Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
AMU Receives Ultimatum for House Tax Dues
Why in News?
Aligarh Municipal Corporation (AMC) issued a notice to Aligarh Muslim University (AMU), demanding the clearance of pending house tax dues totaling Rs 24.4 crore within 15 days.
Key Points
- AMC also warned of legal action under the Uttar Pradesh Municipal Corporation Act, 1959 if the payment is delayed.
- According to AMC, the dues pertain to 40 properties owned by the university.
- Tax payments for 22 properties had been cleared earlier, leaving Rs 24.4 crore unpaid for 18 properties.
- According to AMC's revenue assessment officer, the dues have been outstanding since 2017.
- The AMU had applied for a grant from the UGC to make payment timely.
- There is a provision that allows the University Grant Commission (UGC) to reimburse such payments, and the university is in communication with the commission regarding this.
University Grants Commission (UGC)
- It came into existence on 28th December, 1953 and became a statutory body by an Act of Parliament in 1956, for the coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of teaching, examination and research in university education.
- It also regulates the recognition of fake universities, autonomous colleges, deemed to be universities, and distance education institutions.
- The head office of the UGC is located in New Delhi.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
High Court Postpones Hearing on Wild Elephants
Why in News?
A division bench of the Madhya Pradesh (MP) High Court, postponed the hearing of a Public Interest Litigation (PIL).
- The PIL seeks protection and proper care of wild elephants straying from Chhattisgarh to Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- The MP High court instructed that the case be presented before the regular bench hearing the matter.
- In the previous hearing before the bench headed by the Chief Justice, the state government informed the court that a committee, comprising a chairman and six experts, was constituted to examine the issues raised in the petition regarding the protection and well-being of wild elephants entering the jungles of Madhya Pradesh from Chhattisgarh.
- The petitioner presented a list of experts in controlling wild elephants before the court.
- The state government requested time to consult experts from outside the state, as suggested by the petitioner.
- During a previous hearing the petitioner raised the issue of the death of 11 wild elephants in the Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve area, stating that there is no expert in the state of MP to control the wild elephants.
Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve
- It is located in the Umaria district of Madhya Pradesh and is spread over the Vindhya hills.
- It holds significant historical importance, evidenced by the presence of the renowned Bandhavgarh Fort, along with numerous caves, rock paintings, and carvings throughout the protected area.
- In 1968, it was designated as a national park and in 1993 was declared a tiger reserve.
- It is known for the Royal Bengal Tigers.
- Other important prey species consist of chital, sambhar, barking deer, nilgai, chinkara, wild pig, chowsingha, langur and rhesus macaque.
- Dependent upon them are the major predators like tiger, leopard, wild dog, wolf and jackal.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Clay Rudraksha Garlands
Why in News?
Madhya Pradesh has become a leading state for women's empowerment and sustainable craftsmanship with the rising popularity of clay Rudraksha garlands.
- This is skillfully crafted by women artisans using the soil from the Narmada River.
Key Points
- The women's empowerment and sustainable craftsmanship, spearheaded by the Madhya Pradesh Tourism Board (MPTB), has not only celebrated local artistry but also opened new avenues of employment for women.
- As part of MPTB's Safe Tourist Places for Women initiative, women and girls in the Sanchi cluster receive clay art training through the ‘Maati Kala Shilp' scheme.
- The training programme emphasizes a balance between preserving traditional clay craft methods and incorporating modern techniques.
- Women artisans are taught soil preparation, moulding, drying, finishing, and quality control processes to meet market demands.
- The training programme emphasizes a balance between preserving traditional clay craft methods and incorporating modern techniques.
- Over 200 women have been trained in various clay techniques, both fired and unfired, allowing them to produce a diverse range of items, including Sanchi stupas, diyas, ornamental vessels, animal figurines, and toys.
- The initiative has significantly boosted the livelihood of women in Sanchi, where many now earn a stable monthly income of ₹14,000 to ₹15,000.
- The artisans have also expanded their reach beyond Sanchi to cities like Bhopal and Jabalpur, receiving recognition and encouragement from various quarters.
- A key milestone in their success came when a private hotel chain began ordering approximately 2,000 garlands per month.
- Currently, the women’s group has scaled production to around 5,000 garlands monthly and continues to explore new market opportunities with the support of MPTB.
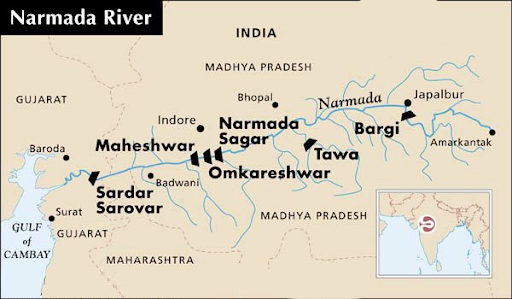
Narmada River
- About:
- The Narmada River (also known as Rewa) serves as a traditional boundary between North and South India.
- It is 1,312 km west of its origin from the Amarkantak peak of Maikal mountain. It flows into the Gulf of Khambhat.
- It drains a large area in Madhya Pradesh besides some areas in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- It is a West flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south.
- Tributaries:
- The predominant tributaries from the right are Hiran, Tendori, Barna, Kolar, Man, Uri, Hatni and Orsang.
- The predominant left tributaries are Burner, Banjar, Sher, Shakkar, Dudhi, Tawa, Ganjal, Chhota Tawa, Kundi, Goi, and Karjan.
- Dams:
- The Major dams on the river include Omkareshwar and Maheshwar dams.


Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana Couples Seek Illegal Sex Determination Tests in UP
Why in News?
Haryana has witnessed a troubling increase in couples traveling to Uttar Pradesh for illegal sex determination tests.
- This shift is mainly attributed to the enforcement against female foeticide in Haryana, particularly following the launch of the ‘Beti Bachao Beti Padhao’ campaign in January 2015.
Key Points
- Over the past decade, Haryana authorities have filed approximately 400 First Information Reports (FIR) related to these illegal activities, with 205 of those lodged in Uttar Pradesh alone.
- The FIRs have been registered under the Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques (PCPNDT) Act, 1994.
- It is an act of the Parliament of India that was enacted to stop female foeticides and arrest the declining sex ratio in India. The act banned prenatal sex determination.
- Since authorities in Haryana launched a crackdown on illegal sex determination and female foeticide, over 800 FIRs have been registered under the PCPNDT Act, 1994 in the state and more than 4,000 people, including doctors, quacks and touts, have been arrested in the state and outside.
- However, the ‘Beti Bachao Beti Padhao’ initiative has had some success in improving the sex ratio in Haryana, which has risen from 871 girls per 1,000 boys in 2014 to 910 currently.
- This increase reflects the ongoing efforts to combat gender discrimination and promote the value of female children.
Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- About:
- It was launched in January 2015 with the aim to address sex selective abortion and the declining child sex ratio which was at 918 girls for every 1,000 boys in 2011.
- This is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and Ministry of Human Resource Development.
- The programme is being implemented across 405 districts in the country.
- Main Objectives:
- Prevention of gender-biased sex-selective elimination.
- Ensuring survival & protection of the girl child.
- Ensuring education and participation of the girl child.
- Protecting rights of Girl children.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
38th National Games
Why in News?
Uttarakhand is preparing to host the 38th National Games, set to begin on 28th January, 2025.
- The 38th National Games will be the largest sporting event in Uttarakhand’s history, with athletes from across India competing in 35 sports.
Key Points
- The State has unveiled three significant symbols in line with the event: the logo, the mascot Mauli, and the torch Tejaswini.
- These symbols reflect the essence of Uttarakhand’s rich culture, breathtaking landscapes, and unwavering spirit, while marking the State’s 25th anniversary with pride and celebration.
- This sporting event promises to be not just a grand competition, but also a unique opportunity for Uttarakhand to showcase its cultural and natural identity to the nation.
- The Logo:
- The official logo of the 38th National Games is a harmonious blend of Uttarakhand’s natural beauty and cultural heritage. It prominently features:
- The Himalayan Peaks: Representing the State’s grandeur and resilience.
- The Himalayan Monal: Highlighting biodiversity and cultural pride.
- The Ganga River: A sacred symbol of purity and spirituality central to Uttarakhand’s identity.
- The Mascot Mauli:
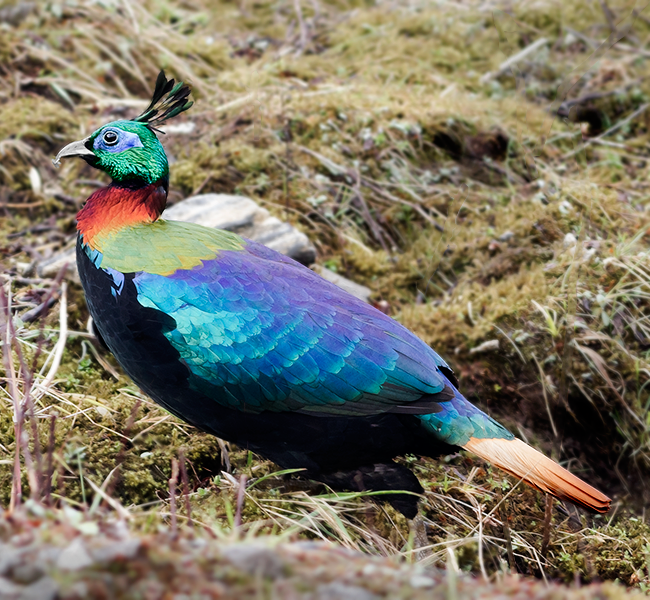
- Named after Uttarakhand’s State bird, the Himalayan Monal, the mascot Mauli embodies the natural beauty, vibrant wildlife, and enduring spirit of the region.
- The Himalayan Monal, known for its dazzling colors and grace, is a symbol of Uttarakhand’s pristine environment, from its majestic mountains to its lush forests.
- Mauli reflects the determination, energy, and perseverance of the people of Uttarakhand and mirrors the same qualities that athletes bring to the games.
- By choosing Mauli as the mascot, the State celebrates its harmonious connection with nature and the resilience of its people, making it a fitting emblem of the National Games.
- The Torch Tejaswini:
- The official torch of the 38th National Games, named Tejaswini, represents power, inspiration, and the relentless pursuit of excellence.
- The torch will carry the flame of sportsmanship and competition across Uttarakhand, uniting the State and the nation in the spirit of the games.
- Designed to reflect the grandeur of Uttarakhand’s mountains and the vibrant energy of its people.
- Tejaswini is a testament to the State’s commitment to excellence and unity.
- Its radiant light symbolizes a bright future for Uttarakhand’s athletes, inspiring them to achieve greatness while fostering a sense of pride and togetherness.
Himalayan Monal
- The Himalayan Monal, also known as the Impeyan monal, Impeyan pheasant, is a bird in the pheasant family, Phasianidae.
- It is the state bird of Uttarakhand. It has been selected as the mascot for the 38th National games that were held in Uttarakhand in 2018.
- Himalayan monal is a Schedule – I bird, according to the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 and classified as Least Concern (LC) by the IUCN.





-UPPCS-English%20(web).png)
-UPPCS-English%20(mobile).png)






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)

.jpg)









.png)







 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan