Indian Economy
90 Years of RBI: Towards The Banking Vision of “Viksit Bharat”
- 05 Apr 2024
- 19 min read
This editorial is based on “ 90 years of RBI: Prepare for upcoming challenges” which was published in The Indian Express on 02/04/2024. The article delves into the achievements and challenges encountered by the Reserve Bank of India as it commemorates 90 years since its establishment.
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, Prompt Corrective Action (PCA) Framework, Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999, Non-performing assets (NPAs), Consumer Price Index (CPI), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC), Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) Framework, Marginal Cost of Funds based Lending Rate (MCLR), Raghuram Rajan committee (2008), Nachiket Mor Committee, P.J. Nayak Committee.
For Mains: Key Achievements and Challenges of the Reserve Bank of India.
In a recent milestone, the Reserve Bank of India has marked its significant 90-year journey. Throughout its history, the central bank has experienced various challenges and successes, showcasing a remarkable trajectory of accomplishments.
Nevertheless, with changes in payment mechanisms, the advent of central bank digital currency, and the emergence of new risks, the central bank must remain prepared to ensure effective regulation and supervision.
What is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)?
- About:
- RBI is the central bank of India.
- It was established on April 1, 1935 in accordance with the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- It was originally set up as a private entity in 1935, but it was nationalized in 1949.
- Objectives: The Preamble of the RBI describes the basic functions of the Reserve Bank as:
- To regulate the issue of Bank notes and keeping of reserves with a view to securing monetary stability in India and generally to operate the currency and credit system of the country to its advantage.
- To have a modern monetary policy framework to meet the challenge of an increasingly complex economy,
- To maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth.
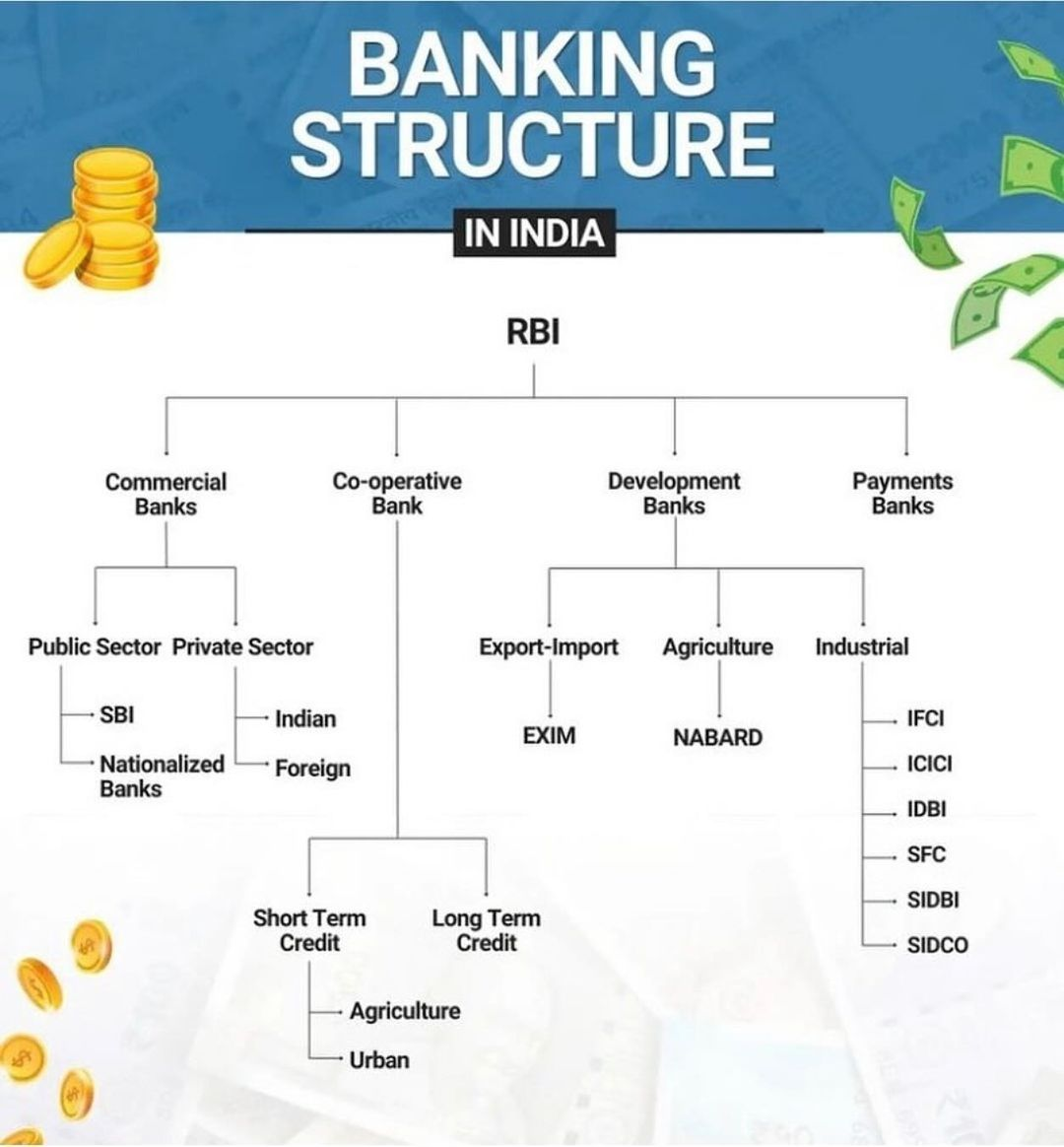
- Structure of RBI:
- The Reserve Bank's affairs are governed by a central board of directors.
- The board is appointed by the Government of India in keeping with the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- The directors are appointed/nominated for a period of four years.
- Acts Administered by the RBI:
- Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934
