Indian Economy
Infrastructure Development in India
- 04 Feb 2025
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Infrastructure, Power, Coal, Petroleum, Cement, Railways, Ports, Civil Aviation, Roads, Telecommunications, National Highways (NH), Bio-toilets, Aviation Market, Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) – UDAN, Smart Cities Mission (SCM), Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0, Metro Network, Jal Jeevan Mission, National Monetisation Plan, Urban Challenge Fund, Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs), Infrastructure Project Development Fund (IIPDF), SWAMIH Fund, PM SVANidhi.
For Mains: Infrastructure push in the Union Budget 2025-26. Status of infrastructure in India.
Why in News?
India has made remarkable progress in infrastructure development over the past decade that is the backbone of economic development.
- The total infrastructure investment (capital expenditure) in India has increased to Rs 11.2 lakh crore in 2025-26 from Rs 10 lakh crore in 2023-24.
What Infrastructure Initiatives were Announced in Budget 2025-26?
- Infrastructure Financing: Rs 10 lakh crore worth of assets would be monetised in the next 5 years (2025-30) under the National Monetisation Plan.
- Urban Challenge Fund of Rs 1 lakh crore will be set up to implement the proposals for 'cities as growth hubs', 'creative redevelopment of cities' and 'water and sanitation'.
- Government to provide certainty in taxation of Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) in infrastructure.
- States to propose projects funded by India Infrastructure Project Development Fund (IIPDF) loans.
- Railways: India aims to become the 2nd-largest cargo-carrying railway in the world after China and producing indigenous high-speed ‘bullet’ trains.
- Indian Railways will complete 100% electrification of its network in FY 2025-26.
- Shipbuilding: A Rs 25,000 crore fund will be established to support the maritime industry, promoting competition and long-term financing.
- Large ships will be given infrastructure status reducing financial costs by up to 10 percentage points.
- infrastructure status enables better financing, tax benefits, government support, and fewer regulatory hurdles.
- Credit notes will be introduced for shipbreaking in Indian yards to promote a circular economy.
- Credit notes are commonly used when a buyer returns goods. It can help shipbreaking companies to return or recycle materials, such as steel, copper, and aluminum obtained from dismantled ships.
- Large ships will be given infrastructure status reducing financial costs by up to 10 percentage points.
- Aviation Sector: UDAN scheme has been extended for another 10 years and a revamped UDAN scheme will connect 120 new destinations, serving 40 million more passengers.
- New greenfield airports in Bihar will complement Patna and Bihta (in Patna) airport expansions in Bihar.
- Housing: SWAMIH Fund 2 of Rs 15,000 crore will be set up to speed up completion of 1 lakh incomplete housing units with contributions from the government, banks, and private investors.
- Local Economy: PM SVANidhi will be revamped to provide enhanced loans from banks and UPI-linked credit cards with a Rs 30,000 limit.
What is the Status of Infrastructure Development in India?
- Highways and Roads: India has the 2nd-largest road network globally (after the United States), with National Highways (NH) standing at 1,46,145 km in 2024.
- The length of operational high-speed corridors has increased to 2,138 km (2024), NH construction pace has risen 2.8 times (12.1 km/day in 2014-15 to 33.8 km/day in 2023-24), and capital expenditure increased 5.7 times (2013-24).
- Railways: As of December 2023, 93.83% of the broad-gauge tracks (called large line and distance between the two tracks is 5 feet 6 inches) were electrified, up from 21,801 km in 2014.
- The provision of Bio-toilets in coaches stands at 80,478 coaches in the year 2014-2023.
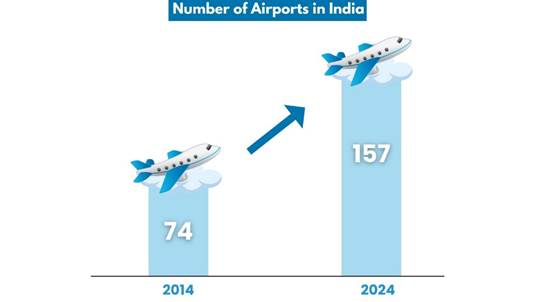
- Civil Aviation: India is the 3rd-largest domestic aviation market globally with operational airports increased from 74 (2014) to 157 (2024).
- Under the Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) – UDAN, 147 lakh passengers benefited as of December, 2024.
