Infographics
Economy
Foreign Trade Policy 2023
For Prelims: Major components of Foreign Trade Policy 2023, PM-MITRA
For Mains: Foreign Trade Policy 2023, Comparison with previous trade policies.
Why in News?
Recently, Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and Textiles launched the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023 which comes into effect from April 1, 2023.
- FTP 2023 is a policy document which is based on continuity of time-tested schemes facilitating exports as well as a document which is nimble and responsive to the requirements of trade.
What are Details of FTP 2023?
- About:
- The policy is based on the principles of trust and partnership with exporters and aims at process re-engineering and automation to facilitate ease of doing business for exporters.
- The Key Approach is based on Four Pillars:
- Incentive to Remission,
- Export promotion through collaboration - Exporters, States, Districts, Indian Missions,
- Ease of doing business, reduction in transaction cost and e-initiatives, and
- Emerging Areas – E-Commerce Developing Districts as Export Hubs and streamlining Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment, and Technologies (SCOMET) policy.
- Goals and Targets:
- The government aims to increase India’s overall exports to USD 2 trillion by 2030, with equal contributions from the merchandise and services sectors.
- The government also intends to encourage the use of the Indian currency in cross-border trade, aided by a new payment settlement framework introduced by the RBI in July 2022.
- This could be particularly advantageous in the case of countries with which India enjoys a trade surplus.
What are the Salient or Important features of FTP 2023?
- Process Re-Engineering and Automation:
- The policy emphasizes export promotion and development, moving away from an incentive regime to a regime which is facilitating, based on technology interface and principles of collaboration.
- Reduction in fee structures and IT-based schemes will make it easier for MSMEs and others to access export benefits.
- Duty exemption schemes for export production will now be implemented through Regional Offices in a rule-based IT system environment, eliminating the need for manual interface
- Towns of Export Excellence (TEE):
- Four new towns, namely Faridabad, Mirzapur, Moradabad, and Varanasi, have been designated as TEE in addition to the existing 39 towns.
- The TEEs will have priority access to export promotion funds under the MAI scheme and will be able to avail Common Service Provider (CSP) benefits for export fulfillment under the Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme.
- Recognition of Exporters:
- Exporter firms recognized with 'status' based on export performance will now be partners in capacity-building initiatives on a best-endeavor basis.
- Similar to the 'each one teach one' initiative, 2-star and above status holders would be encouraged to provide trade-related training based on a model curriculum to interested individuals.
- Status recognition norms have been re-calibrated to enable more exporting firms to achieve 4 and 5-star ratings, leading to better branding opportunities in export markets.
- Promoting Export from the Districts:
- The FTP aims at building partnerships with State governments and taking forward the Districts as Export Hubs (DEH) initiative to promote exports at the district level and accelerate the development of grassroots trade ecosystem.
- Efforts to identify export worthy products & services and resolve concerns at the district level will be made through an institutional mechanism – State Export Promotion Committee and District Export Promotion Committee at the State and District level, respectively.
- District specific export action plans to be prepared for each district outlining the district specific strategy to promote export of identified products and services.
- Streamlining SCOMET Policy:
- India is placing more emphasis on the "export control" regime as its integration with export control regime countries strengthens.
- There is a wider outreach and understanding of SCOMET among stakeholders, and the policy regime is being made more robust to implement international treaties and agreements entered into by India.
- A robust export control system in India would provide access of dual-use High end goods and technologies to Indian exporters while facilitating exports of controlled items/technologies under SCOMET from India.
- Facilitating E-Commerce Exports:
- Various estimates suggest e-commerce export potential in the range of USD 200 to USD 300 billion by 2030.
- FTP 2023 outlines the intent and roadmap for establishing e-commerce hubs and related elements such as payment reconciliation, book-keeping, returns policy, and export entitlements.
- As a starting point, the consignment wise cap on E-Commerce exports through courier has been raised from ₹5Lakh to ₹10 Lakh in the FTP 2023.
- Depending on the feedback of exporters, this cap will be further revised or eventually removed.
- Facilitation under (EPCG) Scheme:
- The EPCG Scheme, which allows import of capital goods at zero Customs duty for export production, is being further rationalized. Some key changes being added are:
- Prime Minister Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel Parks (PM MITRA) scheme has been added as an additional scheme eligible to claim benefits under CSP(Common Service Provider) Scheme of EPCG.
- Dairy sector to be exempted from maintaining Average Export Obligation – to support the dairy sector to upgrade the technology.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) of all types, Vertical Farming equipment, Wastewater Treatment and Recycling, Rainwater harvesting system and Rainwater Filters, and Green Hydrogen are added to Green Technology products – will now be eligible for reduced Export Obligation requirement under EPCG Scheme
- The EPCG Scheme, which allows import of capital goods at zero Customs duty for export production, is being further rationalized. Some key changes being added are:
- Facilitation under Advance authorization Scheme:
- Advance authorisation Scheme accessed by DTA (Domestic tariff area) units provides duty-free import of raw materials for manufacturing export items and is placed at a similar footing to EOU and SEZ Scheme.
- Special Advance Authorisation Scheme extended to export of Apparel and Clothing sector on self-declaration basis to facilitate prompt execution of export orders.
- Benefits of Self-Ratification Scheme for fixation of Input-Output Norms extended to 2 star and above status holders in addition to Authorized Economic Operators at present.
- Amnesty Scheme:
- Under the amnesty scheme, an online portal will be launched for registration and a six-month window will be available to exporters to avail the scheme.
- It will cover all pending cases of default in export obligation of authorisations, these can be regularised on payment of all customs duties exempted in proportion to unfulfilled export obligation.
What About Previous Trade Policy?
- The previous foreign trade policy for 2015-2020 had targeted exports of USD 900 billion by 2020;
- This target was extended along with the policy for three years till March 2023.
- India is, however, likely to end 2022-23 with total exports of USD 760-770 billion as against USD 676 billion in 2021-22.