- Public Debt Act, 1944/Government Securities Act, 2006
- Government Securities Regulations, 2007
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
- Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002 (Chapter II)
- Credit Information Companies (Regulation) Act, 2005
- Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007
- Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 As Amended up to 2019
- Payment and Settlement Systems Regulations, 2008 As Amended up to 2022
- Factoring Regulation Act, 2011
What are the Key Accomplishments of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)?
- Maintaining Monetary Stability:
- The Reserve Bank of India Act, of 1934, provides the legislative mandate to the RBI to operate a modern monetary policy framework. Therefore, the RBI has adopted flexible inflation targeting (FIT) as the framework for monetary policy.
- The Government of India, in consultation with RBI, sets the inflation target in terms of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) every five years.
- Financial Sector Regulation:
- The RBI has implemented various measures to strengthen the banking sector and enhance financial stability.
- It regularly reviews and updates banking regulations to ensure the soundness of financial institutions.
- For example, the RBI introduced the Prompt Corrective Action (PCA) framework to tackle Non-performing Assets (NPAs) in banks and maintain their solvency.
- Successful Management of Public Debt:
- The Reserve Bank has successfully managed the public debt. It has floated loans for the Government at low rates of interest.
- It has helped in raising funds for the expansion of the public sector in the economy. It has also provided short-term advances to the Government.
- Financial Inclusion:
- The RBI has taken several initiatives to promote financial inclusion and access to banking services, especially in rural and remote areas.
- Measures such as branch licensing guidelines, priority sector lending norms, and the introduction of payment banks and small finance banks have expanded the reach of formal banking services to previously underserved segments of the population.
- Foreign Exchange Management:
- The RBI also manages all foreign exchange under the Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999.
- The RBI intervenes in the foreign exchange market to prevent excessive volatility in the exchange rate and maintain external sector stability. India's robust foreign exchange reserves are a testament to the RBI's effective management in this regard.
