International Relations
Katchatheevu Island: Strategic Geography
- 03 Apr 2024
- 19 min read
This editorial is based on “Katchatheevu and beyond, islands and India’s new geopolitics” which was published in Indian Express on 03/04/2024. The article describes how a review of Indian foreign policy in the past decade reveals that island states and territories, spanning from the South Pacific to the African coast, have emerged as new focal points in India's evolving strategic landscape, particularly highlighting the significance of Katchatheevu islands in current times. This island is also important for India-Sri Lanka Relations.
For Prelims: India-Sri Lanka Relations, Buddhism, Renewable Energy, Indian Ocean, Katchatheevu, Indo-Pacific, Agalega Islands, Quad, Mauritius.
For Mains: Significance of Katchatheevu Islands for India and Implications for Future.
Whether it is the Maldives that now occupies much Indian mind space in the growing maritime joust with China, or India’s new engagement with the resource-rich Papua New Guinea in the Pacific Islands, the joint development of infrastructure on the Agalega island of Mauritius, the collaboration with Australia in the eastern Indian Ocean islands, or the government’s focus on developing the Andamans to our east, the Lakshadweep to the west and Katchatheevu adjoining Sri Lanka, islands have emerged as an important part of India’s new geopolitics.
The Katchatheevu Islands have re-entered the discourse, driven by the upcoming 2024 Lok Sabha elections, presenting an opportune platform to court voters in Tamil Nadu, where the longstanding fisherman issues with Sri Lanka are fiercely discussed.
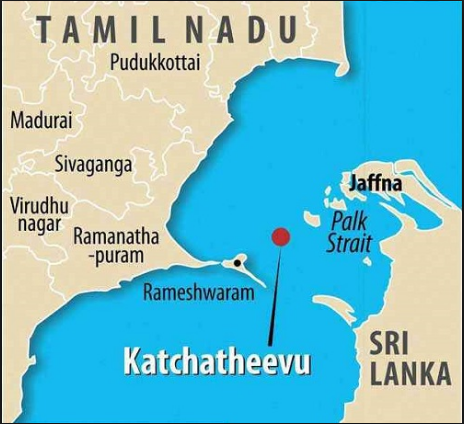
What is Katchatheevu Island?
- About:
- The Katchatheevu Islands are a pair of uninhabited islands located in the Palk Strait, between the southeastern coast of India (Tamil Nadu) and the northern coast of Sri Lanka.
- The larger island is known as Katchatheevu, while the smaller one is called Imaravan. These islands have been historically significant due to their strategic location and their importance in the fishing activities of both India and Sri Lanka.
- Fishermen Issue:
- The ownership of Katchatheevu has been a significant point of contention between India and Sri Lanka, especially concerning fishing rights in the surrounding waters. Fishermen from Tamil Nadu have been particularly affected, as they claim traditional fishing rights in the area.
- The ceding of Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka has resulted in restrictions on Indian fishermen accessing traditional fishing grounds around the island. This has led to numerous conflicts and arrests of Indian fishermen by the Sri Lankan authorities.
- Political and Legal Stand:
- Politically, the issue of Katchatheevu has been used by various parties in India to criticise the government's stance on the matter. Legal challenges have also been raised regarding the legality of the agreements ceding the island to Sri Lanka.
- Bilateral Discussions:
- Despite the contentious nature of the issue, both India and Sri Lanka have engaged in bilateral discussions to address the concerns of fishermen from Tamil Nadu. Various proposals, such as joint patrolling and fishing zones, have been suggested to resolve the issue amicably.
What is the Current Status of India-Sri Lanka Relations?
- Historical Ties:
- India and Sri Lanka have a long history of cultural, religious, and trade ties dating back to ancient times.
- There are strong cultural ties between the two countries, with many Sri Lankans tracing their heritage to India. Buddhism, which originated in India, is also an important religion in Sri Lanka.
- Financial Assistance from India:
- India provided approximately USD 4 billion worth of aid to Sri Lanka during an unprecedented economic crisis, which was crucial for the country to survive the crisis.
- Sri Lanka was hit by a catastrophic financial crisis in 2022, the worst since its independence from Britain in 1948, due to a severe paucity of foreign exchange reserves.
- Role in Debt Restructuring:
- India has played a role in collaborating with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and creditors to help Sri Lanka in restructuring its debt.
- India was also the first country amongst India, China and Japan to hand over its letter of support for financing and debt restructuring of Sri Lanka.
- Joint Vision for Connectivity:
- Both countries have agreed on a joint vision that emphasises comprehensive connectivity, including People to People connectivity, renewable energy cooperation, logistics, port connectivity, and grid connectivity for electricity trade.
- Sri Lanka is also a member of groupings like BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) and SAARC in which India plays a leading role.
