Geography
Earthquake in Tibetan China and Nepal
For Prelims: Earthquake, Mt Everest, Indian Tectonic Plate, Himalayan mountain range, Pangaea, Bureau of Indian Standards
For Mains: Tectonic Plate Movements , Seismic Zones of India, Tibetan Plateau and Earthquakes
Why in News?
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck the Tibetan region of China and parts of Nepal, causing widespread devastation. The quake’s epicenter was in Tingri County, within the Lhasa Terrane, near the Mt Everest region.
- This event aligns with findings from research identifying the Qixiang Co Fault, a newly discovered tectonic fault facilitating the eastward movement of the Tibetan Plateau, thereby increasing seismic activity in the region.
What are the Causes of Earthquake in Lhasa Terrane?
- Tectonic Plate Activity: The earthquake is a result of the ongoing collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates, which began around 50 million years ago.
- The Indian plate continues to push into the Eurasian plate at a rate of about 60 mm per year, causing tension to build up and eventually leading to earthquakes.
- Historical Context: Since 1950, more than 21 earthquakes of magnitude 6 or higher have been recorded in the Lhasa terrane.
- The strongest of these was in 2017 near Mainling, Tibet Autonomous Region of China, with a magnitude of 6.9.
Indian Tectonic Plate
- Around 200 million years ago, during the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea, the Indian plate, once part of Gondwana, began drifting northwards at 9 cm per year.
- This movement led to a collision with the Eurasian Plate, resulting in the uplift of the Himalayan mountain range, a process that continues today.
- The Indian plate moves northeast at approximately 5 per year, driving Himalayan growth by underthrusting the Eurasian Plate.
- The Indian Plate is bordered by the Eurasian Plate to the north, the Australian Plate to the south-east, the African Plate to the south-west, and the Arabian Plate to the west.
What is the Significance of Lhasa Terrane?
- Lhasa Terrane: The earthquake occurred in the Lhasa terrane, this region is home to large-scale infrastructure projects, including China’s world’s largest hydroelectric dam, which is being built on the Yarlung Tsangpo River.
- The Yarlung Tsangpo River enters India as the Siang and later the Brahmaputra. This raises concerns in India regarding the potential impact on water flow in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- In 2004, a landslide in Tibet created a glacial lake that nearly flooded the Sutlej River, prompting India to monitor the situation closely.
- The Yarlung Tsangpo River enters India as the Siang and later the Brahmaputra. This raises concerns in India regarding the potential impact on water flow in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- Environmental Risks: The Tibetan plateau holds significant water resources and is referred to as the 'third pole' due to its glaciers, rivers, and lakes.
- Earthquakes in the area can destabilize glaciers and change the course of rivers, increasing the risk of flooding.
What is the Qixiang Co Fault?
- Geological Characteristics: The QXCF is a sinistral fault (left-lateral fault), meaning the blocks on either side of the fault move laterally in a left-handed direction relative to each other.
- Significance in Tectonic Dynamics: The QXCF serves as the most significant tectonic boundary across the Qiangtang Terrane, a major geological feature of the Tibetan Plateau seismic zone (one of China’s five major seismic zones)
- The QXCF helps central Tibet move eastward, adding to the region's complex changes caused by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates.
- QXCF dynamics may influence the frequency and intensity of earthquakes in the area.
Why is the Himalayan Zone Seismically Active?
- Tectonic Plate Convergence: The Himalayas are the result of the collision between the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates which are still converging at a rate of 40-50 mm/year, causing constant tectonic stress and leading to seismic activity.
- Continual Plate Subduction: The Indian plate is being continuously subducted beneath the Eurasian plate, generating strain that is released through frequent earthquakes.
- Presence of Fault Lines: The region is crisscrossed by multiple fault lines, including the Main Himalayan Thrust, that are responsible for frequent seismic events.
- These faults store elastic energy that, when released, causes earthquakes.
- Complex Tectonic Interactions: Besides the India-Eurasia collision, other tectonic features, such as the subduction of the Eurasian plate beneath the Pamir Mountains, also contribute to the region's seismicity.
- This convergence of various tectonic forces increases the likelihood of earthquakes.
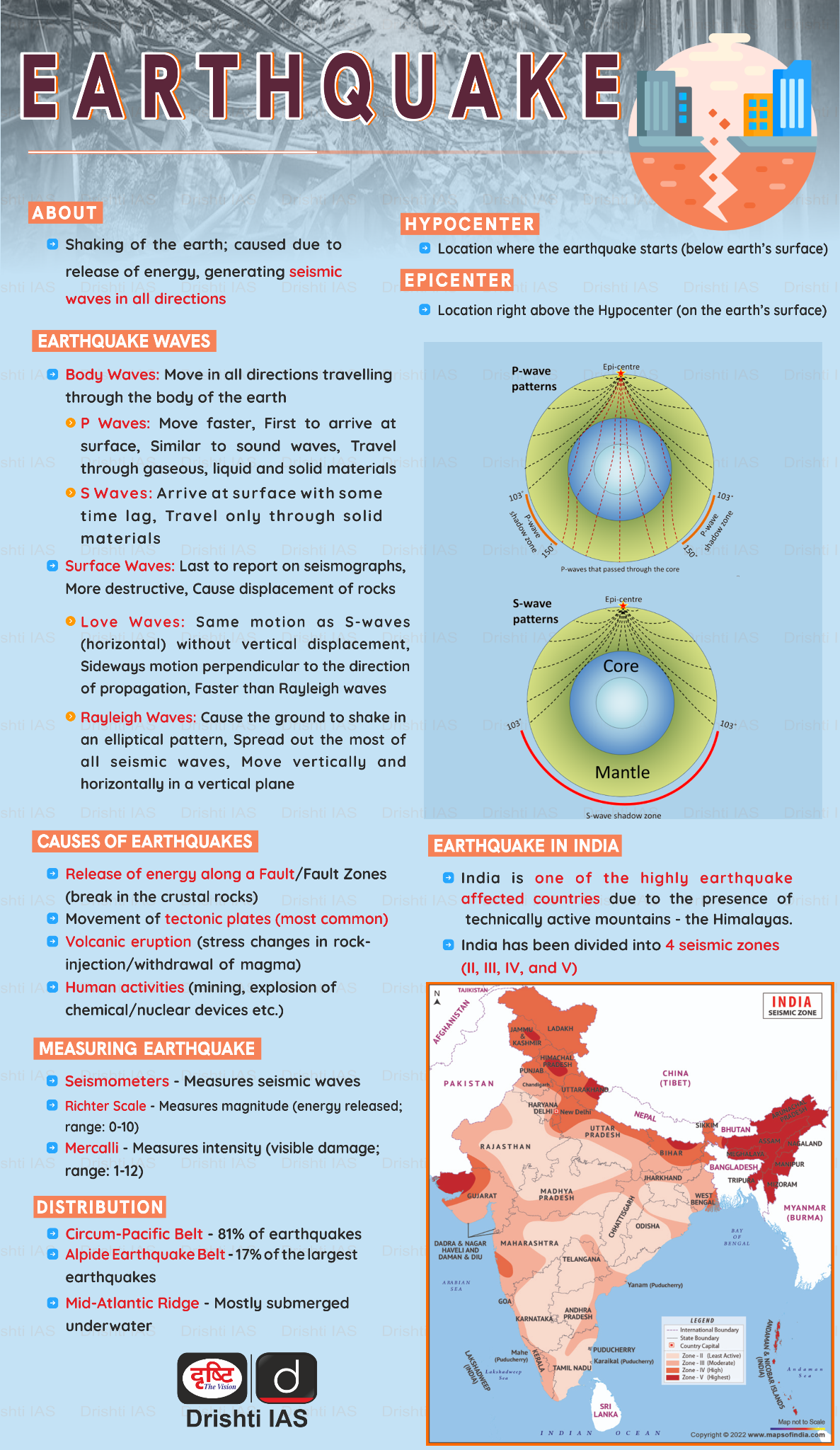
What is an Earthquake?