- Payment and Settlement Systems:
- The RBI has been proactive in modernizing payment and settlement systems to facilitate efficient and secure transactions.
- The RBI has overseen the modernization of payment systems, introducing initiatives such as Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS), National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT), and Unified Payments Interface (UPI), facilitating faster and seamless transactions.
- Technological Advancements:
- The RBI has embraced technological advancements in banking and finance, promoting digital banking, electronic payments, and fintech innovation to enhance efficiency and inclusivity in the financial sector.
- Regulation of Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs):
- With the growing importance of NBFCs in India's financial system, the RBI has strengthened regulations to enhance their resilience and mitigate systemic risks.
- It introduced guidelines for asset-liability management, capital adequacy, and corporate governance to ensure the stability of the NBFC sector.
- Economic Development Support:
- Through its monetary policy measures and developmental initiatives, the RBI has contributed to fostering economic growth, employment generation, and overall development of the economy.
- It has helped in setting up a sound structure of Development Banking. Several Industrial, Agricultural, Export and other specialised financial institutions have been established.
- Enhanced Public Confidence in the Banking Sector:
- The Reserve Bank has taken appropriate measures to enhance public confidence in the banking systems. It strictly supervises the working of the Scheduled Commercial banks so as to avoid their failures.
- The Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee System has also been introduced to protect the interests of the depositors. It has proved an important factor in promoting depositors’ confidence in banks.
What are the Challenges Encountered by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)?
- Autonomy of RBI:
- Under section 7 of the RBI Act, the central government may from time to time give such directions to the RBI as it may, after consultation with the Governor of the Bank, consider necessary in the public interest. Moreover, there is no legal act mandating the autonomy of the RBI.
- There have been instances where the government has sought to exert influence over RBI's decision-making process, particularly in matters related to monetary policy, regulatory actions, and the use of reserves.
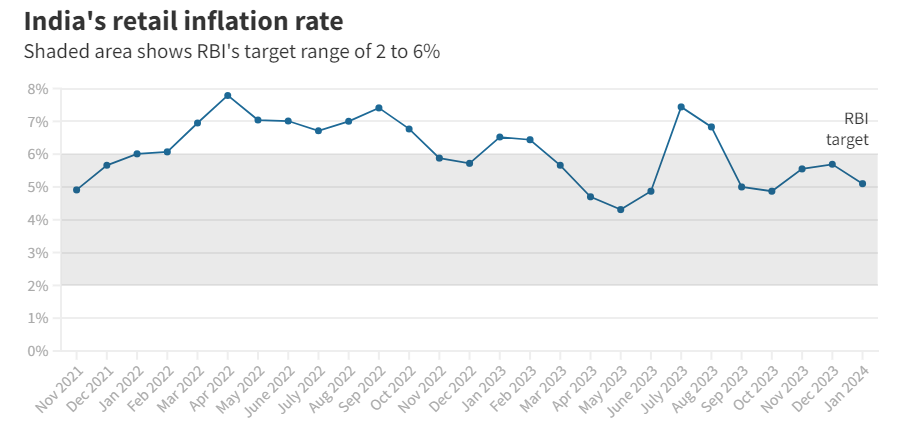
- Inflation Management:
- Despite the RBI's efforts to implement a flexible inflation-targeting framework, controlling inflation remains a significant challenge.
- As per the data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), the rate of price rise in the food basket, which constitutes nearly half of the CPI, increased to 9.53% in December 2023.
- India's complex economic structure, supply-side constraints, and external factors such as oil prices often pose challenges to achieving the inflation target.
- For example, fluctuations in global commodity prices can impact domestic inflation dynamics, making it difficult for the RBI to maintain price stability.
- Despite the RBI's efforts to implement a flexible inflation-targeting framework, controlling inflation remains a significant challenge.
