PM's Visit to Nigeria, Brazil and Guyana | 21 Nov 2024
For Prelims: India-Brazil Relations, WTO, Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Line of Credit BRICS, IBSA, G4, G20, Africa, African Continental Free Trade Area, African Union, India’s 2023 G20 Presidency, International Solar Alliance, Indian Ocean Region, Rare earth elements
For Mains: Areas of Cooperation between India and Brazil, India’s relations with Nigeria and Guyana, Significance of Africa for India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India has commenced a significant three-nation visit to Nigeria (Africa), Brazil, and Guyana in South America.
- Following his visit to Nigeria, the PM travelled to Brazil to participate in the 19th G20 Summit and subsequently proceeded to Guyana.
What are the Key Highlights of India-Nigeria Relations?
- Recent Diplomatic Engagement:
- The recent visit by the Indian Prime Minister (PM) to Nigeria in November 2024 marked a significant moment in bilateral relations, being the first visit by an Indian prime minister in 17 years.
- During this visit, his reception included the conferral of Nigeria’s second-highest national award, the Grand Commander of the Order of Niger.
- The recent visit by the Indian Prime Minister (PM) to Nigeria in November 2024 marked a significant moment in bilateral relations, being the first visit by an Indian prime minister in 17 years.
- India-Nigeria Relations:
- Historical Ties: India established its diplomatic presence in Lagos in 1958, just two years before Nigeria gained independence from British colonial rule in 1960, marking the beginning of their bilateral relationship.
- In 2007, both nations elevated their relationship to a "Strategic Partnership".
- Cultural and Educational Exchange: India has played a significant role in Nigeria's development, especially in the fields of education and healthcare.
- India established the National Defence Academy in Kaduna and the Naval War College in Port Harcourt, contributing to Nigeria’s military training and capacity-building.
- Economic Engagement: India-Nigeria economic ties hold significant importance, with over 200 Indian companies investing approximately USD 27 billion across key sectors such as manufacturing, telecommunications, and pharmaceuticals.
- This robust partnership positions India as the second-largest employer in Nigeria after the Federal Government.
- Developmental Assistance: India has positioned itself as a key development partner for Nigeria, offering developmental assistance through concessional loans totalling USD 100 million.
- This assistance reflects India's commitment to supporting Nigeria’s socio-economic development and aligns with India's broader vision of fostering growth in the Global South.
- Regional Influence: Nigeria, known as the "Giant of Africa," has Africa's largest population (~220 million) and the largest economy in the continent.
- As a founding member of the African Union (AU), Nigeria plays a pivotal role in African politics and regional stability.
- Strategic Interests: India seeks stronger ties with Nigeria to counter China's growing influence, as China has become Africa's largest trading partner over the past two decades.
- India acknowledges Africa's wealth of critical minerals, which are essential for industries like electric vehicles and vital for India's economic goals.
- Focus on Common Challenges: Both nations share common challenges such as terrorism, separatism, piracy, and drug trafficking.
- Cultural Significance: The relationship is enriched by a large Indian expatriate (about 60,000) community in Nigeria, which is the largest in West Africa.
- This fosters cultural ties and economic collaboration through cultural exchanges, educational initiatives, and people-to-people interactions.
- Historical Ties: India established its diplomatic presence in Lagos in 1958, just two years before Nigeria gained independence from British colonial rule in 1960, marking the beginning of their bilateral relationship.
- Opportunities in India-Nigeria Relations:
- Healthcare Cooperation: India is the leading destination for Nigerian medical tourists, with affordable and quality healthcare services.
- Defence Collaboration: Nigeria seeks enhanced defence cooperation with India in areas like training, equipment supply, and counter-insurgency strategies, particularly to combat groups like Boko Haram.
- Business and Economic Cooperation: To boost trade and investment, forming an India-Nigeria Business Council with leading business houses from both countries could help identify and develop new opportunities.
