India’s Goods Exports Touches New Height | 17 Apr 2024
For Prelims: Status of India’s Exports, Trends in Exports
For Mains: India's Export Outlook, challenges and Way forward
Why in News?
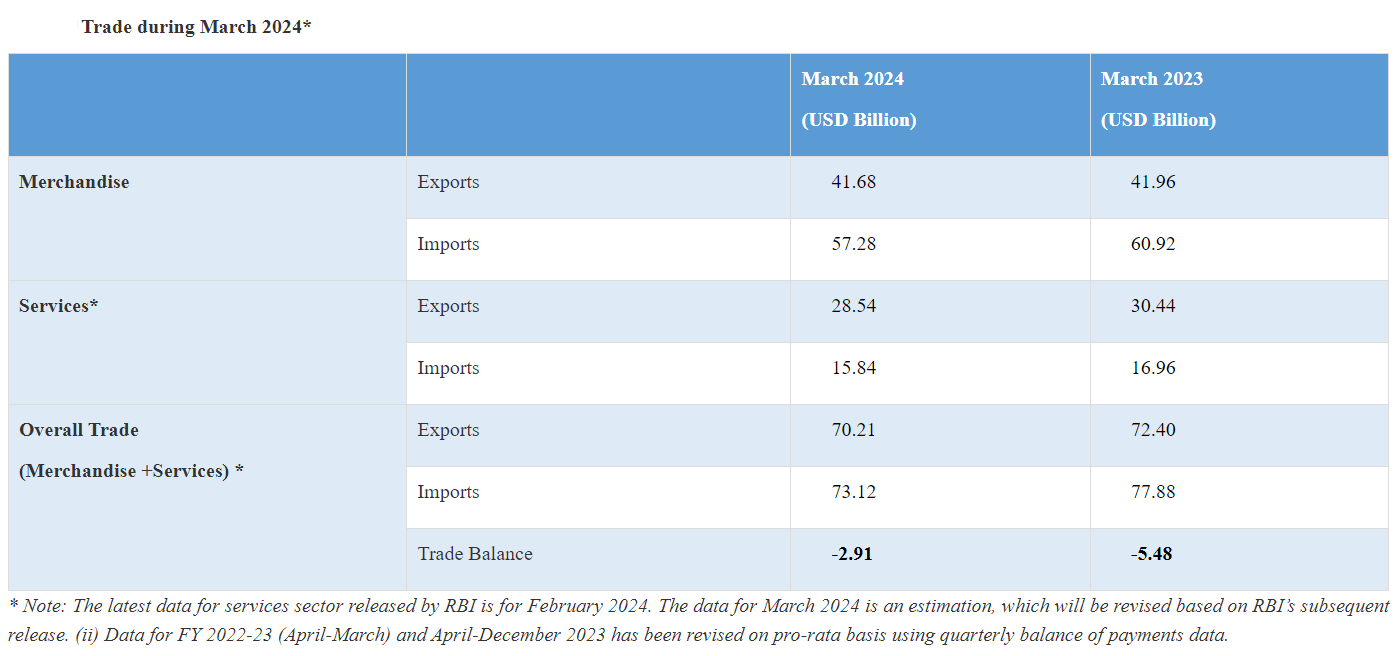
India's merchandise exports reached a peak of USD 41.68 billion in March 2024 compared to the FY 2022-23.
What does the Current Export Data Reveal?
- About:
- India’s goods exports reached USD 41.68 billion in March 2024 compared to the FY 2022-23, despite a 0.67% decline from last year’s tally,
- Imports, on the other hand, dropped by 6% to USD 57.3 billion during the same period.
- The goods trade deficit contracted to USD 15.6 billion, the lowest in 11 months.
- Key Factors:
- Gold Imports Decline: Gold imports fell sharply by 53.6% in March to USD 1.53 billion.
- Non-Oil, Non-Gold Imports: The drop in non-petroleum, non-gold imports contributed to the overall decline.
- Silver Imports Surge: Interestingly, silver imports jumped to USD 816.6 million.