- Writing off Loans without Adequate Recovery:
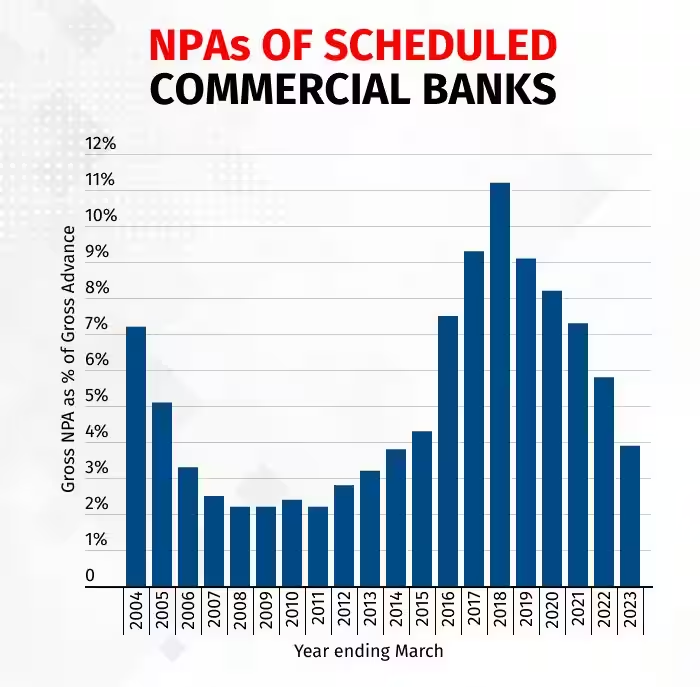
- This huge loan write-off aided banks in bringing down Gross Non-performing Assets (GNPA) – or loans defaulted by borrowers — to a 10-year low of 3.9% of advances in March 2023.
- While writing off loans without adequate recovery efforts may improve the short-term balance sheet, it does not address the underlying issues causing NPAs, leading to concerns about transparency and reliability of financial reporting.
- Financial Stability and Systemic Risks:
- Ensuring financial stability and mitigating systemic risks are ongoing challenges for the RBI. Rapid credit growth, interconnectedness among financial institutions, and vulnerabilities in certain segments such as shadow banking pose risks to the stability of the financial system.
- The recent episodes such as those involving the financial crisis in YES Bank and Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services Ltd underscore the need for enhanced oversight mechanisms.
- Incomplete Transmission of Monetary Policy:
- Incomplete Transmission of Monetary Policy means that the cumulative easing in policy rates by RBI has not yet been reflected in the lowering of their lending rates by banks.
- Factors such as rigidities in the banking system, liquidity conditions, and risk perceptions influence the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission.
- Digitalization and Cybersecurity:
- The rapid pace of technological advancements in the banking sector often outpaces regulatory frameworks, leading to challenges in ensuring compliance with evolving cybersecurity standards, data protection regulations, and consumer protection laws.
- The recent Paytm crisis has not only rocked the banking sector, but also unsettled the entire startup ecosystem in India.
- The rise in cyber threats, including hacking, phishing, and ransomware attacks, poses risks to the integrity and resilience of the financial infrastructure.
- The rapid pace of technological advancements in the banking sector often outpaces regulatory frameworks, leading to challenges in ensuring compliance with evolving cybersecurity standards, data protection regulations, and consumer protection laws.
- Financial Inclusion and Access to Credit:
- While the RBI has made significant efforts to promote financial inclusion, access to credit remains a challenge, especially for small and marginalized borrowers.
- Rural areas often lack sufficient bank branches, making it challenging for residents to access financial services. Rural areas often lack the high-speed internet connectivity needed to fully support digital banking services.
- A recent report by PhonePe and Boston Consulting Group concluded that India's digital payments market will more than triple from USD 3 trillion to USD 10 trillion by 2026, with much of this growth driven by rural areas.
What Strategies Should be Adopted to Improve the Functioning of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)?