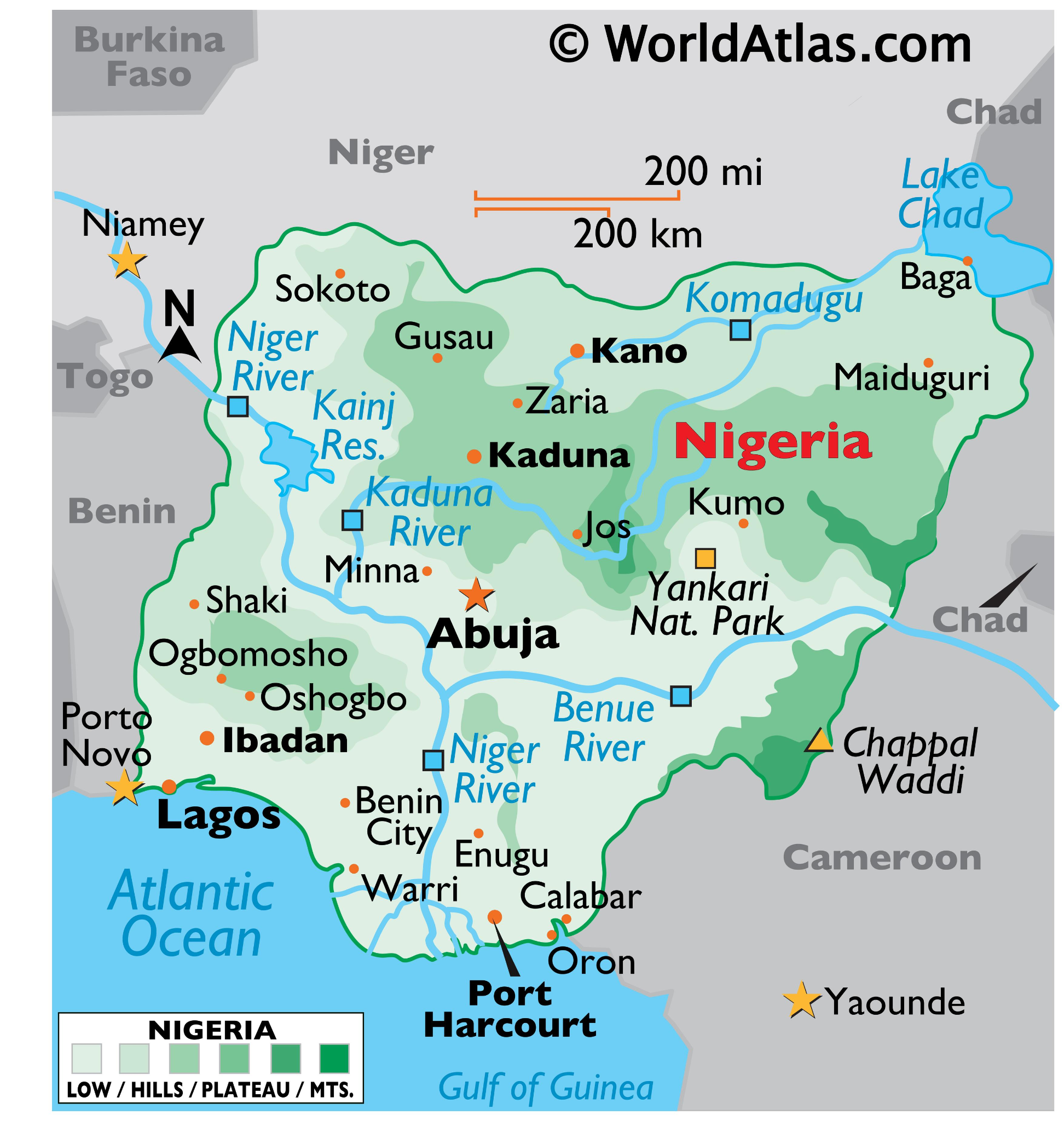
Nigeria
- Location: Western coast of Africa, often called the "Giant of Africa."
- Borders: North – Niger, East – Chad and Cameroon, South – Gulf of Guinea, West – Benin.
- Independence: Gained independence from Britain in 1960.
- Official Language: English; local languages include Hausa, Yoruba, Igbo, and Ijaw.
- Geography: Diverse, with climates ranging from arid to humid equatorial.
- Drainage: Major basins include Niger-Benue, Lake Chad, and Gulf of Guinea. The Niger River and its largest tributary, the Benue River, are principal rivers.
What are the Key Highlights of India-Brazil Relations?
- Recent Diplomatic Engagement:
- India and Brazil held bilateral discussions on the sidelines of the 19th G20 Summit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- Both nations focused on strengthening cooperation in sectors such as energy, biofuels, defence, agriculture, healthcare, and digital technology.
- India expressed strong support for Brazil's ‘Global Alliance against Hunger and Poverty’ initiative and appreciated Brazil's leadership during its G20 Presidency.
