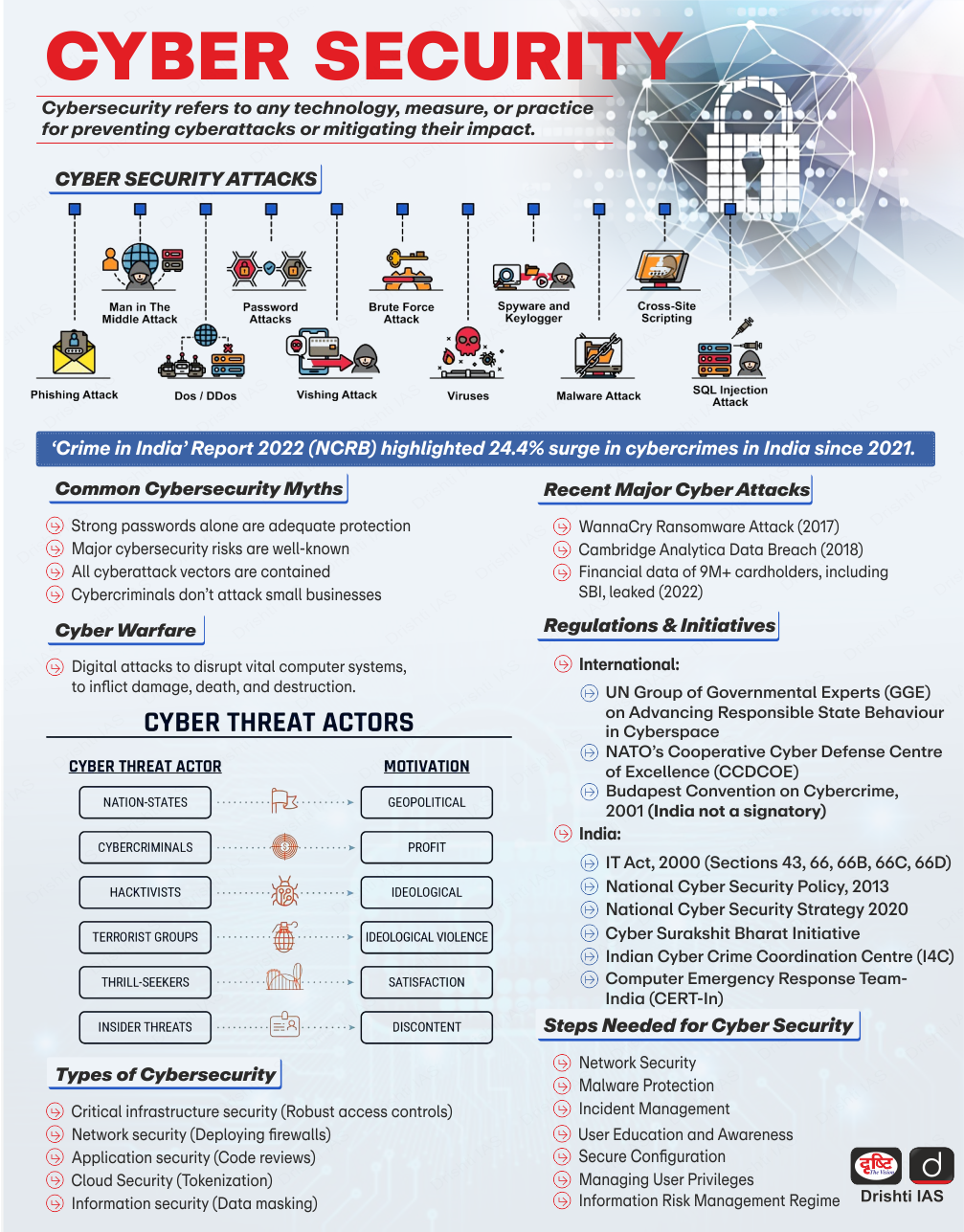
Important Facts For Prelims
Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024
- 27 Sep 2024
- 6 min read
Why in News?
Recently, India has achieved a major milestone in cybersecurity by securing Tier 1 status in the 5th edition of Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024, published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
- The 4th edition of the GCI report was published in 2020.
What is the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI)?
- About:
- GCI, launched in 2015 by ITU measures the comprehensive development and commitment to cybersecurity at a global level.
- The GCI utilises a multi-stakeholder approach and leverages the capacity and expertise of different organisations.
- Aim:
- It aims to improve the quality of the survey, foster international cooperation, promote knowledge exchange and raise awareness of the importance and different dimensions of cybersecurity.
