Quad Marks 20 Years of Cooperation
For Prelims: Quad, Indo-Pacific, Malabar exercise, Information Fusion Center, Cancer Moonshot, Artificial Intelligence, String of Pearls, Blue Dot Network, Indo-Pacific Economic Framework
For Mains: Significance of Quad in India’s foreign policy, Significance of Quad in the Indo-Pacific region, India and its Bilateral Relations
Why in News?
The Quad Foreign Ministers marked the 20th anniversary of Quad cooperation, reaffirming their commitment to a free, open, and peaceful Indo-Pacific amid China’s growing assertiveness.
What are the Key Facts About Quad?
- About: Quad, or Quadrilateral Security Dialogue is a strategic forum of the US, Japan, India, and Australia aimed at regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Objectives: Promoting a free and open Indo-Pacific, upholding democracy, human rights, and rule of law, and countering China's expanding influence.
- Formation of Quad:
- 2004 Tsunami Origins: The group’s roots lie in the 2004 tsunami relief efforts when India, the US, Japan, and Australia collaborated for rescue operations.
- 2007 Formation: The Quad formally emerged in 2007, with Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe proposing the idea.
- Australia withdrew in 2008 due to Chinese pressure and regional tensions.
- Revival in 2017: Enhanced US-Australia military ties led to Australia's return. The first official Quad talks were held in the Philippines in 2017.
- Malabar Exercise: The Malabar exercises began in 1992 as a bilateral naval drill between India and the US. Japan joined in 2015, and Australia participated in Malabar 2020.
- Nature of Quad: The Quad operates without a formal alliance structure, secretariat, or decision-making body.
- The forum is sustained through regular meetings, including ministerial and leader-level summits, as well as information exchanges and military drills.
- Key Initiatives of the Quad:
- Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA): Enhances real-time monitoring of illegal fishing and maritime activities.
- IPMDA collaborates with regional bodies like the Pacific Islands Forum Fisheries Agency and India’s Information Fusion Center–Indian Ocean Region.
- Maritime Initiative for Training in the Indo-Pacific (MAITRI): Supports capacity-building for maritime security and law enforcement training.
- Indo-Pacific Logistics Network: Aims to leverage shared airlift and logistical capacities for rapid disaster response in the region.
- Quad Cancer Moonshot: Targets cervical cancer prevention and treatment, with plans to save hundreds of thousands of lives over coming decades.
- Quad Ports of the Future Partnership: Develops sustainable and resilient port infrastructure across the Indo-Pacific, with India hosting a Regional Ports and Transportation Conference in 2025.
- Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN): Quad with Open RAN facilitates secure and resilient 5G ecosystems.
- Advancing Innovations for Empowering NextGen Agriculture (AI-ENGAGE): Uses Artificial Intelligence (AI), robotics, and sensing to improve agricultural practices and empower farmers in the Indo-Pacific.
- BioExplore Initiative: A USD 2 million project to leverage AI for biological research, with applications in healthcare, clean energy, and sustainable agriculture.
- Semiconductor Supply Chain Contingency Network: Enhances collaboration to mitigate risks in semiconductor supply chains.
- Quad Fellowship: Funds graduate STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) education in member countries and recently expanded to include ASEAN students.
- India’s Quad Scholarships program supports 50 engineering students from the Indo-Pacific annually.
- Counter Terrorism Working Group (CTWG): Focuses on countering the misuse of unmanned aerial systems, chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear threats (CBRN), and the internet for terrorist purposes.
- Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA): Enhances real-time monitoring of illegal fishing and maritime activities.
What is the Significance of Quad for India?
- Maritime Security: Ensures India's maritime interests are safeguarded by promoting freedom of navigation and countering piracy and illegal fishing.
- Joint naval exercises enhance interoperability and maritime domain awareness.
- Strategic Importance: Quad provides a platform to address challenges in the Indo-Pacific region, particularly countering China's assertive policies like the "String of Pearls."
- Quad aligns with India's Act East Policy to strengthen ties with East and Southeast Asia.
- Economic Opportunities: Encourages economic cooperation through initiatives like the Blue Dot Network and Supply Chain Resilience Initiative.
- Post-Covid, India has the opportunity to attract manufacturing units shifting from China, enhancing supply chain resilience in the global economy.
- Scientific Collaboration: The Quad Fellowship encourages academic and scientific research in STEM fields.
- People-to-People Ties: Enhances cultural and academic exchanges, boosting India’s soft power diplomacy.
What is the Relevance of Quad in Contemporary Global Context?
- Quad’s Continued Relevance
- Strategic Significance: The Quad remains a crucial platform to counterbalance China’s growing influence in the Indo-Pacific, particularly in contested regions like the South China Sea.
- The Quad pledged support for the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific, the Pacific Islands Forum, and the Indian Ocean Rim Association, highlighting its role in collaborating with existing regional frameworks.
- Maritime Security: Initiatives like the IPMDA enhance member countries' abilities to monitor illegal activities and protect their Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs).
- Diverse Agenda: The Quad addresses multiple issues beyond security, such as health, technology, infrastructure, and climate change, showing its adaptability and multi-dimensional focus.
- Programs like the Quad Cancer Moonshot, pandemic preparedness initiatives, and climate adaptation measures demonstrate its practical contributions to regional stability.
- Institutional Strengthening: Regular summits, ministerial dialogues, have institutionalized the Quad, ensuring its sustainability and ability to evolve.
- People-Centric Initiatives: Fellowships, scholarships, and people-to-people ties strengthen the Quad’s soft power and build trust in the region.
- Strategic Significance: The Quad remains a crucial platform to counterbalance China’s growing influence in the Indo-Pacific, particularly in contested regions like the South China Sea.
- Challenges to Quad’s Relevance:
- Lack of formal structure: The Quad lacks a secretariat, or permanent decision-making body, limiting coordinated action and consensus on critical issues and hampers its ability to address global challenges effectively.