- Brazil emphasised the urgency of addressing global climate challenges, calling for decisive action at UNFCCC COP29 climate talks in Azerbaijan, ahead of the COP30 summit in Belem, Brazil, in 2025.
- Brazil supports India's candidature for a non-permanent seat of the UNSC for the 2028-2029 term.
- India-Brazil Relations:
- Institutional Engagements:
- India and Brazil share a robust and multifaceted relationship, marked by collaborations at bilateral and multilateral levels through platforms such as BRICS, IBSA, G4, G20, BASIC, International Solar Alliance (ISA), WTO, UNESCO, and WIPO.
- Institutional mechanisms like the Strategic Dialogue led by National Security Advisors (NSA), India-Brazil Business Leaders Forum, Economic and Financial Dialogue, and Joint Committee on Science & Technology foster collaboration on trade, defence, science, and economic policy.
- Trade and Investment:
- Bilateral trade between the two nations reached USD 15.2 billion in 2022.
- In 2021, India became the 5th largest trading partner of Brazil with investments spanning sectors such as automobiles, IT, mining, energy, and biofuels.
- The Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) signed with MERCOSUR (Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay) in 2004 further strengthens economic ties.
- Defence Cooperation:
- Defence cooperation is anchored by a 2003 agreement and institutionalised through Joint Defence Committee (JDC) meetings.
- Strategic Dialogue addresses defence and global issues, while a 2020 MoU on Cyber Security with CERT-In highlights cyber cooperation.
- Energy Security:
- Energy security is a vital area, with a 2020 MoU between Indian Oil Corporation and Brazil’s CNPEM promoting bioenergy research.
- Both countries, along with the US, launched the Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) during the G20 summit in 2023 to enhance biofuel production and demand.
- Brazil's expertise in ethanol production supports India’s Ethanol Blending Programme, with Brazil achieving a 27% blend and India targeting 20% by 2025-26, building on its current 15.83%.
- Institutional Engagements:
What are the Key Areas of Engagement Between India and Guyana?
- Recent Diplomatic Engagement:
- The PM's recent visit to Guyana, the first in 56 years, shows India's renewed interest in the Caribbean and Latin America, supported by historical ties with the Indian diaspora and Guyana's growing oil sector.
- India-Guyana Relations:
- Historical and Diplomatic Ties:
- India established its diplomatic presence in Guyana with the Commission of India in 1965, upgraded to a full-fledged High Commission in 1968.
- Guyana reciprocated by reopening its mission in India in 2004 after economic constraints led to its closure in 1990.
- Development Cooperation and Technical Assistance:
- India provides developmental support through the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program, offering scholarships in diverse fields.
- The ICCR scholarship program also facilitates academic exchange, with over 600 Guyanese scholars trained under these schemes.
- India provides developmental support through the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program, offering scholarships in diverse fields.
- Economic and Trade Relations:
- Indian companies are exploring opportunities in biofuel, energy, minerals, and pharmaceuticals.
- The Joint Business Council between FICCI and the Georgetown Chamber of Commerce facilitates economic cooperation.
- Guyana has engaged actively with India in renewable energy projects, particularly under the International Solar Alliance (ISA). Bilateral collaboration extends to solar energy, biofuels, and sustainable development initiatives.
- Cultural and People-to-People Ties:
- Guyana, with a population where approximately 43.5% are of Indian origin, represents one of the oldest Indian diasporas, having migrated over 185 years ago.
- Cricket serves as a unifying force, with Guyanese players participating in the Indian Premier League (IPL).
- Ayurveda and yoga are gaining popularity, further enhancing cultural connections.
- Competition from China:
- India's efforts to strengthen ties with Guyana face competition from China, which has a significant presence through Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) projects.
- While India committed USD 100 million to a road project in Georgetown, China's larger investments dominate, despite mixed local sentiments about Chinese practices and benefits.