Indian Economy
India and Malaysia Agree to Settle Trade in Indian Rupees
For Prelims: Trade Settlement in Rupees, ASEAN region, Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVAs), India’s Forex Reserves, Monetary policy.
For Mains: Significance of India's Move to Settle Trade in Indian Rupee, Challenges Related to Internationalisation of Rupees.
Why in News?
India and Malaysia have agreed to settle trade in Indian rupees.This mechanism is expected to enhance India-Malaysia bilateral trade which touched USD 19.4 billion during 2021-22.
- Malaysia is the third largest trading partner of India in the ASEAN region, after Singapore and Indonesia that account for USD 30.1 billion and USD 26.1 billion bilateral trade with India respectively.
What is the Significance of India's Move to Settle Trade in Indian Rupee?
- About:
- In July 2022, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allowed the settlement of international trade in Indian rupees.
- In December 2022, India saw its first settlement of foreign trade in rupee with Russia – as part of the 'International Settlement of Trade in Indian Rupee' mechanism initiated by the RBI.
- In March 2023, banks from 18 countries were allowed by the RBI to open Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVAs) to settle payments in Indian rupees.
- It includes: Botswana, Fiji, Germany, Guyana, Israel, Kenya, Malaysia, Mauritius, Myanmar, New Zealand, Oman, Russia, Seychelles, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Uganda, and the United Kingdom.
- Benefits of Trading in Indian Rupees:
- Controlling Depreciation of Rupees:
- India is a net importer and the value of the Indian rupee has been declining consistently.
- Using the rupee for international trade transactions will help check the flow of dollars out of India and slow the depreciation of the currency albeit to a “very limited extent.
- Thus most importantly, the move is expected to reduce the pressure on India’s forex reserves.
- India is a net importer and the value of the Indian rupee has been declining consistently.
- Better Pricing for Goods and Services:
- With the ability to invoice trade in Indian rupees, Indian traders can achieve better pricing for their goods and services.
- Also, this mechanism is expected to benefit both sides of the trade by reducing currency conversion spreads.
- With the ability to invoice trade in Indian rupees, Indian traders can achieve better pricing for their goods and services.
- Towards Global Acceptance of Rupees:
- International trade settlements in rupee are expected to gradually contribute to the global acceptance of the currency, and later make it possible to repay loans taken from fund banks like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank.
- Controlling Depreciation of Rupees:
- Challenges:
- Volatility of the Indian Rupee:
- The Indian rupee is known to be volatile and subject to fluctuations in the foreign exchange market, which may make it less attractive as a settlement currency for some international traders.
- Complication in Controlling Domestic Supply:
- RBI’s report warns that the ‘internationalisation’ of the rupee can potentially limit the ability of the central bank to control domestic money supply and influence interest rates as per the domestic macroeconomic conditions.
- Ultimately, it may lead to complications in terms of formulating the monetary policy.
- Competition with Other Currencies: The Indian rupee may face competition from other major currencies, such as the US dollar, Euro, and Yen, which are already widely accepted for international trade settlements.
- Volatility of the Indian Rupee:
What is a Vostro Account?
- It is an account that domestic banks hold for foreign banks in the former’s domestic currency, in this case, the rupee.
- Domestic banks use it to provide international banking services to their clients who have global banking needs.
- The bank holding the Vostro account acts as a custodian of the foreign bank's funds and provides various services such as currency conversion, payment processing, and account reconciliation.
Conclusion
India's willingness to take concrete steps towards de-dollarisation of its international trade and to make the rupee a tradable currency is a significant step towards internationalisation of rupees. But India must increase its exports, supported by critical reforms that include capital account convertibility, deepening financial markets to manage the large-scale inflow and outflow of capital.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Convertibility of rupee implies (2015)
(a) being able to convert rupee notes into gold
(b) allowing the value of rupee to be fixed by market forces
(c) freely permitting the conversion of rupee to other currencies and vice versa
(d) developing an international market for currencies in India
Ans: (c)
Q2. With reference to Balance of Payments, which of the following constitutes/constitute the Current Account? (2014)
- Balance of trade
- Foreign assets
- Balance of invisibles
- Special Drawing Rights
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 4
Ans: (c)


International Relations
U.K. Signed CPTPP
For Prelims: CPTPP, Brexit, FTA, Indo-Pacific.
For Mains: International Treaties & Agreements
Why in News?
Recently, the U.K. Signed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). Prime Minister of U.K cited the agreement's success as an example of "post-Brexit freedoms". The agreement will now need to be ratified by Westminster and each of the CPTPP countries.
What is CPTPP?
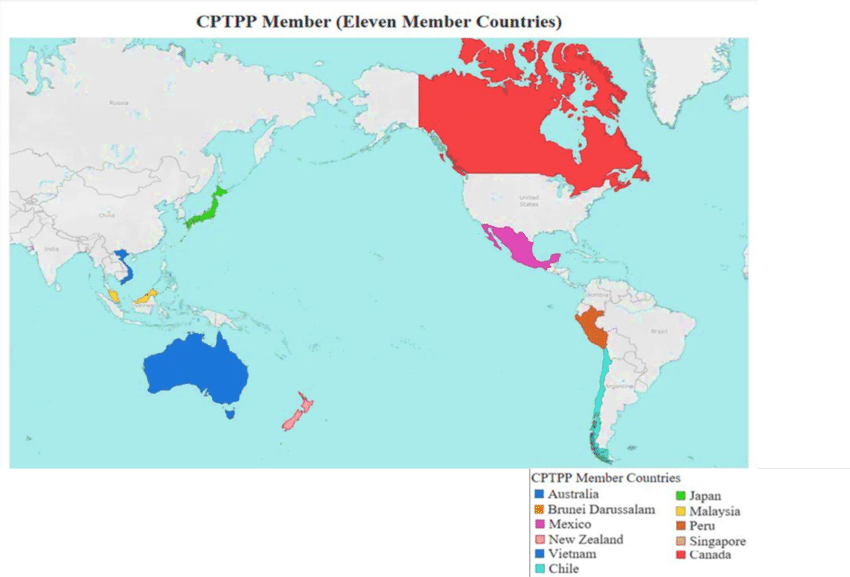
- About:
- The CPTPP is a Free trade agreement (FTA) between Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, Peru, New Zealand, Singapore and Vietnam.