- Divergent Priorities: Quad members have varied national interests. For instance, India’s non-alignment policy and reluctance to join formal military alliances can limit the grouping's strategic cohesion.
- Security vs. Development: While the US and Japan focus heavily on countering China.
- India and Australia majorly emphasize development-oriented goals, leading to differing approaches.
- China’s Growing Influence: Despite Quad efforts, China’s influence in the Indo-Pacific continues to grow, especially through its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and investments in Pacific Island nations.
- Resource Constraints: Many Quad initiatives require substantial funding and institutional support.
- Delays or insufficient resource allocation could hinder their implementation and impact.
- Overlaps with Other Groupings: The Quad’s objectives often overlap with other multilateral forums like ASEAN, Australia, the UK and the US (AUKUS), and the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), leading to redundancy and dilution of focus.
Way Forward
- Institutionalization: Formalize mechanisms for decision-making and implementation to improve efficiency and accountability.
- Strengthen ties with regional organizations like ASEAN and ensure complementary, not competing, efforts.
- Quad Plus: Expanding the Quad to include South Korea, New Zealand, Vietnam, ASEAN, and other regions would enhance inclusivity.
- Focusing on climate change, healthcare, and disaster resilience, along with strengthening institutional mechanisms, would boost regional support and effectiveness.
- Enhanced Resource Commitment: Secure robust funding for initiatives like infrastructure, digital connectivity, and renewable energy projects to ensure long-term impact.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the strategic significance of the Quad for India. How does it help in addressing China’s growing influence in the Indo-Pacific region? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. The new tri-nation partnership AUKUS is aimed at countering China’s ambitions in the Indo-Pacific region. Is it going to supersede the existing partnerships in the region? Discuss the strength and impact of AUKUS in the present scenario. (2021)
Q.Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) is transforming itself into a trade bloc from a military alliance, in present times Discuss. (2020)
CGWB Report on Groundwater Contamination
For Prelims: Central Groundwater Board, Fluoride, Uranium, Central Ground Water Authority, Waterborne Diseases, Blue baby syndrome, Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA), National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM), Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY).
For Mains: Environmental Pollution and Management, Water Resources Management, Water Quality
Why in News?
The Central Groundwater Board (CGWB) report reveals a troubling rise in groundwater contamination across India, with more districts showing excessive nitrate levels.
- This chemical contaminant poses significant health risks, particularly to young children, while also raising environmental concerns.
What are the Key Findings of the CGWB Report?
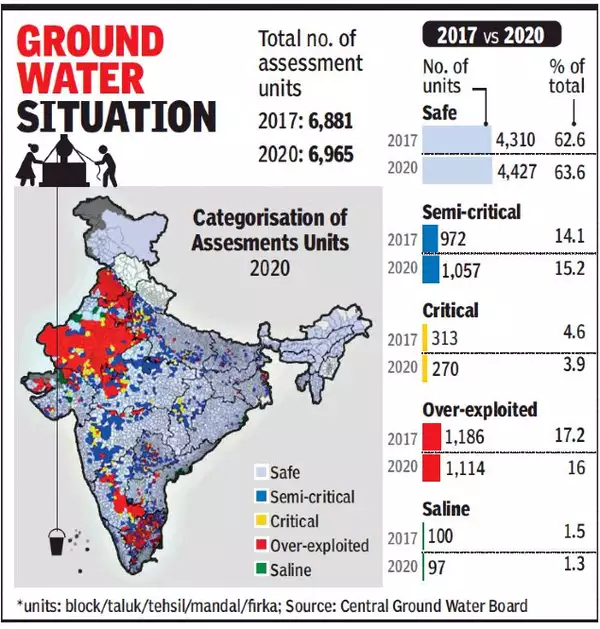
- Increase in Nitrate Contamination: As of 2023, 440 districts reported excessive nitrate levels in groundwater, up from 359 districts in 2017.
- 56% of India’s districts have nitrate concentrations exceeding the safe limit of 45 mg per litre.
- Regional Hotspots: Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) reported the highest levels of nitrate contamination.
- Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh are showing notable levels of nitrate contamination, with growing concerns in central and southern India.
- Monsoon Impact: Nitrate contamination increases after the monsoon, with 32.66% of samples exceeding safe limits during the rainy season, compared to 30.77% pre-monsoon.
- Other Groundwater Contaminants: Fluoride contamination remains a major issue in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Uranium contamination exceeds safe levels in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka, particularly in over-exploited groundwater zones.
- Groundwater Extraction: 60.4% of groundwater is being extracted across India, maintaining a steady rate since 2009.
- However, there has been an improvement in the availability of groundwater, with 73% of the blocks classified as being in the 'safe' zone, a significant increase from 67.4% in 2022.
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB)
- About: The CGWB, established under the Ministry of Water Resources, (now Ministry of Jal Shakti), is the apex body for managing, exploring, monitoring, assessing, and regulating groundwater resources in India.
- Established in 1970, CGWB was initially formed by renaming the Exploratory Tube Wells Organization and was later merged with the Ground Water Wing of the Geological Survey of India in 1972.
- The Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA), constituted under the Environmental Protection Act, 1986, regulates groundwater development to ensure its sustainability.
- Key Functions and Responsibilities: CGWB provides scientific expertise for groundwater management, including exploration, monitoring, and water quality assessments.
- It also implements schemes for artificial recharge and rainwater harvesting to augment groundwater levels.
- Scientific Reports: CGWB releases State and District hydrogeological reports, ground water year books and Atlases.
What are the Sources of Groundwater Contamination?
- Agricultural Practices: Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture leads to nitrate and phosphate leaching into the soil, contaminating groundwater.
- Improper irrigation and over-extraction of water further exacerbate the issue.
- Storage Tanks: Corroding tanks may leak gasoline, oil, or chemicals into the groundwater.
- Hazardous Waste Sites: Abandoned sites with leaking materials pose risks to groundwater.
- Landfills: Contaminants from landfills can seep into groundwater if protective layers are damaged.
- Septic Systems: Poorly maintained systems can leak waste and chemicals, polluting groundwater.
