Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan’s River-Link Project
Why in News?
The proposed river-linking project in Rajasthan, which aims to address the state’s growing water scarcity, has sparked significant debate over its potential environmental impact.
- The canal project is expected to channel surplus water of the Chambal river basin for irrigation, drinking and industrial use to 23 districts of Rajasthan, benefitting 3.45 crore people.
Key Points
- This river linking project is mounting over the possible submergence of approximately 37 square kilometers within the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
- The submergence will be caused by the largest dam proposed under the Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (PKC-ERCP), which is part of the ambitious Interlinking of Rivers (ILR) program.
- The PKC-ERCP project in Rajasthan involves a total submergence area of 408.86 sq km. Of this, 227 sq km will be submerged under the reservoir of a proposed dam across the Banas River, a Chambal tributary.
- The dam, planned to be 39 meters high and 1.6 km long, will be located near Doongri village, about 30 km from Sawai Madhopur.
- The project details show, 37.03 sq km belong to Ranthambore National Park (392 sq km) and Keladevi Wildlife Sanctuary (674 sq km), both part of the Ranthambhore tiger reserve (1,113 sq km), currently home to 57 tigers.
- Ranthambhore is the third tiger reserve facing loss of land to upcoming reservoirs.
- The PKC-ERCP project in Rajasthan involves a total submergence area of 408.86 sq km. Of this, 227 sq km will be submerged under the reservoir of a proposed dam across the Banas River, a Chambal tributary.
- The environmental cost of the project has become a contentious issue. Conservationists warn that submerging parts of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve could threaten the biodiversity of one of India’s most celebrated wildlife sanctuaries.
- Ranthambore, home to a stable population of tigers and other species, plays a crucial role in the nation’s conservation efforts.
Note:
- Other projects that are facing land loss include:
- The North Koel Reservoir Project will submerge 10.07 sq km of Palamu tiger reserve in Jharkhand, the Ken-Betwa river link project is expected to drown 41.41 sq km of Panna tiger reserve in Madhya Pradesh.
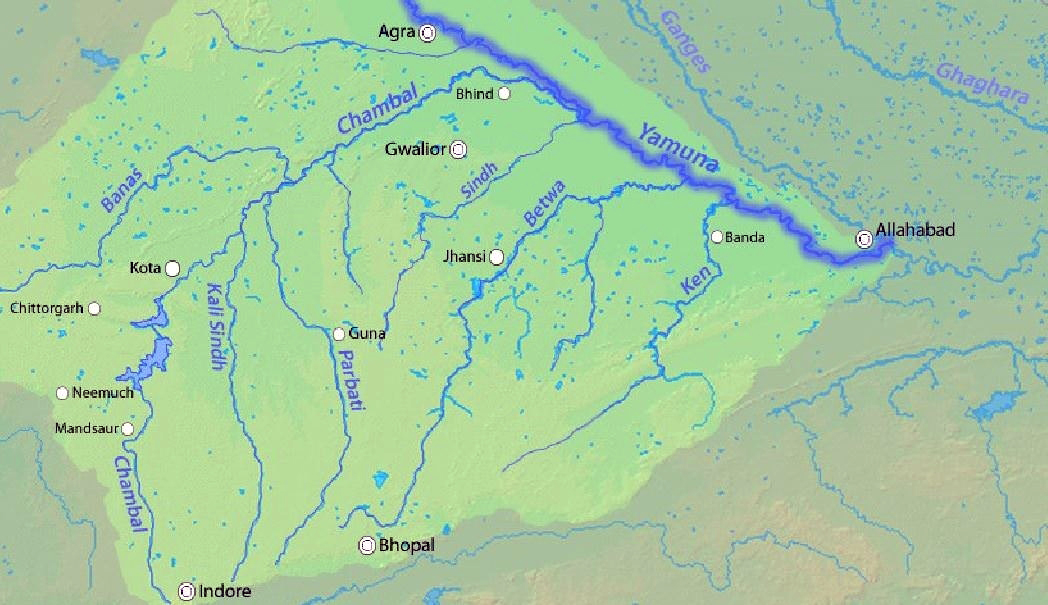
Chambal River
- Chambal River originates at the Singar Chouri peak in the northern slopes of the Vindhya mountains (Indore, Madhya Pradesh). From there, it flows in the North direction in Madhya Pradesh for a length of about 346 km and then follows a north-easterly direction for a length of 225 km through Rajasthan.
