Social Justice
Fair Share for Health and Care Report
- 26 Mar 2024
- 7 min read
For Prelims: World Health Organization (WHO), Fair Share for Health and Care Report, Devaluation of Caregiving, Gender Pay Gaps, Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
For Mains: Fair Share for Health and Care Report, Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, and Human Resources.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) released a new report titled- Fair Share for Health and Care report, addressing the gender gap in global healthcare.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Gender Disparities in Health and Care Workforce:
- Women comprise 67% of the paid global health and care workforce. Additionally, they perform an estimated 76% of all unpaid care activities.
- This highlights significant gender disparities in both paid and unpaid care work.
- Women in low- or middle-income countries could be USD 9 trillion better off if their pay and access to paid work were equal to that of men.
- Not Adequately Represented on Decision-Making:
- Women are not adequately represented on decision-making tables. Women are overrepresented in lower-status roles, comprising the majority of nurses and midwives.
- They are, however, underrepresented in leadership roles. Medical specialties are still dominated by men. Women made up 25% to 60% of doctors but between 30% and 100% of nursing staff across 35 countries.
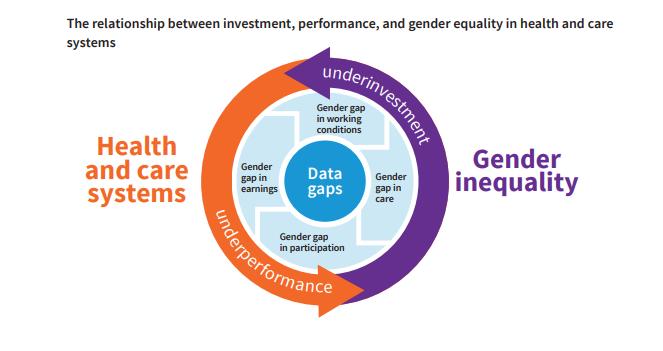
- Underinvestment in Health Systems:
- Chronic underinvestment in health and care work has led to a vicious cycle of unpaid care work, reducing women's participation in paid labour markets, hindering economic empowerment, and impeding gender equality.
- Devaluation of Caregiving:
- Caregiving, primarily performed by women, tends to be undervalued, leading to lower wages, poor working conditions, decreased productivity, and a negative economic impact on the sector.
- Implications of Gender Pay Gaps:
- Pay gaps limit women’s investment in their family and community, which is where they are likely to reinvest.
- Globally, on average, 90% of women’s earnings are directed towards their families’ well-being, compared to only 30-40% of men’s.
- Higher Levels of Violence:
- Women in healthcare disproportionately experienced higher levels of gender-based violence.
- According to some estimates, a quarter of workplace violence across all sectors of the globe occurs in healthcare.
- At least half of all employees in the healthcare sector have reported experiencing violence at some point in the workplace.
- Indian Scenario:
- In India, women spent around 73% of their total daily working time (that is, the combined average time spent on unpaid and paid work recorded through national daily time-use surveys) on unpaid work, compared to men who spent around only 11% of their daily working time on unpaid work.
- In the United Kingdom, nearly 4.5 million people took on unpaid work during Covid-19, 59% of whom were women, with nearly 3 million working simultaneously.
- In India, women spent around 73% of their total daily working time (that is, the combined average time spent on unpaid and paid work recorded through national daily time-use surveys) on unpaid work, compared to men who spent around only 11% of their daily working time on unpaid work.
- Global Crisis of Care:
- Decades of underinvestment in health and care work contribute to a growing global crisis of care.
- Stagnation in progress towards Universal Health Coverage (UHC) leaves billions without full access to essential health services, further burdening women with unpaid care work.
- Key Recommendations:
- Improve working conditions for all forms of health and care work, especially for highly feminised occupations.
- Include women more equitably in the paid labour workforce
- Enhance conditions of work and wages in the health and care workforce and ensure equal pay for work of equal value.
- Address the gender gap in care, support quality care work and uphold the rights and well-being of caregivers.
- Ensure that national statistics account for, measure and value all health and care work.
- Invest in robust public health systems.
What are the Government Initiatives to Deal with Gender Disparity?
- Economic Participation and Health and Survival:
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao: It ensures the protection, survival and education of the girl child.
- Mahila Shakti Kendra: Aim to empower rural women with opportunities for skill development and employment.
- Mahila Police Volunteers: It envisages the engagement of Mahila Police Volunteers in States/UTs who act as a link between police and community and facilitate women in distress.
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh: It is an apex micro-finance organisation that provides micro-credit at concessional terms to poor women for various livelihood and income-generating activities.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojna: Under this scheme, girls have been economically empowered by opening their bank accounts.
- Female Entrepreneurship: To promote female entrepreneurship, the Government has initiated Programmes like Stand-Up India and Mahila e-Haat (online marketing platform to support women entrepreneurs/ SHGs/NGOs), Entrepreneurship and Skill Development Programme (ESSDP).
- Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya: They have been opened in Educationally Backward Blocks (EBBs).
- Political Reservation: Government has reserved 33% of the seats in Panchayati Raj Institutions for women.
- Capacity Building of Elected Women Representatives: It is conducted with a view to empowering women to participate effectively in the governance processes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.1 Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Q.2 ‘Doctors Without Borders (Medecins Sans Frontiers)’, often in the news, is (2016)
(a) a division of World Health Organisation
(b) a non-governmental international organisation
(c) an inter-governmental agency sponsored by European Union
(d) a specialized agency of the United Nations
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (2019)

.png)