- Atmospheric Contaminants: Contaminants from the atmosphere or surface water can eventually reach groundwater.
- Deforestation: Disrupts natural filtration processes in the soil, leading to increased runoff and the entry of pollutants into groundwater systems.
What are the Implications of Groundwater Contamination?
- Health Risks: Contaminants such as fluoride, nitrates, and heavy metals pose serious health risks and lead to Waterborne Diseases.
- Excessive nitrate contamination, particularly for infants and young children, can cause methemoglobinemia, also known as "blue baby syndrome."
- Food Production: Groundwater contamination with heavy metals and pollutants used for irrigation can lead to toxic substances accumulating in crops, compromising food safety and human health.
- Environmental Impact: Nitrate pollution can disrupt local ecosystems, impacting plant and aquatic life.
- Contaminants in groundwater can cause soil contamination and salinization.
- Increased Costs: Contaminated groundwater requires costly treatment processes to make it safe for consumption.
- Groundwater contamination can spread to surface water, worsening water quality. Chronic contamination reduces freshwater availability, leading to water shortages and potential socio economic crises.
What are the Measures Taken to Curtail Groundwater Contamination?
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA).
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM).
- Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY).
- Pollution Control Programs: Central Pollution Control Board's (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards enforce pollution control measures under the Water (Prevention & Control) Act, 1974, focusing on the prevention of contamination.
- Installation of Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) and Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) to treat water before release into the environment.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Training stakeholders through institutions like the Rajiv Gandhi National Ground Water Training & Research Institute (RGNGT&RI).
- Efforts like “Catch the Rain” and Swachh Bharat Mission educate communities about groundwater protection.
Way Forward
- Regulating Fertilizer Use: Greater attention must be paid to the overuse of nitrogenous fertilizers in agriculture. Implementing sustainable farming practices could help mitigate this issue.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Encouraging rainwater harvesting and the replenishment of groundwater through natural processes can help reduce the reliance on overexploited aquifers.
- Improved Waste Management: Efficient waste management systems in urban areas can prevent groundwater contamination. Decentralized waste treatment and recycling initiatives are effective solutions.
- Better Monitoring and Policies: Increasing the monitoring of groundwater quality and creating stricter regulations regarding chemical contaminants can help prevent further contamination.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the impacts of groundwater contamination in India? How can groundwater be better managed?" |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Which one of the following ancient towns is well known for its elaborate system of water harvesting and management by building a series of dams and channelizing water into connected reservoirs? (2021)
(a) Dholavira
(b) Kalibangan
(c) Rakhigarhi
(d) Ropar
Ans: (a)
Q.2 With reference to ‘Water Credit’, consider the following statements: (2021)
- It puts microfinance tools to work in the water and sanitation sector.
- It is a global initiative launched under the aegis of the World Health Organization and the World Bank.
- It aims to enable the poor people to meet their water needs without depending on subsidies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 What are the salient features of the Jal Shakti Abhiyan launched by the Government of India for water conservation and water security? (2020)
Q.2 Suggest measures to improve water storage and irrigation system to make its judicious use under the depleting scenario. (2020)
Tapping Renewable Energy Potential in India
For Prelims: Renewable Energy, Wind Power, 500-Gw Non-Fossil, Solar Power, Grid-Connected Rooftop Solar, Small Hydro Power, Biomass Energy, Waste-To-Energy, Fragmented Land Ownership, Grid Infrastructure, Green Hydrogen, Digitized Land Records, Transmission Lines
For Mains: Significance of Boosting Renewable Energy Capacity to achieve Renewable Energy Targets.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has asked states to ease land availability for renewable energy projects with a focus on wind power.
- With a current wind power capacity of 47.95 GW, the government aims to double it to 100 GW and enhance land access to reach the 500-GW non-fossil energy target by 2030.
What is Renewable Energy?
- Renewable Energy: Renewable energy is energy derived from natural, replenishable sources such as solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, geothermal, and tidal.
- These sources are sustainable and environmentally friendly, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Types:
- Solar Energy: Harnessed from the sun’s radiation using solar panels or solar thermal systems.
- Wind Energy: Generated by converting the kinetic energy of wind into electricity with wind turbines.
- Hydropower: Produced by harnessing the energy of flowing water (rivers, dams, waterfalls).
- Biomass Energy: Created from organic materials like plant residues and animal waste for heating, electricity, and biofuels.
- Geothermal Energy: Derived from Earth’s internal heat (hot water, steam) for electricity generation and direct heating.
- Tidal & Wave Energy: Uses ocean water movement (gravitational pull or surface waves) to generate electricity.
What is the Status of Renewable Energy in India?
- Renewable Energy Capacity: As of November 2024, India’s total installed renewable energy capacity stands at 158.55 GW, showcasing significant strides in transitioning to cleaner energy sources.
- Wind Power: Wind Power accounts for 47.96 GW, with 2.07 GW added during FY 2024-25.
- Solar power: Solar power in India leads with an installed capacity of 94.17 GW, including 15.16 GW from grid-connected rooftop solar and 4.10 GW from off-grid solar solutions.
- Hydro Power: Small Hydro Power has an installed capacity of 5.08 GW, focusing on utilizing river streams for clean energy.
- Biomass Energy: Biomass Energy contributes a combined total of 10.72 GW, with 9.80 GW from bagasse-based cogeneration and 0.92 GW from non-bagasse-based cogeneration.
- Waste-to-Energy: Waste-to-Energy projects, including off-grid systems, contribute 0.61 GW, emphasizing efforts to utilize waste for sustainable energy generation.
What is India's Potential in Renewable Energy ?
- Solar Energy: With over 300 sunny days annually, the National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) estimates its potential at 748 GW, assuming 3% of wasteland is covered by Solar PV modules.
- States like Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu lead in solar energy development, with massive solar parks contributing to the national grid.
- Wind Energy: India’s wind energy potential exceeds 300 GW, primarily concentrated in Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- Emerging offshore wind projects in coastal areas, such as Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, could significantly boost capacity.
- Hydro Energy: India has an estimated more than 148 GW of hydroelectric potential, of which 46 GW remains untapped.
- Small hydropower plants (<25 MW) offer 20 GW of potential, particularly in the Himalayan and northeastern regions.
- Geothermal Energy: India has significant geothermal potential, with notable sites in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and Jharkhand, capable of generating 10 GW.
- Projects in Puga Valley (Ladakh) highlight the untapped potential of geothermal energy.
- Ocean Energy: Seawater stores tidal, wave and Ocean thermal energy. Among them, the harnessing of 40GW wave energy is possible in India.
- Coastal areas such as the Gulf of Kutch and the Sundarbans offer tidal energy potential.
What are Challenges in Expanding Renewable Energy Including Wind Energy in India?
- Land Scarcity and Use Conflicts: The renewable energy sector, especially wind sector faces challenges in accessing land and ideal wind sites, especially in densely populated or ecologically sensitive areas.
- Farmers and local communities are resistant to reallocating land for wind energy projects.
- Consolidating suitable parcels of land is particularly challenging in states such as Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu, where land is often divided among multiple owners.
- Financing and Investment Issues: Wind energy projects have substantial upfront capital requirements.Uncertainty in returns and long payback periods deter private investors.
- Grid Integration and Curtailments: Wind power’s intermittent nature and seasonal wind patterns cause supply instability, with grid curtailments during peak seasons reducing profitability.
- Exhaustion of High-Quality Sites: Many prime locations with optimal wind speeds are already occupied, forcing new projects into less viable areas.
- Approval Delays and Policy Gaps: Wind projects face prolonged delays in obtaining environmental, wildlife and forest clearances.
- The lack of consistent financial incentives or long-term policies reduces investor confidence.
- Offshore Wind Challenges: Offshore wind potential remains untapped due to high installation costs, advanced technology needs, and limited government support.
What is India's Initiative to Boost Renewable Energy?
Way Forward
- Improving Land Access: Establish transparent policies for acquiring unused government land and streamline processes through digitized land records and designated renewable zones.
- Promote dual-use projects where solar farms coexist with agriculture or grazing to optimize land use.
- Strengthening Transmission Infrastructure: Speed up development of green energy corridors to link renewable projects with demand centers.
- Accelerate the setup of transmission lines and invest in hybrid systems (solar + wind + storage) to stabilize power output and reduce variability.
- Harmonizing Policies: Formulate a unified national renewable energy policy to address state-level inconsistencies.
- Provide long-term incentives such as tax breaks, interest subsidies, and performance-based rewards to attract investments.
- Encourage local production of solar panels and wind turbines under "Make in India" by offering subsidies and reducing dependence on imports.
- Focusing on Offshore Wind: Pilot offshore wind projects and offer financial incentives while reducing import duties on specialized equipment to promote development.
- Financing and R&D: Set up green banks to provide affordable financing and invest in research for advanced technologies to improve efficiency and lower costs.
- Environmental Sustainability and Skill Development: Ensure rigorous environmental assessments, promote recycling of energy components, and conduct community engagement programs.
|
Drishti Mains Question What are the key challenges in expanding renewable energy capacity in India, and how can they be addressed to meet the 500 GW non-fossil fuel target by 2030? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Which one of the following is a purpose of ‘UDAY’, a scheme of the Government? (2016)
(a) Providing technical and financial assistance to start-up entrepreneurs in the field of renewable sources of energy
(b) Providing electricity to every household in the country by 2018
(c) Replacing the coal-based power plants with natural gas, nuclear, solar, wind and tidal power plants over a period of time
(d) Providing for financial turnaround and revival of power distribution companies
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Write a note on India’s green energy corridor to alleviate the problem of conventional energy.(2013)
India as Global Hub For Data Centres
For Prelims: Data Centers, Artificial Intelligence (AI), 5G, Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023, Reserve Bank of India
For Mains: India Initiatives related to data centres, Opportunities and Challenges in data centre industry, Way forward
Why in News?
India’s data centre sector is witnessing significant growth, projected to double its capacity by FY27, driven by digitalization, the adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the rollout of 5G, and data localization laws.
- However, challenges remain, such as infrastructure gaps, the need for sustainable power solutions, and competition from global players like China.
What are Data Centres?
- About:
- Data centres are specialized facilities used to store, manage, and process large volumes of electronic data.
- These centres house critical Information Technology (IT) infrastructure, including servers, storage devices, and networking equipment, along with systems for cooling, power supply, and security.
- They are designed to provide reliable and scalable solutions for data storage, processing, and management.
- Components of a Data Centre:
- Servers and Storage Systems: These are responsible for handling workloads such as hosting websites, running applications, and managing cloud storage.
- Networking Equipment: Routers, switches, and firewalls that facilitate communication between various servers and external networks.
- Power Supply Systems: Uninterrupted power supply (UPS) and backup generators to ensure continuous power availability.
- Cooling Systems: Since servers generate a significant amount of heat, efficient cooling mechanisms, such as air conditioning or liquid cooling systems, are crucial to prevent overheating and ensure smooth operation.
