National Chambal Sanctuary | 21 Jun 2022
Why in News?
Recently, the Madhya Pradesh government has proposed to open 292 hectares for mining in five stretches on Chambal and its tributary Parvati rivers.
- The step is taken to free its forest department from devoting too much time, resources, and efforts in fighting illegal mining in the National Chambal Sanctuary.
- Sand mining has been banned in the sanctuary since 2006.
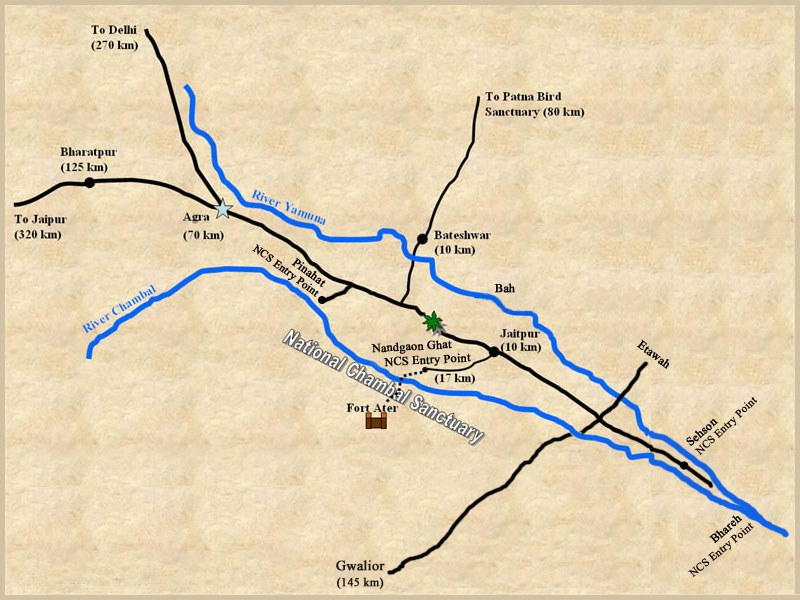
Where is National Chambal Sanctuary?
- About:
- It was set up in 1979 as a riverine sanctuary along an approximately 425 km length of the Chambal River.
- Its ravines stretches over 2-6 km wide along the Chambal River near the tri-point of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- The National Chambal Sanctuary is listed as an Important Bird Area (IBA) and is a proposed Ramsar site.
What are Important Bird Areas (IBAs)?
- Birds are excellent indicators of ecosystem health.
- The IBA programme of Birdlife International aims to identify, monitor and protect a global network of IBAs for conservation of the world's birds and associated biodiversity.
- The Bombay Natural History Society and Birdlife International have identified 554 IBAs in India.
- 40% of these IBAs fall outside the Protected Area network and thus form an important tool for landscape-level conservation planning.
- According to Birdlife International, designation of IBAs is based on standardized criteria, namely:
- A: Global
- A1: Species of Global Conservation Concern:
- The site regularly holds significant numbers of a globally threatened species, or other species of global conservation concern.
- A3: Biome-Restricted Species:
- The site is known or thought to hold a significant assemblage of the species whose breeding distributions are largely or wholly confined to one biome.
- A4: Congregations
- The site is known or thought to hold, on a regular basis, ≥ 1% of the biogeographic population of a congregatory waterbird species.
- The site is known or thought to hold, on a regular basis, ≥ 1% of the global population of a congregatory seabird or terrestrial species.
- The site is known or thought to hold, on a regular basis, ≥ 20,000 waterbirds or ≥10,000 pairs of seabird of one or more species.
- A1: Species of Global Conservation Concern:
- A: Global
- Ecological Significance:
- The National Chambal Sanctuary is home to critically endangered Gharial (small crocodiles), the red-crowned roof turtle and the endangered Ganges River dolphin.
- Chambal supports the largest population of Gharials in the wild.
- Only known place where nesting of Indian Skimmers is recorded in large numbers.
- Chambal supports 8 rare turtle species out of the 26 found in the country.
- Chambal is one of the cleanest rivers in the country.
- Chambal supports more than 320 resident and migrant birds.
- The National Chambal Sanctuary is home to critically endangered Gharial (small crocodiles), the red-crowned roof turtle and the endangered Ganges River dolphin.
- Economic Support:
- Locals directly depended on various resources of the Sanctuary. They farm along the river, extract river water for irrigation, practice sustenance and commercial fishing, and quarry sand.
What are the Other Sanctuaries and National Parks of Madhya Pradesh?
- Madhya Pradesh has 9 National Parks and 25 Sanctuaries spread over an area of 10,862 square km constituting 11.40% of the total forest area and 3.52% of the geographical area of the state.
- At present, the state has 5 Project Tiger areas in the state namely –
- It is also known as the ‘Tiger State’ as it occupies around 19% of India’s Tiger Population and 10% of the world’s tiger population.