- It enters Uttar Pradesh and flows for about 32 km before joining the Yamuna River in Etawah District.
- It is a rainfed river and its basin is bounded by the Vindhyan mountain ranges and the Aravallis. The Chambal and its tributaries drain the Malwa region of northwestern Madhya Pradesh.
- The Hadauti plateau in Rajasthan occurs in the upper catchment of the Chambal River to the southeast of the Mewar Plains.
- Tributaries: Banas, Kali Sindh, Sipra, Parbati, etc.
- Main Power Projects/ Dam: Gandhi Sagar Dam, Rana Pratap Sagar Dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam, and Kota Barrage.
- The National Chambal Sanctuary is located along river Chambal on the tri-junction of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- It is known for critically endangered gharial, the red-crowned roof turtle, and the endangered Ganges river dolphin.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Concerns Regarding Groundwater Contamination
Why in News?
According to a recent report released by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, groundwater quality varies considerably across India, with certain states and UT such as Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Meghalaya and J&K fully meeting Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) standards while states like Rajasthan, Haryana and Andhra Pradesh facing widespread contamination.
Key Points
- The northeastern states of Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, and Nagaland, along with Jammu & Kashmir, have showcased exceptional groundwater management practices.
- A notable concern in the report, based on quality data at 15,259 groundwater monitoring locations and focused assessment at 4,982 trend stations across the country in 2023, is the "elevated levels of uranium in several regions".
- The samples with high uranium concentrations were clustered in areas identified as over-exploited, critical, and semi-critical groundwater stress zones, such as Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
- Rajasthan and Punjab are shown as regional hotspots of uranium contamination.
- The report also reflects significant concerns over the quality of water due to high concentrations of nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and iron in groundwater.
- Almost 20% of the samples exceeded the permissible limit for nitrate while 9% of samples had fluoride levels above the acceptable limit.
- Arsenic contamination was found in 3.5% of samples.
- Fluoride concentration exceeding the permissible limit is a major concern in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra have some of the highest incidences of nitrate contamination, with over 40% of water samples exceeding the permissible limit.
- The report attributed it primarily to agricultural run-off and overuse of fertilizers.
- Elevated arsenic levels were found in several states, particularly in the floodplains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers, during the assessment.
- This includes regions of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur, as well as areas in the Punjab, and Rajnandgaor district in Chhattisgarh.
- The report underlined that Rajasthan, Delhi, Gujarat, Haryan, Punjab, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are the most severely affected by high Electrical Conductivity (EC) value in groundwater.
- EC which is a measure of the ease with which water conducts electricity. It is actually the measure of mineralization of water and indicative of the degree of salinity of ground water.
- It tells about how much dissolved substances, chemicals, and minerals are present in the water. Higher amounts of these impurities will lead to a higher conductivity.
- A rising trend in EC levels signals a deeper issue of groundwater salinization.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
UCC in Uttarakhand with Stringent Registration Norms
Why in News?
The Uttarakhand government is preparing to implement its Uniform Civil Code (UCC) on 26th January, 2025, introducing a host of mandatory requirements for registrations related to personal and civil matters.
Key Points
- UCC Portal:
- Services available on the portal include:
- Registration of marriages, divorces, and live-in relationships.
- Termination of live-in relationships.
- Intestate succession and legal heir declaration.
- Testamentary successions.
- Complaint registration and appeals in case of rejected applications.
- Services available on the portal include:
- Requirements for Various Personal and Civil Matters Include:
- Live-in Relationship Registration:
- Both existing and new live-in couples must register their relationship.
- Applicants must provide details like proof of age, nationality, religion, phone number, and previous relationship status.
- Photos and declarations from both partners are mandatory.
- Children born in such relationships must be registered within seven days of receiving their birth certificates.
- Marriage and Divorce Registration:
- Strict requirements for marriages and divorces have been implemented through the UCC portal to promote transparency and accountability.
- Testamentary Succession:
- Declarants must submit Aadhaar-linked details of themselves, their heirs, and witnesses.
- Witnesses are required to upload video recordings of themselves reading the succession declaration to prevent forgery or disputes.
- Complaint Mechanism for Marriages and Relationships:
- A third party can object to a marriage or live-in relationship through a complaint on the UCC portal.
- Verification of such complaints will be carried out by a sub-registrar to counter false allegations.
- Live-in Relationship Registration:
Uniform Civil Code (UCC)
- The Uniform Civil Code refers to a single set of laws governing personal matters such as marriage, divorce, adoption, inheritance, and succession for all citizens of India.