- Security Infrastructure: Physical and cybersecurity measures to protect data and infrastructure from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
- Current Status of Data Centres in India:
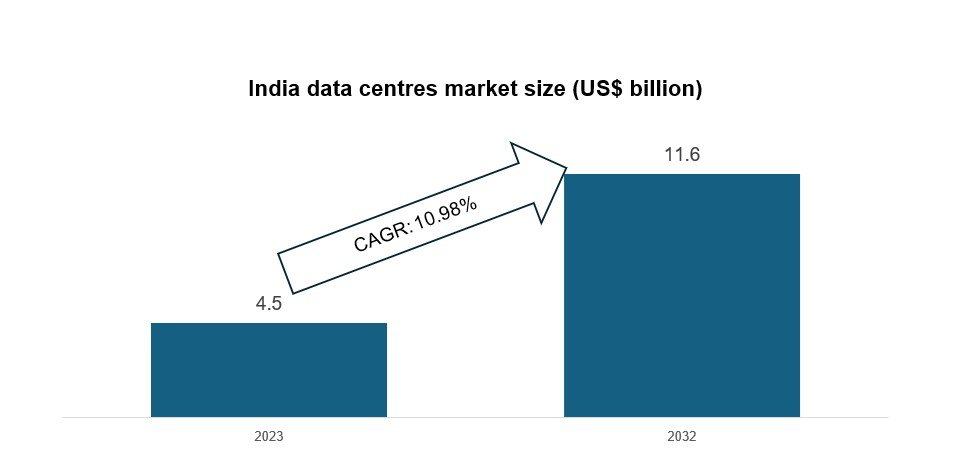
- Growth Projection: India's data centre market is forecasted to grow significantly, from USD 4.5 billion in 2023 to USD 11.6 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.98%.
- Global Data Share vs. Local Capacity: While India accounts for 20% of global data production, it currently holds only 3% of the global data centre capacity, showcasing a significant growth opportunity for the sector.
- Geographical Distribution of Data Centres: Over 50% of India’s data centre capacity is concentrated in Mumbai, benefiting from its strategic location, reliable power supply, and cable landing stations.
- Smaller cities such as Ahmedabad, Pune, and Vizag are also emerging as important hubs due to lower costs and improving infrastructure.
- India hosts around 150 data centres, with prominent players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, CtrlS, Sify, and Yotta leading the market.
- Geographical Distribution of Data Centres: Over 50% of India’s data centre capacity is concentrated in Mumbai, benefiting from its strategic location, reliable power supply, and cable landing stations.
What are the Key Reasons for Growth of Data Centres in India?
- Digitalization: The increasing adoption of digital technologies, especially in AI, cloud computing, and data storage, has led to rising demand for data processing and storage solutions.
- With 751.5 million internet users and a penetration rate of 52.4% in 2024, India’s growing reliance on mobile internet and digital solutions has driven the expansion of data centre networks to meet the rising demand for data processing and storage.
- RBI Mandate on Financial Data Storage: In 2018, the Reserve Bank of India issued a data localization mandate that required all payment system data related to Indian customers to be stored in India except in few cases, ensuring secure local storage and processing of sensitive financial data within India.
- AI and 5G Rollout: The surge in AI and generative AI projects, along with the nationwide rollout of 5G networks, is expected to increase data consumption and necessitate a corresponding rise in data centre capacity.
- Data Localization Laws: India’s data localization regulations mandate that certain types of data be stored within the country, creating further demand for local data centres. The key Legislation includes:
- Public Records Act, 1993: Public Records Act, 1993 prohibits the removal of public records from India, introducing the first local data storage requirement.
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023: Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 establishes baseline privacy protections and allows for sector-specific regulations to impose stricter data localization requirements.
What is the Significance of Data Centres in India’s Economic Growth?
- Data Processing for Digital Economy: Data centres are vital for cloud services, data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) offering the computational capacity for processing vast data.
- Enabling Digital Services: Data centres are the backbone of digital services such as e-commerce, social media, banking, entertainment, and communication. They ensure the smooth delivery of online services to billions of users worldwide.
- Major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud rely on data centres to offer scalable and reliable services to global businesses and consumers.
- Supporting Critical Infrastructure: In sectors like healthcare, finance, and government, data centres host critical systems that support national security, emergency services, and financial transactions.
- Boosting Economic Growth: The expansion of data centres contributes to job creation, infrastructure development, and the growth of the digital economy. The sector also attracts investments in technology, power infrastructure, and real estate.
- As per Crisil Ratings, India's data centre capacity is expected to double by FY27, creating significant investment opportunities and potentially generating over Rs 50,000 crore in economic activity.
- Reducing Latency with Edge Computing: The rise of IoT and real-time applications has increased the demand for edge data centres, which minimize latency by processing data closer to users.
- The rollout of 5G is expected to further boost this trend, enhancing application speed and reliability.
What are the Key Challenges Hindering the Growth of India’s Data Centre Sector?
- Infrastructure Constraints: Infrastructure deficits, including unreliable power supply and limited connectivity, increase costs and risks for data centres, especially in non-metro areas. High capital investment such as in cooling systems, particularly for smaller businesses, hampers growth.
- Although relatively cost-effective compared to countries like Japan and Singapore, substantial investment (Rs 55,000-65,000 crore) is needed for land acquisition, building construction, and power equipment over the 3 three years.
- Also, meeting stringent regulations and safeguarding sensitive data require constant investment in advanced security systems, adding to operational costs.
- Regional Disparities: Large metros like Mumbai dominate the market, while smaller cities lack adequate investments in infrastructure and power supply, leading to an uneven distribution of data centres across the country.
- Environmental Sustainability: Data centres are energy-intensive, contributing to carbon emissions. The industry faces pressure to adopt renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies to minimize environmental impacts.
- Skill Shortages and Competition: A lack of skilled professionals in data centre management and operations hampers sectoral growth.
- Countries like China, with advanced data centre capacity, present significant competition.
- Cybersecurity Threats: As data centres handle vast amounts of sensitive information, they are prime targets for cyberattacks. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to safeguard personal and corporate data.
- Scalability: As demand grows, scaling infrastructure to meet requirements while maintaining efficiency and cost-effectiveness remains a challenge.
Initiatives to Promote the Data Centre Ecosystem in India
- Digital India (2015): Digital India scheme aimed at enhancing online infrastructure and internet connectivity, fostering the growth of digital services across the country.
- National Informatics Centre (NIC): NIC established advanced National Data Centres to support government initiatives and digital infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Status for Data Centres: The government has granted infrastructure status to data centres with an IT load of more than 5 MW, facilitating easier access to financing and incentives.
- State-Level Policies: Policies like Maharashtra’s IT and ITES Policy 2023 offer targeted benefits and incentives to the data centre industry, promoting regional development.
