Important Facts For Prelims
Narmada River
- 20 Sep 2023
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Narmada and other rivers have caused widespread flooding in Gujarat and cut off various villages from the mainstream in the southern and central regions of the State.
- The water level of the Narmada is beyond the danger mark and the India Meteorological Department (IMD) issued red and orange alerts in parts of Gujarat.
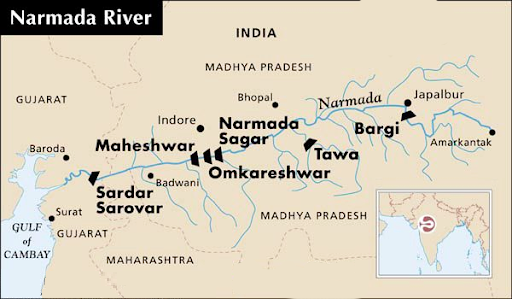
- Narmada River’s major dam is Sardar Sarovar Dam, which is one of the important reasons behind the rising levels.
What is the Sardar Sarovar Project ?
- About:
- The Sardar Sarovar project is the Gravity dam on Narmada River crossing Gujarat.
- Gravity dam is constructed of concrete or stone designed to transfer the entire water load downward.
- It is primarily meant for large scale irrigation and Hydroelectric multi-purpose projects.
- The Sardar Sarovar project is the Gravity dam on Narmada River crossing Gujarat.
- Features:
- The Project was conceived in 1979 majorly for the purposes of Agricultural and Mitigating power Crisis in the state.
- The Hydro electric Power generated would be shared between the states of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra, whereas the irrigation benefits can be utilized by Gujarat and Rajasthan.
What are Key Facts of Narmada River?
- About:
- The Narmada River (also known as Rewa) serves as a traditional boundary between North and South India.
- It is 1,312 km west of its origin from the Amarkantak peak of Maikal mountain. It flows into the Gulf of Khambhat.
- It drains a large area in Madhya Pradesh besides some areas in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- It is a West flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south.
- Tributaries:
- The predominant tributaries from the right are – Hiran, Tendori, Barna, Kolar, Man, Uri, Hatni, and Orsang.
- The predominant left tributaries are – Burner, Banjar, Sher, Shakkar, Dudhi, Tawa, Ganjal, Chhota Tawa, Kundi, Goi, and Karjan.
- Dams:
- The Major dams on the river include Omkareshwar and Maheshwar dams.
What are the Different Color-coded Alerts Issued by the IMD?
- The IMD uses 4 colour codes are:
- Green (All is well): No advisory is issued.
- Yellow (Be Aware): Yellow indicates severely bad weather spanning across several days. It also suggests that the weather could change for the worse, causing disruption in day-to-day activities.
- Orange/Amber (Be prepared): The orange alert is issued as a warning of extremely bad weather with the potential of disruption in commute with road and rail closures, and interruption of power supply.
- Red (Take Action): When the extremely bad weather conditions are certainly going to disrupt travel and power and have significant risk to life, the red alert is issued.
Q 1. The Narmada River flows to the west, while most other large peninsular rivers flow to the east. Why? (2013)
- It occupies a linear rift valley.
- It flows between the Vindhyas and the Satpuras.
- The land slopes to the west from Central India.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (a)