- The CPTPP was signed by the 11 countries on 8 March 2018 in Santiago, Chile.
- Background:
- In 2005, a trade agreement between a small group of Pacific Rim countries comprising Brunei, Chile, New Zealand, and Singapore led to the formation of Trans Pacific Partnership (TPP) consisting of 12 nation-states.
- After the withdrawal of the US, the remaining eleven signatories, known as the TPP-11, continued talks and their efforts led to the formation of CPTPP.
- Significance:
- CPTPP removes 99% of tariffs on goods and services, just like the original TPP did, all the member countries have agreed to cut down on wildlife trafficking. That helps elephants, rhinoceroses, and marine species the most.
- It prevents environmental abuses, such as unsustainable logging and fishing. Countries that don't comply will face trade penalties.
Note: All 11 countries of CPTPP are also members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC).
What is Brexit?
- About:
- Brexit refers to the U.K.'s decision to leave the European Union (EU). The country formally left the EU in January 2020, after a referendum in 2016.
- Impact of Brexit on the U.K.:
- The impact of Brexit on the U.K. has been significant. Some of the impacts of Brexit include:
- Changes in trade policies and tariffs with the EU and other countries.
- Reduced access to the EU market for U.K. businesses.
- Increased regulatory burden on U.K. businesses trading with the EU.
- The impact of Brexit on the U.K. has been significant. Some of the impacts of Brexit include:
What are the Benefits of the CPTPP for the U.K.?
- More than 99% of British exports, including key markets such as cheese, cars, chocolate, machinery, gin, and whisky, will have zero tariffs.
- The deal is expected to add GBP 1.8 billion (USD 2.2 billion) annually to the U.K. economy in the long run, a modest boost of 0.08% to GDP.
- The CPTPP is a "gateway" to the Indo-Pacific region, which is expected to account for a majority (54%) of global economic growth in the future.
- As a CPTPP member, the U.K. will have a veto on whether China joins the treaty. U.K. firms will not need to establish a local office or be resident to provide services and will be able to operate on a par with firms in host countries.
What is India's stand on CPTPP?
- India did not join CPTPP as it seeks to place greater labor and environmental standards on its other partners and CPTPP draft includes narrowly detailed qualifications on standards for investment protection, provisions to protect the host state’s right to regulate, and the imposition of detailed transparency requirements.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to the ‘Trans-Pacific Partnership’, consider the following statements: (2016)
- It is an agreement among all the Pacific Rim countries except China and Russia.
- It is a strategic alliance for the purpose of maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)


Governance
Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2022
For Prelims: Competition Commission of India (CCI), Competition Act, 2002, National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
For Mains: Significance of Competition Commission due to the changing dynamics of the market.
Why in News?
Recently, the Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2022, which seeks to amend the Competition Act, 2002, was passed in the Lower House amid protests from the Opposition. And the Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill, 2023 is also introduced in parliament.
What is the Competition Act, 2002?
- The Competition Act, 2002, regulates competition in the Indian market and prohibits anti-competitive practices such as cartels, abuse of dominant market position, and mergers and acquisitions that may have an adverse effect on competition. The Act has been amended by the Competition (Amendment) Act, 2007.
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI) is responsible for implementing and enforcing the Act.
- The Competition Appellate Tribunal is a statutory body created in accordance with the Competition Act, 2002 to hear and regulate on appeals against any rules made, decisions made, or orders made by the Competition Commission of India.
- The government replaced the Competition Appellate Tribunal with the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) in 2017.
What are the Amendments to the Competition Act Proposed?
- Penalties for Competition Law Violations:
- The Bill amends the definition of "turnover" to include global turnover derived from all products and services by a person or an enterprise.
- The amendment allows for the imposition of penalties for competition law violations based on a company's global turnover, rather than just its turnover in India.
- Timelines for Approving Combinations:
- The Bill reduces the time limit for the CCI to form a prima facie opinion on a combination from 30 working days to 30 days.
- The change aims to speed up the process of approving mergers and acquisitions in India.
- Review of Regulations:
- The Bill seeks to amend the Competition Act, 2002, to regulate mergers and acquisitions based on the value of transactions. Deals with transaction value of more than Rs 2,000 crore will require CCI’s approval.
- The Bill proposes to reduce the timeline for the CCI to pass an order on such transactions from 210 days to 150 days.
- The Bill decriminalizes certain offences under the Act by changing the nature of punishment from imposition of fine to civil penalties.
- These offences include failure to comply with orders of the CCI and directions of the Director General related to anti-competitive agreements and abuse of dominant position.
- The Bill seeks to amend the Competition Act, 2002, to regulate mergers and acquisitions based on the value of transactions. Deals with transaction value of more than Rs 2,000 crore will require CCI’s approval.
What are the Benefits of the Competition (Amendment) Bill?
- Promoting Ease of Doing Business:
- The amendments to the Competition Act aim to reduce regulatory hurdles and promote ease of doing business in India. The amendments are expected to provide greater clarity to businesses operating in India and reduce the compliance burden for companies.
- Enhancing Transparency:
- The inclusion of global turnover in the definition of "turnover" aims to enhance transparency and accountability in the Indian market. The amendment ensures that companies cannot escape penalties for competition law violations by shifting their revenue to other countries.
What is Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill, 2023?
- The Bill aims to bring clarity to India’s forest conservation law and fast-track strategic and security-related projects.