- About: An earthquake is the shaking of the Earth's surface caused by the release of energy, generating seismic waves.
- These waves travel in all directions and are recorded on seismographs. The starting point beneath the surface is the hypocenter, and the point directly above it on the surface is the epicenter.
- Types of Earthquakes: There are four different types of earthquakes they are tectonic, volcanic, collapse and explosion.
- A tectonic earthquake occurs when the Earth's crust breaks due to geological forces acting on rocks and adjacent plates, leading to physical and chemical changes.
- A volcanic earthquake is triggered by volcanic activity, typically due to the movement of magma within a volcano.
- A collapse earthquake occurs in underground caverns or mines, caused by seismic waves from surface explosions. These earthquakes are usually minor tremors.
- An explosion earthquake is an earthquake that is the result of the detonation of a nuclear and/or chemical device.
- Earthquake in India: India is divided into four seismic zones by the Bureau of Indian Standards: II, III, IV, and V. Zone V is the most seismically active, while Zone II is the least.
- The Indian Himalayan Region, being geologically active, primarily falls within Seismic Zones IV and V.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the factors contributing to high seismic activity in the Himalayan region, and how do the convergence of tectonic plates and fault lines increase earthquake likelihood? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. The frequency of earthquakes appears to have increased in the Indian subcontinent. However, India’s preparedness for mitigating their impact has significant gaps. Discuss various aspects. (2015)
Q. Discuss about the vulnerability of India to earthquake related hazards. Give examples including the salient features of major disasters caused by earthquakes in different parts of India during the last three decades. (2021)
Geography
La Nina: Impacts, Mechanisms, and Predictions
For Prelims: La Nina, Pacific Ocean, El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO), Trade Winds, Monsoon, Palm Oil Production, Oceanic Nino Index.
For Mains: El NiNo and La NiNa, its effect on weather conditions.
Why in News?
The long-anticipated La Nina has emerged, but the Pacific Ocean's cooling is mild and unlikely to cause as many weather problems as usual.
- Its delayed arrival may have been influenced by the world's oceans being much warmer than the last few years.
- La Nina conditions emerge in the tropical Pacific in December.
What is La Nina?
- About: La Niña, meaning "The Little Girl" in Spanish, is a cool phase of the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
- It is characterized by colder-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific Ocean.
- La Nina is one of the three phases of ENSO, alongside El Nino (the warm phase) and the neutral phase.
- Mechanism: In La Nina, the trade winds strengthen, pushing warm water toward the western Pacific.
- Cooler waters from below rise in the eastern Pacific, causing a temperature drop in that region.
- Cycles: La Niña occurs in irregular cycles, typically lasting from two to seven years, and often follows an El Nino event.
- Recent Events: The most recent La Nina phase lasted from 2020 to 2023, before transitioning to an El Nino phase in mid-2023.
- Climate Change: The intensity of La Nina's impacts, such as extreme temperatures and unusual weather patterns, is exacerbated by anthropogenic climate change.
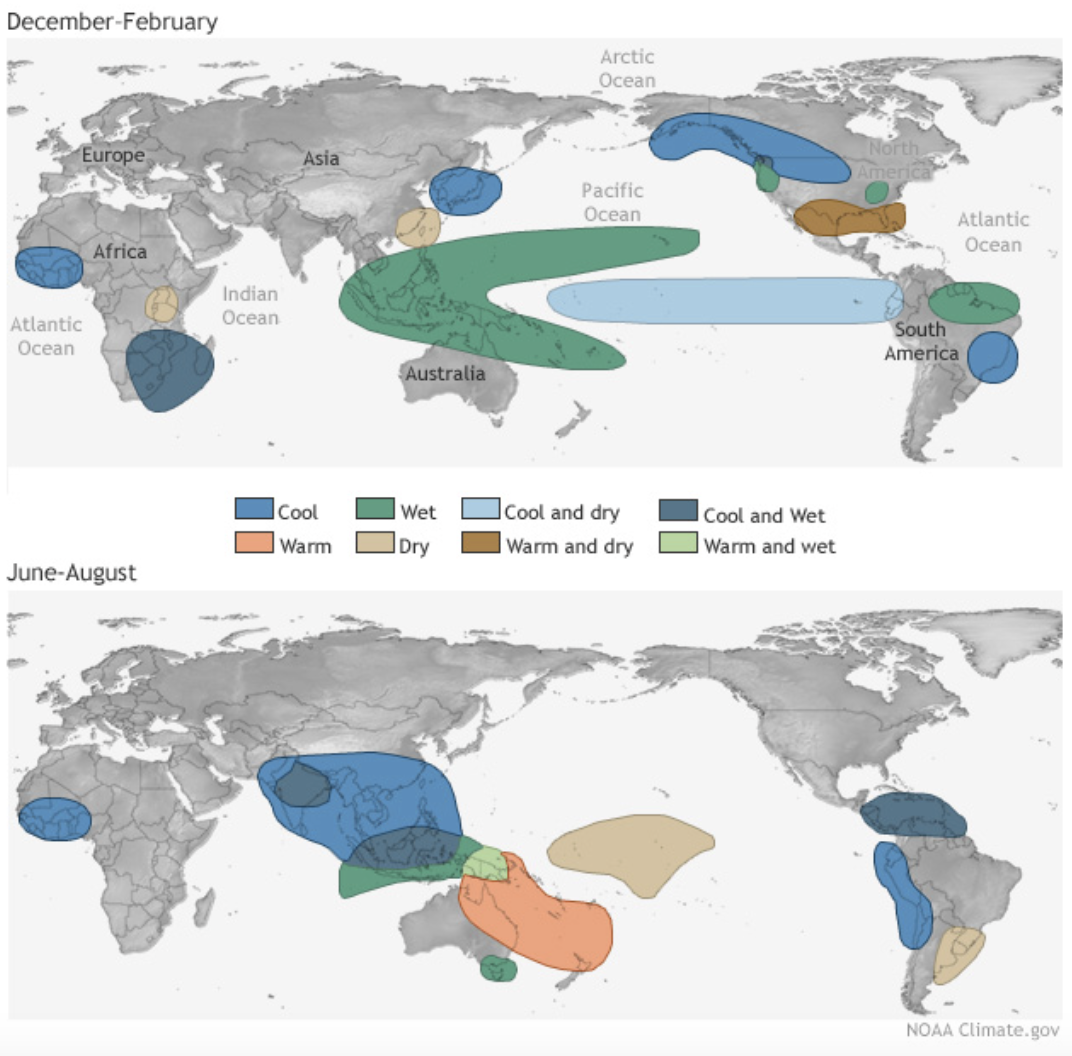
What are the Potential Regional Impacts of La Nina?
