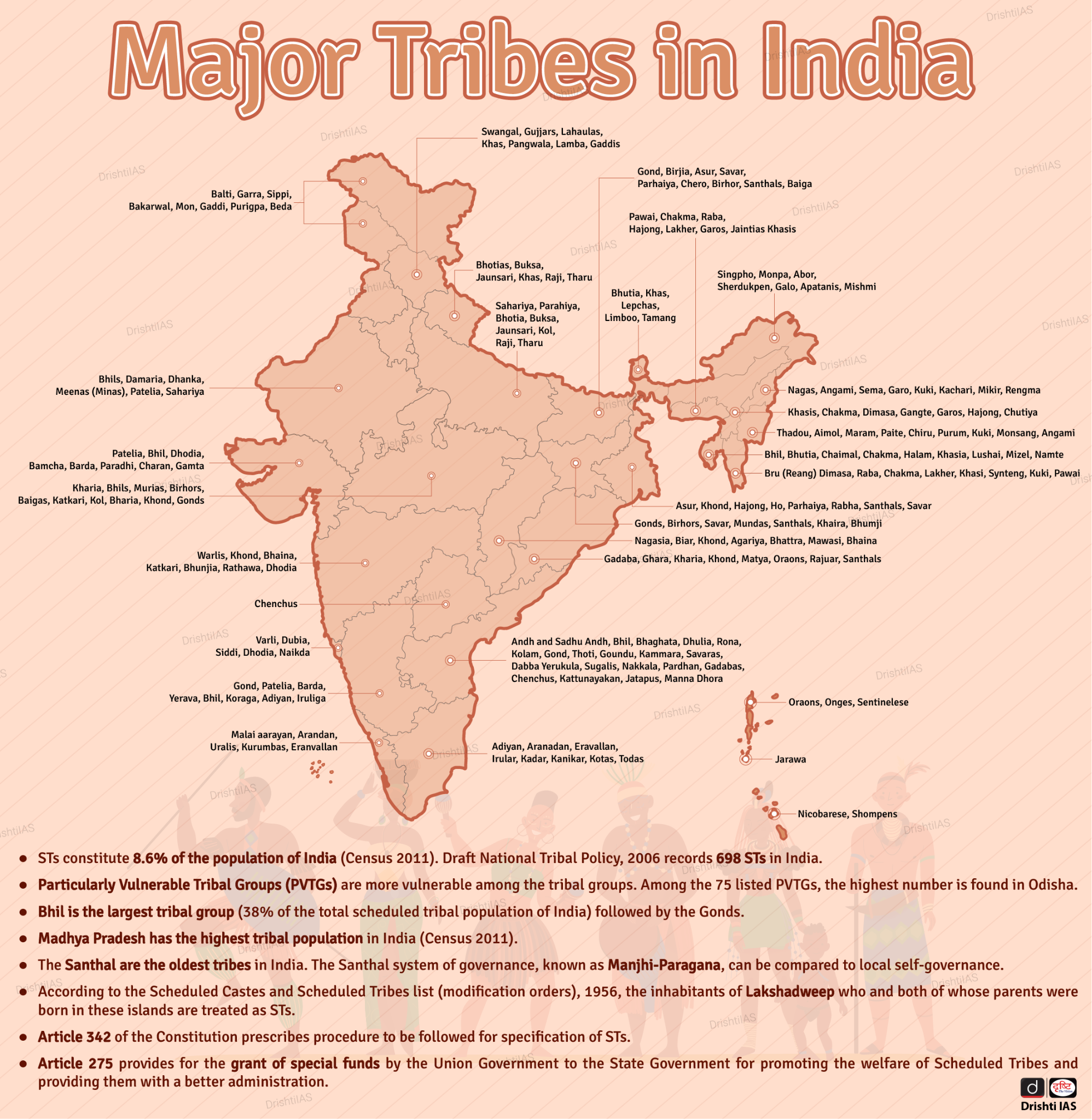
Indian History
Janjatiya Gaurav Divas
- 15 Nov 2024
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Janjatiya Gaurav Divas, Birsa Munda, Santhals, Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan, Van Dhan Vikas Kendras, Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, National Overseas Scholarship
For Mains: Tribal Development Initiatives, Tribal Movements and India's Freedom Struggle
Why in News?
Janjatiya Gaurav Divas, celebrated annually on 15th November, honors the invaluable contributions of India’s tribal communities, especially in the nation’s freedom struggle.
- This day marks the birth anniversary of Birsa Munda, a revered tribal leader and freedom fighter. The Prime Minister of India released a commemorative coin and postal stamp in honour of Birsa Munda, paying tribute to his enduring legacy.
What is Janjatiya Gaurav Divas?
- Background: First celebrated in 2021, the day was instituted to recognize the sacrifices of tribal freedom fighters as part of the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, celebrating 75 years of India's independence.
