West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Bengali Omission From Sahitya Akademi Award
Why in News?
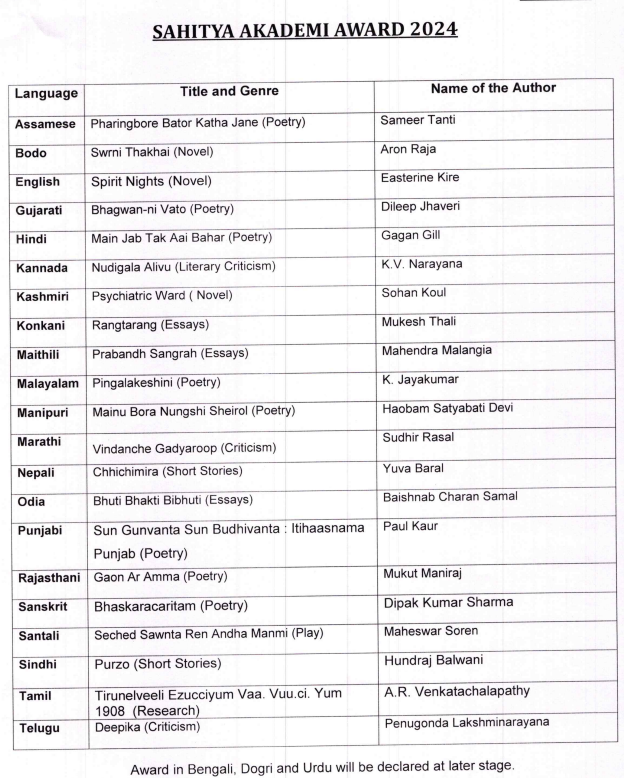
The exclusion of Bengali literature from the Sahitya Akademi Award 2024 has sparked controversy in West Bengal’s literary circles.
Key Points
- Omission of Bengali Literature:
- Bengali literature, despite being granted classical language status by the Government of India in 2024, was excluded from the awards.
- This is the first time in 52 years that Bengali writers and works were left out of the prestigious award.
- The Sahitya Akademi’s Executive Board attributed the omission to "technical issues."
- The West Bengal Democratic Writers Artists Association wrote to Sahitya Akademi Secretary, seeking an explanation for the exclusion.
- RTI Application for Transparency:
- Journalist and former Sahitya Akademi council member filed a Right to Information (RTI) application seeking clarity on the omission.
- The RTI request asks for details about Bengali nominees, jury members, and documents related to the decision.
- Past Instances of Omission:
- Bengali literature was previously omitted from the Sahitya Akademi Awards in 1960, 1968, and 1973.
Sahitya Akademi Awards
- About:
- The Sahitya Akademi Awards honor exceptional literary contributions in categories like novels, poetry, essays, and plays.
- It is the 2nd-highest literary honor in India, after the Jnanpith Award.
- It was established in 1954 as an autonomous body under the Ministry of Culture.
- Eligibility:
- Award categories include works in 22 languages of the Eighth Schedule, along with English and Rajasthani (total: 24 languages), and translations of Indian literary works.
- The author must be an Indian citizen.
- Recipients:


Haryana Switch to Hindi
International Workshop on Land Governance
Why in News?
The Ministry of Panchayati Raj, in collaboration with the Haryana Institute of Public Administration (HIPA), is hosting an “International Workshop on Land Governance” from 24 to 29 March 2025, at the HIPA Complex in Gurugram, Haryana.
- It is organised with the help of the Ministry of External Affairs under its Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program.
Key Points
- Global Participation and Focus Areas:
- The workshop will bring together delegates from 22 countries across Africa, Latin America, and South-East Asia.
- Participants will explore innovative solutions to address land governance challenges worldwide.
- India’s pioneering SVAMITVA Scheme, which uses drone technology to map rural inhabited areas and provide legal property ownership documents, will be showcased.
- Technical and Field Sessions:
- Sessions will cover drone-based land survey techniques, high-resolution mapping, and geospatial technologies for improved land administration.
- Participants will engage in hands-on demonstrations of drone survey methods, data processing, ground verification, and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) integration.
- The Survey of India will conduct live drone survey demonstrations in a village to offer practical exposure.
- Field visits and exhibitions will further provide real-world insights into modern land governance technologies.
- Ten drone vendors will set up stalls displaying innovations in drone-based land mapping and survey techniques.
- Sessions will cover drone-based land survey techniques, high-resolution mapping, and geospatial technologies for improved land administration.
