RBI Imposes Restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank | 17 Feb 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has imposed strict restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank Ltd (PPBL). This move comes after an audit report highlighted persistent non-compliances and supervisory concerns within the bank.
What are the Key Restrictions Imposed on PPBL?
- Background: Section 35A of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, confers authority upon the RBI to issue directives to banks and undertake necessary actions to prevent the operations of any banking entity from being conducted in a manner detrimental to the interests of depositors or prejudicial to the bank's own interests.
- In this case, sources indicate concerns over dubious transactions involving significant sums of money between Paytm and its associated banking entity prompted the RBI to take action against the business.
- PPBL reportedly had numerous non-compliant accounts lacking proper KYC verification, with thousands of instances where a single PAN was used to open multiple accounts.
- Additionally, transactions exceeding regulatory limits in minimum KYC prepaid instruments raised red flags about potential money laundering activities.
- In this case, sources indicate concerns over dubious transactions involving significant sums of money between Paytm and its associated banking entity prompted the RBI to take action against the business.
- Key Restrictions:
- Deposit Bar: PPBL is barred from accepting further deposits, top-ups, or credit transactions into its accounts or wallets from 29th February, 2024.
- This also applies to its prepaid instruments for FASTags and National Common Mobility Cards (NCMC) cards.
- Service Limitations: The ban extends to banking services such as Aadhaar Enabled Payment System, Immediate Payment Service, bill payments, and UPI transactions.
- The bank must settle all pipeline and nodal account transactions by 29th March, with no further transactions permitted thereafter.
- Closure of Nodal Accounts: PPBL is directed to terminate nodal accounts of its parent company and Paytm Payments Services before 29th February, 2024.
- Deposit Bar: PPBL is barred from accepting further deposits, top-ups, or credit transactions into its accounts or wallets from 29th February, 2024.
Note
Nodal accounts serve as specialized bank accounts established by businesses, acting as financial intermediaries.
- These accounts are designed to hold funds collected from participating banks on behalf of consumers, with the primary purpose of later transferring these funds to specific merchants.
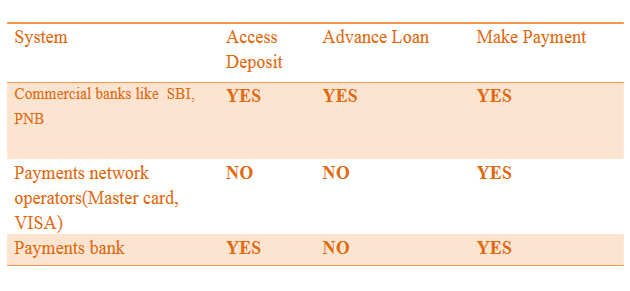
What are Payment Banks?
- About:
- Payment banks are a specialized type of bank introduced by the RBI in 2014. They are designed to promote financial inclusion by offering basic banking services to the unbanked and underbanked population.
- They were introduced on the recommendations of the Nachiket Mor committee set up by the RBI to examine financial services for small businesses and low-income households.
- Example: Airtel Payments Bank, India Post Payments Bank, etc.
- Licensing Requirements: They are licenced under Section 22 (1) of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949
- They fall under the differentiated bank license category of RBI as they are restricted from offering the full range of services provided by commercial banks.
- RBI grants two types of banking licenses: universal bank licenses and differentiated bank licenses.
- They fall under the differentiated bank license category of RBI as they are restricted from offering the full range of services provided by commercial banks.
- Features:
- Reserve Requirements: They are required to maintain the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR).
- Minimum 75% of its demand deposit balances in Statutory Liquidity Ratio eligible G-securities/ T-bills with maturity up to one year.
- Maximum 25% in current and time/ fixed deposits with other scheduled commercial banks apart from maintaining CRR requirements
- Minimum Paid-up Capital: The minimum paid-up equity capital has been fixed at Rs 100 crore.
- The promoter’s minimum initial contribution to the paid-up equity capital shall be at least 40% for the first 5 years.
- Prohibited Services: They are prohibited from conducting lending operations or issuing credit cards.
- Therefore, they are also exempt from priority sector lending regulations that typically apply to traditional banks.
- Rural Outreach Requirements: At least 25% of a Payments Bank’s physical access points have to be in rural centers.
- Reserve Requirements: They are required to maintain the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR).
- Major Activities Performed by Payment Banks:
- Accepting deposits from individuals and small businesses, up to a certain limit (currently set at Rs 2 lakh per account).
- Providing remittance services, and facilitating domestic money transfers.
- Issuing ATM/debit cards, prepaid payment instruments, and other electronic payment methods.
- Offering internet banking services, including online fund transfers and bill payments.