CSR’s Contributions to Agriculture Sustainability | 18 Nov 2024
For Prelims: Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), Small and Marginal Farmers, Fertilisers, Irrigation Systems, Cyclones, Livestock Farming, Precision Agriculture, Solar Power, Wind Energy, Biogas, Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs), Grain Banks, Water Conservation, Companies Act, 2013, NGOs, Companies (CSR Policy) Rules, 2014, Supply Chains.
For Mains: Role of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in development of agriculture.
Why in News?
With increasing contributions, the focus is on how Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) can support Indian agriculture to become both economically viable and ecologically sustainable.
Why is CSR Needed in Agriculture?
- High Dependence on Agriculture: Nearly 47% of India's population depends on agriculture for employment, compared to a global average of 25%.
- Small and Marginal Farmers: Over 70% of rural households rely primarily on agriculture for their sustenance. Of this, 82% of farmers are classified as small and marginal.
- Poor Access to Finance: High Interest rates and the lack of formal credit sources often prevent farmers from purchasing necessary equipment, seeds and fertilisers, limiting their growth and productivity.
- Building Market Linkages: Poor rural infrastructure, such as inadequate storage facilities, transportation, and irrigation systems, leads to post-harvest losses, inefficient supply chains, and reduced access to markets.
- Environmental Challenges: Unpredictable weather patterns lead to crop failures, loss of livestock, and increased vulnerability to natural disasters like floods, droughts, and cyclones.
- Soil Degradation: Improper irrigation practices and excessive use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides have led to soil degradation leading to reduced soil fertility, lower crop yields, and environmental damage.
- Water Scarcity: Water scarcity threatens both crop production and livestock farming, making irrigation and water management a critical issue.
How CSR Can Help in Agriculture?
- Technological Innovations: CSR initiatives can help integrate advanced technologies like sensors, drones, GPS, and data analytics into Precision Agriculture.
- It will enable farmers to optimise irrigation, fertilisation, pest control, and crop health for more efficient and sustainable farming.
- Financial Access: Companies can collaborate with financial institutions to offer low-interest loans and subsidies to facilitate access to affordable financing and credit.
- Renewable Energy: CSR can encourage the use of renewable energy sources such as solar power, wind energy, and biogas in farming operations which can contribute to environmentally friendly and sustainable farming practices.
- Biotechnology and GMOs: CSR efforts can promote the development of biotechnology and Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs), making crops more resistant to pests, diseases, and stress, boosting yields, reducing pesticide use, and improving food security.
- Empowering Farmers: By providing access to knowledge, skill-building programs, and hands-on experience with modern farming practices, farmers can be better equipped to increase productivity, and reduce risks.
- Improved Market Access: CSR can help create market linkages by integrating farmers into value chains, ensuring they receive fair prices for their products, and enabling them to access larger and more lucrative markets.
Note
"Environment and sustainability" is the second priority for companies with healthcare, water, sanitation, and hygiene being the top priority.
- Examples of CSR-supported initiatives include grain banks, farmer schools, water conservation, and energy-efficient irrigation.
What are Challenges in CSR Implementation in Agriculture?
- No Clear Demarcation: CSR activities to Agriculture are not clearly demarcated and well-defined.
- Under Schedule VII of the Companies Act, 2013, activities targeting agricultural sustainability could fall under 11 of the 29 development sectors of CSR. E.g., gender equality, poverty, technology incubators, animal welfare etc.
- Short-Term Focus: CSR programs often focus on short-term goals and deliverables, while agriculture requires long-term investments and sustained support to yield significant outcomes.
- Measurement of Social Impact: The social impact of CSR in agriculture is often harder to measure, especially in rural areas.
- Evaluating improvements in farmers' incomes, livelihoods, or well-being due to CSR projects can be subjective and complex.
- Not-Aligned with Business Goals: Many companies may find it difficult to integrate CSR in agriculture with their business strategies in a way that is mutually beneficial. E.g., Cosmetic companies have little incentive to invest in farming practices.
- Ignorance of Agriculture: Education and health dominate CSR funding leaving agricultural initiatives with limited focus.
- Also, a major CSR fund is diverted to other purposes like the PM CARES Fund which leads to a dip in CSR expenditure in specific sectors.
- Fragmented Approach: CSR initiatives often focus on isolated aspects of agriculture such as providing training, technology, missing broader challenges like climate change, market access, and financing.
- Lack of Suitable NGOs: Corporations often struggle to find NGOs in rural areas that align with their CSR objectives, leading to challenges in identifying the right partners for project implementation.
- Disparity in CSR Spending: A significant portion of CSR funds (more than 30%) is directed to more industrialized states like Maharashtra, Karnataka, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu. This leaves less funding for less-developed regions.
- Inefficient Allocation: Many companies focus their CSR efforts in regions where they have existing operations or deeper ties, rather than strategically directing funds to areas with the most significant need.
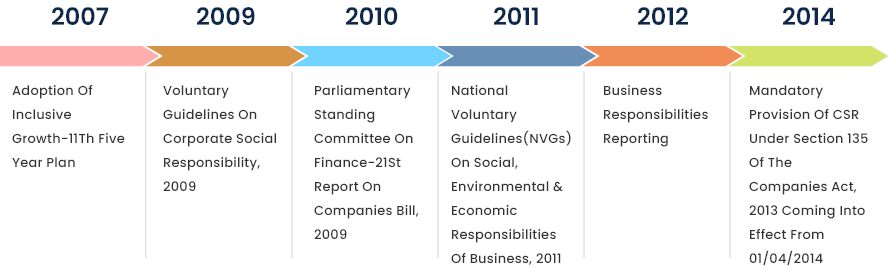
What is CSR?
- About: CSR is a business practice in which companies voluntarily integrate social, environmental, and ethical concerns into their operations and interactions with stakeholders.
- E.g., environmental sustainability, poverty reduction, education, and healthcare etc.
- India's CSR Mandate: India became the first country to legally mandate CSR in 2013 under Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- From 2014 to 2023, Rs 1.84 lakh crore of CSR funds were disbursed.
- Legislative Framework: The CSR concept in India is governed by Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013, Schedule VII of the Companies Act, 2013 and Companies (CSR Policy) Rules, 2014.
- CSR is a mandatory requirement for certain companies with effect from 1st April 2014.
- CSR Criteria: CSR provisions apply to companies that meet any of the following criteria in the preceding financial year: a net worth of over Rs 5 billion, a turnover exceeding Rs 10 billion, or a net profit greater than Rs 50 million.
- Such companies must spend a minimum of 2% of their net profit over the last three years on CSR activities.
- For newly incorporated companies with less than three years of operations, the average net profit of available years is considered.
- National CSR Data Portal: It is an initiative by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs to disseminate CSR-related data and information.
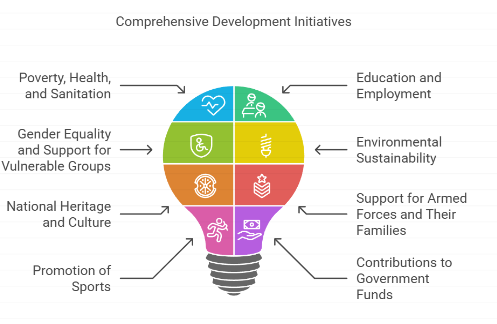
- CSR Activities: Companies can include the following activities in their CSR policies, as specified in Schedule VII.
Way Forward
- Clearer Definition: Establishing a distinct sector for agricultural CSR initiatives will help channel resources more effectively and ensure that funds are directly contributing to the sector's development.
- Financial Inclusion: By providing farmers with access to affordable financial services, CSR can empower them to invest in quality inputs, adopt new technologies, and increase their resilience to environmental challenges.
- Supply Chain Stability: Agriculture is a critical part of many industries’ supply chains, such as food, clothing, and pharmaceuticals. By investing in sustainable agricultural practices through CSR, companies help ensure the long-term stability of their supply chains.
- Competitive Advantage: By solving agricultural challenges such as water conservation, precision farming, and renewable energy use, companies can develop new technologies or services that set them apart from competitors.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Companies can align CSR programs with their core values, such as food companies supporting sustainable farming and tech companies investing in agricultural technology, benefiting both their business and the sector.
- Equitable Development: Companies should direct CSR efforts to regions with agricultural challenges, even if they don't operate there, to promote broader, more equitable development.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the role of CSR in promoting agricultural sustainability and the challenges faced in its implementation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is issued by registered foreign portfolio investors to overseas investors who want to be part of the Indian stock market without registering themselves directly? (2019)
(a) Certificate of Deposit
(b) Commercial Paper
(c) Promissory Note
(d) Participatory Note
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. With a consideration towards the strategy of inclusive growth, the new Companies Bill, 2013 has indirectly made CSR a mandatory obligation. Discuss the challenges expected in its implementation in right earnest. Also discuss other provisions in the Bill and their implications. (2013)