- Shipping and Ports: India has 12 major ports and 217 minor/intermediate ports.
- Cargo handling capacity rose from 800.5 MT (2014) to 1,630 MT (2024) (+87%), boosting India’s shipping rank to 22nd in International Shipment category as against 44th rank in 2014.
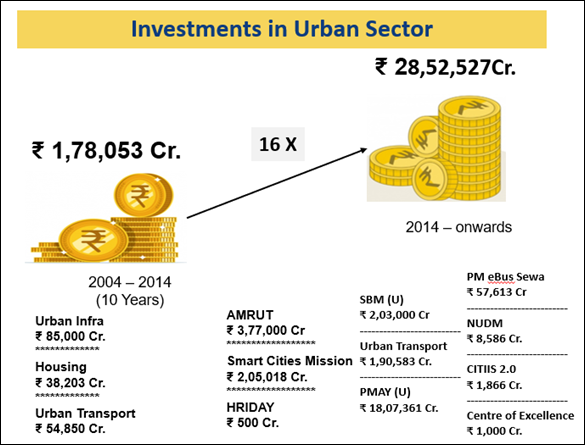
- Urban Affairs and Housing: Under the Smart Cities Mission (SCM), around 91% projects have been completed.
- Under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0, urban waste collection has increased by 97% (2014-15 to 2024-25), while waste processing has risen from 18% to 78% in the same period.
- During 2015-2024, 118.64 lakh houses were approved under PMAY-U.
- Metro Rail: India's metro network expanded from 248 km (2014) to 993 km (2024), with commissioning rising from 0.68 km to 6 km/month and metro cities increasing from 5 to 23.
- Tap Water Connections: Jal Jeevan Mission increased rural tap water coverage from 3.23 crore (17%) to 15.44 crore (79.74%) households by February, 2025.
What is Infrastructure?
- About: Infrastructure (capex) refers to the basic systems essential for the functioning of a business, region, or nation.
- Sectors like power, coal, petroleum, cement, railways, ports, civil aviation, roads, Cybersecurity and telecommunications are part of infrastructure.
- Features:
- Long-Term Investments: Involves large-scale, long-lived structures like power grids and transport systems.
- Public Utilities and Works: Includes utilities (e.g., power, water) and public works (e.g., roads, railways).
- Natural Monopoly: High initial costs make competitive supply inefficient (e.g., power grids).
- Non-Tradable Services: Services like water and electricity can't be sold across borders.
- Public and Private Good: Benefits society but often requires usage charges.
- High-Sunk Costs: Once invested, resources in infrastructure projects cannot be recovered, regardless of success or failure.
- Infrastructure as a Public Service:
- Non-Rival Nature: One person's consumption does not reduce availability for others.
- Price Exclusion: They are provided on a paid basis, unlike pure public goods.
- Social Infrastructure: Infrastructure also includes social sector facilities like hospitals and schools, though lacking monopoly characteristics.
What are Government Initiatives for Infrastructure Development?
- PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP): NMP has onboarded 44 Central Ministries and 36 States/UTs.
- National Logistics Policy: India’s World Bank Logistics Performance Index (LPI) ranking improved by 6 places from 44 in 2018 to 38 out of 139 countries in 2023.
- Bharatmala Pariyojana: A total of 18,926 km of roads have been completed under the project by November 2024.
- Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana: In 2024-25, 7,71,950 km of roads were completed.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) - UDAN: 619 RCS routes have so far commenced operations connecting 88 airports including 13 heliports & 2 water aerodromes.
Conclusion
India's infrastructure development has seen significant growth with advancements in roads, railways, civil aviation, and urban affairs. The government's initiatives, including financing schemes and project proposals, aim to further boost infrastructure, making it crucial for economic growth and improving citizens' quality of life.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How can infrastructure development contribute to the overall socio-economic well-being of India? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (2020)
(a) Digital security infrastructure
(b) Food security infrastructure
(c) Health care and education infrastructure
(d) Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure
Ans: (a)
Q. With reference to ‘National Investment and Infrastructure Fund’, which of the following are statements is/are correct? (2017)
- It is an organ of NITI Aayog.
- It has a corpus of `4,00,000 crore at present.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. “Investment in infrastructure is essential for more rapid and inclusive economic growth.” Discuss in the light of India’s experience. (2021)