- Asia: In India, La Nina is expected to lead to above-average monsoon rainfall from July to September, which may result in a decrease in the production of pulses in the Indo-Gangetic Plains, but rice production may see an increase.
- In Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippine, La Nina brings above-average rainfall, causing flooding but boosting rice and palm oil production.
- South America: In Southern Brazil, Uruguay, northern Argentina, and southern Bolivia, La Nina causes below-average rainfall, leading to drought and affecting soybeans and maize.
- In contrast, Northern Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and parts of Ecuador and Peru experience wetter conditions, leading to potential flooding.
- Africa: In East Africa, La Nina brings drier conditions in December and January, negatively impacting crops harvested in February and March.
- In Southern Africa, La Nina causes above-average summer rainfall, benefiting agriculture with higher yields of maize, sorghum, wheat, and soybeans.
- Oceania: In Australia, the region experiences above-average rainfall in the northern and eastern regions, often linked to severe flooding.
- North America: In the US, La Nina causes drier conditions in the south and wetter, stormier weather in the north, including Alaska and Canada.
What is El Nino-Southern Oscillation?
- About: ENSO is a recurring climate pattern involving periodic changes in the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, affecting global weather patterns.
- Historical Context: The term El Nino was used by South American fishermen for warm Christmas waters.
- Sir Gilbert Walker discovered the Southern Oscillation, linking sea pressure changes to atmospheric conditions in the 1960s, leading to the ENSO term.
- La Nina and Neutral became widely used in the 1980s.
- Phases of ENSO:
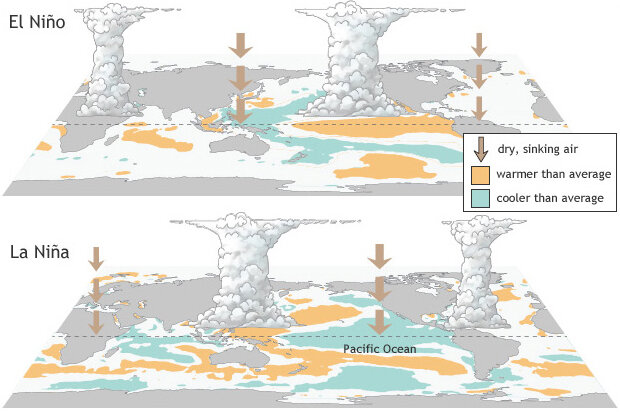
- El Nino: Warming ocean temperatures in the central/eastern Pacific, weakens easterly winds, reducing rainfall in Indonesia and increasing it in the central/eastern Pacific.
- La Nina: Cooling ocean temperatures in the central/eastern Pacific, strengthens easterly winds, increasing rainfall in Indonesia and decreasing it in the central/eastern Pacific.
- Neutral: Tropical Pacific sea surface temperatures are average, with atmospheric conditions showing signs of either El Nino or La Nina.
- ENSO Cycle: The ENSO cycle oscillates every 3 to 7 years, with sea surface temperatures varying between 1°C to 3°C above or below average.
How La Nina and El Nino are Predicted?
- Climate and Observational Data: Scientists use climate models alongside observational data (such as sea surface temperatures, trade wind strength, and data from satellites and ocean buoys) to predict the onset of ENSO events (El Nino and La Nina).
- Ocean buoys are floating devices placed in the ocean for various purposes, including environmental monitoring, data collection, and navigation.
- Oceanic Nino Index: ONI It compares the 3-month average sea surface temperatures in the East-Central Tropical Pacific with the 30-year average.
- When the difference between the two is 0.5º C or higher, it is an El Nino, and when it is –0.5º C or lower, it is a La Nina.
- Nino-3.4 Index: This index helps to identify the thresholds that define El Nino and La Nina events.
- A value of 0.5°C or greater is indicative of the event's initiation, while a strong event requires a temperature anomaly of 1.5°C or more.
- Lead Time for Predictions: La Nina events can be forecasted up to two years in advance if they follow a strong El Niño.
Conclusion
La Nina, the cool phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), influences global weather patterns, affecting rainfall, agriculture, and climate extremes. Accurate forecasting through models and indices like ONI and Nino-3.4 is vital for mitigating its impacts, especially as anthropogenic climate change amplifies its intensity and unpredictability.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. How does the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) influence weather patterns across the globe? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino?(2011)
- La Nina is characterised by an usually cold ocean temperature in equatorial Indian Ocean whereas El Nino is characterised by unusually warm ocean temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- El Nino has an adverse effect on the south-west monsoon of India but La Nina has no effect on monsoon climate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Drought has been recognized as a disaster in view of its spatial expanse, temporal duration, slow onset and lasting effects on vulnerable sections. With a focus on the September 2010 guidelines from the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), discuss the mechanisms for preparedness to deal with likely El Nino and La Nina fallouts in India? (2014)
Social Issues
Burqa Ban in Switzerland
For Prelims: Supreme Court, Hijab, Fundamental Rights, Cases Related to Freedom of Religion
For mains: Fundamental Rights, Judiciary, Government Policies & Interventions, Women's Issues, Cases Related to Freedom of Religion.
Why in News?
Switzerland's prohibition on face-covering garments, including burqas and niqabs, has come into effect from 1st January 2025.
- This measure, approved through a nationwide referendum in March 2021, reflects the ongoing global debate over wearing hijabs and burqas, an issue that has also sparked significant discourse in India.
Note: In addition to Switzerland, countries such as France, Belgium, Germany, Australia, Austria, and Canada have also imposed bans on various types of face veils, including hijabs and burqas.