- Participation of Industry Leaders:
- Knowledge partners include Survey of India, State Land Revenue Departments, National Informatics Centre, Geo-Spatial World, Hexagon, Trimble, Aereo, Marvell Geospatial, Idea Forge Tech, and AWS.
- Classroom demonstrations will cover:
- Drone use cases in land governance.
- Ortho-rectified imaging and feature-extracted mapping.
- Ground verification technologies for high-resolution mapping and property card finalization.
- Addressing the Global Land Governance Challenge:
- The 2017 World Bank report states that only 30% of the global population holds legally registered land titles.
- India’s SVAMITVA Scheme provides a model for global land governance, offering 5cm accuracy mapping at a 1:500 resolution.
- The workshop aims to help participating nations achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) related to land rights by learning from India's model.
SVAMITVA Scheme
- About:
- SVAMITVA stands for Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas.
- It is a center sector scheme which was launched nationally on the occasion of National Panchayati Raj Day on 24th April 2021.
- Aim:
- To provide an integrated property validation solution for rural India.
- Features:
- The demarcation of rural inhabited areas would be done using Drone survey and CORS (Continuously Operating Reference Stations) Networks which provides mapping accuracy of 5 cm.
- This would provide the ‘record of rights’ to village household owners possessing houses in inhabited rural areas in villages.
- It will cover around 6.62 Lakh villages of the entire country during 2021-2025.
Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) Program
- The ITEC program, initiated in 1964, spans 160 partner countries, providing short-term training across diverse disciplines.
- Courses cover areas such as Engineering, Climate Change, Health, and Women Empowerment, contributing to holistic skill enhancement globally.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in News?
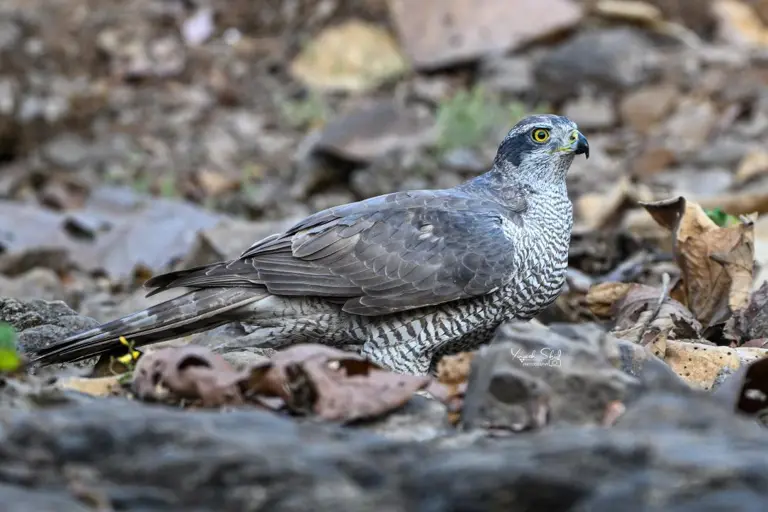
A forest guard spotted a Eurasian goshawk, a medium-large raptor, during routine patrolling at Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary, highlighting the region's ecological richness.
Key Points
- Eurasian Goshawk in Maharashtra:
- About:
- The Eurasian goshawk has been recorded in Maharashtra at least three times before.
- This bird of prey is widely distributed across Europe, Asia, and parts of North America.
- Its Scientific Name is Accipiter gentilis.
- Features:
- It has relatively short, broad wings and a long tail.
- It is blue-grey above or brownish-grey with dark barring or streaking over a grey or white base color below, but Asian subspecies in particular range from nearly white overall to nearly black above.
- Females are significantly larger than males.
- About:
- Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary’s Avian Richness:
- The sanctuary is renowned for its diverse bird species and serves as an important habitat for avifauna.
- Among its most significant discoveries is the critically endangered Forest Owlet in 2014.
- Conservation Significance:
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List classifies the Forest Owlet as critically endangered, indicating a high risk of extinction.
- Earlier, researchers believed this species was endemic only to the Satpura mountain ranges in central India.
Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location and Geography:
- It is situated in Thane District, Maharashtra, about 90 km northeast of Mumbai, in the foothills of the Western Ghats.
- The Tansa and Vaitarna rivers flow through the sanctuary, with the Tansa River dividing it into two parts.
- Water Resources and Catchment Area:
- The sanctuary forms the catchment area of Tansa Lake, along with the surrounding Khardi, Vaitarna, Wada, and Shahapur forests.
- Tansa, Vaitarna, and Bhatsa reservoirs serve as major water sources for Mumbai and Thane.
- Vegetation and Flora:
- Features Southern Tropical Moist Deciduous Forest, with patches of Evergreen forest.