- The concept of UCC is mentioned in Article 44 of the Indian Constitution as a Directive Principle of State Policy, which states that the state shall endeavor to secure a uniform civil code for citizens throughout the territory of India.
- However, it's important to note that this is not a legally enforceable right but a guiding principle for the state.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Explores Privatisation of Loss-Making Discoms
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government has initiated steps toward privatizing or forming Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) for two of its loss-making electricity distribution companies (discoms).
- This move has sparked protests from employees concerned about job security and the potential impacts on service delivery.
Key Points
- The state’s power corporation recently floated a tender inviting consultants and transaction advisers to devise a privatization or PPP model for Dakshinanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Ltd (DVVNL) and Purvanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Ltd (PVVNL).
- Both discoms have been grappling with substantial financial losses, prompting the government to explore alternatives to improve efficiency and service quality.
- The government has clarified that the specifics of the partnership, including the shareholding structure, will be determined based on recommendations from consultants.
- These experts will analyse the current state of the discoms and propose a suitable model for privatisation or PPP.
- The model is expected to allow private entities to bring in operational expertise and investment while maintaining some level of government oversight to ensure public accountability.
What is DISCOM?
- About:
- DISCOM stands for Distribution Company in the power sector. It refers to entities responsible for the distribution of electricity to consumers, including households, businesses, and industries.
- Role of DISCOMs:
- Electricity Distribution: They manage the infrastructure and operations for delivering electricity to consumers within their designated areas.
- Billing and Revenue Collection: DISCOMs handle metering, billing, and collecting payments for electricity consumption.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: They are responsible for maintaining the distribution network, including transformers, substations, and power lines.
- Customer Service: DISCOMs address issues like power outages, meter installations, and grievances related to electricity supply.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Mahakumbh Mela 2025: World's Largest Religious Gathering
Why in News?
The Mahakumbh Mela 2025, celebrated as the largest human gathering on Earth, commenced with the auspicious 'Shahi Snan' (royal bath) on the occasion of Paush Purnima.
- Held every 144 years during a rare celestial alignment, the event is expected to draw over 1.5 crore (15 million) devotees to the sacred confluence of the Ganga, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati at the Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh.
Key Points
- The 45-day spiritual festival, which concludes on 26 February, will feature several significant bathing rituals, including:
- Makar Sankranti: 14 January
- Mauni Amavasya: 29 January
- Basant Panchami: 3 February
- These events hold immense religious significance, drawing devotees, saints, and pilgrims from across India and the globe.
- Namami Gange Yagya:
- On the eve of the festival, the Namami Gange team organized a grand 'yagya' at the Sangam to pledge continued efforts toward preserving the purity and flow of the Ganga River.
- The event saw participation from over 200 Ganga Sevadoots and thousands of volunteers, with a special recognition of youth contributions to the Ganga Swachhata Abhiyan.
- Safety and Security Measures:
- To ensure the safety of millions of pilgrims, the Uttar Pradesh Police and National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) teams have been deployed across the Maha Kumbh area.
- Special water police units are stationed at the Sangam to manage the massive influx of devotees during the ritual baths.
- Maha Kumbh Mela 2025:
- The Maha Kumbh Mela 2025, a sacred pilgrimage, will be held in Prayagraj from 13th January to 26th February 2025.
- It occurs every 12 years, rotating among four locations i.e., Prayagraj (UP), Haridwar (UK), Nashik (MH), and Ujjain (MP).
- The word Kumbh refers to a pot or vessel, which, in Hindu mythology, is said to have held the nectar of immortality (amrit).
- Uttar Pradesh has declared the Maha Kumbh area in Prayagraj as a new district called Maha Kumbh Mela for 4 months i.e., 1st December 2024 to 31st March 2025.
- The Maha Kumbh Mela 2025, a sacred pilgrimage, will be held in Prayagraj from 13th January to 26th February 2025.
National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
- About: NDRF is a specialised force constituted for the purpose of specialized response to natural and man-made disasters in India.
- Formation and Purpose: The NDRF was formed in 2006 under the Disaster Management Act, 2005. Its primary purpose is to respond quickly and effectively to natural and man-made disasters.
- Structure: The NDRF consists of battalions from the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) including the Border Security Force (BSF), Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), Central Industrial Security Force (CISF), Indo Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), and Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB).
- Each battalion has specialized training and equipment for disaster response.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan 1.jpg)
.png)
 2.jpg)
.png)