Karnataka Government on Hijab Ban
- In 2022, the Karnataka government passed an order prohibiting the wearing of hijab (headscarf) in government educational institutions.
- The order cited Section 133(2) of the Karnataka Education Act, 1983, which grants the state powers to issue directives for government schools to follow.
- In 2013, the state used this provision to make uniforms compulsory. The latest order states that the hijab is not an essential religious practice for Muslims that can be protected under the Constitution.
Iranian Hijab Movement
- Historical Background: Post-1979 Iranian Revolution, the hijab was made mandatory for women, sparking decades of resistance.
- Protests and Symbolism: Iconic acts like the "Girl of Enghelab Street" protest, where a woman waved her white headscarf on a stick, symbolize defiance against the dress code.
- Protests reignited after the death of Mahsa Amini, allegedly due to strict hijab enforcement, leading to widespread demonstrations.
- Government Crackdown: Iran enforces the hijab mandate with fines and imprisonment for non-compliance, intensifying societal tensions.
- Currently the movement is supported by both men and women who oppose the compulsory dress code, reflecting broader demands for personal freedoms and women’s rights.
What is the Status of Hijab Wearing in India?
- Amna Bint Basheer v CBSE, 2016: In Amna Bint Basheer v CBSE, 2016, the Kerala HC ruled that wearing a hijab is an essential religious practice but upheld the CBSE dress code, allowing additional measures and safeguards as in 2015.
- The Central Board of School Education (CBSE) argued that the dress code was to prevent unfair practices.
- Kerala High Court, 2018: In Fathima Thasneem v State of Kerala, 2019, the case involved two girls who wanted to wear the headscarf and the Christian missionary school refused to allow the headscarf.
- The court ruled in favour of the school's decision, stating that the "collective rights" of the school must take precedence over individual student rights.
- Resham v. State of Karnataka, 2022: Karnataka HC in March 2022, validated the state government's ban on hijabs in government colleges.
- HC upheld the ban stating that wearing a hijab did not qualify as an essential religious practice and the ban did not violate the Freedom of Speech and Expression.
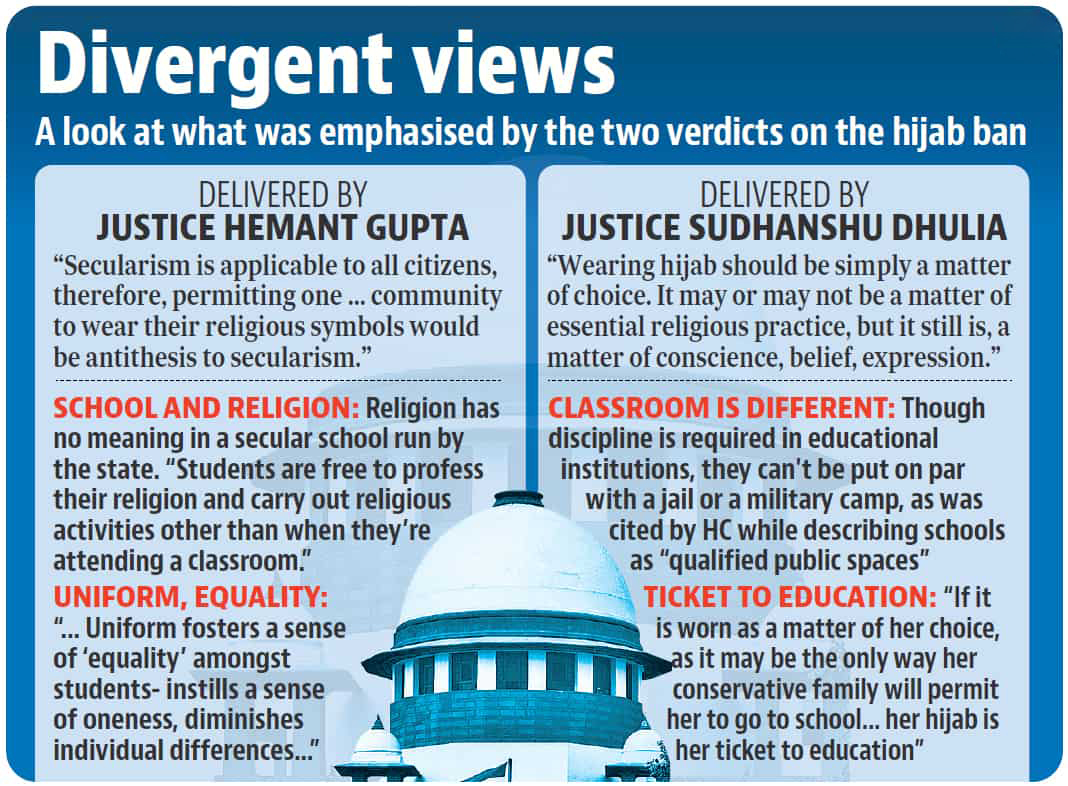
- Split Verdict by Supreme Court (SC), 2022: In Resham v. State of Karnataka, 2022 case 2-judge bench of SC delivered a split verdict. The case has now been referred to a larger bench of the SC.
Constitutional Framework for Religious Freedom in India
- The Indian Constitution guarantees the Right to Freedom of Religion under Articles 25-28, enshrined in Part III (Fundamental Rights):
- Article 25(1): Ensures the "freedom of conscience and the right to freely profess, practice, and propagate religion," providing a negative liberty where the state cannot interfere with religious practices.
- Article 26: Grants the "freedom to manage religious affairs," allowing religious denominations to establish and manage institutions for religious and charitable purposes, subject to public order, morality, and health.
- Article 27: Prohibits the state from compelling citizens to pay taxes for promoting or maintaining any particular religion, reinforcing the principle of secularism.
- Article 28: Regulates religious instruction in educational institutions, restricting religious instruction in state-funded or state-recognized institutions, except where explicitly permitted.
- Additionally, Articles 29 and 30 safeguard the cultural and educational rights of minorities, emphasizing the protection of their unique identities.
What are the Arguments in Favour and Against Such Ban?
- Arguments in Favour of Ban:
- Uniformity and Discipline: Enforcing a dress code promotes uniformity and fosters discipline in educational institutions.
- It prevents the display of overt religious symbols, maintaining a neutral and inclusive space free from religious divisions.
- Gender Equality: Hijab and similar practices are often viewed as tools of patriarchy that perpetuate gender inequality and restrict women’s freedom.
- Integration into Society: Prohibiting such practices can encourage integration into the broader society, avoiding potential alienation caused by visible religious markers.
- Not Absolute Fundamental Right: Fundamental rights are not absolute and are subject to reasonable restrictions.
