International Relations
India’s Act East Policy
- 15 Feb 2024
- 10 min read
For Prelims: India’s Act East Policy, Inland Water Transport, Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), Look East Policy.
For Mains: India’s Act East Policy, India and its neighborhood- relations.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways has flagged off the first batch of trial Cargo Vessels from Maia Inland Custom Port in West Bengal to Sultanganj Port in Bangladesh, marking a significant step under India’s Act East Policy, with a focus on enhancing Inland Water Transport.
- It has been organised by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), marking a new beginning for improved connectivity and cooperation between India and Bangladesh.
What is the Significance of this Trial Shipment?
- Operationalization of Maia Terminal is expected to be a game-changer as it would shift 2.6 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) of Bangladesh-bound export cargo from road to waterways.
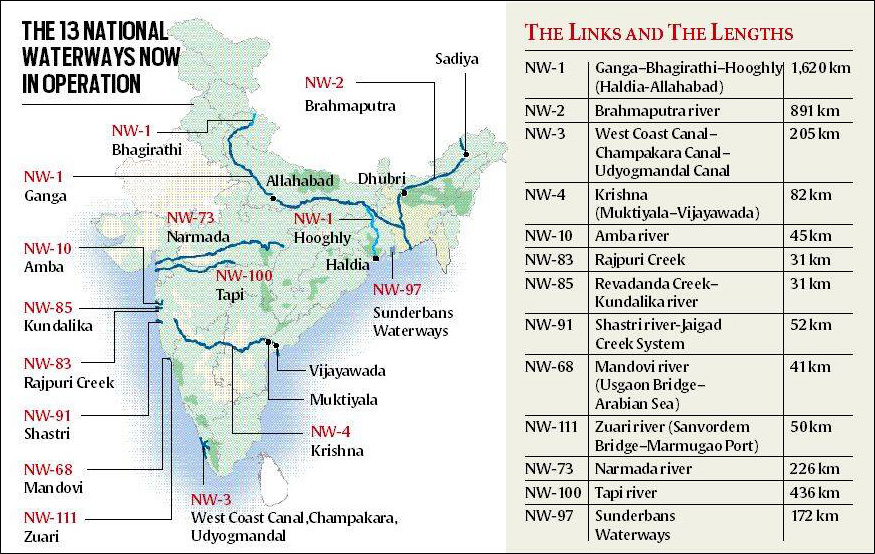
- The Maia-Aricha route (Protocol Route 5 & 6) will reduce the distance from NW1 (National Waterways 1) to Bangladesh and the North Eastern Region by 930 kilometres.
What is Inland Water Transport (IWT)?
- About:
- IWT refers to the transportation of goods and passengers via navigable rivers, canals, lakes, and other inland waterways.
- This mode of transport utilises watercraft such as boats, barges, and ships to move cargo and people within a country's interior regions, connecting various ports and terminals along the water routes.
- Significance:
- IWT is a highly cost-effective mode of transportation, particularly for bulk cargo like coal, iron ore, cement, food grains, and fertiliser.
- Despite its advantages, its current share in India's modal mix is only 2%. The government aims to increase this share to 5% by 2030 under the Maritime India Vision (MIV)-2030.
- To achieve this goal, the IWAI has identified 25 new National Waterways (NWs) through feasibility studies to make them navigable for transportation.
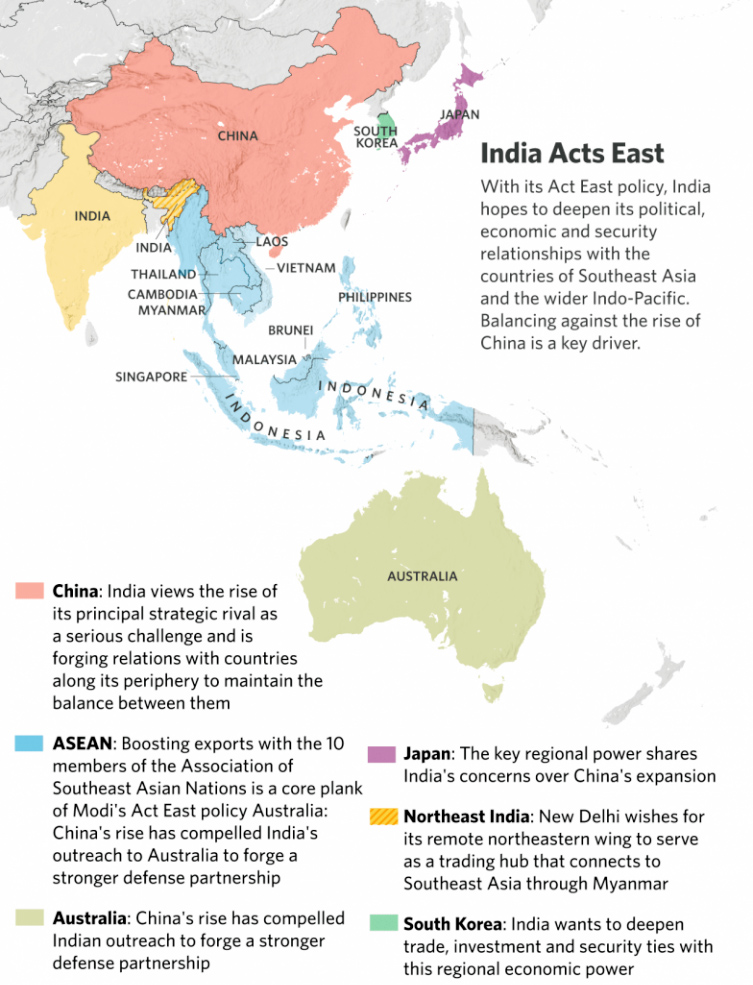
What is Act East Policy?