- Both countries are exploring the possibility of an Economic and Technology Cooperation Agreement (ETCA) to integrate their economies and foster development.
- Agreement on a Multi-Project Petroleum Pipeline:
- Both India and Sri Lanka have agreed to establish a multi-product petroleum pipeline from the southern part of India to Sri Lanka.
- This pipeline aims to ensure an affordable and reliable supply of energy resources to Sri Lanka. Recognition of energy's critical role in economic development and progress is driving the focus on establishing the petroleum pipeline.
- Adoption of India's UPI:
- Sri Lanka has now adopted India's UPI service, which is a significant step towards enhancing fintech connectivity between the two countries.
- The use of the rupee for trade settlement is further helping Sri Lanka’s economy. These are concrete steps to help Sri Lanka’s economic recovery and growth.
- Economic Ties:
- India is Sri Lanka’s third largest export destination, after the US and UK. More than 60% of Sri Lanka’s exports enjoy the benefits of the India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement. India is also a major investor in Sri Lanka.
- India has traditionally been among Sri Lanka’s largest trade partners and Sri Lanka remains among the largest trade partners of India in the SAARC. India was Sri Lanka’s largest trading partner with an overall bilateral merchandise trade of USD 5.45 billion in 2021.
- In 2022, India was the largest source of tourists for Sri Lanka with over 100,000 tourists.
- Defence:
- India and Sri Lanka conduct joint military (Mitra Shakti) and Naval exercise (SLINEX).
How have the India-Sri lanka Relations Evolved Regarding Katchatheevu Islands?
- Colonial Times-Till 19th Century: Sri Lanka asserted its sovereignty over Katchatheevu by citing the Portuguese occupation of the island from 1505 to 1658 CE as evidence of jurisdiction.
- The small island was administered by the British in the colonial era. Historically, the Raja of Ramnad or present-day Ramanathapuram in Tamil Nadu is said to have owned the island, which later became part of the Madras Presidency.
- Transformations in 20th Century: Both Sri Lanka and India sought exclusive fishing rights over Katchatheevu in the 1920s, leading to a longstanding dispute. The issue persisted after both countries gained independence in the 1940s. In 1968, the Sri Lankan Prime Minister officially raised the matter during a visit to India, asserting Sri Lanka's sovereignty over Katchatheevu.
- Subsequent talks between the Prime Ministers of India and Sri Lanka, Indira Gandhi and Sirimavo Bandaranaike, led to the signing of the 1974 Agreement on the Boundary in Historic Waters between the two countries.
- This agreement defined a boundary that placed Katchatheevu one mile off Sri Lanka's west coast, based on historical evidence, legal principles, and precedents.
- Significance for Indian Fishermen: Article 4 of the Agreement stipulated that each State shall have sovereignty and exclusive jurisdiction and control over the waters, the Islands, the Continental Shelf and the subsoil on its side of the Maritime boundary in the Palk Strait and Palk Bay and Katchatheevu Island was determined as falling within Sri Lankan waters.
- The following article added that “Indian fishermen and pilgrims would enjoy access to the island as before and would not be required by Sri Lanka to obtain travel documents or visas for these purposes”.
What are Some Other Strategic Geographies for India Across the World?
- Indo-Pacific:
- The idea was first proposed by the late Japanese Premier Shinzo Abe, in a speech to the Indian Parliament in 2007. He urged India to reflect on the “confluence of the two oceans” — the Indian and the Pacific.
- It took over a decade after that call for India to formally embrace the Indo-Pacific idea - in a speech by the Prime Minister at the annual Shangri La Dialogue in Singapore during the summer of 2018.
- India’s deteriorating relations with China, marked by a series of military crises in 2013, 2014, and 2017, was an important factor in Delhi’s rethink; so was the growing strategic partnership with the US.
- The Indo-Pacific is now well-established in the Indian discourse, and so is its institutional anchor, the Quad, which brings together Australia, India, Japan and the US.
- Eurasia:
- If Japan and the US popularised “Indo-Pacific”, Russia has driven the “Eurasian” idea. As a great power straddling Europe and Asia, Russia sees the vast Eurasian landmass as its natural sphere of influence.
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, built jointly by Russia and China, was the institutional expression of the Eurasian idea.
- Given India’s stakes in continental Asia, its long-standing ties to Russia, and its quest for a multipolar world, Eurasia offers much significance for India in multiple aspects.
- If Japan and the US popularised “Indo-Pacific”, Russia has driven the “Eurasian” idea. As a great power straddling Europe and Asia, Russia sees the vast Eurasian landmass as its natural sphere of influence.