- Hyperscale Data Centres: India’s first hyperscale data centre, Yotta D1, has been set up in Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, marking a significant milestone in India’s data centre capacity.
Way Forward
- Infrastructural Improvements: To become a global hub, India must invest in upgrading its power infrastructure, including renewable energy solutions, to provide reliable, cost-efficient energy to data centres.
- Policy Support: India should continue to develop and refine policies to facilitate the growth of the data centre industry, including easing land acquisition processes and providing incentives for infrastructure development.
- Regional Development: Encouraging the growth of data centres in non-metro cities by improving local infrastructure and offering incentives can help reduce regional disparities and foster more equitable growth.
- Human Resource Development: There is a need for cooperation and collaboration with global companies and nations for technology transfer and investment for enhancing human resource skills through training and international partnerships to support sustainable growth.
Conclusion
India has significant potential to become a global leader in the data centre market, driven by digital growth, rising data consumption, and advancements in AI and 5G. However, addressing challenges like infrastructure gaps, competition from China, and the need for investments in power and cooling solutions is crucial. With supportive policies and infrastructure development, India can emerge as a prominent data centre hub in the near future.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the growth, challenges, and opportunities in India's data center sector and its role in advancing the country's digital economy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
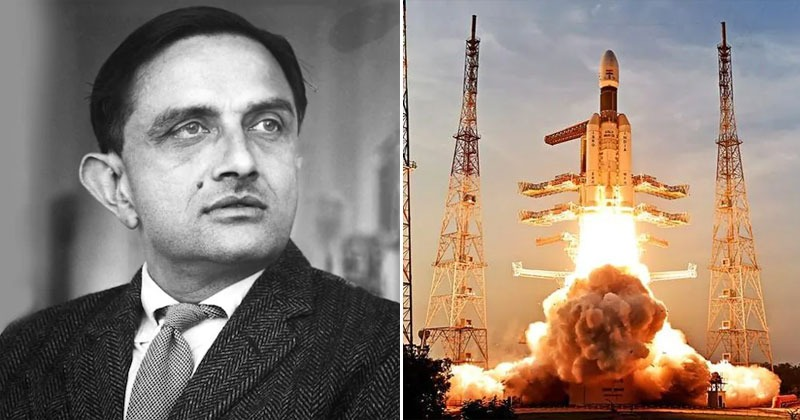
Vikram Sarabhai’s 52nd Death Anniversary
Why in News?
- Every year, the 30th December is observed as the death anniversary of Vikram Sarabhai.
- Vikram Ambalal Sarabhai was an Indian physicist and industrialist who initiated space research and helped develop nuclear power in India.
What are the Contributions of Vikram Sarabhai?
- Early Life and Education:
- Born on 12th August 1919, in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, to an affluent Jain family, Sarabhai was one of eight children of Ambalal and Sarla Devi.
- He showed creative promise early, building a working model of a train engine at 15, now preserved at the Community Science Centre (CSC) in Ahmedabad.
- He completed his Tripos (undergraduate degree) in Natural Sciences from St. John's College, Cambridge (1940).
- He returned to India during World War II to research cosmic rays under Dr. CV Raman at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru.
- He was awarded a PhD from Cambridge in 1947 for his thesis on cosmic rays.
- Institutional Legacy: Dr. Sarabhai was instrumental in establishing several institutions that continue to shape India’s scientific and industrial landscape:
- Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad: Founded in 1947, PRL marked the beginning of Sarabhai’s journey in institution building.
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Ahmedabad: Played a pivotal role in its creation.
- Community Science Centre, Ahmedabad: Founded in 1966 to promote science education.
- Darpan Academy for Performing Arts, Ahmedabad: Co-founded with his wife, Mrinalini Swaminathan.
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram: A hub for India’s space missions.
- Space Applications Centre, Ahmedabad: Formed by merging six institutions.
- Electronics Corporation of India Limited (ECIL), Hyderabad.
- Uranium Corporation of India Limited (UCIL), Jaduguda, Bihar.
- Contributions to Indian Space and Nuclear Programs:
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO): He founded the ISRO, emphasizing the importance of space technology for societal development.
- Advocated for satellite applications to address India’s developmental challenges.
- Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE): Conceptualized with NASA, SITE beamed educational programs to rural areas, laying the foundation for programs like Doordarshan’s Krishi Darshan.
- Aryabhata Satellite: Initiated the fabrication of India’s first satellite, Aryabhata, launched in 1975 from a Russian cosmodrome.
- Atomic Energy Commission: Took over as chairman after Homi Bhabha’s death, advancing nuclear science.
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO): He founded the ISRO, emphasizing the importance of space technology for societal development.
- Awards and Honors:
- Awards:
- Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award (1962)
- Padma Bhushan (1966)
- Padma Vibhushan (posthumously, 1972)
- Distinguished Positions:
- President, Physics Section, Indian Science Congress (1962)
- President, General Conference of the IAEA, Vienna (1970)
- Vice-President, Fourth UN Conference on Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy (1971)
- Title: Mahatma Gandhi of Indian Science (By former President APJ Abdul Kalam).
- Legacy:
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) was named in his honor.
- A lunar crater, “Sarabhai Crater,” was named after him.
- Awards:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs):
Q. Consider the following statements:
- The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission.
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA.
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c )
Q. What is ‘Greased Lightning-10 (GL-10)’, recently in the news?
(a) Electric plane tested by NASA
(b) Solar-powered two-seater aircraft designed by Japan
(c) Space observatory launched by China
(d) Reusable rocket designed by ISRO
Ans: (a)
World Malaria Report 2024
Why in News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) highlighted India’s remarkable progress in its World Malaria Report 2024. India significantly reduced malaria cases and related deaths between 2017 and 2023, marking a major milestone.
- India aims to achieve malaria-free status by 2030, with zero indigenous cases by 2027.
Malaria
- Malaria is a life-threatening vector-borne disease caused by the Plasmodium parasites, transmitted through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- There are 5 Plasmodium parasite species that cause malaria in humans and 2 of these species – P. falciparum and P. vivax – pose the greatest threat.
