Indian History
Iron Age and and Urbanization
- 28 Jan 2025
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Iron Age, Indus Valley Civilisation, Bronze Age, Arthashastra, NBPW Culture, Vindhyas, Megalithic Culture, Urbanization, Ganga Valley.
For Mains: Iron age in India, Role of iron technology in states formation and urbanisation
Why in News?
A report titled ‘Antiquity of Iron: Recent Radiometric Dates from Tamil Nadu’, claims that use of iron in Tamil Nadu dates back to the first quarter of the 4th millennium BCE.
- The Iron Age in India is believed to have emerged between 1500 and 2000 BCE, closely following the Indus Valley Civilisation (Bronze Age).
What is the Iron Age?
- About: The Iron Age is a prehistoric period that followed the Bronze Age, characterized by the widespread use of iron for tools, weapons, and other implements.
- Iron metallurgy involves multiple stages, including ore procurement and manufacturing tools.
- Antiquity of Iron in India:
- Rigvedic Period: No knowledge of iron was recorded.
- Early Historic Period: References to iron smithing are found in early Buddhist literature and Kautilya’s Arthashastra.
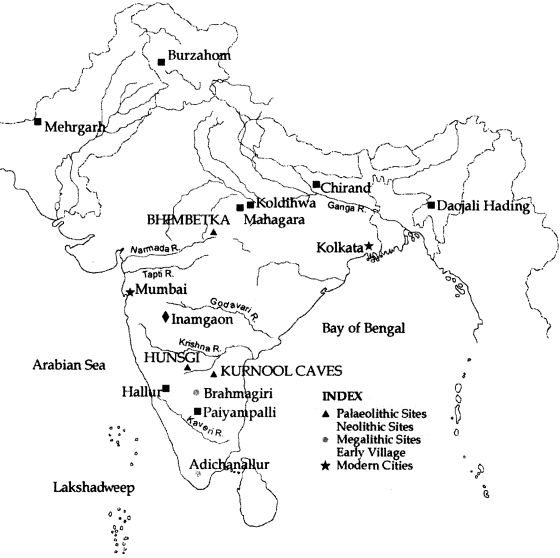
- Significant Excavation Sites:
- Raja Nal Ka Tila (North-Central India): Iron tools and slag found in pre-NBP (Northern Black Polished) deposits (1400–800 BCE).
- Malhar (Chandauli, Uttar Pradesh): Evidence of iron tools, furnaces, and slag indicates it was an important iron metallurgy center.
- Cultural Associations:
- Black-and-Red Ware (BRW): Characterized by distinctive pottery with black interiors and red exteriors due to inverted firing techniques.
- It is found in Harappan context (Gujarat), Pre-PGW context (northern India), and Megalithic context (southern India).
- Painted Grey Ware (PGW) Culture: Characterized by grey pottery with black geometric patterns.
- Iron reported at multiple sites in the Ganga valley and South Indian Megaliths (1st millennium BCE).
- Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW) Culture: Wheel-made pottery which is fine, black, and highly polished. Significant in north India.
- During 700 BCE-100 BCE (NBPW Culture period), the formation of states and emergence of urbanism in the Ganga valley crystallized.
- NBPW Culture was associated with 2nd Urbanization in the Ganga Valley (6th century BCE) during which Buddhism flourished.
- Ahar Chalcolithic Culture:
- Middle phase (2500–2000 BCE): Evidence of iron artifacts.
- Late phase (2000–1700 BCE): Iron usage became more prominent.
- Megalithic Culture: Megaliths (large stones used to construct a prehistoric structure), linked to iron, are found in the Vindhyas (southern Uttar Pradesh), Vidisha region, and much of South India.
- Black-and-Red Ware (BRW): Characterized by distinctive pottery with black interiors and red exteriors due to inverted firing techniques.
Megalithic Culture Relationship with Iron
- Megalithic Culture: It is a prehistoric phase marked by large stone structures used for burials, sacred spaces, and rituals.
- The Megalithic culture in south India is closely associated with the beginning of iron usage.
- Iron Uses: Around 33 types of iron tools have been identified from Megalithic burials. These served various purposes:
- Agriculture: Hoes, sickles, and axes.
- Domestic use: Dishes and tripod stands.
- Artisanal activities: Chisels and nails.
- War and hunting: Swords, daggers, spears, and arrowheads.
- Notable Evidence of Iron Use:
- Naikund (Vidarbha): Discovery of an iron smelting furnace.
- Mahurjhari (Nagpur): Head ornaments for horses made of copper sheets with iron knobs.
- Paiyampalli (Tamil Nadu): Large quantities of iron slag, indicating local iron smelting.
- Advancements in Iron Technology: People learned to control fire and extract iron from ore, marking a key technological advance.
How Iron Technology Helped in Urbanization in the Ganga Valley?
- About Urbanization: According to historian, and archaeologist Gordon V. Childe, urbanization relies on surplus production, leading to ruling classes, social stratification, and monumental architecture.
- It refers to the shift from agriculture-based economies to industries, services, and trade as the primary sources of income.
- Role of Iron Technology: The 2nd Urbanization in the Ganga Valley (6th century BCE) was marked by the proliferation of settlements and Iron technology played a pivotal role by:
- Clearing Forests: Iron tools enabled deforestation, creating arable land.