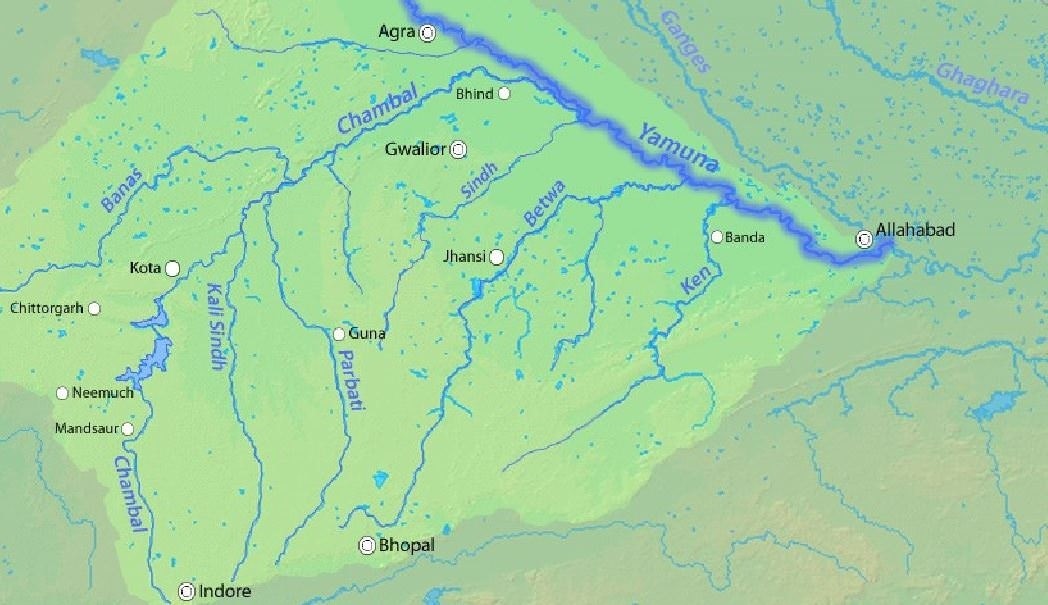
Chambal River
- It is one of the most pollution-free rivers of India.
- It’s a 960 km. long river that originates at the Singar Chouri peak in the northern slopes of the Vindhya mountains (Indore, Madhya Pradesh). From there, it flows in North direction in Madhya Pradesh for a length of about 346 km and then follows a north-easterly direction for a length of 225 km through Rajasthan.
- It enters U.P. and flows for about 32 km before joining the Yamuna River in Etawah District.
- It is a rainfed river and its basin is bounded by the Vindhyan mountain ranges and the Aravallis. The Chambal and its tributaries drain the Malwa region of northwestern Madhya Pradesh.
- Tributaries: Banas, Kali Sindh, Parbati.
- Main Power Projects/ Dam: Gandhi Sagar Dam, Rana Pratap Sagar Dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam, and Kota Barrage.
- The National Chambal Sanctuary is located along river Chambal on the tri-junction of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. It is known for critically endangered gharial, the red-crowned roof turtle, and the endangered Ganges river dolphin.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2010)
| Protected area | Well-known for | |
| 1. | Bhiterkanika, Orissa | Salt Water Crocodile |
| 2. | Desert National Park, Rajasthan | Great Indian Bustard |
| 3. | Eravikulam, Kerala | Hoolak Gibbon |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Bhitarkanika National Park is the core area of the Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary located in the Kendrapara district in the state of Odisha. It was designated as national park in 1998 and as a Ramsar site by the state of Odisha in 2002. The national park is home to saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus), Indian python, king cobra, black ibis, darters and many other species of flora and fauna. It hosts a large number of mangrove species. The national park and wildlife sanctuary are inundated by the rivers Brahmani, Baitarani, Dhamra, Pathsala. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Desert National Park is located in the Thar Desert and is situated near Jaisalmer. The major wildlife found in the park are chinkara, desert fox, blackbuck, Bengal fox, spiny-tail lizard, sandfish, desert monitors, chameleons, etc. The main attraction of the national park is the Great Indian Bustard which is a critically endangered bird species. Hence, pair 2 is correctly matched.
- Eravikulam National Park, located in Kerala, holds the largest viable population of the endangered Nilgiri Tahr and is a famous habitat of Neelakurinji, which blooms once in 12 years. Apart from Tahr, the park is an abode of other little known fauna such as nilgiri marten (endemic), ruddy mongoose, small clawed otter, dusky striped squirrel etc.
- Hoolock Gibbons are found in several states of North- East including Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Tripura and Nagaland. They are also spotted in the Kaziranga National Park, Manas Wildlife Sanctuary and Namdhapha National Park. Hence, pair 3 is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.