- Malaria is predominantly found in the tropical and subtropical areas of Africa, South America as well as Asia.
- The mosquito becomes infected after biting an infected person. The malaria parasites then enter the bloodstream of the next person the mosquito bites. The parasites travel to the liver, mature, and then infect red blood cells.
- Symptoms of malaria include fever and flu-like illness, including shaking chills, headache, muscle aches, and tiredness. Notably, malaria is both preventable and curable.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Global Findings:
- Disease Burden:
- An estimated 263 million malaria cases occurred globally in 2023, an increase of 11 million cases from 2022.
- Malaria mortality stood at 597,000 deaths globally, showing a decline compared to 622,000 deaths in 2020.
- Geographic Distribution:
- The WHO African Region carried 94% of global malaria cases and 95% of malaria deaths in 2023.
- Five countries—Nigeria (26%), Democratic Republic of Congo (13%), Uganda (5%), Ethiopia (4%), and Mozambique (4%)—accounted for nearly 52% of global malaria cases.
- Since 2015, nine countries, including Egypt in 2024, have been certified malaria-free.
- Intervention Uptake:
- The rollout of two malaria vaccines, RTS,S and R21, has significantly increased vaccine coverage in endemic areas.
- Disease Burden:
- India Specific Findings:
- Historical Transformation: At independence, India faced 7.5 crore malaria cases annually with 800,000 deaths, posing a critical public health challenge.
- Persistent efforts have cut cases by over 97%, reducing them to 2 million annually, while deaths have plummeted to just 83 by 2023.
- Latest Achievements (2017-2024): From 2015 to 2023, Malaria cases fell from 11,69,261 to 2,27,564, and deaths dropped from 384 to 83, representing an 80% reduction.
- The Annual Blood Examination Rate increased from 9.58 (2015) to 11.62 (2023), ensuring early detection and intervention.
- In 2024, India exited WHO's High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group, marking a key milestone.
- HBHI is a country-led approach on global malaria response.
- Reduction in Disease Burden:
- States in high-burden decreased from 10 to 2 (Mizoram & Tripura).
- Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Meghalaya transitioned to medium-burden.
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Madhya Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli moved to low-burden.
- Ladakh, Lakshadweep, and Puducherry achieved Zero status, eligible for subnational malaria elimination verification.
- Historical Transformation: At independence, India faced 7.5 crore malaria cases annually with 800,000 deaths, posing a critical public health challenge.
What are the Government Initiatives to Curb Malaria?
- National Framework for Malaria Elimination 2016-2030
- National Vector-Borne Disease Control Programme: Addresses various vector-borne diseases, including malaria, through prevention and control measures.
- National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP): Launched in 1953, to address the severe impact of malaria.
- It focuses on three core activities: insecticidal residual spraying (IRS) with DDT, case monitoring and surveillance, and patient treatment.
- High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) Initiative: Initiated in four states (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh) in 2019.
- It focuses on malaria reduction through insecticidal net distribution.
- Malaria Elimination Research Alliance-India (MERA-India): Established by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), collaborates with partners on malaria control research.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria. Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine? (2010)
(a) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
(b) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
(c) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
(d) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
Ans: (b)
Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI)
The combined Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) recorded a 4.3% growth in November 2024 compared to November 2023.
- The ICI measures the combined and individual performance of production of eight core industries viz. Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement and Electricity.
- The eight core industries comprise 40.27% of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
|
Industry |
Weight (%) |
Growth (November 2024) |
|
Refinery Products |
28.04% |
2.90% |
|
Electricity |
19.85% |
3.80% |
|
Steel |
17.92% |
4.80% |
|
Coal |
10.33% |
7.50% |
|
Crude Oil |
8.98% |
-2.10% |
|
Natural Gas |
6.88% |
-1.90% |
|
Cement |
5.37% |
13.00% |
|
Fertilizers |
2.63% |
2.00% |
- About IIP: It is an index that measures short-term changes in the volume of production across key economic sectors like mining, electricity, and manufacturing in India.
- It is published monthly by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO). Data is released six weeks after the reference month.
- Reflects production changes compared to a base year (2011-2012).
Read More: Core Sector Industries
Memorials for Leaders
Recently, the cremation of former Prime Minister (PM) Manmohan Singh was held at open-to-public Nigambodh Ghat, a departure from previous practices of cremating at designated sites followed by the establishment of memorials.
- Rules and Conventions: Although there are no specific rules mandating memorials for former PMs, they were generally cremated at designated sites, and most have memorials in Delhi or elsewhere.
- Origins and Legacy of Memorials: Raj Ghat (Mahatma Gandhi) set the precedent for leader memorials, signifying peace and national unity.
- Leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru (Shanti Van), Lal Bahadur Shastri (Vijay Ghat), Indira Gandhi (Shakti Sthal) and Atal Bihari Vajpayee (Smriti Sthal) followed the tradition of memorials symbolizing their legacies.
- Political Ideologies: Memorials often reflect political ideologies, for instance, P.V. Narasimha Rao's Gyan Bhumi was established by the current NDA government after being previously denied by Congress, while VP Singh remains the only former PM without a memorial.
- Maintenance of Memorials: Memorials are primarily maintained by State Governments, local municipalities, and occasionally the Central Government through the Ministry of Urban Development.
- Memorials Across India & Symbolism: Rajendra Prasad (Bihar), B R Ambedkar (Mumbai), Morarji Desai (Ahmedabad) and Gulzarilal Nanda- Interim PM (Ahmedabad).
- Memorial names reflect leader identities, e.g., Shastri’s Vijay Ghat (victory), Indira’s Shakti Sthal (strength), and Charan Singh’s Kisan Ghat (farmer leadership).
