Cyberfraud Costs 0.7% of GDP | 28 Oct 2024
For Prelims: Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), Cyber Frauds, Money Laundering, Phishing, Malware, Cyberbullying, Cyber Spying, Pegasus, National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal, National Cyber Security Policy, Computer Emergency Response Team - India (CERT-In), Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative, Cyber Swachhta Kendra, National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC), Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
For Mains: Economic cost of cyber fraud, threats and way forward.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), which runs under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) made important projections related to cyber frauds.
What is the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)?
- About:
- I4C was launched by the Ministry of Home Affairs in 2020 to deal with all types of cyber crimes including cyber fraud in a comprehensive and coordinated manner.
- Objectives of I4C:
- To act as a nodal point to curb Cybercrime in the country.
- To strengthen the fight against Cybercrime committed against women and children.
- Facilitate easy filing Cybercrime related complaints and identifying Cybercrime trends and patterns.
- To act as an early warning system for Law Enforcement Agencies for proactive Cybercrime prevention and detection.
- Awareness creation among public about preventing Cybercrime.
- Assist States/UTs in capacity building of Police Officers, Public Prosecutors and Judicial Officers in the area of cyber forensic, investigation, cyber hygiene, cyber-criminology, etc
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal:
- Under I4C, the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal is a citizen-centric initiative which will enable citizens to report cyber fraud online and all the complaints will be accessed by the concerned law enforcement agencies for taking action as per law.
What are the Key Highlights of the I4C Projection?
- Financial Impact: Indians are expected to lose over Rs 1.2 lakh crore in 2025 to cyber fraud, siphoning off 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- From January to June, 2024 Rs 11,269 crore was lost to financial fraud.
- Contributors to Cyber Fraud: Approximately 4,000 mule bank accounts are identified daily by I4C.
- I4C has identified 18 ATM hotspots across the country from where money was fraudulently withdrawn.
- A mule account refers to a bank account that is used to facilitate illegal activities such as money laundering and fraudulent transactions.
- Origin of Scam: The government has identified “scam compounds” in South East Asian countries such as Cambodia, Myanmar and Laos from cyber fraudsters.
- Most scams have origins in China or Chinese-linked entities.
- Modus Operandi: International Scam Compounds resemble call centres and have emerged as a hub of investment scams.
- Fraudsters make calls to unsuspecting people from Indian mobile phone numbers and dupe people of their money through various methods like lottery and prize scams, etc.
- Illegal Activities: Cyber scams can be used for terror-financing and money laundering.
- For instance, during March to May 2024, crypto currency worth Rs 5.5 crore was purchased using Indian accounts and laundered outside India.
- Cash withdrawals using mule account debit cards have been reported at overseas ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia.
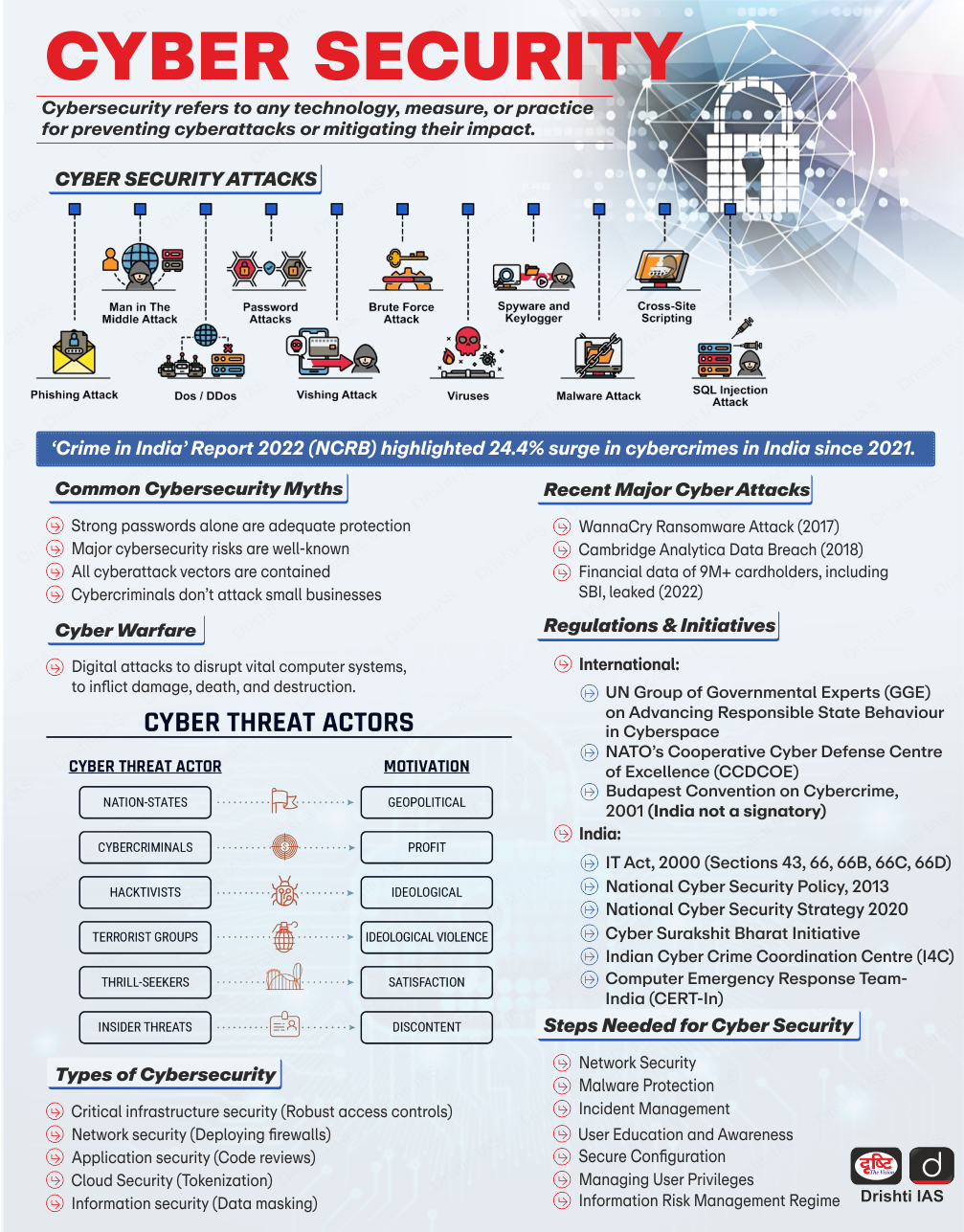
What is Cyberfraud?