- About:
- The ‘Act East Policy’ announced in November, 2014 is the upgrade of the “Look East Policy”.
- It is a diplomatic initiative to promote economic, strategic and cultural relations with the vast Asia-Pacific region at different levels.
- It involves intensive and continuous engagement with Southeast Asian countries in the field of connectivity, trade, culture, defence and people-to-people-contact at bilateral, regional and multilateral levels.
- Aim:
- To promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and developing a strategic relationship with countries in Indo-pacific region with a proactive and pragmatic approach and thereby improving the economic development of the North Eastern Region (NER) which is a gateway to the South East Asia Region.
What is the Look East Policy?
- In order to recover from the loss of the strategic partner -USSR (end of the Cold war 1991), India sought to build up a relationship with the USA and allies of the USA in Southeast Asia.
- In this pursuit, former Prime minister of India P V Narasimha Rao launched Look East policy in 1992, to give a strategic push to India’s engagement with the South-East Asia region, to bolster its standing as a regional power and a counterweight to the strategic influence of the People’s Republic of China.
What is the Difference Between Look East Policy and Act East Policy?
- Look East:
- Look East policy focused on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries+Economic Integration.
- India became a dialogue partner of ASEAN in 1996 and summit level partner in 2002.
- In 2012 the relationship got up-graded into a Strategic Partnership.
- The time when India launched the Look East Policy in 1992, India's trade with ASEAN was USD 2 billion. After signing the Free Trade Agreement in 2010 with ASEAN, the trade has grown to USD 72 billion (2017-18).
- India is also an active participant in several regional forums like the East Asia Summit (EAS), ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) etc.
- Act East:
- Act East Policy focused on ASEAN countries + Economic Integration + East Asian countries + Security cooperation.
- Prime minister of India highlighted 4C's of Act East Policy.
- Culture
- Commerce
- Connectivity
- Capacity building
- Prime minister of India highlighted 4C's of Act East Policy.
- Security is an important dimension of India's Act East Policy.
- In the context of growing Chinese assertiveness in the South China Sea and the Indian Ocean, securing freedom of navigation and India's own role in the Indian Ocean is a key feature of Act East Policy.
- In pursuance of this, India has been engaged under the narrative of Indo-pacific and informal grouping called Quad.
- Act East Policy focused on ASEAN countries + Economic Integration + East Asian countries + Security cooperation.
- Look East policy focused on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries+Economic Integration.
What are the Initiatives to Enhance Connectivity under Act East Policy?
- Agartala-Akhaura Rail Link between India and Bangladesh.
- Intermodal transport linkages and inland waterways through Bangladesh.
- Kaladan Multimodal Transit Transport Project and the Trilateral Highway Project connecting the North East with Myanmar and Thailand.
- Under India-Japan Act East Forum, projects such as Road and Bridges and modernization of Hydro-electric power projects have been undertaken.
- India-Japan Act East Forum was established in 2017 which aims to provide a platform for India-Japan collaboration under the rubric of India’s "Act East Policy” and Japan’s "Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy”.
- The Forum will identify specific projects for economic modernization of India’s North-East region including those pertaining to connectivity, developmental infrastructure, industrial linkages as well as people-to-people contacts through tourism, culture and sports-related activities.
- Other Initiatives:
- Assistance extended in the form of medicines/medical supplies to ASEAN countries during the pandemic.
- Scholarships with offers of 1000 PhD fellowships have been offered at IITs for ASEAN countries participants.
- India is also implementing Quick Impact Projects in Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar and Vietnam to provide development assistance to grass-root level communities in the fields of education, water resources, health etc.
- Quick Impact Projects (QIPs) are small-scale, low cost projects that are planned and implemented within a short timeframe.
- To enhance the modal share of coastal shipping and inland water transport, 46 initiatives have been identified in Amrit Kaal Vision 2047.
- Key initiatives include the creation of port-based agglomeration centres, coastal berths near production/demand centers, and projects to improve road, rail, and inland waterway connectivity.
- The plan also aims to operationalize 50 waterways by 2047 and introduce low-draft vessel designs with possible tug-barge combinations to enhance efficiency and accessibility.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the five countries (Australia, China, Japan, South Korea and New Zealand) with which ASEAN has existing FTAs.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q.2 In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants? (2015)
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 5
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Analyze internalsecurity threats and transborder crimes along Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan borders including Line of Control (LoC). Also discuss the role played by various security forces in this regard. (2020)
Q. How far are India’s internal security challenges linked with border management particularly in view of the long porous borders with most countries of South Asia and Myanmar? (2013)