- The Bill seeks to clarify the scope of applicability of the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, on various lands.
- It aims to broaden the horizons of the Act, keeping in view India’s aim to increase forest cover for creation of a carbon sink of additional 2.5-3.0 billion Tonnes of CO2 equivalent by 2030.
- The Bill amends the short title of the Act to be called the Van (Sanrakshan Evam Samvardhan) Adhiniyam, 1980.
- The Bill proposes to insert a preamble to the Act to encompass the country’s rich tradition of preserving forests and their biodiversity.
- The bill amends to exempt certain categories of lands from the purview of the Act which includes the following:
- forest land situated alongside a rail line, or a public road maintained by the Government, which provides access to a habitation, or to a rail, and roadside amenity up to a maximum size of 0.10 hectare.
- The forest land as is situated within a distance of one hundred kilometers along international borders or Line of Control or Line of Actual Control proposed to be used for the construction of strategic linear projects of national importance and concerning national security.


International Relations
India's Role in the Korean War
For Prelims: Korean War, Second World War, USSR, UN, Non-Alignment Movement, Russia and Ukraine.
For Mains: India's Role in the Korean War.
Why in News?
During its G20 Presidency Year 2023, India is recalling its diplomatic role in the Korean War seven decades ago.
- India’s role in the Korean War was partially successful, yet India is counted among the countries that contributed to bringing the war to a close.
What is the Timeline of the Korean War?
- Background:
- The root of the conflict lies in the Japanese occupation of Korea between 1910- 1945.
- When Japan was defeated in the Second World War, the Allied forces agreed to establish a “four-power trusteeship over Korea” at the Yalta Conference (1945).
- However, the USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics) invaded Korea and took control of the north while the south remained under the rest of the allies, mainly the USA.
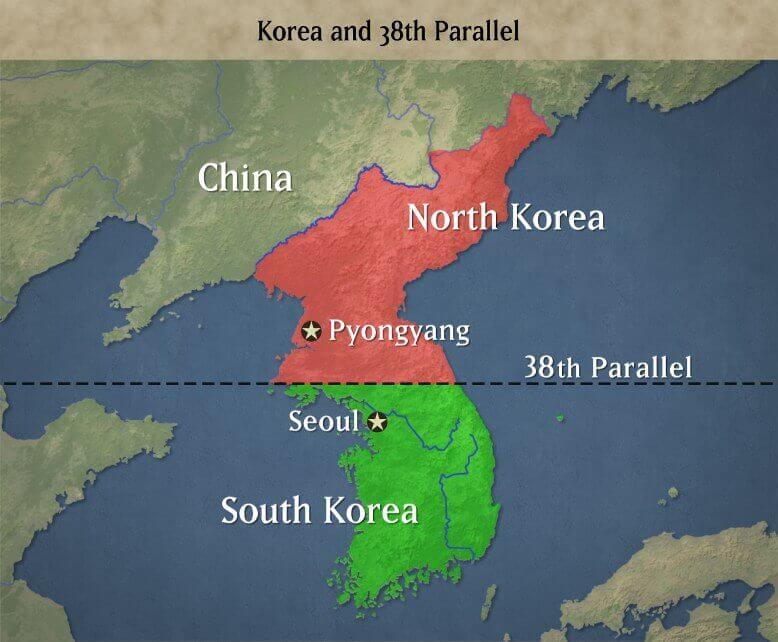
- The division of the two regions was along the 38th parallel north, which still continues to be the official border dividing the two Koreas.
- In 1948, the Republic of Korea (South Korea) and the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea) were established.
- As both tried to enhance their reach, territorially and ideologically, the Korean Conflict emerged between the two nations.
- Timeline of the War:
- In 1950, North Korea, backed by the USSR, launched an attack on South Korea and occupied most of the country.
- In response, the United Nations force led by the US retaliated.
- In 1951, the US forces led by Douglas MacArthur crossed the 38th parallel and triggered the entry of China in support of North Korea.
- To prevent further escalation, peace talks began later in 1951.
- India was actively involved in negotiating peace in the Korean peninsula by engaging all the major stakeholders – US, USSR and China.
- In 1952, the Indian resolution on Korea was adopted at the United Nations (UN).
- In 1953, the Korean Armistice Agreement was signed between the UN Command, the Korean People's Army and the Chinese People's Volunteer Army.
- It led to an official ceasefire without a Peace treaty. Thus, the war officially never ended.
- This also led to the establishment of the Korean Demilitarised Zone (DMZ) – a strip of land running across the Korean Peninsula to serve as a buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea.
- In December 1991, North and South Korea signed a pact agreeing to refrain from aggression.
- In 1950, North Korea, backed by the USSR, launched an attack on South Korea and occupied most of the country.
What was India's Role in the Korean War?
- In 1950 Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru made a huge diplomatic push to prevent an escalation into another world war, and for the parties to arrive at a quick ceasefire.
- A couple of attempts by India to bring about a ceasefire ended in failure. However, its 1952 proposals for the exchange of prisoners enabled the July 1953 armistice agreement, which marks 70 years this year.
- India proposed a commission to resolve the issue of prisoners of war (PoWs) during talks between the UN and communist sides in 1952, but the proposal was initially shelved. However, when negotiations resumed in 1953, India was selected to chair the Neutral Nations Repatriation Committee, which successfully held PoWs for 90 days and eventually signed the Armistice Agreement on July 27, 1953.
- India has consistently voiced its opposition to North Korean nuclear and missile tests. However, it has maintained a neutral stance regarding sanctions.
- India also sent the 60th Parachute Field Ambulance, which did outstanding work treating more than 200,000 people between 1950 and 1954.
How has been India's Relations with North and South Korea?
- In May 2015, the bilateral relationship with South Korea was upgraded to ‘special strategic partnership’.
- India has a major role to play in South Korea’s Southern Policy under which the latter is looking at expanding relations beyond its immediate region.
