India to host G20 Summit in 2023
For Prelims: G20, International Organisation, India and International Groupings
For Mains: India’s foreign policy, Significance of G20 in India’s Foreign Policy, Challenges of global happenings on international groupings
Why in the News?
Recently, the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) announced that India is hosting the G-20 (Group of 20) leaders’ summit in New Delhi next year 2023.
- The 17th G20 Heads of State and Government Summit will happen in November 2022 in Indonesia, after which India will assume the presidency of G20 from December 2022.
- India is assuming the Presidency of the G20 for one year.
What are the Key Points?
- Guest Countries:
- India, as G20 Presidency, will be inviting Bangladesh, Egypt, Mauritius, Netherlands, Nigeria, Oman, Singapore, Spain and UAE as Guest countries.
- Troika:
- During the Presidency, India, Indonesia and Brazil would form the troika. This would be the first time when the troika would consist of three developing countries and emerging economies, providing them a greater voice.
- Troika refers to the top grouping within the G20 that consists of the current, previous and the upcoming presidencies (Indonesia, India and Brazil).
- During the Presidency, India, Indonesia and Brazil would form the troika. This would be the first time when the troika would consist of three developing countries and emerging economies, providing them a greater voice.
- Key Priorities:
- Inclusive, Equitable and Sustainable Growth,
- LiFE (Lifestyle For Environment),
- Women’s Empowerment,
- Digital public infrastructure and tech-enabled development in areas ranging from health, agriculture and education to commerce,
- Skill-mapping, culture and tourism, climate financing, circular economy, global food security, energy security, green hydrogen, disaster risk reduction and resilience,
- Developmental cooperation, fight against economic crime, and multilateral reforms.
What is the G20?
- About:
- The G20 was formed in 1999 in the backdrop of the financial crisis of the late 1990s that hit East Asia and Southeast Asia in particular.
- It aims to secure global financial stability by involving middle-income countries.
- Together, the G20 countries include 60 % of the world’s population, 80 % of global GDP, and 75 % of global trade.
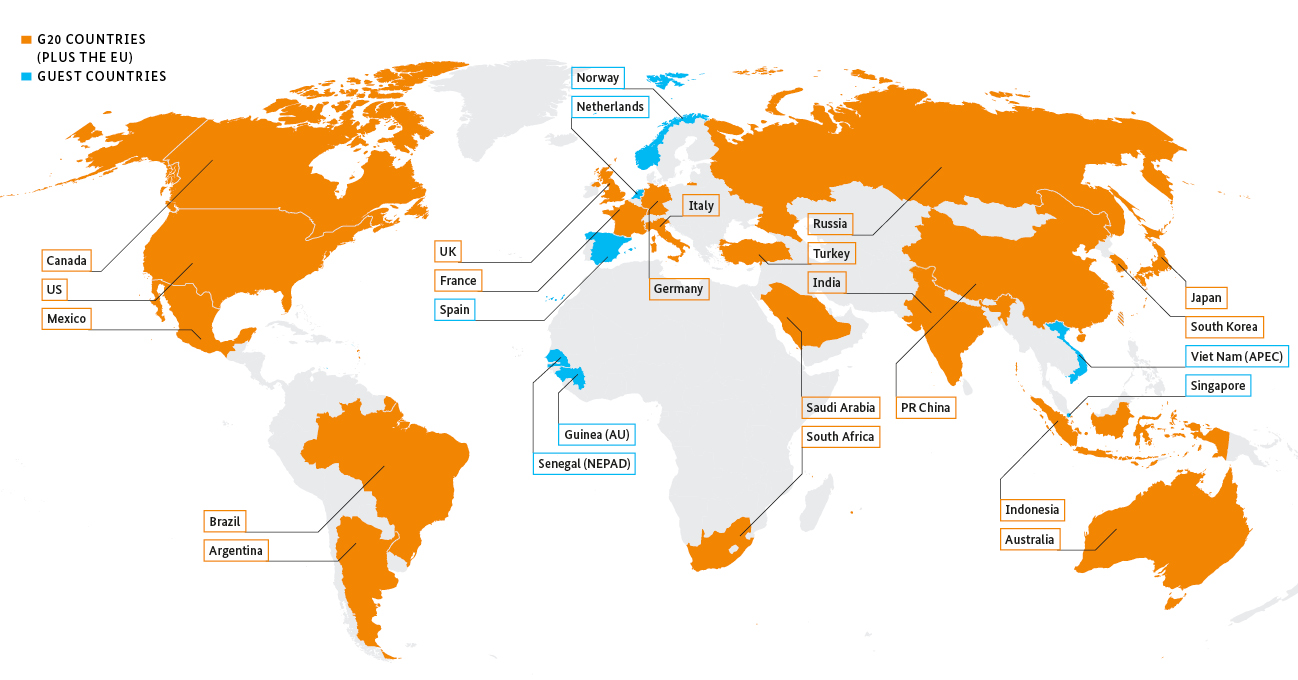
- Members:
- Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the EU.
- Spain is invited as a permanent guest.
- Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the EU.
- Presidency:
- The presidency of the G20 rotates every year among members, and the country holding the presidency, together with the previous and next presidency-holder, forms the ‘Troika’ to ensure continuity of the G20 agenda.
- Italy, Indonesia, and India are the Troika countries right now and Indonesia holds the current Presidency.
- The presidency of the G20 rotates every year among members, and the country holding the presidency, together with the previous and next presidency-holder, forms the ‘Troika’ to ensure continuity of the G20 agenda.
- Mandate:
- The G20 has no permanent secretariat. The agenda and work are coordinated by representatives of the G20 countries, known as ‘Sherpas’, who work together with the finance ministers and governors of the central banks.
- The primary mandate of the grouping is for International Economic cooperation with particular emphasis to prevent future financial crises across the world.
- It plays a significant role in shaping the global economic agenda.
- From 1999-2008 the forum exalted from a grouping of Central bank governors and finance ministers to Heads of states.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)