- Boosting Agricultural Productivity: Iron plows enhanced efficiency and yields.
- Agricultural Surplus: Increased productivity supported large populations and complex societies.
- The first urbanization (2500 and 1900 BCE) in India was during the Indus Valley Civilization.
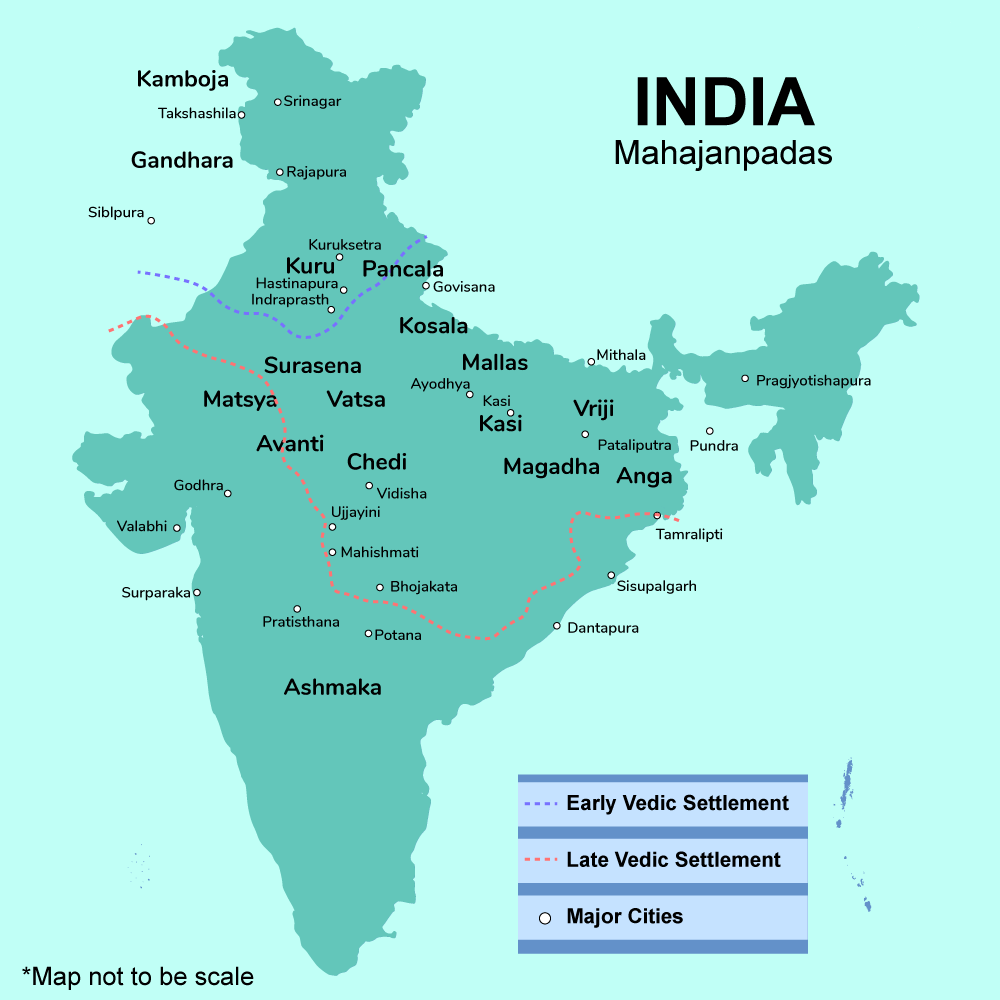
- Impact on Urbanization: It led to development of 16 Mahajanapadas in the Indian subcontinent.
- Population Growth: The agricultural surplus facilitated population growth, essential for the development of urban centers.
- Development of Settlements: Settlements grew in number and complexity, showing a clear hierarchy.
- Social Stratification and State Formation: Surplus production enabled the emergence of ruling classes, social hierarchy (e.g., varna system), and centralized power structures.
- Trade and Craft Specialization: Surplus allowed people to engage in non-agricultural activities like trade and crafts, leading to economic diversification and urban growth.
Conclusion
Iron technology played a crucial role in the development of urban centers in ancient India, especially in the Ganga Valley. It boosted agricultural productivity, supported population growth, and enabled the rise of social hierarchies and state formation, marking a significant shift towards urbanization during the second urbanization phase.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the role of iron technology in the urbanization of the Ganga Valley. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.With reference to the difference between the culture of Rigvedic Aryans and Indus Valley people, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- Rigvedic Aryans used the coat of mail and helmet in warfare whereas the people of Indus Valley Civilization did not leave any evidence of using them.
- Rigvedic Aryans knew gold, silver and copper whereas Indus Valley people knew only copper and iron.
- Rigvedic Aryans had domesticated the horse whereas there is no evidence of Indus Valley people having been aware of this animal.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. Which of the following Kingdoms were associated with the life of the Buddha? (2014)
- Avanti
- Gandhara
- Kosala
- Magadha
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2 and 4
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. The ancient civilization in the Indian sub-continent differed from those of Egypt, Mesopotamia and Greece in that its culture and traditions have been preserved without a breakdown to the present day. Comment. (2015)