- Historical and Diplomatic Ties:
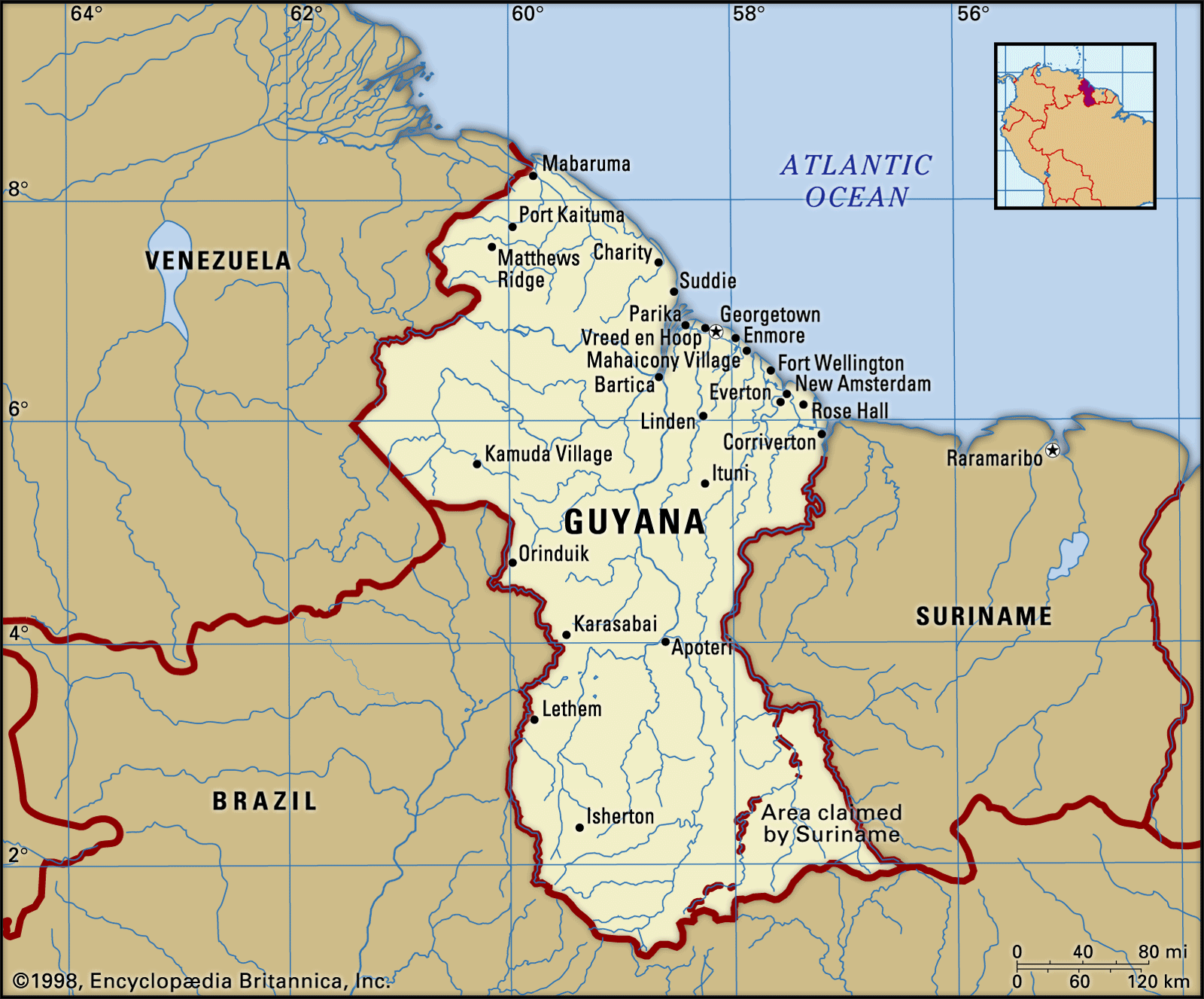
Guyana
- Capital: Georgetown
- Colonised by the UK: Guyana gained independence from the United Kingdom (UK) in 1966 and became a republic in 1970.
- Geography: Located on the northern coast of South America, bordered by Venezuela, Brazil, and Suriname, with the Atlantic Ocean to the north.
- Major Rivers: Essequibo River (largest), Demerara River, and Berbice River.
- Mountains: Pakaraima Mountains, Kanuku Mountains, Acarai Mountains.
PM Received Top National Awards from Guyana, Barbados and Dominica
- The PM of India received the highest national honours from Guyana (Order of Excellence), Barbados (Honorary Order of Freedom of Barbados) and Dominica (Dominica Award of Honour).
- PM was conferred with Dominica's highest National Award for his statesmanship, support to Dominica during the Covid-19 pandemic, and commitment to strengthening India-Dominica ties.
- With these awards, PM international recognition tally now stands at 19.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the key opportunities and challenges in strengthening India-Africa relations in the context of global strategic and economic shifts. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘The long-sustained image of India as a leader of the oppressed and marginalised nations has disappeared on account of its new found role in the emerging global order.’ Elaborate. (2019)