- Impact on Full-Year Figures (2023-24):
- While goods exports averaged USD 35.4 billion in the first ten months, the last two months’ spike lifted the full-year export figure to USD 437.1 billion.
- This performance is 3.1% below the record USD 451.1 billion achieved in the previous year.
- FY 2023-24 Projections:
- Despite persistent global challenges like the Ukraine war, and the West Asian crisis, overall exports are estimated to surpass last year’s record.
- India’s overall exports (merchandise + services) are estimated to reach USD 776.68 billion.
- This represents a positive growth of 0.04% over the previous fiscal year (FY 2022-23).
- Despite global challenges, this figure slightly edges out the USD 776.40 billion recorded in FY 2022-23.
- Despite persistent global challenges like the Ukraine war, and the West Asian crisis, overall exports are estimated to surpass last year’s record.
- Merchandise Export Drivers: Key contributors to merchandise export growth include:
- Electronic Goods: Exports increased by 23.64% to USD 29.12 billion.
- Drugs & Pharmaceuticals: Exports rose by 9.67% to USD 27.85 billion.
- Engineering Goods: Exports grew by 2.13% to USD 109.32 billion.
- Agricultural Commodities Show Positive Growth:
- Exports of agricultural commodities, such as tobacco, fruits, vegetables, meat, dairy products, spices, and oil seeds, exhibited positive growth in FY 2023-24.
- Trade Deficit Improvement:
- The overall trade deficit is estimated to significantly improve by 35.77% to USD 78.12 billion in FY 2023-24.
- Merchandise trade deficit improved by 9.33% to USD 240.17 billion compared to FY 2022-23.
- Current Account Balance Outlook:
- The easing of the goods trade deficit in March is expected to augur well for the current account balance in the final quarter of FY 2023-24.
What Should be the Strategy to Further Enhance India’s Exports?
- Cost Optimisation:
- Land, Power, and Capital Costs: The government must urgently address cost-related challenges associated with land acquisition, power tariffs, and capital availability.
- Scale and Efficiency: Encouraging economies of scale can significantly reduce cost disabilities for businesses.
- Enhancing Competitiveness:
- Infrastructure and Logistics: Improving transportation networks, ports, and warehousing facilities will enhance supply chain efficiency.
- Labour Flexibility: Streamlining labour laws and ensuring flexibility can make Indian companies more competitive.
- MSME Support: Strengthening Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) will contribute to overall competitiveness.
- Market Access via Trade Treaties:
- India should actively negotiate and sign trade agreements with key trading partners to facilitate market access for its exports.
- Bilateral and multilateral treaties can open up new avenues for Indian products globally.
- Technology and Quality Focus:
- Investing in research and development (R&D) and adopting advanced technologies will enhance product quality.
- Quality certifications and adherence to international standards are crucial for gaining consumer trust.
- Promoting Brand India:
- The government and industry bodies should collaboratively promote “Brand India” on the global stage.
- Highlighting India’s rich cultural heritage, skilled workforce, and innovative capabilities will attract international buyers.
- China Plus One Strategy:
- Encouraging multinational companies to diversify their manufacturing base away from China is essential.
- India can position itself as an attractive alternative for investment and production.
- By implementing these strategies, India can not only sustain its export growth but also surpass previous records, contributing to economic prosperity and global trade dynamics
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the potential and challenges of enhancing India's export competitiveness in the global market. Highlight key sectors with high export potential and strategies to leverage them for sustainable economic growth. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The SEZ Act, 2005 which came into effect in February 2006 has certain objectives. In this context, consider the following: (2010)
- Development of infrastructure facilities.
- Promotion of investment from foreign sources.
- Promotion of exports of services only.
Which of the above are the objectives of this Act?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2021)
The effect of devaluation of a currency is that it necessarily
- improves the competitiveness of the domestic exports in the foreign markets
- increases the foreign value of domestic currency
- improves the trade balance
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. How would the recent phenomena of protectionism and currency manipulations in world trade affect macroeconomic stability of India? (2018)