object is cleaned, cured, assembled, and tested for precision and performance.
- Materials Used: It uses a variety of materials including thermoplastics, metals and alloys, ceramics, and biomaterials like bioinks for medical applications.
- Common Methods of 3D Printing: Common 3D printing methods include Material Jetting, Directed Energy Deposition (DED), and Sheet Lamination, which build complex objects layer-by-layer with precision.
- Key Applications:
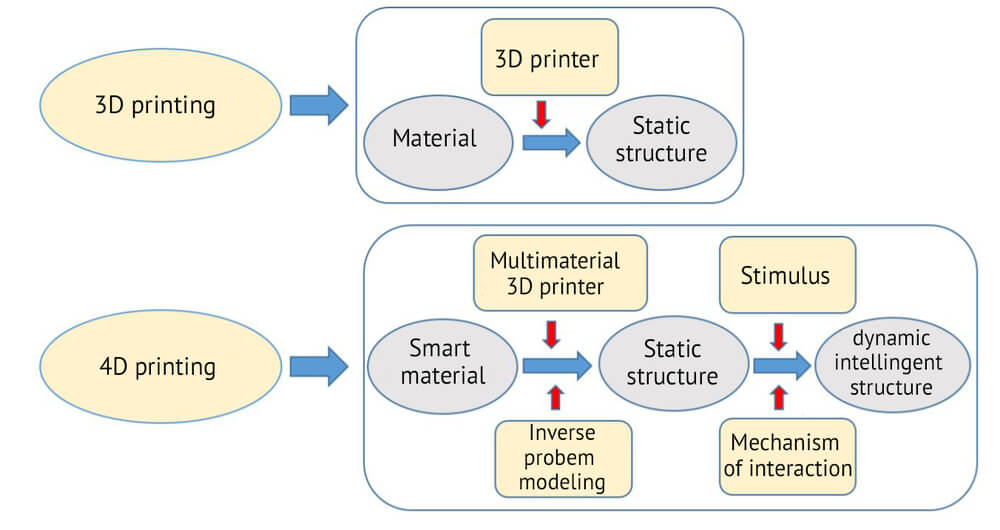
What is 4D Printing Technology?
- About: 4D printing is an advanced form of 3D printing where objects made using smart/intelligent materials (like hydrogels, active polymers) can change shape, structure, or properties over time in response to external stimuli like heat, light, moisture, or pressure.
- Unlike static 3D prints, 4D-printed objects can bend, self-assemble, repair, or transform autonomously, enabling dynamic and responsive structures without the need for electronics or human intervention.
- Key Applications:
- Medicine: Adaptive implants like dissolvable stents and smart devices that adapt to body growth or temperature, used in life-saving surgeries and targeted drug delivery.
- Clothing & Footwear: Enables adaptive wearables that respond to environmental conditions, military uniforms and sportswear can adjust ventilation, color, or fit dynamically.
- Aerospace & Automotive: NASA's 4D-printed smart fabrics for astronaut suits and intelligent materials for impact-resistant airbags and cooling aircraft engines.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following is the context in which the term “Qubit” is mentioned?
(a) Cloud Services
(b) Quantum computing
(c) Visible light communication technologies
(d) Wireless Communication Technologies
Ans: (b)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?(2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Debt Metrics
Why in News?
Household debt in India rose from 36.6% of GDP to 42.9% between June-2021 and June 2024, signaling a macroeconomic shift and underscoring the need to examine key debt metrics such as Debt-to-GDP ratio, public debt, and internal vs external debt.
What are the Key Debt Metrics?
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio:
- It is the ratio of a country’s total debt to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- It indicates the country’s ability to repay its debt. A high ratio suggests a potential risk to fiscal sustainability, while a moderate ratio is manageable if economic growth is strong.
- India's Context: For the central government, the debt-to-GDP ratio is estimated to be 57.1% in 2024-25 and 56.1% in 2025-26.
- Government aims to bring it down to 50 ± 1% by 2030–31.
- State governments account for nearly one-third of total public debt and contributed to over 50% of the rise in overall public debt between 2014-15 and 2019-20.
- Public Debt:
- About: Public debt refers to the total liabilities incurred by the government to finance its developmental and fiscal needs.
- It is repaid from the Consolidated Fund of India and includes both internal and external borrowings.
- Constitutional Basis: As per Article 292 of the Constitution, the Union government defines public debt as liabilities contracted against the Consolidated Fund of India within such limits, if any, as may be fixed by Parliament by law.
- Classification:
- Debt under the Consolidated Fund of India (includes market borrowings like G-Secs and T-Bills).
- Public Account Liabilities (like provident funds, small savings, etc.).
- About: Public debt refers to the total liabilities incurred by the government to finance its developmental and fiscal needs.
- Internal vs External Debt:
- Internal Debt refers to public loans raised within the country, primarily from domestic sources like individuals, banks, and financial institutions. It is denominated in Indian Rupees.
- It forms over 93% of the centre's public debt and is divided into marketable (G-Secs, T-Bills) and non-marketable (special securities, etc.).
- External debt refers to the obligations of the country to foreign governments, international institutions, or foreign investors, usually denominated in foreign currencies.
- It includes loans from foreign sources and multilateral institutions.
- The external debt to GDP ratio stood at 19.4% as of September 2024.
- Internal Debt refers to public loans raised within the country, primarily from domestic sources like individuals, banks, and financial institutions. It is denominated in Indian Rupees.
Key Provisions Related to Debt Management in India:
- Article 292 & 293:
- Article 292: Allows the Union government to borrow money on the security of the Consolidated Fund of India, within limits set by Parliament.
- Article 293: Enables State governments to borrow money domestically upon the security of the Consolidated Fund of the State, with prior Centre approval if they owe existing loans to the Union.
- RBI Act, 1934: RBI Act, 1934 authorizes the Reserve Bank of India to manage public debt on behalf of the Central Government.
- FRBM Act, 2003: The FRBM Act, 2003 aims to institutionalize fiscal discipline, reduce fiscal deficits, and ensure long-term macroeconomic stability by setting targets for deficits, enhancing transparency, and ensuring timely fiscal reporting.
|
Factor |
Effect on Public Debt |
Explanation |
|
Fiscal Deficit Increase |
Increase |
A higher fiscal deficit requires borrowing to meet the gap between revenue and expenditure. |
|
Revenue Increase (Taxes) |
Decrease |
Higher revenue reduces the need for borrowing and public debt. |
|
Expenditure Increase (e.g., Welfare Schemes) |
Increase |
Increased government spending leads to higher borrowing to finance the deficit. |
|
Interest Rate Increase |
Increase |
Higher interest rates increase the cost of servicing debt, leading to more borrowing or higher debt. |
|
Privatization/Asset Sales |
Decrease |
Proceeds from asset sales can reduce the fiscal deficit and thus lower the need for borrowing. |
|
Foreign Borrowing |
Increase |
Borrowing from foreign sources increases external debt. |
|
Currency Depreciation |
Increase |
Depreciation increases the cost of repaying foreign-denominated debt, leading to higher overall debt. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Review Committee Report has recommended a debt to GDP ratio of 60% for the general (combined) government by 2023, comprising 40% for the Central Government and 20% for the State Governments.
- The Central Government has domestic liabilities of 21% of GDP as compared to that of 49% of GDP of the State Governments.