- Nordic Region:
- The Nordic region, the Nordic-Baltic coalition and the Caucasus have emerged as new geographies of consequence for India in Europe and around it.Ukraine recently underlined India’s potential role in shaping war and peace in Central Europe, whose turbulent politics have triggered two world wars and threatens to unleash a third.
- India-Middle East Geography:
- The proposal for an economic corridor linking India and Europe through the Middle East, the Abraham Accords, the conflict in Gaza, the increasing influence of the Arab Gulf, India's strengthening ties with the UAE and Saudi Arabia, the deployment of approximately 20 Indian naval vessels in the Red Sea area, and the expanding interaction with Africa are leading to a more interconnected perspective of the Middle East, Africa, the eastern Mediterranean, and the Western Indian Ocean.
- Previously considered distinct regions, they now highlight their significant relevance for India's developmental path.
- The proposal for an economic corridor linking India and Europe through the Middle East, the Abraham Accords, the conflict in Gaza, the increasing influence of the Arab Gulf, India's strengthening ties with the UAE and Saudi Arabia, the deployment of approximately 20 Indian naval vessels in the Red Sea area, and the expanding interaction with Africa are leading to a more interconnected perspective of the Middle East, Africa, the eastern Mediterranean, and the Western Indian Ocean.
What is the Relevance of Katchatheevu Islands for India?
- Strategic Importance:
- Geopolitical Location: Katchatheevu is strategically located in the Palk Strait, which serves as a crucial maritime route connecting the Bay of Bengal with the Gulf of Mannar and the Indian Ocean.
- Security Concerns: Control over Katchatheevu provides India with strategic leverage in monitoring maritime activities in the region, including movements of vessels and potential security threats.
- Economic Significance:
- Fishing Resources: The waters around Katchatheevu are rich in marine resources, including fish and other seafood, which are vital for the livelihoods of fishermen from Tamil Nadu.
- Commercial Potential: Control over Katchatheevu could facilitate the development of commercial activities such as fishing, aquaculture, and tourism, thereby boosting economic growth in the region.
- Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Historical Claims: Katchatheevu holds historical significance for India, with claims of traditional fishing rights by fishermen from Tamil Nadu dating back centuries.
- Cultural Ties: The island has historical and cultural significance for the Tamil communities in India and Sri Lanka, as it is associated with the legendary Tamil sage Thiruvalluvar.
- Legal and Diplomatic Implications:
- Diplomatic Relations: Despite the cession of Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka through agreements in 1974 and 1976, the Katchatheevu issue has implications for India-Sri Lanka relations, often influencing bilateral discussions and negotiations on various matters, including fishing rights and maritime cooperation.
- International Law: The dispute over Katchatheevu raises broader questions about the application of international law, particularly concerning territorial sovereignty, maritime boundaries, and the rights of coastal states.
- Territorial Waters: The island's possession by Sri Lanka has implications for India's territorial waters and Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) in the region.
- Humanitarian Considerations:
- Human Rights Concerns: Restrictions on fishing activities around Katchatheevu imposed by Sri Lanka have led to humanitarian concerns, including instances of arrests, harassment, and loss of lives among Indian fishermen.
- Need for Resolution: Addressing the Katchatheevu issue is essential from a humanitarian perspective to ensure the welfare and safety of fishermen and their families who depend on the waters for their sustenance.
- Security and Anti-Smuggling Operations:
- Smuggling Activities: Katchatheevu's proximity to the Indian coast makes it a potential hub for smuggling activities, including arms, drugs, and contraband.
- Preventing Smuggling Activities: The island's possession by Sri Lanka has implications for India's ability to monitor and curb such activities in the region.
- India has expressed concerns over the use of Katchatheevu for smuggling and other illegal activities that could pose a security threat.
Conclusion
Despite its small size, Katchatheevu Island remains a complex issue between India and Sri Lanka due to its strategic location, impact on fishing rights, and cultural significance. The transfer of the island to Sri Lanka has strained bilateral ties and highlighted the need for a comprehensive resolution addressing maritime security, livelihood concerns of fishermen, and respecting the historical sentiments of both nations. Resolving this long-standing dispute through sustained dialogue, mutual understanding, and innovative resource-sharing mechanisms is crucial for fostering cooperation and stability in the region.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Evaluate the socio-economic implications of the Katchatheevu Agreement on fishing communities in Tamil Nadu and its influence on India-Sri Lanka relations. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. Elephant Pass, sometimes seen in the news, is mentioned in the context of the affairs of which one of the following? (2009)
(a) Bangladesh
(b) India
(c) Nepal
(d) Sri Lanka
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q2. In respect of India-Sri Lanka relations, discuss how domestic factors influence foreign policy. (2013)
Q3. ‘India is an age-old friend of Sri Lanka.’ Discuss India's role in the recent crisis in Sri Lanka in the light of the preceding statement. (2022)