- Similarly, South Korea is a major player in India’s Act East Policy under which India aims to promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and develop strategic relationships with countries in the Asia-Pacific.
- India has had diplomatic relations with North Korea for over 47 years, which reflects the legacy of India’s commitment to the Non-Alignment Movement.
Way Forward
- With the post-Covid geopolitical order undergoing major changes and global economic conditions deteriorating, North Korea will want to focus on strengthening its already weak economy, especially when the country has been hit hard by the pandemic.
- Furthermore, at some point, dialogue between North Korea, the United States, South Korea, Japan and other stakeholders on the Korean Peninsula will reopen.
- At that juncture, India would be poised to play a constructive role in promoting peace and security on the Korean Peninsula.
- Continuing India’s engagement with North Korean leadership may pay off in these foreseeable situations.
- In the Current Scenario of War between Russia and Ukraine Indian Prime Minister’s message that “This is not the era of war” has given rise to expectations that India, which often casts itself in the role of “Vishwaguru”, can mediate between Russia and Ukraine to bring the war to an end.


International Relations
India-Romania Defense Agreement
For Prelims: Indo-Pacific, EU, NATO, MFN, Climate Change, INSTC.
For Mains: India-Romania Defense Agreement.
Why in News?
Recently, India and Romania have signed the Defense Cooperation Agreement, aiming to set up and expand Military Cooperation between both countries.
What is the Agreement About?
- The agreement will provide the legal framework for future cooperation in the field of defense through the exchange of expertise and knowledge on subjects of mutual interest including co-development and co-production of military hardware.
- The agreement will promote cooperation in the field of defense between both countries and open up enormous opportunities in sectors like defense medicine, scientific research, cyber defense, technology and research and development.
What is the Significance of the Agreement?
- The EU (European Union) Strategy for cooperation in the Indo-Pacific is an opportunity to strengthen EU-India cooperation in the region. Romania is committed to active involvement in the Indo-Pacific within the framework of this strategy.
- The EU-India Strategic Partnership roadmap and commitments from the EU-India Leaders’ Meeting in May 2021 provide a good basis to enhance cooperation and promote regional security in the Indo-Pacific.
- Strengthening relations with Indo-Pacific partners is crucial for addressing global challenges and upholding the rule-based international order at both bilateral and multilateral levels.
How have been the India-Romania Relations?
- Diplomatic Relation:
- India-Romania bilateral ties, formally established in 1948, have witnessed a steady growth.
- Both maintained friendly and cordial relations, culminating in the celebration of 70 years of diplomatic ties in 2018.
- Since the 1989 revolution in Romania, which overthrew the communist government, both countries have steadily increased trade and investments in each other.
- At the multilateral level, India and Romania have extended support to each other at the UN.
- Trade and Investments:
- Romania has in the past collaborated in projects involving petroleum, petrochemicals, power, and metallurgy industries in India. Romania was engaged in oil refinery projects in Assam and Bihar. Romania also shared their technology know-how for a thermal power plant in Singareni, the Mangalore pellet plant, the Durgapur steel plant, and a Hyderabad tractor plant.
- An Agreement on Trade and Economic Cooperation, granting mutual Most Favored Nation (MFN) status to each other was signed in 1993.
- Since 2013, the trade volume has been around USD 600-800 million; both sides expect this figure to touch the one billion mark soon.
- Green Energy:
- Romania has engaged in reducing its carbon blueprint and is committed to achieve the EU ambitious new targets to curb further the climate change.
- Romania together with India can certainly cooperate and collaborate in this key sector.
- The two nations can work together to reduce carbon footprint and focus on harnessing sustainable sources of power, such as solar energy.
- Romania is determined to become shortly a member of the International Solar Alliance, positive steps have already been taken.
- Connectivity:
- Romanian infrastructure companies can work with Indian partners to expand connectivity across Europe and India.
- Through the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), India remains committed to building a multimode network, connecting India to Iran, Azerbaijan, Iran, Afghanistan, Russia, Central Asia, and Europe.
- This will enhance the movement of freight North-South.
- The Romanian government has also undertaken expansion of the trans-European transport network.
- These mega connectivity projects will have many meeting points and scope for collaboration.
Way Forward
- There are many challenges in the International Fora such as supply chain disruption, War and Conflicts and climate change etc.