- Key tree species include Kalamb, Bibla, Khair, Hed, Teak, and Bamboo.
- Fauna and Avian Diversity:
- Home to 54 species of animals and 200 species of birds.
- Major wild animals include Panther, Barking Deer, Mouse Deer, Hyena, and Wild Boar.
- Hosts two Critically Endangered Gyps vulture species and the Vulnerable Pallas’s Fish-Eagle (Haliaeetus leucoryphus).


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Special Category Status for Bihar
Why in News?
The Bihar chief minister reiterated the long-standing demand for granting Special Category Status (SCS) to the state before the 16th Finance Commission , which would increase the state's tax revenue from the Centre.
Key Points
- Special Category Status:
- Historical and structural challenges: Bihar faces significant economic challenges , including lack of industrial development and limited investment opportunities
- As a result of the division of the state, most of the industries shifted to Jharkhand , which increased the problems of employment and economic development in Bihar.
- Natural Calamities: The state is facing natural calamities like floods in the northern region and severe drought in the southern part .
- The recurrence of these disasters disrupts agricultural activities , especially in the case of irrigation facilities, and leads to inadequate water supply, affecting livelihoods and economic stability .
- Lack of Infrastructure: Bihar's inadequate infrastructure hinders the overall development of the state , with challenges such as poor road network, limited healthcare access, and lack of educational facilities .
- In 2013, the Raghuram Rajan Committee constituted by the Centre placed Bihar in the "least developed category".
- Poverty and Social Development: Bihar has a high poverty rate and a large number of families live below the poverty line.
- According to a survey by NITI Aayog, Bihar tops the list of poor states, with multidimensional poverty at 26.59% in 2022-23 , which is higher than the national average of 11.28%.
- Bihar's per capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for the year 2022-23 is only Rs 60,000 compared to the national average of Rs 1,69,496.
- Historical and structural challenges: Bihar faces significant economic challenges , including lack of industrial development and limited investment opportunities
Special Category Rating
- Introduction:
- Special Category Status (SCS) is a classification granted by the Centre to aid the development of geographically and socio-economically backward states.
- The Constitution does not provide for SCS and this classification was done later in 1969 based on the recommendations of the Fifth Finance Commission .
- This status was first given to Jammu and Kashmir, Assam and Nagaland in 1969. Telangana is the latest state in India to receive this status.
- SCS is different from special status, which provides enhanced legislative and political rights, while SCS deals only with economic and financial aspects.
- For example, before the abrogation of Article 370, Jammu and Kashmir had special status.
- Criteria for getting the rating ( based on Gadgil recommendations ):
- Mountainous terrain
- Low population density and/or large proportion of tribal population
- Strategic location on borders with neighbouring countries
- Backwardness in economic and infrastructure
- The unviable nature of state finances
- Benefit:
- 90% of the funds required in a centrally sponsored scheme is paid to the special category states, compared to 60% or 75% in the case of other states , while the remaining funds are provided by the state governments.
- Unspent funds in a financial year do not lapse and are carried forward.
- These states are given significant concessions in excise and customs duties, income tax and corporate tax.
- 30% of the Centre's gross budget is provided to special category states.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Zaid Crops Under Kisan Credit Card (KCC)
Why in News?
On 19th March,2025, the Uttar Pradesh government decided to include 9 zaid crops under Kisan Credit Card (KCC) and Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) .
Key Points
- About Zaid Crops:
- Zaid crops are those crops which are grown in the period between Rabi and Kharif seasons. These crops have greater ability to tolerate intense heat and dry winds
- Major zaid crops include crops like cucumber, pumpkin, bitter gourd, watermelon, cucumber, sugarcane and peanut .
- In North India, zaid crop is usually sown in March-April .
- Farmers will now be able to avail the benefits of KCC and crop insurance scheme for crops like groundnut, maize, green gram, urad, papaya, litchi, watermelon, melon and amla .
- This will provide them easy loans for agricultural work and compensation for crop loss due to natural calamities .
- Under KCC , loans are provided to farmers at low interest rates as per their needs . If farmers repay the loan on time, then an interest discount of up to 3% is also given.
- Under PMFBY , if a farmer's crop is destroyed due to famine, excessive rain or other natural disasters , he is given compensation in the form of insurance money by the government. This helps farmers avoid financial crises .
Kisan Credit Card
- About:
- Kisan Credit Card Scheme was started in 1998. To provide adequate and timely credit facility to meet the credit requirements of farmers (agricultural expenses), as well as to meet the expenses related to ancillary activities apart from contingency expenses. This loan facility is provided on a need basis through a simple procedure.