- About: Cyber fraud is a kind of cyber crime that aims to steal money (or other valuable assets) from an entity.
- It involves using online solutions (internet based) to commit fraud.
- Types of Cyberfraud:
| Cyber Threat | Description |
| Phishing | Phishing involves emails that appear to be from trusted sources, tricking users into clicking links that lead to fake websites and attackers gain sensitive details e.g., credit card numbers. |
| Malware | Malware is used to steal personal information that allows cyber criminals to gain control of a victim's computer. |
| Ransomware | Ransomware encrypts a victim's files and demands payment for decryption. E.g., WannaCry attack in 2016 |
| Cyberbullying | Cyberbullying includes any threat to a person’s safety, coercion to say or do anything. |
| Cyber Spying | Cyber Spying target a public or private entity’s network to gain access to classified data, private information, or intellectual property. |
| Business Email Compromise (BEC) | Scammers hack legitimate email accounts to impersonate suppliers, employees, or tax office members, considered a white-collar crime. |
| Dating Hoodwinks | Hackers use dating websites, chat rooms, and online dating apps to pose as potential partners and gain access to personal data. |
- Consequences of Cyber Fraud:
- For Individuals: Cyber crimes can lead to unauthorised purchases on credit cards and loss of access to financial accounts. Personal data may be used to harass and blackmail victims, creating further personal distress.
- For Businesses: Companies that fail to protect client data may be subject to heavy fines and legal penalties. Cyber attacks can reduce the overall value of a firm, impacting stock prices.
- For Government: Cyber breaches are often intended to corrupt or monetise national defence and security information, posing severe risks to a country's safety.
What is the Scenario of Cyber Fraud in India?
- Overview: India has approximately 658 million internet users, making it the world's second-largest internet population.
- According to the “The ThreatLabz 2024 Phishing Report” by cybersecurity firm Zscaler, India ranked as the third-largest country globally for phishing attacks after the US and UK.
- Commitment to Cybersecurity: India has achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024 published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
- With a remarkable score of 98.49 out of 100, India joins the ranks of ‘role-modelling’ countries, demonstrating a strong commitment to cybersecurity practices across the globe.
- Notable Cyberfraud Incidents:
- Aadhar Data Breach (2018): Personal data of 1.1 billion Aadhar cardholders was compromised, including information such as Aadhar numbers, Permanent Account Number (PAN), and bank details.
- Canara Bank ATM Attack (2018): Hackers used skimming devices on 300 debit cards, stealing over Rs 20 lakh.
- Pegasus Spyware: This Israeli-made spyware, Pegasus, was used to collect data from devices without user consent, affecting over 300 verified Indian phone numbers.
What are the Key Government Initiatives Related to Cyberfraud in India?
- National Cyber Security Policy
- Computer Emergency Response Team - India (CERT-In)
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
- Cyber Crime Coordination Centre
- Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System
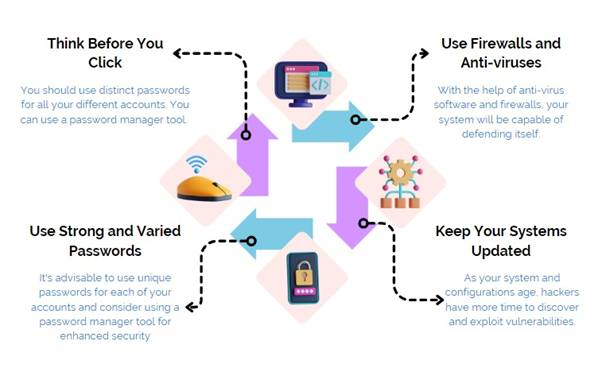
What can be Done to Address Cyber Fraud?
- Adopt Cybersecurity Best Practices: Use firewalls that act as the first line of defence for computers, monitoring and filtering network traffic to prevent unauthorised access.
- Keep all software and hardware systems up-to-date to patch security vulnerabilities.
- For Individuals: Be cautious of unsolicited emails, texts, and phone calls, especially those that attempt to coerce users into bypassing security measures.
- Use strong, unique passwords that combine numbers, letters, and special characters for each account.
- For Businesses: Implement two-factor authentication for all employee accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Use encryption to protect sensitive business data, including financial records, customer information, and intellectual property.
- Role of Banks: Banks should monitor for unusually high-value transactions in low-balance or salaried accounts and alert authorities.
- Typically, the stolen money is temporarily parked in these accounts before being converted into cryptocurrency and transferred abroad.
- System Upgrades Needed: Banks should upgrade their systems to detect multiple account logins from a single IP address, especially if the IP is outside the country.
- For Content Creators: Invest in creator insurance to safeguard intellectual property, legal fees, and potential financial losses from disputes or data breaches.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the growing menace of cyber fraud in India and its financial impact on the economy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialised consultant to minimise the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the different elements of cyber security ? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)