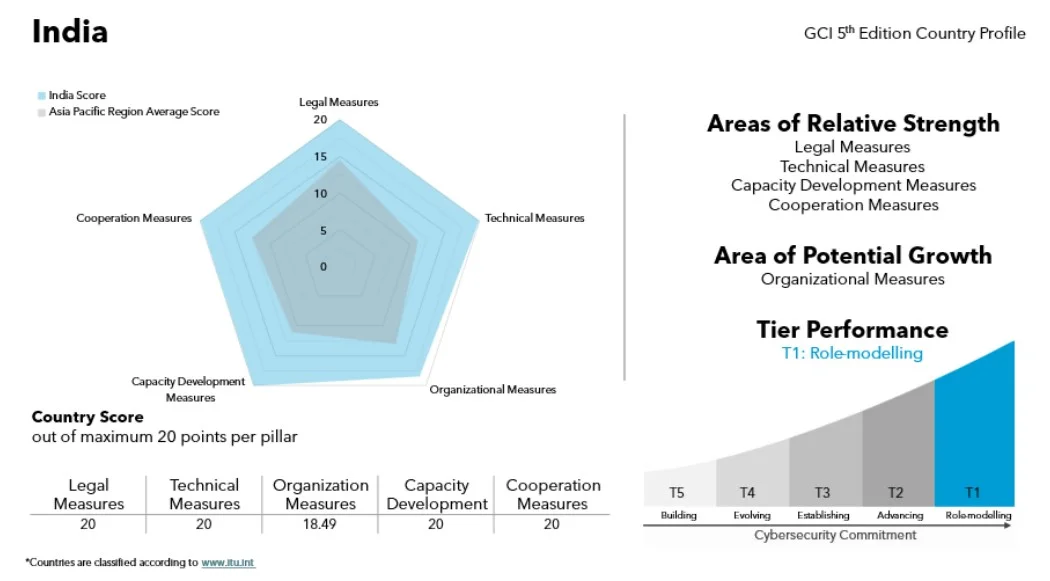
- Pillars of Assessment:
- The assessment is based on 5 pillars: Legal Measures, Technical Measures, Organisational Measures, Capacity Development, and Cooperation.
- The index aggregates the assessment into an overall score for each country.
- 5- Tier Analysis: Countries are categorised into five tiers based on their cybersecurity efforts, with Tier 1 representing the highest level.
- Tier 1- Role-modelling (score of 95–100)
- Tier 2- Advancing (score of 85–95)
- Tier 3- Establishing (score of 55–85)
- Tier 4- Evolving (score of 20–55)
- Tier 5- Building (score of 0–20).
- Key Highlights of GCI 2024: The GCI 2024 evaluated 194 countries and highlighted threats such as ransomware attacks, breaches in critical industries, system outages, and privacy violations.
- Global: Since 2021, countries have increasingly prioritised cybersecurity, raising the global average score to 65.7/100.
- GCI 2024 placed 46 countries in Tier 1, compared to 30 in the previous edition.
- Most countries (105) are ranked in Tiers 3 and 4, reflecting progress in expanding digital services but also highlighting the need for stronger cybersecurity measures in their digital transformation strategies.
- India’s Performance in GCI 2024
- India ranks in Tier 1 with countries like the US, Japan and Australia.
- India scored 98.49/100, an improvement from 97.5 in the 2020 edition due to its robust legal framework like the Information Technology Act (2000), the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (2023).
- Key Issues Highlighted in Report:
- Worrisome Threats: Increasing ransomware attacks, cyber breaches in critical industries, and costly system outages.
- Cyber Capacity Gap: Persistent limitations in skills, staffing, equipment, and funding for cybersecurity.
- Implementation Challenges: Difficulty in operationalising cybersecurity agreements effectively.
- Key Recommendations:
- National Cybersecurity Strategy: Develop and regularly update a comprehensive national cybersecurity framework.
- Capacity Building: Enhance training for cybersecurity professionals, youth, and vulnerable groups.
- Cooperation: Strengthen both domestic and international collaboration on information sharing, training, and cybersecurity initiatives.
- Global: Since 2021, countries have increasingly prioritised cybersecurity, raising the global average score to 65.7/100.
What is ITU?
- It is the United Nations (UN) specialised agency for Information and Communication Technologies (ICT)s.
- It was founded in 1865 to facilitate international connectivity in communications networks.
- It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits, develops the technical standards that ensure networks and technologies seamlessly interconnect, and strives to improve access to ICTs to underserved communities worldwide.
- ITU currently has a membership of 193 countries and over 900 private-sector entities and academic institutions.
- India has been a member of ITU since 1869 and has been a member of the ITU Governing Council since its inception in 1952.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In India, which of the following review the Independent regulators in sectors like telecommunications, insurance, electricity, etc.? (2019)
- Ad Hoc Committees set up by the Parliament
- Parliamentary Department Related Standing Committees
- Finance Commission
- Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission
- NITI Aayog
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q. In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (2020)
(a) Digital security infrastructure
(b) Food security infrastructure
(c) Health care and education infrastructure
(d) Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure
Ans: (a)
Q. Which of the following is/are the aims/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)