Social Justice
Global Gender Gap Report 2024
- 14 Jun 2024
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Global Gender Gap Report 2024, WEF, Global Gender Gap Index, Gender Parity, Local Governance
For Mains: Global Gender Gap Report 2024, Issues of Gender Inequality in Different Sectors.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Economic Forum released the 18th edition of its annual Global Gender Gap Report for 2024, comprehensively benchmarking gender parity across 146 economies worldwide.
What is the Global Gender Gap Index?
- About:
- It benchmarks countries on their progress towards gender parity in four Key dimensions with Submatrices.

- On each of the four sub-indices as well as on the overall index the GGG index provides scores between 0 and 1, where 1 shows full gender parity and 0 is complete imparity.
- It is the longest-standing index, which tracks progress towards closing these gaps over time since its inception in 2006.
- Objectives:
- To serve as a compass to track progress on relative gaps between women and men in health, education, economy and politics.
- Through this annual yardstick, the stakeholders within each country are able to set priorities relevant to each specific economic, political and cultural context.
- It benchmarks countries on their progress towards gender parity in four Key dimensions with Submatrices.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- Overall Findings:
- The global gender gap score in 2024 is 68.5%, meaning 31.5% of the gap remains unaddressed. Progress has been extremely slow, with only a 0.1% point improvement from 2023.
- At the current rate, it will take 134 years to reach full gender parity globally far beyond the 2030 SDG target.
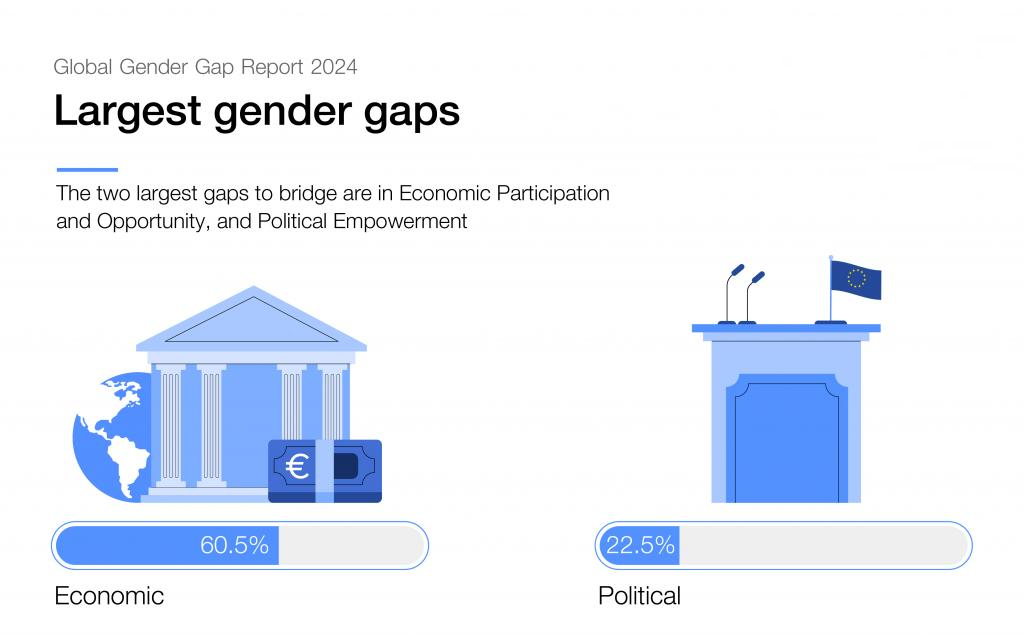
- The gender gaps remain largest in Political Empowerment (77.5% unaddressed) and Economic Participation & Opportunity (39.5% unaddressed).
- Top-Ranking Countries:
- Iceland (93.5%) remains the world's most gender-equal society for the 15th consecutive year. It is followed by Finland, Norway, New Zealand and Sweden in the top 5 rankings.
- 7 out of the top 10 countries are from Europe (Iceland, Finland, Norway, Sweden, Germany, Ireland, Spain).
- Other regions represented are Eastern Asia and the Pacific (New Zealand at 4), Latin America and the Caribbean (Nicaragua at 6), and Sub-Saharan Africa (Namibia at 8).
- Spain and Ireland made notable jumps into the top 10 in 2024, climbing 8 and 2 ranks respectively compared to 2023.
- Regional Performance:
- Europe leads with 75% of its gender gap closed, followed by Northern America (74.8%) and Latin America & Caribbean (74.2%).
- The Middle East and North Africa region ranks last at 61.7% of its gender gap closed.
- Southern Asia region ranks 7th out of 8 regions with a gender parity score of only 63.7%.
- Economic & Employment Gaps:
- Women's workforce representation lags behind men's across nearly every industry and economy at 42% overall and only 31.7% in senior leadership roles.
- The "leadership pipeline" shows a 21.5% point drop from entry-level to managerial level for women globally.
- Women's hiring into leadership roles deteriorated in 2023-24 due to worsening economic conditions.
- Care Burden Impact:
- Women’s workforce participation is recovering from the recent surge in caregiving responsibilities, highlighting the urgent need for equitable care systems.
- Equitable care policies like paid parental leave are increasing but remain inadequate in many countries.
- Technology & Skills Gaps:
- Women remain underrepresented in STEM at 28.2% of that workforce versus 47.3% in non-STEM roles.
- Gender gaps exist in skills like AI, big data and cybersecurity which will be crucial for the future of work.
How has India Fared in the Gender Gap Report 2024?
- India’s Rank: India has slipped two places in the global rankings to 129th in 2024 from 127th in 2023 out of 146 countries.
- Within South Asia, India ranked fifth after Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bhutan. Pakistan ranked last in the region.
- Economic Parity: India is among the countries with the lowest levels of economic parity, similar to Bangladesh, Sudan, Iran, Pakistan, and Morocco, with less than 30% gender parity in estimated earned income.
- Educational Attainment: India showed the best gender parity in secondary education enrolment.
- Political Empowerment: India ranked 65th globally in political empowerment of women and 10th in parity of years with female/male heads of state over the past 50 years.
- However, women's representation at the federal level, in Ministerial positions (6.9%), and in Parliament (17.2%) remains low.
- Gender Gap Closure: India has closed 64.1% of its gender gap as of 2024. The slip in ranking from 127th to 129th was primarily due to small declines in 'Educational Attainment' and 'Political Empowerment' parameters, although 'Economic Participation' and 'Opportunity' scores saw slight improvements.
Indian Initiatives to Reduce Gender Gap in Social, Economic and Political Life
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- Mahila Shakti Kendra
- Mahila Police Volunteers
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojna
- Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya
- Political Reservation: The government has reserved 33% of the seats in Panchayati Raj Institutions for women.
- The Constitution (106th Amendment) Act, 2023, has also reserved one-third of all seats for women in Lok Sabha, State legislative assemblies, and the Legislative Assembly of the National Capital Territory of Delhi, including those reserved for SCs and STs.
- Female Entrepreneurship: To promote female entrepreneurship, the Government has initiated Programmes like Stand-Up India and Mahila-e-Haat (an online marketing platform to support women entrepreneurs/SHGs/NGOs), Entrepreneurship and Skill Development Programme (ESSDP).
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Critically analyse India's performance in the Global Gender Gap Index,2024. Discuss the key areas of improvement and suggest measures to accelerate gender parity in India. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. Discuss the desirability of greater representation to women in the higher judiciary to ensure diversity, equity and inclusiveness. (2021)