Sickle Cell Eradication | 20 Nov 2024
For Prelims: Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas, Sickle Cell Eradication-2047, Chronic anaemia, tribal communities, Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR),
For Mains: Sickle Cell Eradication-2047, National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission, National Sickle Cell Portal
Why in News?
Recently, on Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas (15th November 2024), a commemorative postage stamp on "Sickle Cell Eradication - 2047" was unveiled in Madhya Pradesh.
- The initiative aligns with India’s broader commitment to eradicating sickle cell anemia, a hereditary blood disorder, by 2047, particularly focusing on tribal communities, which are disproportionately affected.
What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
- About:
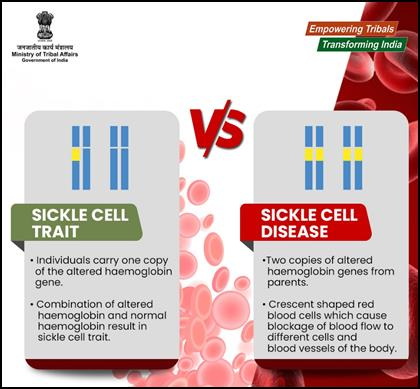
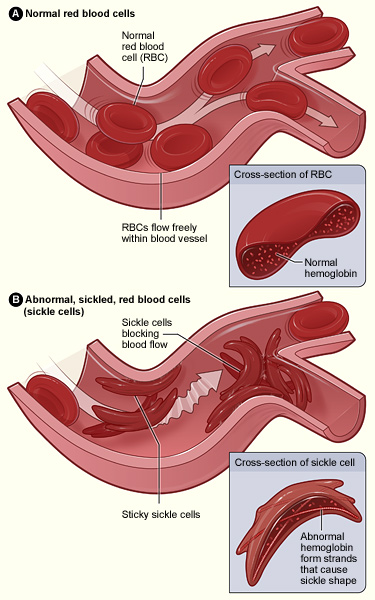
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a genetic blood disorder causing abnormal haemoglobin (the protein that carries oxygen through the body), resulting in sickle-shaped red blood cells.
- This leads to blocked blood flow, severe pain, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) tribal health expert committee has identified SCD as one of the ten major health issues among tribal communities.
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a genetic blood disorder causing abnormal haemoglobin (the protein that carries oxygen through the body), resulting in sickle-shaped red blood cells.
- Symptoms: Some common symptoms of sickle cell disease are
- Chronic anaemia which leads to fatigue, weakness, and paleness.
- Painful episodes (also known as sickle cell crisis) cause sudden and intense pain in the bones, chest, back, arms, and legs.
- Delayed growth and puberty.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: These can help relieve anaemia and reduce the risk of pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: It can help reduce the frequency of painful episodes and prevent some of the disease's long-term complications.
- Gene Therapy: It can also be treated by bone marrow or stem cell transplantation by methods like Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR).
- Challenges Regarding SCD in India:
- India has the world's highest tribal population density, with 67.8 million people (8.6%) as per the 2011 Census.
- MoHFW highlights SCD among the top ten health issues impacting tribal communities disproportionately.
- Limited diagnostic and treatment facilities in remote tribal areas and lack of knowledge among communities about genetic counseling and preventive measures.
- Long-term SCD management can be financially taxing due to medication costs, regular check-ups, and hospitalisations.
- Treatments like CRISPR cost USD 2-3 million, and finding bone marrow donors is challenging.
- India has the world's highest tribal population density, with 67.8 million people (8.6%) as per the 2011 Census.
What are Some Government Initiatives Related to SCD?
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission:
- Vision: The National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission, announced in the Union Budget 2023, targets the health challenges posed by Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), especially among tribal populations.
- The mission aims to eliminate SCD as a public health issue in India by 2047.
- Key Features:
- Community Screening: Identification of at-risk individuals through mass screening programs.
- Genetic Counselling: Educating families about the genetic nature of the disease.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use of tools like HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) machines for accurate diagnosis.
- Prenatal Testing: Collaboration with organisations like Sankalp India for testing during pregnancy.
- Newborn Screening: Specialised labs at AIIMS Bhopal for early detection.
- Technology Integration: Development of a mobile app and National Sickle Cell Portal for tracking and data reporting.
- Objectives:
- Affordable and Accessible Care: Provide care to all SCD patients.
- Quality of Care: Ensure high-quality care for SCD patients.
- Reduce Prevalence: Decrease the prevalence of SCD.
- Progress:
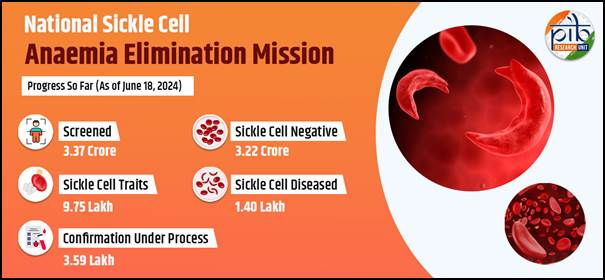
- Over 3.37 crore individuals have been screened under the program, with more than 3.22 crore confirmed negative for sickle cell disease.
- Vision: The National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission, announced in the Union Budget 2023, targets the health challenges posed by Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), especially among tribal populations.
- Beneficiaries:
- Primary target groups include children and adolescents (birth to 18 years) for early detection and intervention, and youth and adults (up to 40 years) for broader age group inclusion over time.
- Over 7 crore individuals targeted for screening, counseling, and care within the first three years (2023-24 to 2025-26).
- National Health Mission (NHM) 2013:
- It encompasses provisions for disease prevention and management, with a specific focus on hereditary anomalies such as sickle cell anaemia.
- Dedicated programs within NHM focus on raising awareness, facilitating early detection, and ensuring timely treatment of sickle cell anaemia.
- NHM facilitates drugs like hydroxyurea to treat SCD in its “essential medicines List”.
- The National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research 2017:
- It restricts the commercialisation of stem cell therapies to clinical trials, except for Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- Gene editing on stem cells is permitted only for in-vitro studies.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy Product Development and Clinical Trials 2019:
- It provides guidelines for the development and clinical trials of gene therapies for inherited genetic disorders.
- India has also approved a five-year project to develop CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) techniques for sickle cell anaemia treatment.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh aims to address the challenges in screening and management of the disease.
World Sickle Cell Awareness Day
- World Sickle Cell Awareness Day is observed annually on 19th June. In 2024, the theme is "Hope Through Progress: Advancing Sickle Cell Care Globally."
- The day aims to highlight the struggles faced by those with SCD, promote understanding of the disease, and streamline efforts towards improving patient care and finding a cure.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Healthcare Infrastructure: Establish more specialised diagnostic and treatment centres in tribal regions.
- Educational Campaigns: Increase awareness about genetic diseases among tribal populations.
- Technology Utilisation: Fully operationalise the National Sickle Cell Portal for seamless tracking.
- Collaboration: Involve civil society, local governance, and international health organisations for funding and technical expertise.
- Continued Awareness and Screening: Enhance awareness and strategic screening initiatives across states and age groups to identify and manage SCD cases effectively.
- Integrated Healthcare Approaches: Strengthen integrated healthcare approaches to provide comprehensive care and treatment for SCD, focusing on high-prevalence and tribal areas.
Conclusion
India's focus on addressing health inequities in vulnerable populations, especially those affected by Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), reflects the government's commitment to public health and tribal welfare. This initiative aligns with UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to create a healthier and more equitable society.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q. Examine the National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission's role in combating sickle cell anemia. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in the context interventions being undertaken under Anemia Mukt Bharat Strategy : (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of child-birth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (2021)