Read More: Dr. Manmohan Singh, PM Dedicates Salt Satyagraha Memorial to Nation
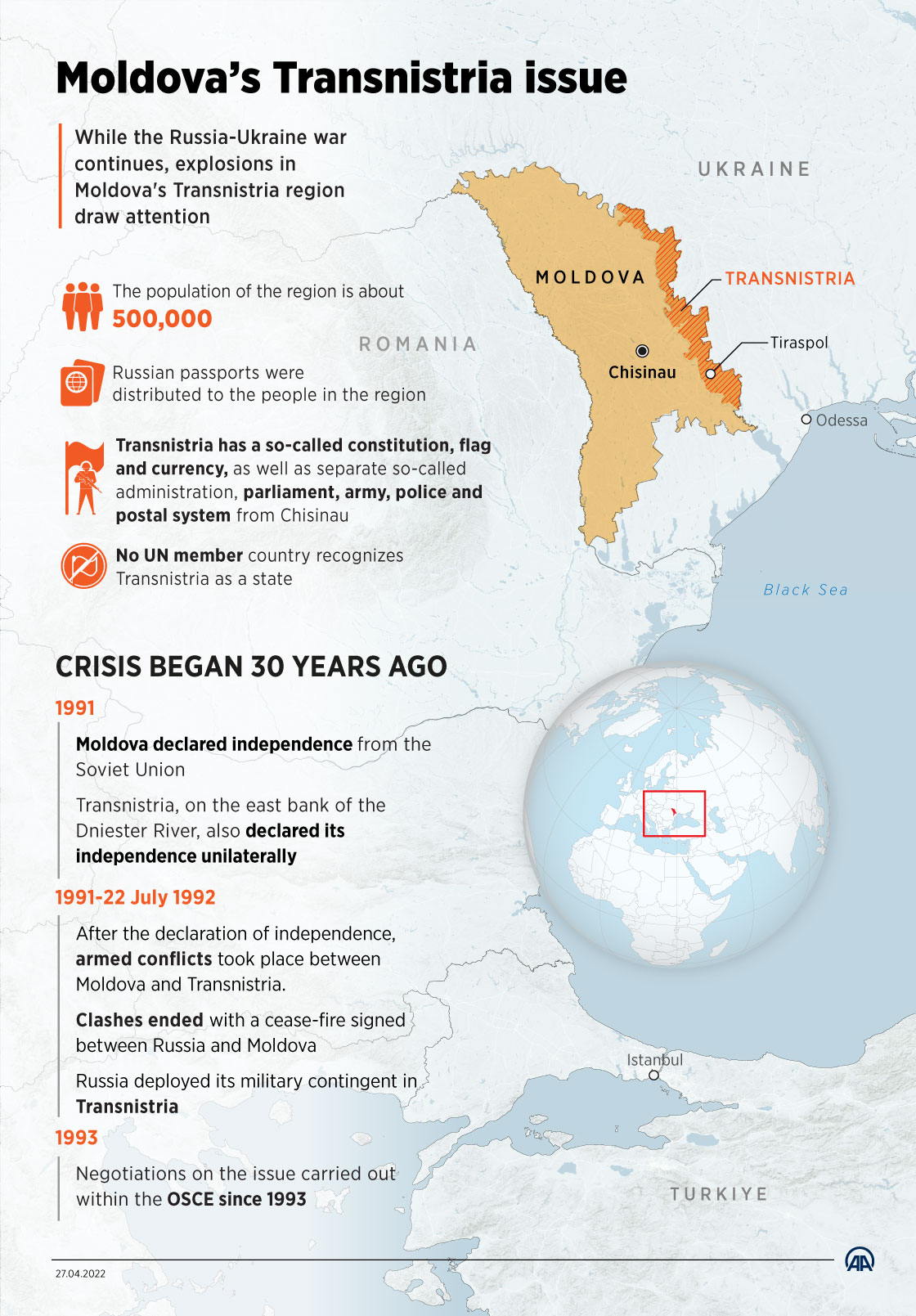
Moldova and Transnistria
Recently, Ukraine has stopped the transit of Russian gas through its territory, ending a major supply route to Europe after a prewar transit deal expired in December 2024.
- It led to an energy crisis in Moldova and Transnistria which heavily relies on Russian gas for power supply and heating amid winter.
- Moldova:
- Moldova is a small eastern european landlocked country bordered by Ukraine to the east and Romania to the west.
- Recently, Moldova has inaugurated its embassy in New Delhi.
- India and Moldova established diplomatic relations in 1992 following Moldova's independence after the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991.
- Transnistria:
- It is a Russian-backed breakaway region in Moldova described as a “remnant of the Soviet Union” that split from the rest of Moldova after the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991.
- When Moldovan troops attempted to take over the territory in 1990-1992, Transnistria was able to resist them because of Russian soldiers based in Transnistria. Since then, it has remained free of Moldovan control.
- However, most countries continue to see Transnistria as part of Moldova. It is not recognized as independent even by Russia.
- Most Transnistrians have dual citizenship of Russia and Transnistria or triple citizenship of Moldova, Transnistria, and Russia.
Read More: Russia-Ukraine Conflict, Opening of Moldova's Embassy in India , Transnistria in the Russia-Ukraine War
Birth of the Commercial Internet
On 1st January 1983, the transition from Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) to Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) marked the birth of the modern Internet, revolutionizing communication globally.
- ARPANET, the first public packet-switched computer network, was initiated during the Cold War by the US Department of Defence to ensure communication survival during potential nuclear attacks.
- However, the protocol governing ARPANET, known as the Network Control Protocol (NCP), became outdated by the late 1970s, unable to support the increasing complexity and diversity of interconnected networks.
- TCP/IP, developed by Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn, American Internet pioneers, standardized communication across diverse networks, enabling scalable and efficient data transmission.
- 1st January 1983, designated as the "flag day," required all ARPANET systems to adopt TCP/IP, leading to the birth of the Internet.
- TCP/IP enabled a "network of networks," breaking geographical, organizational, and technological barriers, allowing for global connectivity.
- This transition laid the foundation for future advancements, including the World Wide Web, social media, and e-commerce.
Read more: All Things Internet