
PRS Capsule - December 2024 | 17 Jan 2025
Key Highlights of PRS
- Polity and Governance
- Constitutional Amendment Bill Introduced in Lok Sabha to Implement Simultaneous Election
- Bill Introduced to Implement Simultaneous Election for Legislative Assemblies of UTs
- Election Rules on Public Access to Poll Documents Amended
- RTE Rules Amended to Allow Holding Back Students in Central Government Schools
- Economy
- Current Account Deficit at 1.2% of GDP in Second Quarter of 2024-25
- Parliament Passes the Bharatiya Vayuyan Vidheyak, 2024
- Amendments to Aircraft Security Rules Notified
- First Supplementary Demands for Grants for 2024-25
- SEBI approves various decisions at board meeting
- RBI Increases Limit For Giving Collateral-Free Agricultural Loans
- RBI Constitutes a Committee to Recommend Framework for Responsible Use of Artificial intelligence (AI)
- The Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024 Introduced in Lok Sabha
- The Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 Introduced in Lok Sabha
- Comments Invited on the Draft Bill to Amend the Warehousing Act, 2007
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Warehousing Receipt-Based Pledge Financing Launched
- Guidelines for National Mission on Natural Farming Released
- Environment
- The Public Liability Insurance (Amendment) Rules, 2024 Notified
- Comments Invited on Draft Rules on Recycling of Certain Packaging Materials
- Comments Invited on the Draft Rules on Solid Waste Management
Polity and Governance
Constitutional Amendment Bill Introduced in Lok Sabha to Implement Simultaneous Election
- The Constitution (One Hundred and Twenty-Ninth Amendment) Bill, 2024, was introduced in Lok Sabha.
- The Bill empowers the Election Commission to conduct elections for Lok Sabha and all State Assemblies at the same time.
- Commencement of Simultaneous Election: The President will issue a notification on the first sitting of Lok Sabha after a general election.
- The terms of all State Assemblies constituted after the date of the notification will expire with the expiry of the full term of Lok Sabha.
- Hence, elections to Lok Sabha and all State Assemblies thereafter will be conducted together.
- Premature Dissolution of Lok Sabha or State Assemblies: If Lok Sabha or a State Assembly is dissolved sooner than its full term of five years, fresh election will be held for a term equal to the remainder of the five-year term. This will synchronise elections for Lok Sabha and all Assemblies every five years.
- Deferring a State election: If the Election Commission believes that the election for a particular State Assembly cannot be held as part of the simultaneous election, it may make a recommendation to the President.
- Upon this recommendation, the President may issue an order to conduct an election for this State Assembly at a later date.
- Where the election for a State Assembly is deferred to after the simultaneous election, its term will end with the end of the Lok Sabha constituted in that simultaneous election.
- The Bill has been referred to a Joint Parliamentary Committee.
Bill Introduced to Implement Simultaneous Election for Legislative Assemblies of UTs
- The Union Territories Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024 was introduced in Lok Sabha.
- It seeks to implement simultaneous election to Union Territories (UTs) with a legislature and amends the following Acts:
- These Acts provide for the structure and functioning of the Legislative Assemblies of Puducherry, Delhi, and Jammu and Kashmir (UT Assemblies).
- The Bill has been referred to the Joint Parliamentary Committee along with the Constitution (129th) Amendment Bill, 2024.
Election Rules on Public Access to Poll Documents Amended
- The Ministry of Law and Justice issued the Conduct of Elections (Second Amendment) Rules, 2024.
- These amend the Conduct of Election Rules, 1961 issued under the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- Under previous Rules, papers relating to elections other than certain restricted papers were open for public inspection.
- The restricted papers include packets of:
- Unused and used ballot papers
- Marked copy of the electoral roll
- Declarations by electors and attestation of their signatures.
- The Amendments instead state that those other papers as specified in the Rules will be open for public inspection.
RTE Rules Amended to Allow Holding Back Students in Central Government Schools
- The Ministry of Education notified the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (Amendment) Rules, 2024.
- These amend the rules issued under the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009.
- The Act guarantees free and compulsory elementary education to children aged between six and 14.
- The Act requires schools to conduct a regular examination for classes fifth and eight at the end of an academic year.
- Students failing this exam can appear for a re-examination within two months.
- The Act empowers the state and central governments to allow schools to hold back students if they fail the reexamination.
- The central government may take this decision for the schools it controls or has established.
- The 2024 Rules require holding back students in classes five or eight if they fail the re-examination.
- During the period in which they are held back, schools must guide the student and his parents by identifying learning gaps and providing necessary resources.
- The head of the school will maintain a list of students who are held back and will monitor their progress.
- Annual exams and re-exams must test competency and not memorisation or procedural skills.
Economy
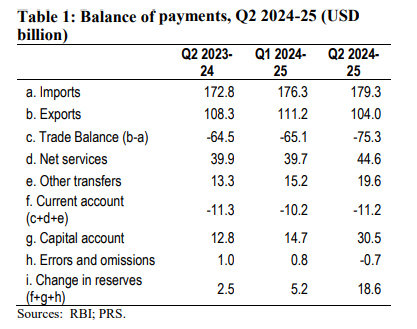
Current Account Deficit at 1.2% of GDP in Second Quarter of 2024-25
- India recorded a current account deficit of 1.2% of GDP (USD 11.2 billion) in the second quarter (July-September) of 2024-25, marginally lower than the same quarter last year (1.3% of GDP).
- Capital account recorded a net inflow of USD 30.5 billion in the second quarter of 2024-25, higher than USD 12.8 billion in the second quarter of 2023-24.
Parliament Passes the Bharatiya Vayuyan Vidheyak, 2024
- The Bharatiya Vayuyan Vidheyak, 2024 was passed by Parliament.
- The Bill seeks to replace the Aircraft Act, 1934.
- The Act regulates civil aviation.
- The Bill retains the regulatory structure and most of the provisions under the Aircraft Act, 1934.
- Key Changes:
- Authorities: It sets up three authorities:
- Regulation of Design of Aircraft: The Act regulates various activities related to aircraft including manufacturing, possession, use, operation, and trade.
- The Bill retains this and also provides for the regulation of the design of aircraft.
- Powers to Make Rules: The Act empowers the central government to frame rules on several matters.
- Appellate Mechanism: The Act empowers the central government to designate an officer to adjudicate penalties. Decisions of the Adjudicating Officer may be appealed before an Appellate Officer.
- The Bill adds one more level of appeal.
- Offences and Penalties: The Bill specifies several offences and penalties.
Amendments to Aircraft Security Rules Notified
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation notified amendments to the Aircraft (Security) Rules, 2023.
- The 2023 Rules specify the framework for the security of airports and aircraft.
- Key Amendments:
- Reserved right of admission in aircraft: The Act establishes the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) to regulate security.
- The Amendments empower the Director General to:
- Refuse a person or group of persons entry into an aircraft
- Require any person or groups of persons to leave an aircraft.
- Such an action may be taken if it is necessary or expedient in the interest of security.
- Prohibition on Communicating False Information: The Amendments prohibit a person from communicating false information.
First Supplementary Demands for Grants for 2024-25
- Lok Sabha approved the first Supplementary Demands for Grants (DFG) for 2024-25.
- Key Allocations:
- Transfers to Farmers: The government sought approval of an additional Rs 3,500 crore for transfers under the PM Kisan Samman Nidhi (PMKISAN) scheme.
- The scheme was introduced in 2019 to offer assistance to cultivable landholding farmers.
- Fertiliser subsidy: The government sought approval for an additional Rs 6,594 crore for subsidy on phosphatic and potassic (P&K) fertilisers.
SEBI Approves Various Decisions at Board Meeting
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) approved various decisions at its board meeting.
- Key Decisions:
- Listing framework for SMEs: SEBI has amended the listing framework for small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
- Such entities can now list their shares only if they have an operating profit of one crore rupees.
- They must meet the profit threshold in two out of three previous financial years at the time of filing their listing prospectus.
- Use of AI tools: SEBI has introduced a framework for the use of artificial intelligence tools by regulated entities such as stock exchanges and clearing corporations.
- Governance Of High-Value Debt-Listed Entities: Entities that have debt securities listed on a stock exchange have certain obligations if the amount is above a threshold. Until now, only companies whose equity shares were listed were counted for the purpose.
RBI Increases Limit For Giving Collateral-Free Agricultural Loans
RBI Constitutes a Committee to Recommend Framework for Responsible Use of Artificial intelligence (AI)
- The Reserve Bank of India constituted a committee under Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya to recommend a framework for responsible and ethical use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the financial sector.
- Terms of Reference:
- Assessing the level of adoption of AI in financial services
- Identifying risks associated with the use of AI and recommending frameworks for risk management by financial institutions such as banks and payment service providers
- Recommending a governance framework for responsible and ethical use of AI.
The Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024 Introduced in Lok Sabha
- The Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024 was introduced in Lok Sabha.