- The right to religion under Article 25 cannot override other fundamental rights, particularly in government-funded educational institutions.
- Security Concerns: Such bans also aim to prevent anonymity that may hinder identification, deter misuse of garments to conceal weapons, and enhance public safety in high-risk areas.
- For example: 2019 Easter bombings in Sri Lanka, the suicide bombers blended in with the public.
- Uniformity and Discipline: Enforcing a dress code promotes uniformity and fosters discipline in educational institutions.
- Arguments Against Ban:
- Freedom of Religion: Article 25 of the Indian Constitution guarantees the right to practice and profess religion, banning such practices may create a sense of alienation and exacerbate social tensions.
- Autonomy and Choice: Imposing a ban infringes on personal liberty and the right of individuals, particularly women, to make choices about their attire.
- Impact on Education: Restricting hijab may discourage female students from conservative backgrounds from attending schools, adversely affecting their education and empowerment.
- For example: In 2019–20, Muslim girls had lower school attendance rates than Hindu girls in most states.
- For instance, in Uttar Pradesh, while only 63.2% of Muslim girls attended school, 81% of Hindus did so.
- For instance, in Uttar Pradesh, while only 63.2% of Muslim girls attended school, 81% of Hindus did so.
- Such bans can also hinder educational access, disproportionately affecting girls from conservative backgrounds and further marginalizing these groups.
- For example: In 2019–20, Muslim girls had lower school attendance rates than Hindu girls in most states.
Conclusion
The hijab/burqa debate highlights the need to balance individual freedoms with societal values and institutional discipline. While religious rights are protected under the Constitution, they are not absolute and must align with public order and equality. Judicial rulings emphasize inclusivity and gender equality, underscoring the importance of fostering dialogue and crafting policies that respect personal freedoms without hindering access to education or marginalizing communities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains:
Q. How the Indian concept of secularism is different from the western model of secularism? Discuss. (2016)
Q. Are tolerance, assimilation and pluralism the key elements in the making of an Indian form of secularism? Justify your answer. (2022)
Q. How is the Indian concept of secularism different from the western model of secularism? Discuss. (2018)
Q. Distinguish between religiousness/religiosity and communalism giving one example of how the former has transformed into the latter in independent India. (2017)
Economy
Future of Jobs Report 2025
For Prelims: World Economic Forum (WEF), Future of Jobs Report, Green Transition, AI, Renewable Energy, Low-Income Economies, Stakeholder Capitalism, Global Competitiveness Index, Global Gender Gap Index, Energy Transition Index, Global Risk Report, Global Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index, GenAI, Semiconductors, Quantum, Encryption.
For Mains: Impact of technological advancements on global labor markets.
Why in News?
The World Economic Forum (WEF) released its 'Future of Jobs Report 2025,' highlighting key findings and changes expected to shape the global job market by 2030.
- The report, based on inputs from 55 economies, projected a net increase of 78 million jobs by 2030 and highlighted how technology, economic shifts, and the green transition impact jobs and skills.
What Are the Key Findings of the WEF Report?
- Fastest-Growing Roles: The fastest-growing roles include frontline jobs (farmworkers, delivery), care economy positions, tech roles, and green transition jobs.
- Declining Roles: The report finds that clerical roles such as cashiers, data entry clerks, and bank tellers are expected to decline significantly.
- Job Displacement and Creation: Automation, investments in renewable energy and aging populations displaces jobs but creates new tech and machine management roles.
- Slower economic growth is expected to displace 1.6 million jobs globally.
- Technological Advancements: Broadening digital access is the most transformative trend, with 60% of employers expecting it to reshape businesses by 2030.
- Key technologies in demand for high skills include Artificial intelligence (AI) and information processing (86%), robotics and automation (58%), and energy technologies (41%).
- Green Transition: Climate-change mitigation and adaptation trends are driving demand for roles such as renewable energy engineers, environmental engineers, and specialists in electric and autonomous vehicles.
- Demographic Shift: Aging populations and shrinking workforces impact labor supply.
- Aging in high-income economies drives demand for healthcare, while growing workforces in low-income economies boost demand for educators and talent managers.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions are prompting business model transformations in 34% of organizations.
- Businesses are more likely to offshore and reshore their operations.
- Geopolitical tensions are boosting demand for security roles and cybersecurity skills.
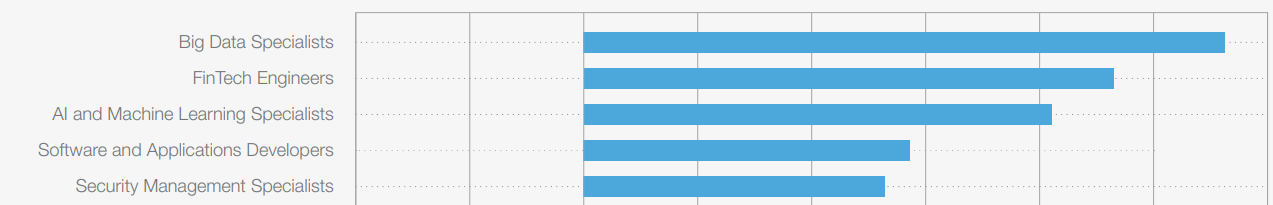
- India Related Findings: India is leading in AI skills enrollments with corporate sponsorship significantly boosting GenAI training.
- Employers in India aim to outpace global tech adoption, with 35% expecting semiconductors and computing technologies, and 21% anticipating quantum and encryption to transform operations.
- India and Sub-Saharan African nations, will supply nearly two-thirds of new workforce entrants in the coming years.
World Economic Forum (WEF)
- About: WEF is an international organization for public-private cooperation, headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It engages global leaders to shape agendas across industries, regions, and globally.
- Foundation: Founded by Klaus Schwab in 1971 as the European Management Forum, WEF introduced "stakeholder capitalism," which emphasizes long-term value for all stakeholders, not just short-term profits for shareholders.
- Evolution: In 1973, the WEF expanded its focus to economic and social issues. It introduced membership for the world’s leading 1,000 companies in 1975.
- In 1987, it became the World Economic Forum, broadening its role as a platform for dialogue. It was recognized as an international organization in 2015.
- Major Reports: WEF publishes key reports, including the Global Competitiveness Index, Global Gender Gap Index, Energy Transition Index, Global Risk Report, and Global Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index.
What are the Challenges to Employment in India due to Emerging Technologies?
- Job Displacement: According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), sectors like manufacturing and services are experiencing automation of repetitive tasks, leading to potential job displacement.
- Skill Mismatch: There's a growing need for expertise in AI, cybersecurity, and data science. However, a significant portion of the workforce lacks these specialized skills, leading to a mismatch between job requirements and available talent.