- Both Romania, a NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) and EU member, and India, fifth economy in the world and one of the largest troop contributors to United Nations peacekeeping missions, could play a constructive role in overcoming these challenges.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
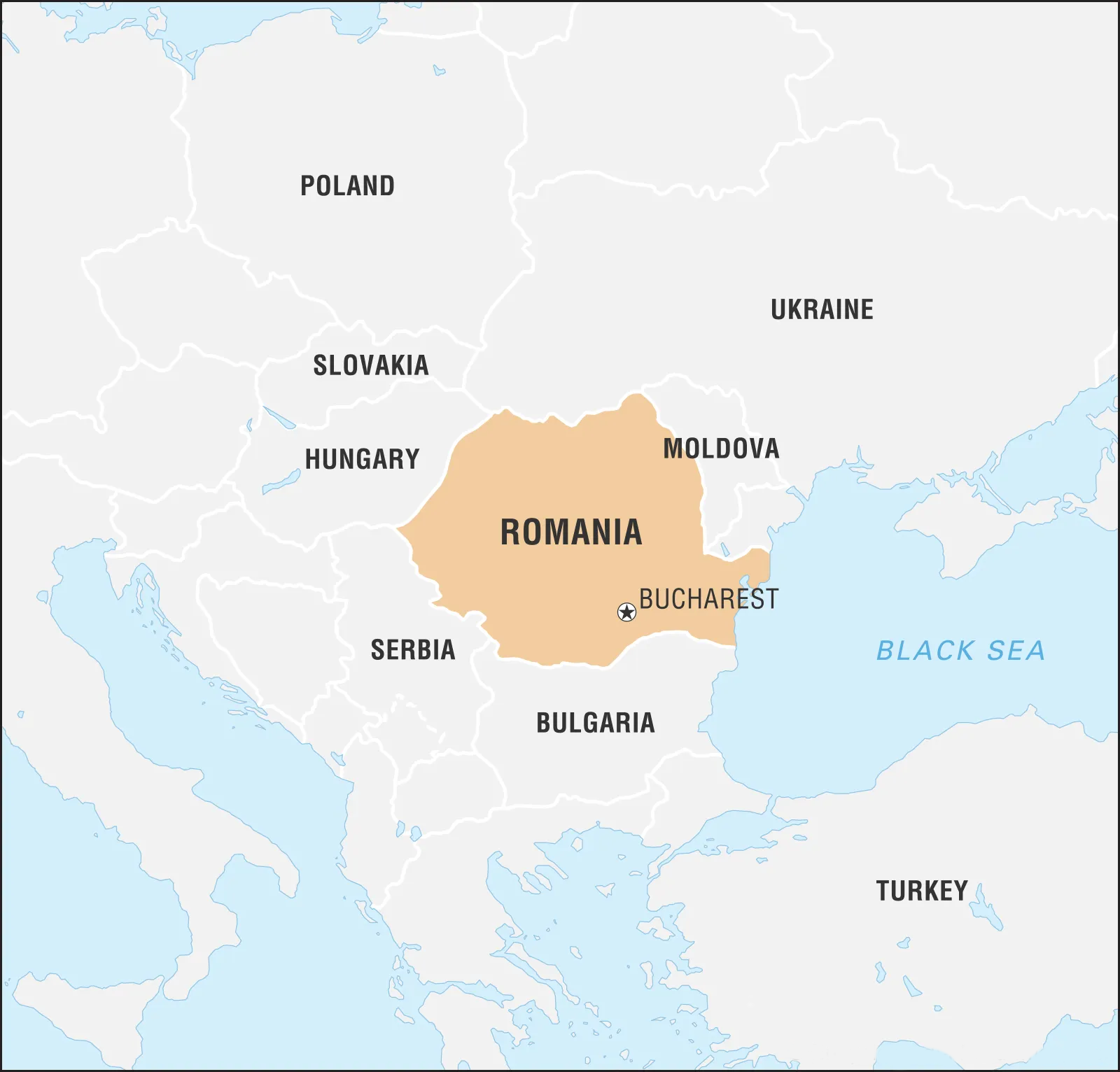
Q. Which of the following countries share borders with Moldova? (2008)
- Ukraine
- Romania
- Belarus
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Code:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Bandipur Tiger Reserve
Why in News?
Bandipur Tiger Reserve, located in Karnataka, completed 50 years as a Project Tiger Reserve on April 1, 2023. The reserve was launched in 1973 by the then Prime Minister, Indira Gandhi, with the aim to stop the decline in population of tigers.
- Initially, there were 12 tigers in Bandipur when Project Tiger was launched, as a result of protection measures, there are currently 173 tigers using the area.
What are the Key Points of Bandipur Tiger Reserve?
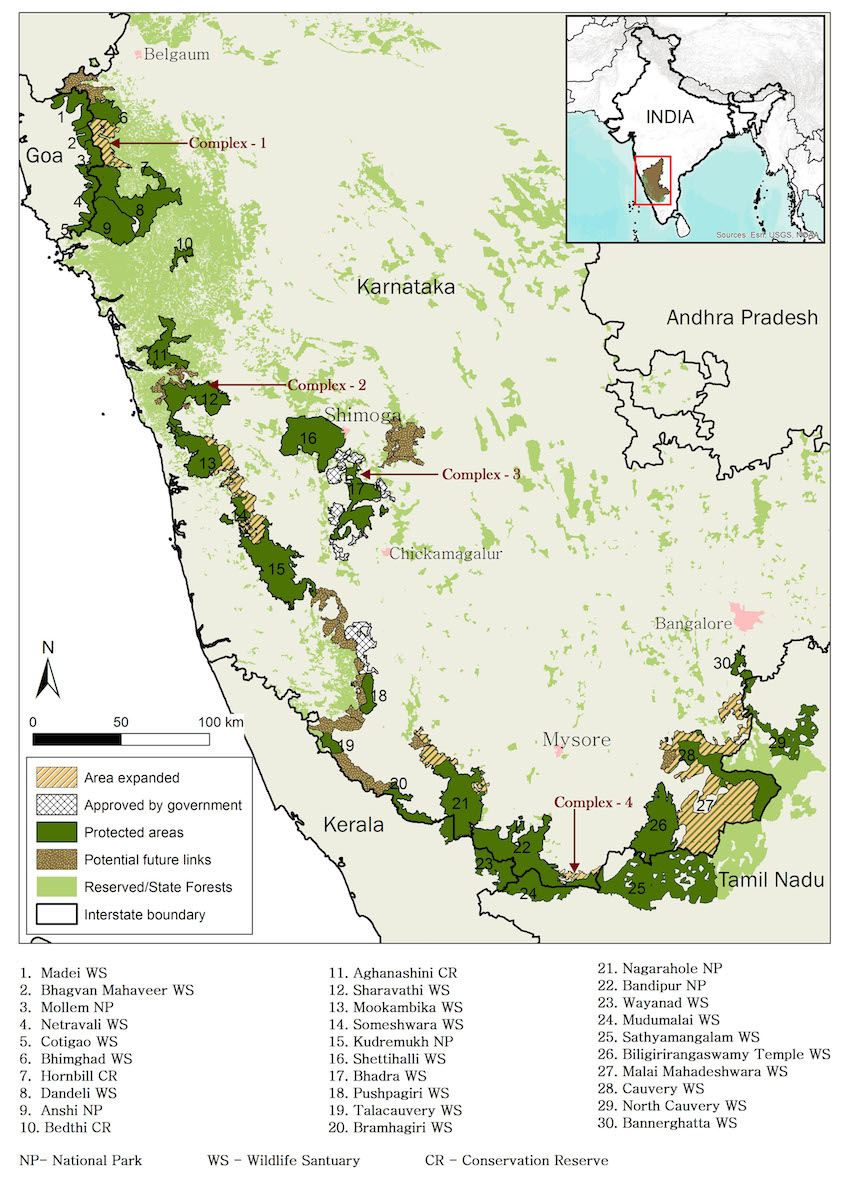
- About:
- Bandipur Tiger Reserve lies in one of the richest biodiversity areas of our country representing “Western Ghats Mountains Biogeography Zone”, surrounded by Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (Tamil Nadu) in the South, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (Kerala) in the Southwest & on the North West Side the Kabini Reservoir separates the Bandipur and Nagarahole Tiger Reserve.