- It seeks to regulate vessels engaged in trade within Indian coastal waters.
- Under the Bill, coastal waters mean the territorial waters of India, along with adjoining maritime zones.
- Territorial waters extend up to 12 nautical miles from the coast (about 22 km).
- Adjoining maritime zones extend up to 200 nautical miles (about 370 km).
- The Bill seeks to repeal Part XIV of the Merchant Shipping Act, 1958, which regulates ships other than sailing vessels engaged in trade within coastal waters.
- The Bill seeks to regulate all types of vessels, including ships, boats, sailing vessels, and mobile offshore drilling units, regardless of the type of propulsion.
The Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 Introduced in Lok Sabha
- The Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 was introduced in Lok Sabha.
- It seeks to replace the Merchant Shipping Act, 1958.
- The Act regulates the shipping sector.
- The Act defines vessels to include any ships, boats, sailing vessels, or other vessels used in navigation.
- The Act establishes Boards to advise the central government:
Comments Invited on the Draft Bill to Amend the Warehousing Act, 2007
- The Department of Food and Public Distribution invited comments on the draft Bill to amend the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act, 2007.
- The Act establishes the Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA).
- It regulates warehousing business and receipts, defines the duties and liabilities of warehousemen, and defines the powers and functions of the WDRA.
- Composition of the WDRA: Under the 2007 Act, the WDRA consists of a Chairperson and two other members appointed by the central government.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Warehousing Receipt-Based Pledge Financing Launched
- The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution launched the Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR-based pledge financing (CGS-NPF).
- An electronic negotiable warehousing receipt (e-NWR) is issued for commodities kept in warehouses accredited by the Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority.
- Farmers/traders can use the e-NWR to avail loans against the commodities.
- The new scheme will provide a guarantee cover for the loans availed against e-NWR.
- It has a total corpus of Rs 1,000 crore and will cover loans up to Rs 75 lakh for agricultural purposes and up to two crore rupees for non-agricultural purposes.
- Eligible borrowers include:
- Small and marginal farmers
- Women/SC/ST/PwD farmers
- Farmer cooperatives.
Guidelines for National Mission on Natural Farming Released
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare notified the guidelines for the National Mission on Natural Farming.
- The Mission aims to promote sustainable systems of farming and improve soil health.
- It aims to initiate natural farming in 7.5 lakh hectares of land by 2026.
- Key Features:
- Priority Areas: The Mission will be implemented in priority areas such as:
- Regions of the five-kilometer corridor along River Ganga
- Districts on the banks of major rivers
- Districts with high and low fertiliser input sales in states
- Districts with tribal areas.
- Training: The Mission aims to create a support ecosystem for farmers to transition to natural farming.
- Training will be extended through:
- Centres of Natural Farming.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras.
- State Agricultural Universities.
- Local Natural Farming Institutions.
- The Mission will also deploy 30,000 community resource persons (or Krishi Sakhis) to scale up natural farming practices.
Environment
The Public Liability Insurance (Amendment) Rules, 2024 Notified
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change notified the Public Liability Insurance (Amendment) Rules, 2024.
- These amend the Public Liability Rules, 1991 issued under the Public Liability Insurance Act, 1991.
- The Act provides a framework for compensation to persons affected by accidents in handling hazardous substances.
- Key Changes:
- Increase in Limit on Liability of Insurers: Under the Act, an owner of an undertaking handling hazardous substances must take insurance for their liability to provide relief in the event of an accident. The 2024 Rules raise the insurer's maximum liability for accidents from Rs 5 crore under the 1991 Rules to Rs 250 crore.
- Reimbursements to be Provided by the Owner: The 2024 Rules specify the amount of relief to be provided by the owner to the affected persons in specified cases.
- Allocation of Funds from Environmental Relief Fund: The Jan Vishwas Act, 2023 amended the 1991 Act to allow the use of the Environmental Relief Fund for restoration of damage in certain cases.
- The Rules provide that upon the receipt of the application, the central government will scrutinise the extent of damage and determine the amount to be allocated.
- Duty to publicise Right to Claim for Relief: In case of an accident, the Amendment Rules require industrial units to publicise among the affected persons the right to claim relief.
Comments Invited on Draft Rules on Recycling of Certain Packaging Materials
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change invited comments on the Draft Environment Protection (Extended Producer Responsibility for Packaging made from paper, glass, and metal as well as Sanitary Products) Rules, 2024.
- The draft Rules have been issued under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Comments Invited on the Draft Rules on Solid Waste Management