- Uneven Technology Adoption: Urban areas are rapidly adopting new technologies, while rural regions lag behind, leading to disparities in employment opportunities and economic growth.
- Informal Sector Challenges: Workers in the informal sector, which constitutes a significant part of India's economy, may find it hard to transition to technology-driven jobs due to lack of access to training and education.
Way Forward
- Upskilling: Governments, businesses, and educational institutions should collaborate to create specialized upskilling programs tailored to emerging sectors.
- Employers should create career progression pathways to help employees transition from declining to growing roles.
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI): Companies should invest in diversity recruitment programs, aiming to tap into underrepresented communities and regions, thus enhancing the talent pool.
- AI Adoption for Workforce: Embrace a mix of human creativity and AI efficiency where humans and machines can collaborate rather than compete, improving productivity without sacrificing employment.
- Retaining Talent: Conduct regular pay reviews, ensure compensation transparency, and offer incentives like stock options, bonuses, and benefits to boost retention and skill development.
- Public Policy Support: Governments should fund reskilling and upskilling initiatives, especially for industries impacted by technology, and offer retraining, financial support, and job placement for displaced workers.
Conclusion
The WEF’s 'Future of Jobs Report 2025' underscores the need for upskilling, adapting to technological shifts, and prioritizing diversity in the workforce. Governments and businesses must collaborate to create resilient labor markets by investing in skills, AI, and inclusive growth strategies to meet future job demands.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the impact of technological advancements and economic conditions on global labor markets by 2030. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The Global Competitiveness Report is published by the (2019)
(a) International Monetary Fund
(b) United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
(c) World Economic Forum
(d) World Bank
Ans: (c)
Q. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. What are the salient features of ‘inclusive growth’? Has India been experiencing such a growth process? Analyse and suggest measures for inclusive growth. (2017)
Important Facts For Prelims
Modhweth Festival
Why in News?
The Toda tribe, one of the oldest Dravidian ethnic groups in the Nilgiris Hills of Tamil Nadu, celebrated their traditional 'Modhweth' festival to mark the New Year.
What is the Modhweth Festival?
- About:
- It is celebrated annually on the last Sunday of December or the first Sunday of January.
- It is held at the Moonpo temple in Muthanadu Mund village, located in the Nilgiri district.
- The Moonpo temple features a unique vertical spire with a thatched roof and a flat stone on top, making it one of the last Toda temples of its kind in the Nilgiris.
- Rituals and Celebrations:
- Prayers are offered to the deity, Thenkish Amman, for good health, rains, and a bountiful harvest in the coming year.
- Participants perform a dance outside the temple as part of the celebrations.
- Unique Customs:
- Toda youth showcase their strength and masculinity by lifting a greased boulder weighing around 80 kg.
- As per traditional customs, women do not participate in the celebrations.
What is the Toda Tribe?
- About:
- Toda Tribe is a pastoral tribe of the Nilgiri Hills of southern India.
- The Todas are classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Tamil Nadu.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but is the most unusual and different among the languages belonging to the Dravidian family.
- Significance:
- Toda lands are part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, designated as an International Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO.
- Their territory is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Religion and Beliefs:
- Their religious practices revolve around a pantheon of gods, with Tökisy (goddess) and Ön (god of the underworld) as the central deities.
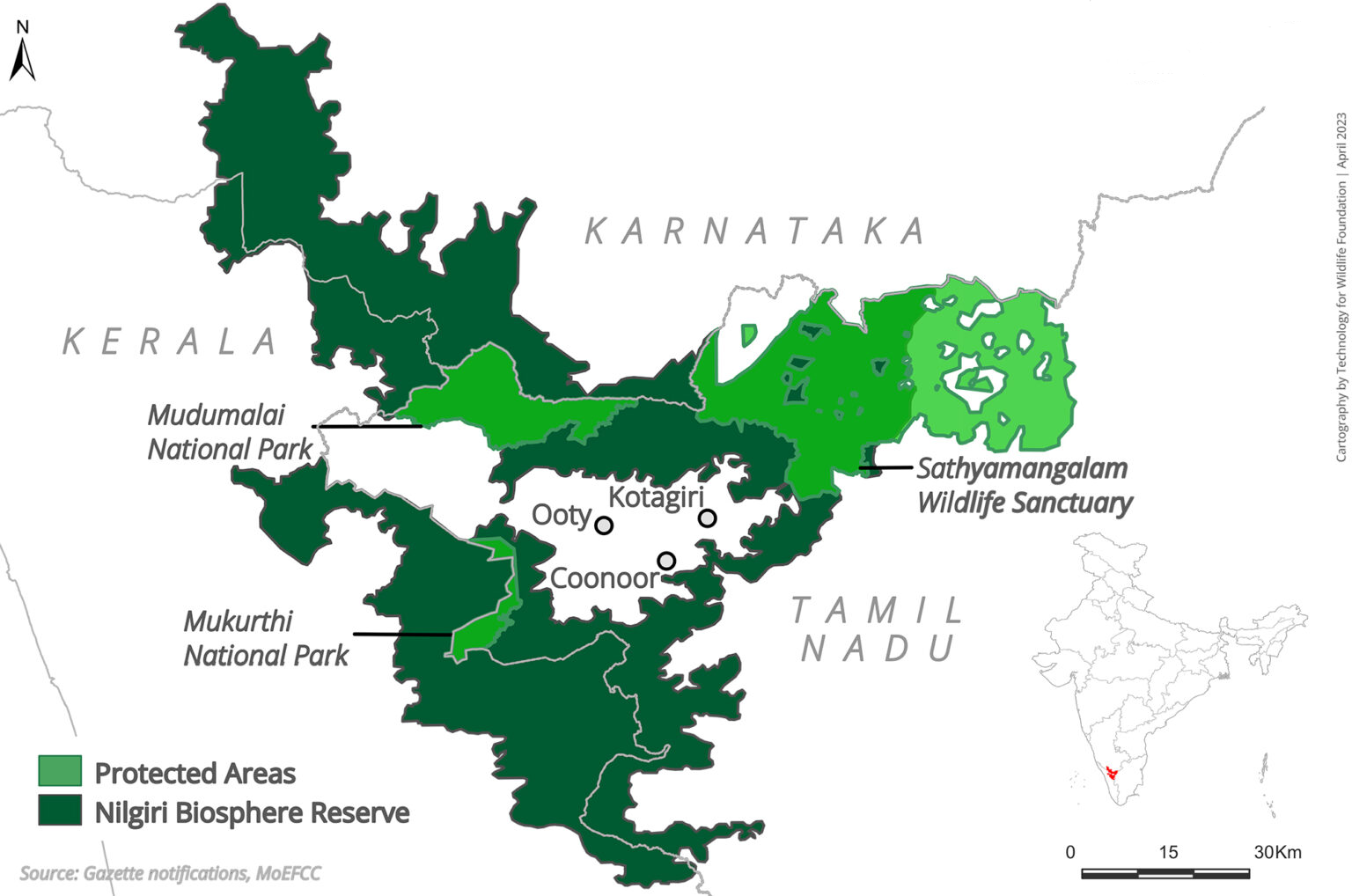
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve
- About:
- It was the first biosphere reserve in India established in 1986.
- The reserve spans across three Indian states: Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- It is India's first biosphere reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- Home to several tribal groups such as the Adiyan, Aranadan , Kader, Kurichian, Kuruman , and Kurumbas.
- It portrays the confluence of Afro-tropical and Indo-Malayan biotic zones of the world.
- Fauna:
- Animals like Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, gaur, Indian elephant and freshwater fishes such as Nilgiri danio (Devario neilgherriensis), Nilgiri barbare are found here.
- Protected Areas in NBR:
- The Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park and Silent Valley are the protected areas present within this reserve.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
Craft - Heritage of
- Puthukkuli shawls — Tamil Nadu
- Sujni embroidery — Maharashtra
- Uppada Jamdani — Karnataka saris
Which of the pairs given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q. Which of the following hills are found where the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats meet? (2008)
(a) Anaimalai Hills
(b) Cardamom Hills
(c) Nilgiri Hills
(d) Shevoroy Hills
Ans: (c)
Important Facts For Prelims
India-US Initiatives in Defence and Nuclear Cooperation
Why in News?
The US National Security Advisor visited India and signed new initiatives in areas such as technology and defence.
What are the new initiatives signed between India and the US?
- Civil Nuclear Cooperation: US announced to remove restrictions e.g., supply of US nuclear reactors on Indian nuclear entities like Bhabha Atomic Research Center (BARC) to implement India-US civil nuclear cooperation agreement.
Sonobuoy Co-Manufacturing: It aims to bolster the Indian Navy's underwater threat detection capabilities, particularly in detecting submarines and other hostile underwater objects.
- Missile Export Control: The US NSA briefed India on updates to missile export controls under the MTCR, enhancing space cooperation and creating new collaboration opportunities.
- India became a member of the MTCR in 2016.
- Advancement of iCET: Both nations reaffirmed cooperation in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, telecommunications, and space.
Note: India and the US decided to curb terrorism through ‘de-radicalisation’ of vulnerable communities.
What are Sonobuoys?
- About: Sonobuoys are expendable, electro-mechanical acoustic sensors designed to detect, classify, and track underwater sounds from ships and submarines.
- They are primarily used in anti-submarine warfare (ASW).
- Functioning: They are dropped in canisters, activate upon hitting water, and deploy an inflatable system with a radio transmitter on the surface.
- They remain active for around 24 hours and are designed to operate only once.
- Communication: The inflatable system on the surface of the water maintains communication with the ship or aircraft tracking the sonobuoy.
India-US Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement
- About: Also known as the 123 Agreement, it allows India to access nuclear fuel, technology, and reactors for peaceful purposes like energy generation, even though India is not a signatory to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
- Key Components: India agreed to place its civilian nuclear facilities under IAEA safeguards to ensure peaceful use of nuclear material.
- The US sought a NSG exemption to enable trade with India’s expanding peaceful nuclear sector.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In India, why are some nuclear reactors kept under “IAEA safeguards” while others are not? (2020)
(a) Some use uranium and others use thorium
(b) Some use imported uranium and others use domestic supplies
(c) Some are operated by foreign enterprises and others are operated by domestic enterprises
(d) Some are State-owned and others are privately owned
Ans: (b)
Q.In the Indian context, what is the implication of ratifying the ‘Additional Protocol’ with the ‘International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’?(2018)
(a) The civilian nuclear reactors come under IAEA safeguards.
(b) The military nuclear installations come under the inspection of IAEA.
(c) The country will have the privilege to buy uranium from the Nuclear Suppliers Group(NSG).
(d) The country automatically becomes a member of the NSG.
Ans: (a)
Rapid Fire
GOBARdhan Scheme
The Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) has highlighted lack of transparency in data of operational Compressed Biogas (CBG) plant on GOBARdhan portal.
- Compressed Biogas (CBG): CBG is a renewable energy source produced from organic waste, including agricultural residues, cattle dung, municipal solid waste, and sewage sludge.
- It helps in replacing fossil fuels, managing agricultural and animal waste, and reducing open burning.
- GOBARdhan Scheme: The Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) initiative focuses on converting waste into wealth to promote a circular economy.
- It aims to establish a strong ecosystem for Biogas/Compressed Biogas (CBG)/Bio-CNG plants to foster sustainable growth.
- The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti, serves as the nodal department.
- Key Issues:
- Slow Adoption: Only 115 CBG plants are functional as of December 2024, against the target of 5,000 by 2030.
- Information Gaps: The GOBARdhan portal lacks details on feedstocks used by specific CBG plants.
- Operational Transparency: The portal lacks a section for operational plants with updated information, making it difficult for policymakers to address entrepreneurs' challenges.