- As per the Constitution of India, it is mandatory for a State to take the Central Government’s consent for raising any loan if the former owes any outstanding liabilities to the latter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: C


Place In News
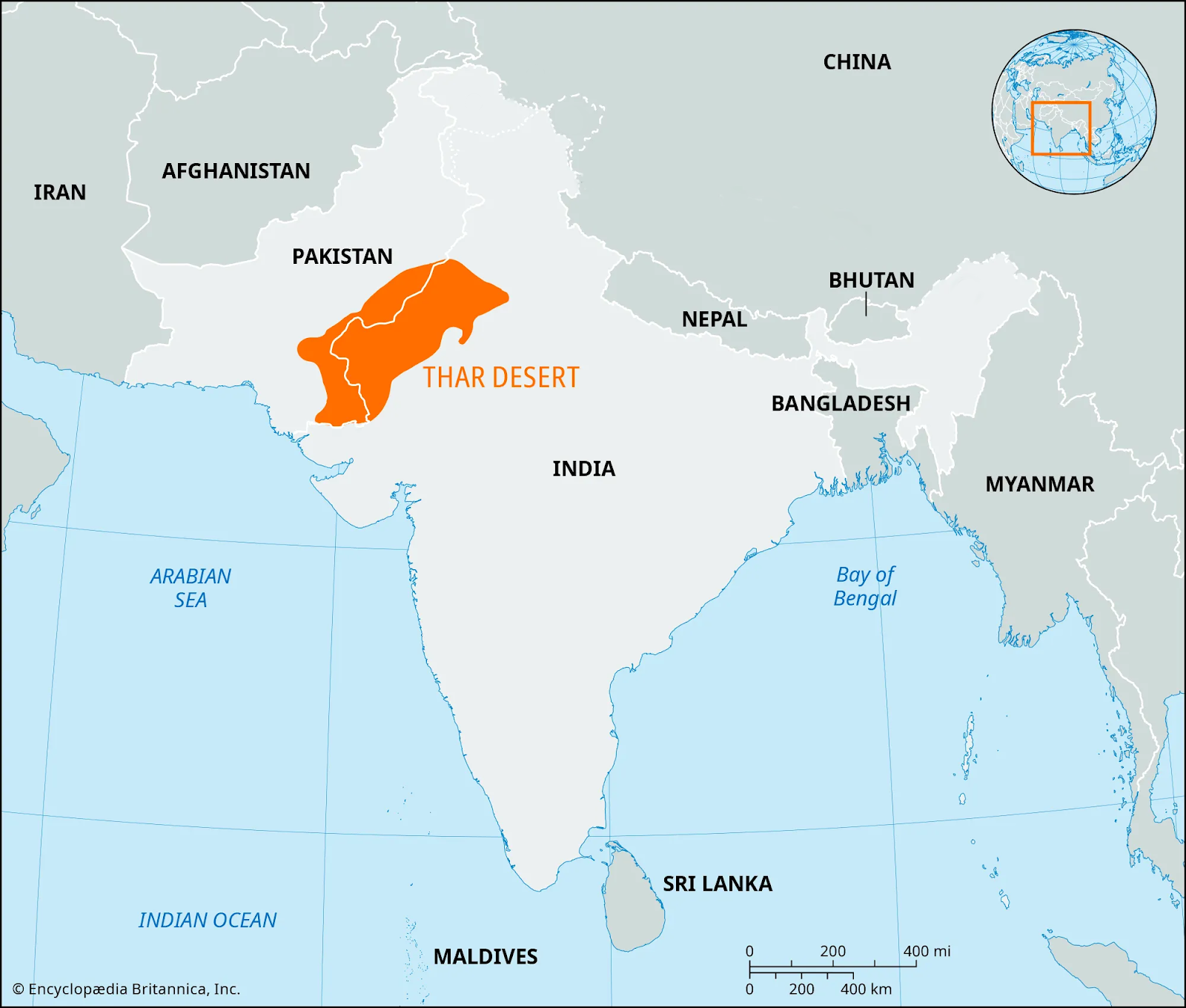
`Thar Desert
According to a new study, the Thar Desert in India has experienced a 38% annual increase in greening over the past two decades, driven by significant monsoon rainfall and agricultural expansion.
- Location of Thar Desert (The Great Indian Desert): It is an arid region of rolling sand hills on the Indian subcontinent. It spans an area of 200,000 sq kms across northwestern India (Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana) and southeastern Pakistan (Sindh and Punjab provinces).
- Geography & Climate: It is bordered by the Indus River plain to the west, the Punjab Plain to the north and northeast, the Aravalli Range to the southeast, and the Rann of Kachchh to the south.
- The desert experiences a subtropical desert climate, characterized by persistent high pressure and subsidence.
- Soil Composition: The desert's soils include Desert, Red Desertic, Sierozems, Red and Yellow, Saline, Lithosols, and Regosols.
- These soils are coarse-textured, well-drained, and calcareous (calcium-bearing), supporting specific vegetation and agriculture.