- Key Highlights of the Janjatiya Gaurav Divas 2024:
- PM-JANMAN: The PM participated in the inauguration of 11,000 houses under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN).
- 23 Mobile Medical Units (MMUs) were launched to improve healthcare accessibility in remote tribal areas.
- DAJGUA: Additional 30 MMUs inaugurated under the Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan (DAJGUA).
- Tribal Entrepreneurship & Education: The PM inaugurated 300 Van Dhan Vikas Kendras (VDVKs) and 10 Eklavya Model Residential Schools(EMRS) for tribal students, while also laying the foundation stone for 25 more EMRS.
- Cultural Preservation: Two Tribal Freedom Fighters' Museums were inaugurated in Chhindwara and Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh along with two Tribal Research Institutes in Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir, and Gangtok, Sikkim.
- PM-JANMAN: The PM participated in the inauguration of 11,000 houses under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN).
Who was Birsa Munda?
- Early Life: Born on 15th November 1875, in the Chota Nagpur Plateau region. He belonged to the Munda tribe, an indigenous community in present-day Jharkhand.
- Spent childhood moving between villages with his parents, experiencing firsthand the challenges faced by tribal communities.
- Founder of the Birsait Sect: Munda became aware of the British colonial rule and missionary efforts to convert tribal populations.
- Birsa Munda established the Birsait sect, which sought to revive tribal identity and resist religious conversion.
- Attracted followers from the Munda and Oraon communities(ethnic group inhabiting the Indian states of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Chhattisgarh), uniting them against colonial and missionary control.
- Role in Tribal Mobilization: Spent significant time in Chaibasa, Jharkhand from 1886 to 1890, where he was influenced by the Sardars' agitation.
- Became deeply involved in anti-British and anti-missionary activities, strengthening his resolve to fight for tribal rights.
- Mobilized the tribal community to challenge the British and protect tribal lands and culture.
- In 1899, he launched the Ulgulan (The Great Tumult) movement, which included guerrilla warfare tactics to resist British authority and promote the establishment of a self-governed tribal state known as "Birsa Raj"
- Became deeply involved in anti-British and anti-missionary activities, strengthening his resolve to fight for tribal rights.
- Arrest and Death: Arrested by British police in 1900, with his guerilla group in the Jamkopai forest.
- Died under mysterious circumstances in Ranchi jail on 9th June 1900, at the young age of 25.
- Legacy: Known for compelling colonial authorities to introduce laws protecting tribal land rights.
- The state of Jharkhand was established on his birth anniversary in 2000, honoring his contributions to tribal rights and the freedom movement.
Sardari Agitation
- The Sardari Agitation(1858-90) was a response to the socio-economic exploitation in Chotanagpur, triggered by agrarian discontent over forced labor (beggars) and illegal rent hikes by intermediaries. Led by the Sardars, the movement aimed to resist these oppressive practices.
What are India’s Key Initiatives Supporting Tribal Development?
- Financial and Social Initiatives:
- Financial Commitments: The Union Budget allocated Rs 13,000 crore to the Ministry of Tribal Affairs in 2024-25, reflecting a 73.6% increase from 2023-24.
- DAJGUA: Launched with a Rs 79,156 crore outlay to address social infrastructure gaps across tribal areas, benefiting over 5.38 crore people in 63,843 villages.
- PM-JANMAN: Initiated in 2023 to support Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) with targeted schemes, including healthcare, financial inclusion, and community support.
- Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana: PMAAGY aims to provide basic infrastructure in villages with a significant tribal population.
- Around 36500 villages having 50% tribal population and 500 Scheduled Tribes (STs) have been identified for providing basic infrastructure facilities, including villages in the Aspirational Districts identified by NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India).
- Education:
- EMRS: Established to offer quality education to Scheduled Tribes students in remote areas, helping bridge educational gaps.
- Adivasi Shiksha Rinn Yojana (ASRY): Offers soft loans for tribal students pursuing higher education.
- Scholarships for Tribal Students: Scholarships include Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarships, National Overseas Scholarship for international education, and National Fellowship for financial support in higher education.
- Income Generation Schemes: The Term Loan Scheme offers up to 90% business loans, Adivasi Mahila Sashaktikaran Yojna provides concessional loans for tribal women to support entrepreneurship, and Micro Credit Scheme supports tribal groups with loans up to Rs 5 lakh.
- Health and Welfare Initiatives:
|
Drishti Mains Question: Tribal communities in India have played a pivotal role in the country’s freedom struggle. Discuss the contributions of various tribal groups in the Indian independence movement. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (2019)
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: C
Q.2 Consider the following pairs: (2013)
| Tribe | State | |
| 1. | Limboo (Limbu) | Sikkim |
| 2. | Karbi | Himachal Pradesh |
| 3. | Dongaria Kondh | Odisha |
| 4. | Bonda | Tamil Nadu |
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)? (2017)
Q. Why are the tribals in India referred to as ‘the Scheduled Tribes’? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. (2016)