Strategic Importance of A&N Islands | 17 Apr 2024
For Prelims: Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Indo-Pacific region, Malacca Strait, UNCLOS, India's Act East Policy
For Mains: Strategic Significance and challenges associated with Andaman and Nicobar Island, Geopolitical Implications on India
Why in News?
The Indian government's renewed focus on developing the Andaman and Nicobar Islands(ANI) underscores their strategic significance in the Indo-Pacific region, prompting efforts to enhance infrastructure and security.
- The recent focus on building strategic infrastructure on the islands, both civilian and military, is long overdue and reflects a lack of strategic maritime vision since Independence.
What is the Strategic Importance of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
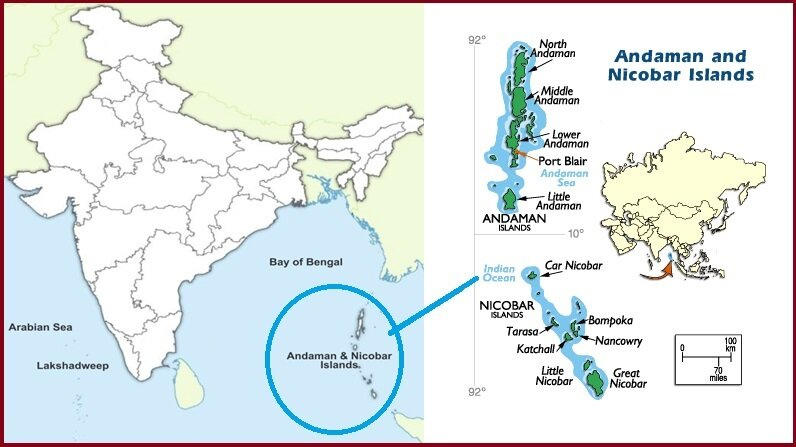
- Located 700 nautical miles southeast of the Indian mainland, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands add 300,000 sq km to India's exclusive economic zone, with the potential for undersea hydrocarbon and mineral deposits.
- The islands' strategic location astride the Malacca Strait, makes them a crucial asset for India's ability to monitor and project power in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The Malacca Strait is a critical maritime choke point, with more than 90,000 merchant ships carrying about 30% of the world's traded goods passing through it annually.
- The islands share maritime boundaries with Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia, and Bangladesh, giving India substantial ocean space under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) in terms of exclusive economic zone and continental shelf.
- The islands can serve as the first line of defence against any attempt from the East to undermine India's maritime security, especially in the face of China's growing influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Port Blair can become a regional hub for navies to collaborate on disaster relief, medical aid, counter-piracy, search and rescue, and other maritime security initiatives.
What are the Challenges to the Development of the ANI?
- The shift from India's Look East policy to a stronger Act East policy, along with the growing recognition of the significance of maritime power and the increasing capabilities of the Chinese PLA Navy, has underscored the need to develop Indian island territories, especially the Andaman and Nicobar group.
- Lack of political prioritisation until recently, with the realisation of the islands' strategic importance only now.
- Challenges of distance from the mainland and difficulties in developing infrastructure.
- Complex environmental clearance procedures and regulations on forest and tribal conservation.
- Coordination challenges due to the involvement of multiple ministries and agencies. The conflict between long-term strategic vision and immediate political gains.
What Strategic Infrastructure Development is Needed in A&N Islands?
- Enhancing Maritime Domain Awareness:
- Ensuring comprehensive maritime domain awareness and surveillance over the islands.
- Bolstering deterrence capabilities against any naval misadventures from the East.
- Bolstering Infrastructure:
- Developing infrastructure to support India's maritime economy, especially in the southern group of islands.
- Improving transportation and connectivity to facilitate development and tourism. Developing Galathea Bay transhipment port on Great Nicobar Island.
- The plan to connect the A&N Islands to the mainland through Submarine Optical Fibre Cable (OFC) needs revitalisation. This will provide cheaper and better connectivity and access to Digital India's benefits.
- Reducing the islands' dependence on mainland support for essential supplies and services.
- Enhancing transportation and connectivity for development and tourism.
- Establishing high-speed inter-island ferry services and a seaplane terminal.
- Developing infrastructure to support India's maritime economy, especially in the southern group of islands.
- Enhancing Military Presence:
- The military must increase forces and deploy the appropriate assets at the Andaman Nicobar Command (ANC) to maintain island security. This includes basing surveillance and fighter aircraft there, as well as conducting frequent detachments.
- International Collaborations:
- Exploring partnerships with the Quad and Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI) for development initiatives.
- Seeking infrastructure development concessions akin to those on India's northern borders.
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- History:
- India's association with Andaman and Nicobar Island dates back to the aftermath of the 1857 War of Independence when the British established a penal colony for Indian revolutionaries.
- The islands were occupied by the Japanese in 1942 and later became the first part of India to be liberated from British rule in 1943 when Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose visited Port Blair.
- After the Japanese surrender in 1945, the British reoccupied the islands. On the eve of Independence islands were given to India.
- The period from Independence until 1962 saw neglect of the islands due to their remote location and dark symbolism.
- In 1962, a naval garrison was established due to concerns about a Chinese submarine. In 2001, the Andaman Nicobar Command (ANC) was established in Port Blair after the post-Kargil War security review, marking India's first joint and Unified operational command.
- The ANC, established in 2001, is India's first joint/unified operational command, placing forces from all three services and the Coast Guard under a single commander-in-chief.
- The ANC is responsible for maintaining comprehensive maritime domain awareness and deterrence capabilities in the strategic Andaman and Nicobar archipelago.
- Key Facts:
- The Ten Degree Channel is a narrow strait that separates the Andaman Islands from the Nicobar Islands. It is located approximately at the 10-degree latitude mark.
- Indira Point is the southernmost tip of the Nicobar Islands. It is situated on Great Nicobar Island and marks the southernmost point of India.
- The ANI is home to 5 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups: Great Andamanese, Jarwas, Onges, Shompens and North Sentinelese.
- Recent Development:
- NITI Aayog is undertaking a project for Great Nicobar which will include an international container transhipment terminal, an airport, a power plant, and a township.
- Additionally, a proposal for Little Andaman calls for the development of a new greenfield coastal city to compete with Singapore and Hong Kong.
- The Kra Canal is a proposed canal in Thailand that would connect the Gulf of Thailand with the Andaman Sea. It aims to create a shortcut for shipping between the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. How should India prioritise development and security in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, considering their historical importance, and geopolitical relevance particularly concerning China's maritime ambitions in the Indo-Pacific region? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following have coral reefs? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q3. In which one of the following places is the Shompen tribe found? (2009)
(a) Nilgiri Hills
(b) Nicobar Islands
(c) Spiti Valley
(d) Lakshadweep Islands
Ans: (b)