- The reserve is recognized as one of the Mega Biodiversity Areas in the country and is home to rich floral and faunal diversity.
- Establishment:
- It was established in 1973 under Project Tiger. In 1985, by including adjacent areas from Venugopala Wildlife Park, it was enlarged and named Bandipur National Park.
- Location:
- It is situated in two contiguous districts (Mysore and Chamarajanagar) of Karnataka and is located at the tri-junction area of the States Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- Biosphere Reserve:
- The Bandipur Tiger Reserve is part of the Mysore Elephant Reserve and is an important component of the country’s first biosphere reserve, the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
- The landscape spanning Bandipur, Nagarahole, Mudumalai, and Wayanad complex is home not only to the highest number of tigers in the country – about 724, but also to the largest Asian Elephant population.
- Rivers and the Highest Point:
- The park is located between the Kabini river in the north and the Moyar river in the south. The Nugu river runs through the park. The highest point in the park is on a hill called Himavad Gopalaswamy Betta.
- Other Tiger Reserves in Karnataka:
- Bhadra Tiger Reserve
- Nagarahole Tiger Reserve
- Dandeli-Anshi Tiger Reserve
- Biligiriranganatha Swamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve, Besides, Malai Mahadeshwara Wildlife Sanctuary has been proposed to be made a tiger reserve.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following protected areas: (2012)
- Bandipur
- Bhitarkanika
- Manas
- Sunderbans
Which of the above are declared Tiger Reserves?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Project Tiger was launched by the Government of India in the year 1973 to save the endangered species of tiger in the country. Starting from nine reserves in 1973‑2016, the number has grown up to fifty. A total area of 71027.10 km2 is covered by these project tiger areas.
- Bandipur Tiger Reserve: It was formed by including most of the forest areas of the then Venugopala Wildlife Park, established under government notification dated 19th February 1941 and the area was enlarged in 1985 extending over an area of 874.20 sq km and named as Bandipur National Park. This reserve was brought under Project Tiger in 1973. It is situated in the contiguous landscape spread in the districts of Southern Karnataka namely the Mysore and Chamarajanagar. It is a distinctive landmass located at the trijunction area of the States of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Faunal biodversity includes common leopard, royal Bengal tiger, jungle cat, sloth bear, Asian elephant, wild boar, grey heron, shaheen falcon, little bustard-quail, common cobra, green vine snake etc. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Sunderbans Tiger Reserve: In 1875 under the Forest Act, 1865 (Act VIII of 1865), a large part of Sunderbans forest was declared as “reserved”Post-independence, it was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1977 and established as a national park on 4th May, 1984. In the year 1978, Sundarbans was declared a national park, and in 1973, it was declared a tiger reserve under Project Tiger. It is located in the state of West Bengal. Some of the common species of plants which are found include sundari tree, golpati, champa, dhundul, genwa and hatal. There are about 78 species of mangroves in these forests. This reserve is home to Royal Bengal Tiger along with other animals such as fishing cats, macaques, leopard cats, Indian grey mongoose, wild boar, flying fox, pangolin, and Indian grey mongoose. Hence, 4 is correct.
- Manas Tiger Reserve: In the year 1907 the forest was declared as Reserve forest. Post independence, in 1950, Manas Reserve forest was declared as a Wildlife Sanctuary. With the launch of Project Tiger in 1973, Manas Tiger Reserve was officially declared. UNESCO declared it as a World Heritage Site (Natural) in 1985 and further designated as Biosphere Reserve under Man and Biosphere Programme of UNESCO in 1989. It is located at the merger of terai grasslands and the bhabar grasslands ascending to semi-evergreen forests and then to Bhutan Himalayas in the state of Assam. This tiger reserve is an example of inter country tiger conservation and it extends from Assam in India to Royal Manas in Bhutan. It is very rich in the population of Royal Bengal Tigers. The last population of the pygmy survives in the wilds of Manas and nowhere else in the world. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Bhitarkanika Wetland: It is represented by as many as 3 protected Areas, namely “the Bhitarkanika National Park”, “the Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary” and “the Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary”. The Bhitarkanika National Park is a prime habitat of leopard cat, fishing cat, wild boar, spotted deer, sambar, dolphin, salt water crocodile. However, Bhitarkanika has not been declared as a tiger reserve. Hence, 2 is not correct. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer
Q2. From the ecological point of view, which one of the following assumes importance in being a good link between the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats? (2017)
(a) Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
(b) Nallamala Forest
(c) Nagarhole National Park
(d) Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve
Ans: (a)
- Sathyamangalam Wildlife Sanctuary and Tiger Reserve is a protected area along the Western Ghats in the Indian State of Tamil Nadu.
- Sathyamangalam forest range is a significant wildlife corridor in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve between the Western Ghats and the rest of the Eastern Ghats and a genetic link between the four other protected areas which it adjoins, including the Biligiriranga Swamy Temple Wildlife Sanctuary, Sigur Plateau, Mudumalai National Park and Bandipur National Park.