- Biodiversity: Supports a relatively rich biodiversity, including Blue Bull (Nilgai), Blackbuck, Great Indian Bustard (GIB) and Indian Gazelle (Chinkara).
- It is home to one of the largest national parks in India– Desert National Park (Rajasthan).
- Mineral Resources: The Desert houses one of the world's largest lignite coal reserves.
- It is rich in gypsum, and salt (with saltwater lakes– Sambhar and Kuchaman).
| Read More: Thar Desert |


Rapid Fire
City Key of Honour Award to Indian President
The President of India received the ‘City Key of Honour’ of Lisbon (Portugal), acknowledging the strong ties and goodwill between India and Portugal.
- It is the highest honour accorded by the city of Lisbon, given by the Mayor to recognise contributions to society or ties with Portugal.
- 2025 marks the 50th anniversary of India-Portugal diplomatic relations.
India-Portugal Relations:
- Historical Background: India- Portugal connection began in 1498 with Vasco da Gama's arrival in Calicut.
- Full diplomatic normalization was achieved after Portugal’s 1974 Carnation Revolution, culminating in the 1975 Goa Treaty.
- Strategic Cooperation: Portugal has consistently backed India’s bid for UNSC permanent membership and NSG entry. It also initiated the India-EU Summits, hosting the first in Lisbon in 2000 under PM Vajpayee.
- Economic and Trade Relations: As of 2025, India-Portugal bilateral trade stands at around USD 1.5 billion, marking a 50% rise since 2020 (USD 951 million).
- Diaspora Linkages: Around 1.25 lakh Indians, including 35,000 nationals and 90,000 persons of Indian origin (PIO) live in Portugal.
- Cultural and Educational Cooperation: India-Portugal cultural ties include the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) Chair at the University of Lisbon and release of joint stamps marking 500 years of ties.
| Read More: Merger of French and Portuguese Territories |


Rapid Fire
Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve
The Supreme Court has directed the Central Empowered Committee (CEC) to carry out a detailed survey of the Agasthyamalai landscape to identify any non-forestry activities and encroachments.
- Aim of the Survey: To identify all instances of non-forestry activities that violate statutory laws like the Forest Conservation Act, 1980 and Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- To provide comparative forest cover data to reveal the extent of degradation.
- Key Areas Under Survey: Periyar Tiger Reserve
- Agasthyamalai: It is part of a 3,500 sq. km biosphere reserve recognised by UNESCO.
- It stretches across Tamil Nadu and Kerala in the southernmost stretch of the Western Ghats.
- The Neelakkurinji flower, which blooms once every 12 years, grows in this landscape.
- Lion-Tailed Macaque, Bengal Tiger, Nilgiri Marten, Nilgiri Tahr, Malabar Spiny Dormouse, Great Pied Hornbill, Gaur (Indian bison), Sloth Bear found in this region.
- The region is inhabited by indigenous communities, especially the Kani tribe.
| Read More: Agasthyavanam Biological Park |


Rapid Fire
WMO Retired Hurricane Names for 2024
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has retired four hurricane names Beryl, Helene, Milton, and John from its Atlantic and East Pacific storm lists due to the devastation they caused in 2024, making their reuse inappropriate due to the associated trauma and sensitivity.
- Beryl became the earliest Category-5 hurricane (Winds exceeding 157 miles per hour) on record, severely impacting the Caribbean.
- Helene and Milton caused catastrophic damage in the United States, while John led to deadly flooding in Mexico.
- WMO has selected Brianna, Holly, and Miguel as replacements in the Atlantic, and Jake in the eastern Pacific. Storm names are reused every six years unless retired due to severe impact.
- Naming of Cyclones in India: India uses a one-time naming system for cyclones in the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea.
- Cyclones are assigned names once wind speeds exceed 34 knots or more, and these names are never reused, even if the cyclone moves into another region.
- The India Meteorological Department names cyclones in coordination with the Tropical Cyclone Regional Body on behalf of littoral countries, which includes 13 countries (India, Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Oman, Thailand, Iran, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Yemen).
| Read more:New List of Names of Tropical Cyclones |