Important Facts For Prelims
Megalithic Burial Sites
- 15 Nov 2022
- 3 min read
Why in News?
According to recent findings, Andhra Pradesh has the largest anthropomorphic burial site collection in Tirupati district.
- Anthropomorphic sites are those marked by a representation of human form above the megalithic burials.
What are Megaliths?
- A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones.
- Megaliths were constructed either as burial sites or commemorative (non-sepulchral) memorials.
- The former are sites with actual burial remains, such as dolmenoid cists (box-shaped stone burial chambers), cairn circles (stone circles with defined peripheries) and capstones (distinctive mushroom-shaped burial chambers found mainly in Kerala).
- The urn or the sarcophagus containing the mortal remains was usually made of terracotta. Non-sepulchral megaliths include memorial sites such as menhirs.
- In India, archaeologists trace the majority of the megaliths to the Iron Age (1500 BC to 500 BC), though some sites precede the Iron Age, extending up to 2000 BC.
- Megaliths are spread across the Indian subcontinent. The majority of megalithic sites are found in Peninsular India, concentrated in the states of Maharashtra (mainly in Vidarbha), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
What are the Different Types of Megalithic Structure?
- Stone Circles: Stone circles are commonly called "cromlechs" (a word in the Welsh language); the English word "cromlech" is sometimes used in that sense.
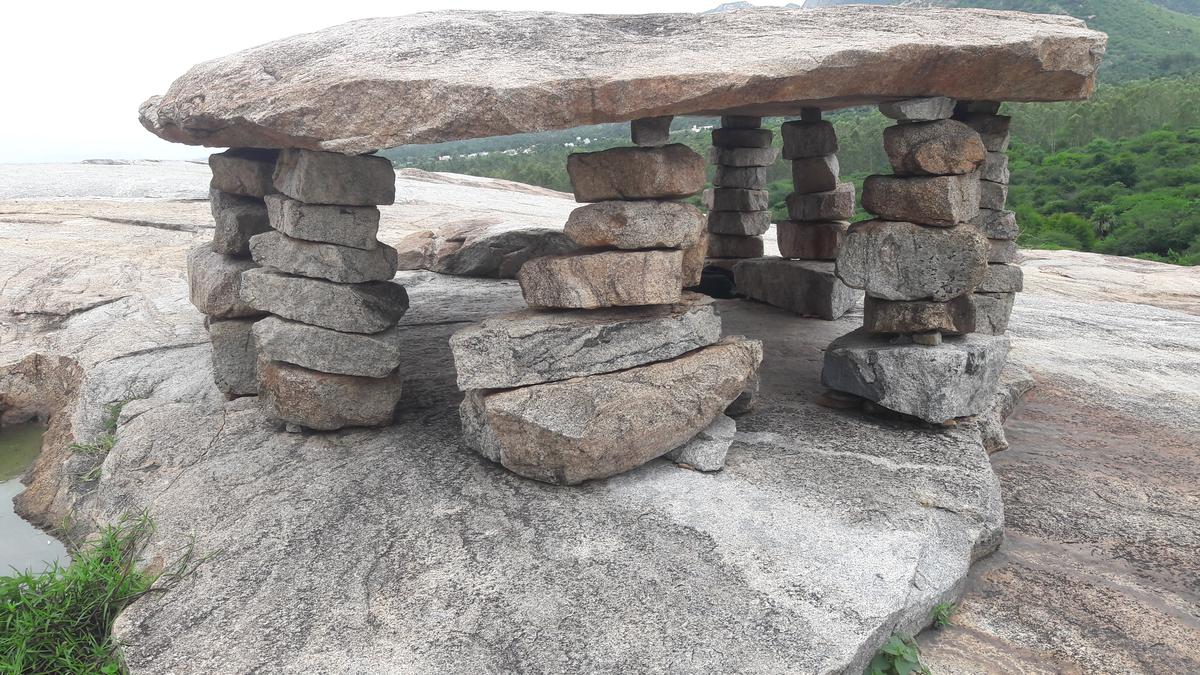
- Dolmen: A dolmen is a megalithic structure formed by placing a large capstone on two or more support stones, forming a chamber below, sometimes closed in on three sides. Often used as a tomb or burial chamber.
- Cist: Cist is a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead. Burials are megalithic forms very similar to dolmens in structure. These types of burials were completely underground. There were single- and multiple-chambered cists.
- Monolith: Any single standing stone erected in prehistoric times. Sometimes synonymous with “megalith” and “menhir”; for later periods, the word monolith is more likely to be used to describe single stones.
- Capstone style: Single megaliths placed horizontally, often over burial chambers, without the use of support stones.