- First declared as a wildlife sanctuary in 2008 and enlarged in 2011, it covers a forest area of 1,411.6 sq km and is the largest wildlife sanctuary in Tamil Nadu. In 2013, it became the fourth tiger reserve as a part of Project Tiger in the State of Tamil Nadu.
- Nallamala Forest is one of the largest undisturbed stretches of forest in South India. It is located in the Nallamala Hill, which is a part of the Eastern Ghats. It is spread over 5 districts, namely Kurnool, Guntur, Kadapa, Mahabubnagar and Prakasam. The forest has a good tiger population and a part of the forest belongs to the Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve.
- Nagarhole National Park is situated in two districts of Mysore and Kodagu in the State of Karnataka. Nagarahole National Park forms a part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve and together with Bandipur National Park and Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary to its South-East and Wayanad to the South-West, is one of the last remaining and best protected habitats for endangered species like the Elephant and the Tiger.
- Seshachalam hills are the hill ranges spread in parts of Chittoor and Kadapa districts of Andhra Pradesh and have been designated as Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve in 2010. The Biosphere Reserve has large reserves of red sandalwood. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Sky Canvas: Artificial Meteor Showers
Why in News?
Recently, a Japanese company, ALE, plans to launch satellites that will trigger an artificial meteor shower, called Sky Canvas in 2025.
What is the Sky Canvas Project?
- The Sky Canvas project aims to give people all over the world “the opportunity to view the world’s first live human-made meteor shower.”
- ALE plans to use a pressure-driven system of gas tanks that will shoot pellets at a speed of 8 kilometers per second to trigger the artificial meteor shower.
- The metal “shooting star” particles will be taken to a low-Earth orbit by small satellites.
- Once the orbit stabilises, the particles will be released, and they will travel around part of the planet before entering the atmosphere at an altitude of 60 to 80 kilometres.
- The company also hopes to collect atmospheric data in the mesosphere (the third layer of the atmosphere) to further scientific understanding of climate change.
- The Mesosphere is too low to be observed by satellites and too high for weather balloons or aircraft.
- The company also hopes to collect atmospheric data in the mesosphere (the third layer of the atmosphere) to further scientific understanding of climate change.
How Does a Natural Meteor Shower Occurs?
- A natural meteor shower occurs when the Earth passes through a stream of debris left behind by a comet or asteroid.
- As the Earth travels in its orbit around the Sun, it encounters these streams of debris, which are composed of tiny particles of dust and rock.
- As the Earth passes through this debris, the particles enter the Earth's atmosphere at high speeds, typically around 40 kilometres per second.
- The friction between the particles and the atmosphere causes them to heat up and vaporise, creating the streaks of light that we see as meteors or "shooting stars."
- The name of the meteor shower is typically derived from the constellation from which the meteors appear to radiate.
- For example, the Perseid meteor shower appears to originate from the constellation Perseus.
- Around 30 meteor showers that are visible to observers on Earth occur every year and some of them have been observed for centuries.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Metropolitan Museum of Art Returns Trafficked Indian Sculptures
The Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York has announced that it will return 15 Indian sculptures that were trafficked and sold. The works date from the 1st century BCE to the 11th century CE and include terracotta, copper, and stone artifacts such as a Celestial Dancer (Apsara) valued at over $1 million and a stone bust of Kamadeva, the God of Love from the 8th century CE and a Svetambara enthroned Jina. from the 8th century CE. The museum has also removed three Turkish pieces from its Greek and Roman galleries.
The Metropolitan Museum of Art has pledged to adhere to responsible purchase of antiquities and has implemented strict standards for new acquisitions and its existing collection. Before Independence, the Antiquities (Export Control) Act was passed in 1947 to ensure that no antiquity could be exported without a license. Antiquities in India are governed by the Antiquities and Art Treasures Act, 1972 which falls within the purview of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), Union Ministry of Culture.
Read more: Menace of Missing Antiquities in India.
Indian Partition Refugee Assistance Scheme
The Central government scheme to provide financial assistance to over 5,000 Hindu and Sikh families who migrated to India from Pakistan’s West Punjab after the 1947 partition has faced several challenges. Out of 5,764 eligible families, only 903 families have received the grant so far, with several claims being unable to process due to the lack of original documents such as refugee cards. The scheme has also been affected by corruption allegations and demands for bribes from revenue officials. Additionally, the division of the grant amount among several members of the family has resulted in a low payout for some families.
The J&K administration conducted special camps to help families apply for the grant, but many have not been able to produce the required documents. The Ministry of Home Affairs reimburses the funds to the J&K administration based on the verification of records done by them, and the scheme has been extended till March 31, 2024, with ₹25 crore allotted for the scheme in the 2023-24 budget.
Read more: India and Refugee Policy
Hue and Cry
Recently, the Punjab government has issued a “hue and cry notice” against the fugitive pro-Khalistan preacher Amritpal Singh. The phrase 'hue and cry' may be commonly associated with public outrage, but its origins lie in England's 13th and 14th-century policing system. The 'Statute of Winchester' signed by King Edward I in 1285 mandated that anyone who witnessed a crime not only had to report it but take up a cry to alert the police.
The ‘hue and cry’ rule simply meant that if a suspect or a criminal was running down the street in front of some bystanders, then each of them had to yell to help the police identify and catch them. This community policing approach was successful in small-knit communities, and the practice has continued in some parts of the world, including India, where 'hue and cry notices' are still used to seek public assistance in cases such as locating missing persons or identifying suspects. These notices are governed by specific rules and procedures and are used sparingly to stress the seriousness of the matter and create panic among the public. While the term 'hue and cry' may have diminished in usage in contemporary times, it remains a legal procedure that must be followed to alert other states about fugitives.
Hush Money
Recently, Former US President Donald Trump is scheduled to appear in court to face charges related to a hush-money payment. Hush money refers to the use of money to silence or buy off individuals or institutions who may have damaging information or allegations against the user.