- Strengthening Regulatory Framework:
- Enhance regulatory frameworks to ensure robust supervision and regulation of banks and financial institutions, including periodic reviews and updates to adapt to changing market dynamics and emerging risks.
- The Raghuram Rajan committee (2008) on financial sector reforms first proposed the creation of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) to strengthen financial stability and coordination among regulators.
- Enhancing Financial Inclusion:
- Implement measures to promote greater financial inclusion, such as expanding access to banking services, promoting digital payments, and supporting initiatives to reach underserved populations and regions.
- The Nachiket Mor Committee (2014) on Comprehensive Financial Services for Small Businesses and Low-Income Households recommended a phased approach towards achieving universal financial inclusion through innovative delivery mechanisms.
- Improving Monetary Policy Transmission:
- Address bottlenecks in monetary policy transmission mechanisms to ensure that policy rate changes effectively influence lending and borrowing rates across the financial system, promoting credit flow to productive sectors of the economy.
- The RBI has introduced measures such as the Marginal Cost of Funds based Lending Rate (MCLR) to improve the transmission of policy rate changes to lending rates by banks.
- Enhancing Risk Management Practices:
- Strengthen risk management frameworks within banks and financial institutions to identify, assess, and mitigate various risks, including credit, liquidity, operational, and cyber risks.
- Efforts such as the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) framework have aided in resolving issues like bad loans, paving the way for healthy credit growth.
- Promoting Technological Innovation:
- Encourage technological innovation and adoption within the financial sector, including fintech solutions, digital banking services, and blockchain technology, while ensuring data security and consumer protection.
- In August 2019, the Reserve Bank of India established its own Regulatory Sandbox (RS) ecosystem, making it one of the few countries to have such a system for enabling the controlled and systematic expansion of the FinTech ecosystem in the country.
- Increasing Transparency and Communication:
- Enhance transparency and communication channels between the RBI, financial institutions, and the public to improve understanding of monetary policy decisions, regulatory changes, and the overall functioning of the central bank.
- The RBI Governor's bi-monthly monetary policy statement and press conferences provide clarity on policy decisions and outlook.
- Capacity Building and Training:
- Invest in capacity building and training programs for RBI staff and stakeholders to enhance skills, knowledge, and expertise in areas such as financial regulation, supervision, monetary policy, and emerging technologies.
- The Damodaran Committee on Customer Service (2011) in Banks recommended enhancing training programs for bank employees to improve customer service and satisfaction
- Strengthening Governance and Accountability:
- Implement measures to enhance governance structures, accountability mechanisms, and internal controls within the RBI to ensure effective decision-making, transparency, and integrity in operations.
- The P.J. Nayak Committee (2014) on Governance in Banks recommended enhancing the autonomy and governance of public sector banks to improve their efficiency and accountability
- Collaboration and Coordination:
- Foster collaboration and coordination with other regulatory authorities, government agencies, international organizations, and stakeholders to address cross-cutting issues, promote financial stability, and achieve common objectives.
- The RBI participates actively in international forums such as the Financial Stability Board (FSB) and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) to exchange information and coordinate policy efforts.
- Foster collaboration and coordination with other regulatory authorities, government agencies, international organizations, and stakeholders to address cross-cutting issues, promote financial stability, and achieve common objectives.
Conclusion
RBI transcends its role as a central bank to become a beacon of excellence and innovation. It serves as a guardian of stability and resilience in the face of global uncertainties, leveraging advanced risk management tools and fostering a culture of prudence and foresight. Together, guided by a shared vision of prosperity and progress, RBI can unleash its full potential as a driving force for creating a “Viksit Bharat”.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the achievements and obstacles encountered by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Propose reforms to unleash the full potential of the RBI as a driving force for the vision of Viksit Bharat. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: A
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: B
Mains
Q. The product diversification of financial institutions and insurance companies, resulting in overlapping of products and services strengthens the case for the merger of the two regulatory agencies, namely SEBI and IRDA. Justify. (2013)