World History
Disintegration of the Soviet Union
- 03 Jan 2025
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Soviet Union, Five-Year Plans, NATO, IMF, World Bank, European Union, Nagorno-Karabakh, ASEAN, BrahMos missile, International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
For Mains: Disintegration of USSR and its Impact on India and the World. World War II, Berlin Wall’s fall in 1989, Bipolar Global Order , Cold War, Liberalization in 1991, Space Technology, Nuclear Energy.
Why in News?
Recently, 25th December marked the anniversary of the day when the Soviet flag was taken down from the Kremlin (Russian government’s ‘power centre’), marking the end of the Soviet Union.
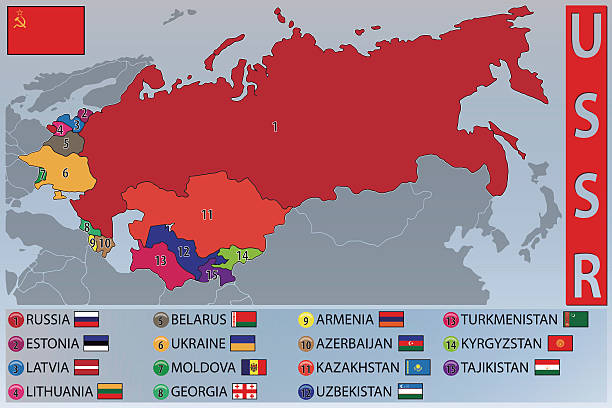
- The Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was a socialist federation from 1922 to 1991, consisting of multiple republics, governed by the Communist Party, with Russia as the dominant power.
What Led to the Formation of the Soviet Union?
- History (Tsarist Regime and Monarchy): The Soviet Union's roots trace back to the Russian Revolution of 1917, which ended the Romanov dynasty's 300-year reign (1613-1917).
- The Tsar wielded absolute power over governance, the military, and society.
- Rising inequality and economic hardship triggered dissatisfaction, setting the stage for revolution.
- February Revolution 1917: Protests and strikes culminated in Tsar Nicholas II’s abdication, ending the monarchy.
- A Provisional Government replaced the Tsar but faced power struggles with the Petrograd Soviet, dominated by socialist factions like the Bolsheviks and Mensheviks.
- October Revolution 1917: Lenin and Trotsky led the Bolsheviks in the October Revolution, overthrowing the Provisional Government and declaring “all power to the Soviets.”
- This marked the establishment of Soviet rule and the start of communist policies like nationalization.
- Russian Civil War 1918-1922: The Red Army battled anti-Bolshevik forces (White Guards) during the civil war.
- The Bolsheviks emerged victorious, consolidating power and paving the way for a unified state.
- Formation of the USSR (30th December 1922): The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was officially declared, becoming the world’s first communist state.
- Lenin’s leadership introduced centralized economic planning and communist governance.
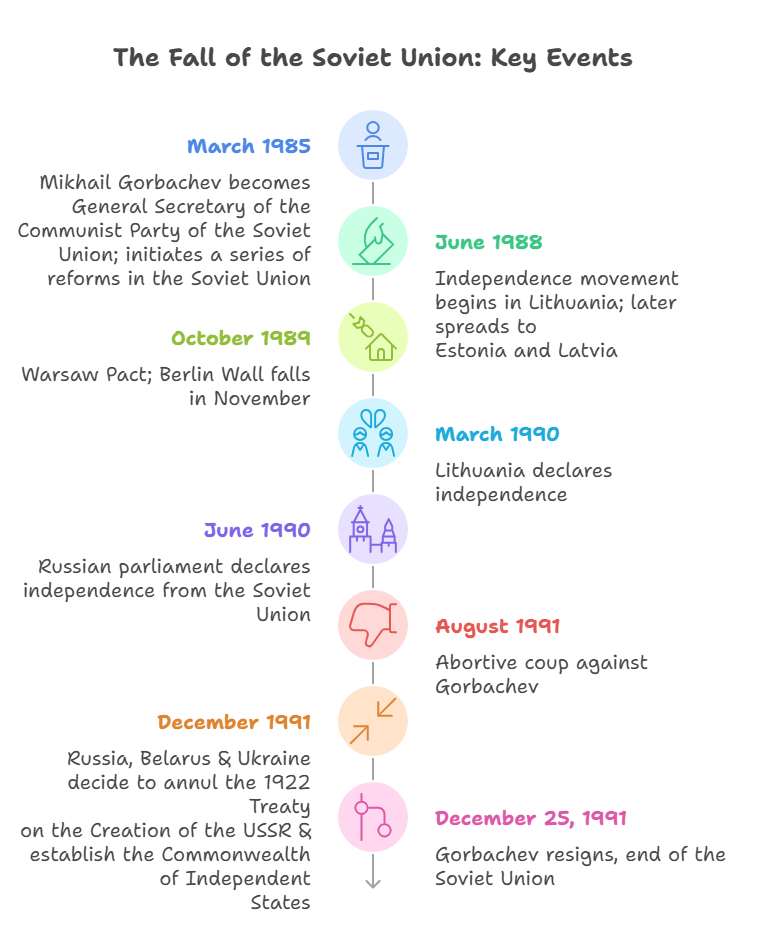
- Soviet leadership evolved from Lenin’s Bolshevik consolidation to Stalin's centralization, the Great Purge of 1936, and Soviet Union’s victory over Nazi Germany, followed by Khrushchev's reforms, Brezhnev's stability, and Gorbachev's restructuring efforts.
- World War II and Lithuania- 1940s: The Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania) were forcibly incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1940 (World War II) following the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.
- These Baltic states had gained independence in 1918, after the collapse of the Russian Empire
- Post-war, the USSR emerged as a superpower (Warsaw Pact), leading the socialist bloc and dominating Cold War geopolitics.
How did Various Challenges Lead to the Dissolution of the USSR?
- Economic Stagnation: By the 1970s, the Soviet economy lagged in productivity and technology, with overemphasis on military and satellite states draining resources.
- Citizens faced consumer shortages and rising dissatisfaction, despite state subsidies ensuring a minimum standard of living .
- Gorbachev’s Reforms: Policies of Gorbachev like glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) aimed at reform but inadvertently weakened the Communist Party’s authority.
- Multi-party elections in 1990 and reduced censorship fueled nationalist movements in republics like Lithuania and Ukraine .
- Collapse due to Cold War Pressures: The costly arms race with the US, the defeat in Afghanistan, and the Berlin Wall’s fall in 1989 undermined Soviet control.
- The USSR’s failure to compete with Western economic models magnified internal inefficiencies .
- Nationalist Movements and Secession: Under leaders like Yeltsin, Russian nationalism weakened central control, while the Baltic states and Ukraine sought independence.
- By December 1991, the USSR dissolved into independent states, marking the end of a bipolar global order .
How Did the Soviet Union's Collapse Reshape Global Power Dynamics?
- Emergence of Unipolar World Order: The USSR’s collapse ended the Cold War, leaving the US as the sole superpower, reshaping global alliances.
- NATO expanded eastward, integrating former Soviet bloc countries like Poland and the Baltic states, reducing Russian influence .
- Capitalism Gained Global Dominance: Western institutions like the IMF and World Bank directed economic transitions in former socialist states, promoting liberal democracy and free-market capitalism.
- Eastern Europe’s integration into the European Union reinforced US-led global hegemony .
- Regional Power Shifts Strengthened Multipolarity: The collapse allowed China and India to assert themselves in global geopolitics.
- Central Asian republics emerged as strategic players, balancing ties with Russia, China, and the West.
How Does the Legacy of the Soviet Union's Collapse Influence Contemporary Conflicts?
- Nationalism And Unresolved Disputes: The disintegration left territorial disputes unresolved, including Crimea and Eastern Ukraine, fueling secessionist movements.
- Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea and the ongoing war in Ukraine reflect its effort to reclaim Soviet-era influence .
- Armenia-Azerbaijan Conflict: The Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh stems from Stalin's 1923 decision to transfer the region to Azerbaijan, despite its majority Armenian population.
- This decision sowed the seeds of ethnic tensions, which escalated into conflict after the Soviet collapse, as Armenia and Azerbaijan competed for control
- Kosovo-Serbia Dispute: Kosovo declared independence from Serbia in 2008, but Serbia and several countries still refuse to recognize it.
- Ethnic tensions persist, particularly in Serb-majority regions like Northern Kosovo, contributing to ongoing instability and complicating the Balkan peace process.
- NATO Expansion Escalates Tensions: NATO’s eastward growth is perceived by Russia as a direct threat, exacerbating its security concerns.
- Also, this led to conflicts like that in Afghanistan, and its legacy continues to fuel geopolitical tensions and instability in Eastern Europe and beyond.
- The Russia-Ukraine war symbolizes broader contestation between Western powers and Russian ambitions .
- Energy Resources And Geopolitics Intertwine: In absence of communist ideology and the USSR, Russia leverages its oil, gas, and defense equipment to exert influence, especially over Europe.
How did the Soviet Union’s Collapse Affect India?
- Economic Diversification And Liberalization: The collapse disrupted India’s trade with the USSR, necessitating economic liberalization in 1991 to attract foreign investment.
- India diversified its partnerships through the Look East policy (now Act East Policy) to strengthen ties with ASEAN countries and the recent Act West policy to enhance trade and strategic relations with Western nations.
- Defence Ties Adapted To New Realities: India transitioned from being a mere importer of Russian military hardware to bridging the gap through joint production agreements, such as the BrahMos missile, to meet mutual defense needs.
- India also expanded defense cooperation with the US, France, and Israel to reduce reliance on any single source.
- Geopolitical Realignment For Strategic Autonomy: India balanced relations with Russia and the US, maintaining strong ties with Moscow while engaging in US-led initiatives like the Quad.
- India also joined other organizations like BRICS and SCO to strengthen its strategic autonomy, enhance multilateral partnerships, and promote a more balanced global order.
- Access to Central Asian resources, especially through initiatives like the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), remained a priority .
- Cultural And Scientific Collaborations: Soviet-era cultural exchanges left a lasting legacy, with Indian films and literature enjoying enduring popularity in former Soviet states.
- Collaboration in space technology and nuclear energy continued, enhancing bilateral relations .
|
Drishti Mains Question How did the Soviet Union’s collapse transform the global power structure into a unipolar world? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Which of the following countries share borders with Moldova? (2008)
- Ukraine
- Romania
- Belarus
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Code:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. The New Economic Policy – 1921 of Lenin had influenced the policies adopted by India soon after independence. Evaluate.(2014)