Read More: India's Green Future through BioCNG
Rapid Fire
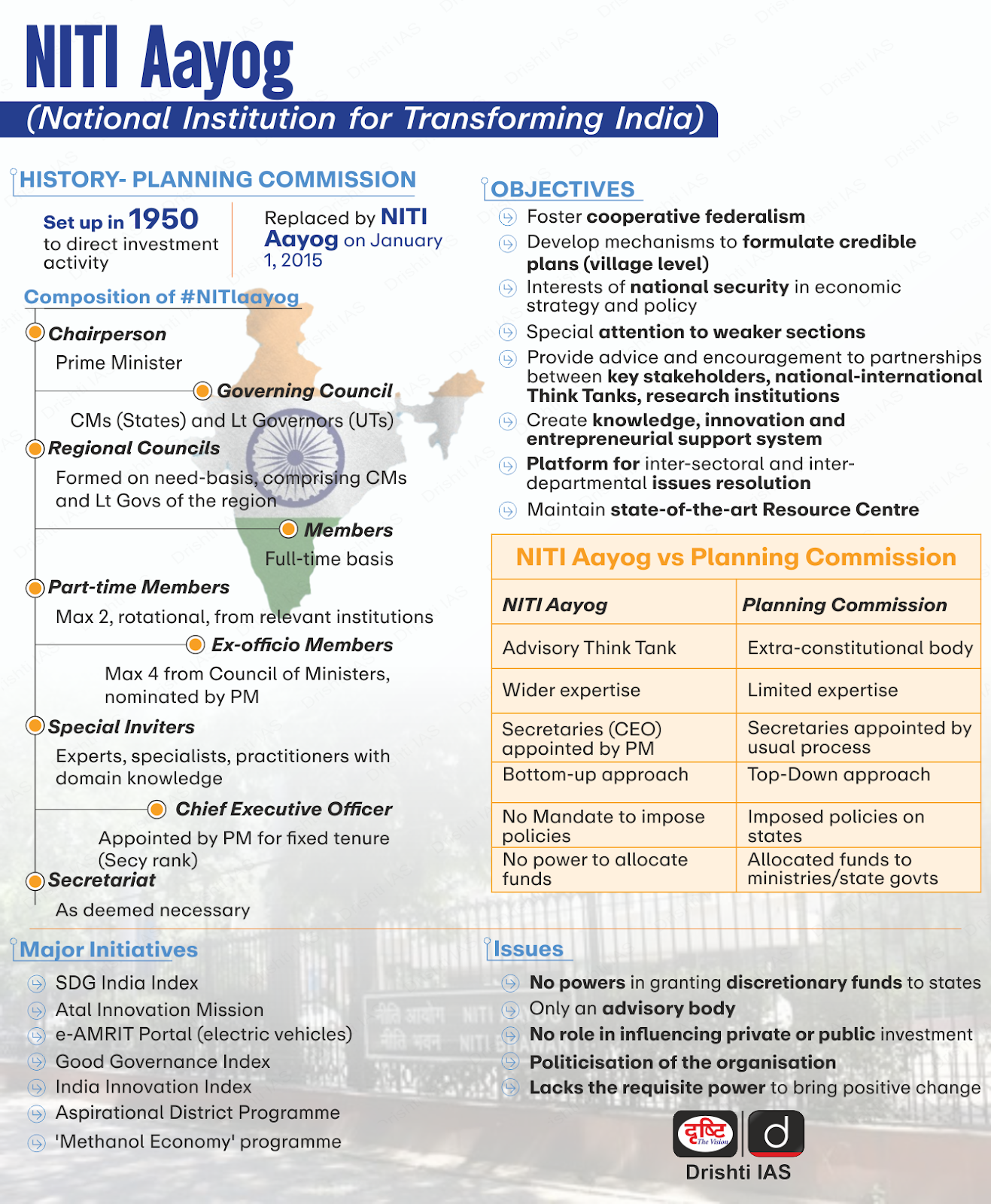
10 Years of NITI Aayog
On 1st January 2025, NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) completed a decade since its establishment on 1st January 2015, replacing the Planning Commission to align with the requirements of a dynamic, market-driven economy.
- NITI Aayog is an advisory body created through a resolution of the union cabinet (i.e. neither constitutional nor statutory body).
Key Achievements & Contribution:
- Shifted focus from financial allocation to policy advisory, promoting decentralized governance.
- Strengthened competitive and cooperative federalism through data-driven indices like the SDG India Index and Composite Water Management Index.
- Assisted states in establishing State Institutions of Transformation (SITs) to improve governance and policy implementation.
- Aspirational Blocks Programme (2023) focused on 500 underdeveloped blocks to achieve 100% coverage of key government schemes.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) trained over one crore students through initiatives like Atal Tinkering Labs and incubation centres to promote innovation and entrepreneurship and expanded innovation ecosystems to regional languages and focuses on tribal and hilly areas.
- Conceptualized initiatives like e-Mobility, Green Hydrogen, and the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
Read More: NITI Aayog
Rapid Fire
Tidal Tail
A study led by Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) researchers has revealed the formation of an ultra-diffuse galaxy at the end of the longest tidal tail ever discovered, associated with the galaxy NGC 3785, located 430 million light-years from Earth in the Leo constellation.
- Tidal Tail: A tidal tail is a long, narrow stream of stars and gas created when galaxies interact or merge.
- Gravitational forces during these interactions pull material from the outer regions of the galaxies, stretching it into elongated streams that extend into space.
- Tidal tails can persist long after the merger, serving as a signature of recent galaxy interactions.
- These tails provide valuable insights into how galaxies evolve and form stars.
- Notably, a small portion of a galaxy's stellar formation occurs within tidal tails, highlighting their role in galaxy dynamics and evolution.
- Galaxy NGC 3785: It is a lenticular galaxy located in the Leo constellation, north of the celestial equator (imaginary circle that extends from Earth's equator into space), making it more visible from the northern hemisphere.
- A galaxy is a vast collection of gas, dust, stars, and solar systems, held together by gravity. Earth is part of one such galaxy.
Read more: Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Rapid Fire
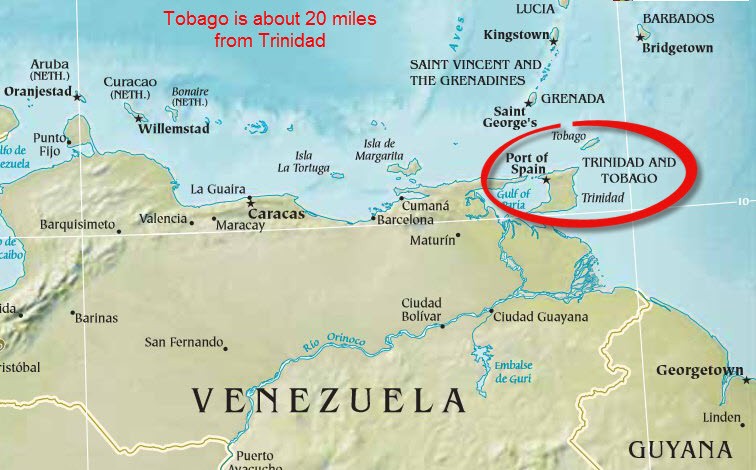
Emergency Declared in Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago has declared a state of emergency following a surge in gang violence in the country, which has led to raising the annual death toll to the highest since 2013.
- Trinidad and Tobago has a population of 1.5 million and records one of the highest murder rates.
- Previous states of emergency were declared in 2014 for gang violence and in 2021 for Covid-19 restrictions.
Engagements with India:
- Trinidad and Tobago became the first Caribbean country to adopt India’s UPI platform.
- Both countries granted each other Most Favored Nation (MFN) status in1997.
- Bilateral trade reached a record USD 368.96 million in FY 2023-24.
- The Indian Diaspora constitutes about 42% of the total population of the country.
About Trinidad and Tobago:
- Capital: Port of Spain.
- Location: Island nation in the southeastern West Indies, near Venezuela and Guyana.
- Independence: Gaining independence from the UK on 31st August 1962, and becoming a republic in 1976, the nation is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM).
- Geographical Features:
- Highest Point: Mount Aripo.
- Major Rivers: Ortoire and Caroni.
- Natural Resource: Pitch Lake, the world’s largest asphalt reservoir.
- Mountain Range: Northern Range, part of the Andes extension.
Read More: 2nd India-CARICOM Summit