Madhya Pradesh
Clay Rudraksha Garlands
- 16 Jan 2025
- 3 min read
Why in News?
Madhya Pradesh has become a leading state for women's empowerment and sustainable craftsmanship with the rising popularity of clay Rudraksha garlands.
- This is skillfully crafted by women artisans using the soil from the Narmada River.
Key Points
- The women's empowerment and sustainable craftsmanship, spearheaded by the Madhya Pradesh Tourism Board (MPTB), has not only celebrated local artistry but also opened new avenues of employment for women.
- As part of MPTB's Safe Tourist Places for Women initiative, women and girls in the Sanchi cluster receive clay art training through the ‘Maati Kala Shilp' scheme.
- The training programme emphasizes a balance between preserving traditional clay craft methods and incorporating modern techniques.
- Women artisans are taught soil preparation, moulding, drying, finishing, and quality control processes to meet market demands.
- The training programme emphasizes a balance between preserving traditional clay craft methods and incorporating modern techniques.
- Over 200 women have been trained in various clay techniques, both fired and unfired, allowing them to produce a diverse range of items, including Sanchi stupas, diyas, ornamental vessels, animal figurines, and toys.
- The initiative has significantly boosted the livelihood of women in Sanchi, where many now earn a stable monthly income of ₹14,000 to ₹15,000.
- The artisans have also expanded their reach beyond Sanchi to cities like Bhopal and Jabalpur, receiving recognition and encouragement from various quarters.
- A key milestone in their success came when a private hotel chain began ordering approximately 2,000 garlands per month.
- Currently, the women’s group has scaled production to around 5,000 garlands monthly and continues to explore new market opportunities with the support of MPTB.
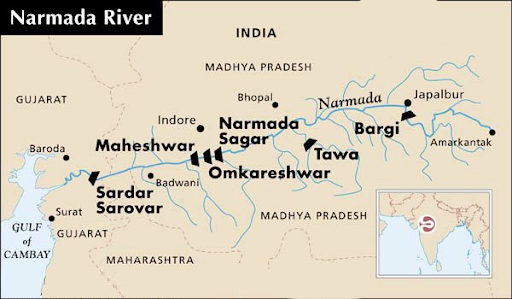
Narmada River
- About:
- The Narmada River (also known as Rewa) serves as a traditional boundary between North and South India.
- It is 1,312 km west of its origin from the Amarkantak peak of Maikal mountain. It flows into the Gulf of Khambhat.
- It drains a large area in Madhya Pradesh besides some areas in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- It is a West flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south.
- Tributaries:
- The predominant tributaries from the right are Hiran, Tendori, Barna, Kolar, Man, Uri, Hatni and Orsang.
- The predominant left tributaries are Burner, Banjar, Sher, Shakkar, Dudhi, Tawa, Ganjal, Chhota Tawa, Kundi, Goi, and Karjan.
- Dams:
- The Major dams on the river include Omkareshwar and Maheshwar dams.