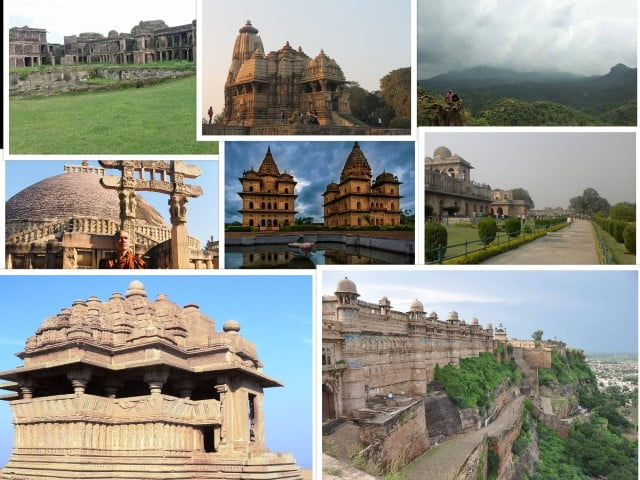
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
New Tourist Destinations
Why in News?
Madhya Pradesh Government has recently been promoting lesser-known tourist spots to offer unique experiences and handle the increasing number of visitors.
Key Points
- Development of Offbeat Destinations:
- The state is developing 50 new offbeat tourist destinations to attract travelers seeking peaceful and less crowded places.
- This initiative is aimed at dispersing tourism across the state, allowing visitors to explore hidden jewels and lesser-known areas of Madhya Pradesh.
- Focus on Sustainability and Responsible Tourism:
- Madhya Pradesh is building a sustainable tourism ecosystem with a focus on green, clean, and safe environments.
- The Pachmarhi hotel, entirely managed by women, reflects the state's leadership in responsible tourism and women empowerment.
- Boosting Employment and Women Participation:
- Over 40,000 women are being trained for tourism-related jobs as part of this initiative, contributing to employment generation in the state.
- Heritage and Natural Beauty:
- Known for its archaeological, geological, and cultural marvels, Madhya Pradesh is enhancing its tourism appeal nationally and internationally by promoting these offbeat destinations.


Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
CoBRA Battalion Soldier Injured in IED Blast
Why in News?
Recently, an IED blast injured a jawan from the CoBRA battalion during an ongoing search operation in Jharkhand’s Chaibasa (Singhbhum district).
Key Points
- Details of the Operation: The operation is targeting Maoist leader, who has a Rs. 1 crore reward announced by the State Government.
- The search operation involving Chaibasa police, 209 CoBRA battalion, and CRPF teams is ongoing in the region to apprehend the Maoist leaders.
- COBRA: COBRA is a special operation unit of the Central Reserve Police Force of India proficient in guerrilla tactics and jungle warfare. Originally established to counter the Naxalite movement,
- CoBRA is deployed to address insurgent groups engaging in asymmetrical warfare.
- Singhbhum district: Singhbhum district was established in 1990 when the original Singhbhum district was bifurcated into East Singhbhum (with Jamshedpur as the district headquarters) and West Singhbhum (with Chaibasa as the district headquarters).
- In 2001, West Singhbhum was further divided, leading to the creation of the Saraikela-Kharsawan district, leaving West Singhbhum with 15 blocks and 3 sub-divisions.
- The district is characterized by hilly terrain, steep mountains, and dense forests, including renowned Sal forests and the globally recognized Saranda forest area.
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including elephants, bison, tigers, panthers, and various deer species, although their populations are declining near human habitation.
- The name "Singhbhum" is believed to originate from either the Singh Rajas of Porahat or a corrupted form of "Singh Bonga," the principal deity of the local tribal population.
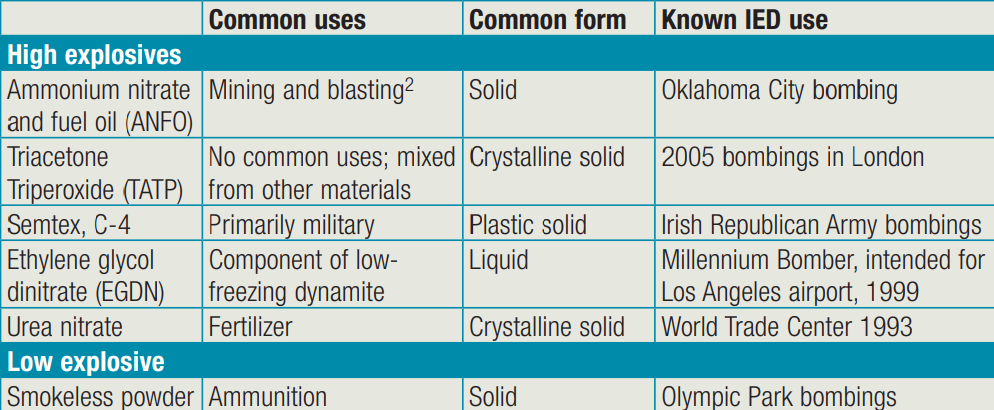
Improvised Explosive Device
- An improvised explosive device (IED) is a homemade bomb designed to destroy or incapacitate targets, commonly used by criminals, terrorists, and insurgents in various forms.
- IEDs can be delivered through multiple means, including vehicles, placement by individuals, or roadside concealment, and gained prominence during the Iraq War that began in 2003.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
"FATF: Terror from ISIL and AQ-Linked Groups in J&K"
Why in News?
Recently, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) released its Mutual Evaluation Report on India, highlighting the terrorism threats India facing, particularly from Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and Al-Qaeda-linked groups active in and around Jammu and Kashmir.
Key Points
- Regional insurgencies in the Northeast and Left-Wing Extremist groups also pose terrorism risks, the report highlighted.
- While the country emphasizes prevention and disruption of terrorist financing, more effort is required to conclude prosecutions and convict terrorist financiers.
- FATF: FATF is the global money laundering and terrorist financing watchdog set up in 1989 out of a G-7 meeting of developed nations in Paris.
- Objective:
- Initially, its objective was to examine and develop measures to combat money laundering.
- After the 9/11 attacks on the US, the FATF in 2001 expanded its mandate to incorporate efforts to combat terrorist financing.
- In April 2012, it added efforts to counter the financing of proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
- Objective:
- FATF Recommendations:
- In April 1990, less than one year after its creation, the FATF issued a report containing a set of Forty Recommendations intended to provide a comprehensive plan of action needed to fight against money laundering.
- In 2004, the FATF published a Ninth Special Recommendations, further strengthening the agreed international standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing - the 40+9 Recommendations.
- In 2012, the FATF revised its recommendations and expanded them to deal with new threats such as the financing of proliferation of WMD.
- Over 200 jurisdictions around the world have committed to the FATF Recommendations through the global network of nine FATF-Style Regional Bodies (FSRBs) and FATF memberships.
FATF’s Recommendations
- Pending Trials: India needs to expedite the conclusion of pending money laundering trials and improve its handling of crimes like human trafficking and drug-related offences.
- Targeted financial sanctions: India must improve its framework to ensure the freezing of funds and assets without delay and streamline communication regarding sanctions.
- Domestic Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs): India needs to define domestic PEPs under its anti-money laundering laws and implement risk-based enhanced measures for them.














.jpg)









.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan