Governance
World's Largest Grain Storage Plan in Cooperative Sector
- 03 Jun 2023
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Cooperative sector, Food security, Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), Inter-Ministerial Committee, Food Corporation of India, District Central Cooperative Banks, Union Budget 2023-24.
For Mains: Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has given its approval for the establishment of the "world's largest grain storage plan in the cooperative sector" with an outlay of around Rs 1 lakh crore.
- The initiative aims to curb crop damages, prevent distress sales by farmers, and bolster the country’s food security.
What are the Major Highlights Related to Grain Storage Plan?
- About:
- The plan focuses on the creation of godowns and other agricultural infrastructure at the level of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) to strengthen food security, reduce wastage, and empower farmers.
- This ambitious project aims to converge eight ongoing schemes of three ministries to address the shortage of agricultural storage infrastructure in India.
- Ministry of Cooperation will implement a pilot project in at least 10 selected districts.
- The plan focuses on the creation of godowns and other agricultural infrastructure at the level of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) to strengthen food security, reduce wastage, and empower farmers.
- Inter-Ministerial Committee:
- An Inter-Ministerial Committee (IMC) will be constituted under the chairmanship of the Minister of Cooperation, with the participation of the Ministers of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution, and Food Processing Industries, along with the concerned secretaries.
- Rationale:
- The Ministry of Cooperation has developed the grain storage plan to leverage the strength of cooperatives and transform them into successful business enterprises, aligning with the vision of "Sahakar-se-Samriddhi" (Cooperation for Prosperity).
- The plan focuses on establishing agri-infrastructure, including warehouses, custom hiring centres, and processing units, at the PACS level.
- India has over 1,00,000 PACS with a vast membership base of more than 13 crore farmers.
- Given their significant role in the agricultural and rural landscape, the plan seeks to empower PACS by creating decentralised storage capacity and other necessary infrastructure.
- This transformation will enhance the economic viability of PACS and contribute to the growth of the Indian agricultural sector.
- Benefits:
- Addressing Infrastructure Shortage: The plan aims to establish godowns at the level of PACS to alleviate the shortage of agricultural storage infrastructure in the country.
- Diversification of PACS Activities: PACS will be empowered to undertake various activities, including functioning as procurement centres for state agencies or the Food Corporation of India (FCI), serving as fair price shops, and setting up custom hiring centres and common processing units.
- This diversification will enhance the incomes of farmer members.
- Reduction of Food Grain Wastage: By creating decentralised storage capacity at the local level, the plan aims to reduce grain wastage, contributing to improved food security.
- Preventing Distress Sale: The plan provides farmers with various options, preventing distress sale of crops and enabling them to realise better prices for their produce.
- Cost Reduction: The establishment of storage facilities at the PACS level will significantly reduce transportation costs of food grains to procurement centres and fair price shops.
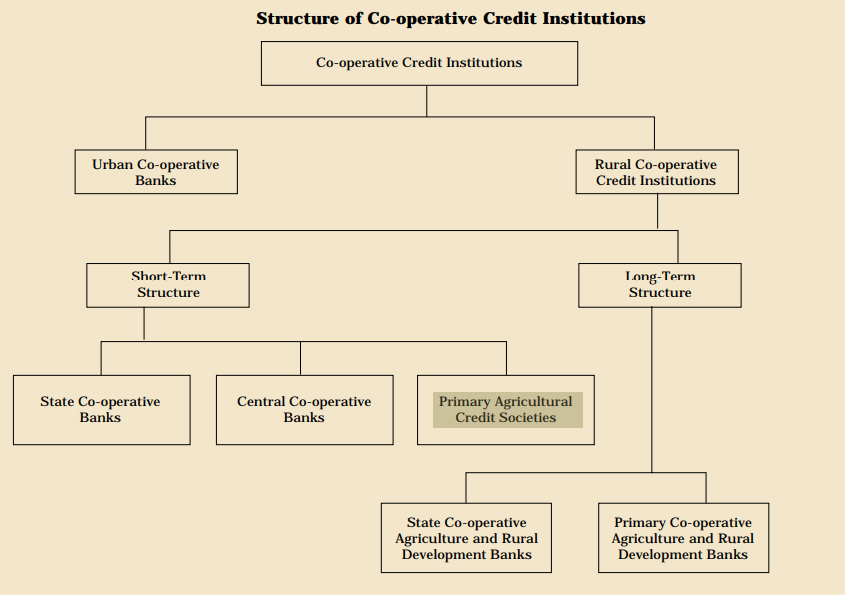
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies?
- PACS constitute the lowest tier of the Short-Term Cooperative Credit (STCC) structure in the country, headed by the State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level.
- Credit from the SCBs is transferred to the District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs), which operate at the district level. The DCCBs work with PACS, which deal directly with farmers.
- The first PACS was established in 1904. They are involved in short term lending. At the start of the cropping cycle, farmers avail credit to finance their requirement of seeds, fertilisers etc.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 has announced Rs 2,516 crore for computerisation of 63,000 PACS over the next five years, with the aim of bringing greater transparency and accountability in their operations and enabling them to diversify their business and undertaking more activities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q2. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. In the villages itself no form of credit organisation will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural finance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural finance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? (2014)