- In 2004 , this scheme was extended to meet the investment credit requirement of farmers for allied and non-agricultural activities.
- In Budget 2018-19, the Government announced expansion of the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) facility to help fisheries and livestock farmers meet their working capital needs .
- Implementing Agencies:
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- About:
- PMFBY was launched in the year 2016 and is being administered by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It replaced the National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS) and the Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (MNAIS) .
- Eligibility:
- All farmers including tenant farmers/holding farmers growing notified crops in the notified areas are eligible for coverage.
- Objective:
- To provide a comprehensive insurance cover in case of crop failure due to natural calamities, pests and diseases or any other reason so as to help stabilize the income of the farmers.
- To stabilise the income of farmers to ensure continuity in farming .
- To encourage farmers to adopt new and modern agricultural methods.
- To ensure flow of credit to the agricultural sector.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Solar Cities in UP
Why in News?
In the National Conference held under the National Clean Air Programme in Gorakhpur the Uttar Pradesh government decided to develop all the 17 municipal corporations of the state as solar cities.
Key Points
- About the issue:
- Under this initiative, the use of renewable energy will be promoted, thereby ensuring energy self-sufficiency and environmental protection.
- The government will implement schemes such as setting up of solar power plants , solar street lights and solar water-heating systems .
- This scheme will reduce energy costs and promote green energy.
- This initiative will help in achieving the 'net-zero' target set by Prime Minister Modi by the year 2070 .
- The following districts in Uttar Pradesh have Municipal Corporations:
- Kanpur, Lucknow, Ghaziabad, Agra, Varanasi, Prayagraj, Meerut, Bareilly, Aligarh, Moradabad, Saharanpur, Gorakhpur, Firozabad, Mathura, Ayodhya, Jhansi, Shahjahanpur.
- Solar City
- It is a city that meets its energy needs mainly from solar energy . In this , electricity generation, transportation, water supply and other basic services depend on solar energy.
- The main objective of this concept is to make maximum use of renewable energy sources and reduce carbon emissions.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
- About:
- The NCAP aims to systematically address air pollution by involving all stakeholders and ensuring necessary action.
- Under NCAP, 131 cities have been identified for implementation of city specific action plans.
- Objective:
- This is the first attempt in the country to develop a national framework for air quality management with the goal of time-bound reduction .
- It aims to reduce the concentration of coarse (PM10) and fine particles (PM2.5) by at least 20% over the next five years (base year for comparison – 2017).
- Monitoring:
- “PRANA” portal has also been launched by MoEFCC :
- To monitor the implementation of NCAP.
- Monitoring action plans and implementation status of cities.
- Sharing best practices adopted by cities for others to emulate.
- “PRANA” portal has also been launched by MoEFCC :


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Give Up Abhiyan
Why in News?
Under the 'Give Up Abhiyan' in Rajasthan, more than 13 lakh eligible beneficiaries voluntarily removed their names from the food security scheme, thereby reducing the financial burden on the government by Rs 246 crore .
Key Points
- About GiveUp Campaign:
- It was launched by the Rajasthan government in November 2024 , with the aim of motivating capable and ineligible people to voluntarily give up the benefits of the food security scheme.
- This campaign targets people who have risen above the poverty line and are no longer eligible for this scheme.
- So far, under this campaign, 13 lakh 58 thousand 498 people have voluntarily given up the benefits of the food security scheme.
- National Food Security Act, 2013 (NFSA):
- This marks a paradigm shift in the approach towards food security from a welfare-based approach to a rights-based approach.
- The NFSA covers 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population through the following means:
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana : It covers the poorest population who are entitled to receive 35 kg of food grains per family per month.
- Priority Households (PHH): Families included under the PHH category are entitled to receive 5 kg of foodgrains per person per month.
- In case of issuing ration cards, it has been made mandatory for the eldest woman of the family aged 18 years or above to be the head of the household.
- In addition, the Act makes special provision for children in the age group of 6 months to 14 years, where they are provided with nutritious food free of cost through a wide network of Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) centres (also known as Anganwadi centres).
Antyodaya Anna Yojana
- 'Antyodaya Anna Yojana' was started in December 2000 .
- The objective of this scheme was to meet the food shortage of the population living below the 'poverty line'.
- Initially, under this scheme, there was a provision to provide 25 kg of foodgrains per month to the beneficiary family, which was increased to 35 kg in April 2002 .












%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)





















 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan