Important Facts For Prelims
Cleaner Methods of Energy Generation
- 25 Feb 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
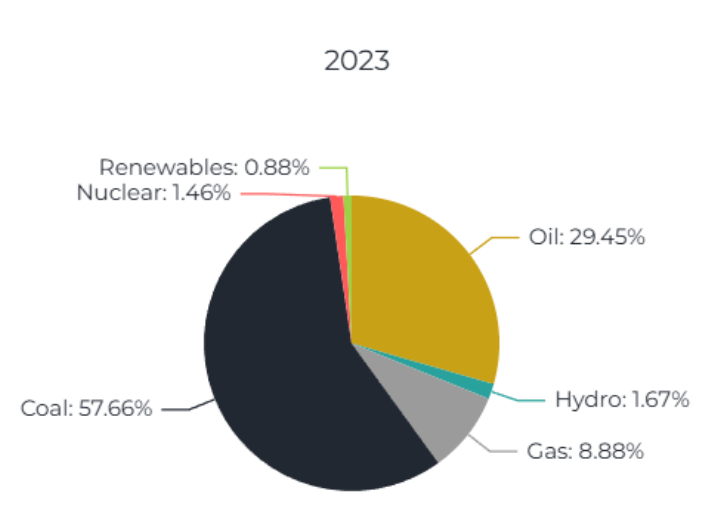
India must adopt cleaner methods of energy generation, as coal-based electricity generation causes significant air pollution, harming crops, humans and animals.
- Cleaner methods of energy generation use renewable, and low-carbon technologies to produce electricity with minimal pollution and environmental impact.
Note: Nitrogen dioxide and ozone from coal plants reduce wheat and rice yields by over 10% in some parts of India.
- It negated six years of agricultural growth despite better crops, irrigation, and mechanization.
What are Available Cleaner Methods of Energy Generation?
- Osmotic Power: It generates electricity using osmotic pressure differences between freshwater and seawater.
- India has a vast coastline of 7,500 km, where rivers drain into the sea, and this technology can effectively generate electricity.
- Osmotic power (salinity gradient energy) generates electricity using the salt concentration difference between freshwater and seawater through osmotic pressure.
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear power plants use nuclear fission to heat water, create steam, and spin turbines to generate electricity.
- India’s Nuclear power generation capacity stands at 8,180 MW in 2024 and is projected to triple to 22,480 MW by 2031-32.
- The government has set an ambitious target of 100 GW nuclear power capacity by 2047.
- Biomass Energy: Organic materials (wood, crop waste, algae) are burned or converted into biofuels to produce electricity.
- India produces 450-500 million tonnes of biomass annually, supplying 32% of the country's primary energy.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: They convert hydrogen into electricity through electrochemical reactions.
- They are used in vehicles and backup power systems, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct.
- Waste-to-Energy (WTE): It converts municipal solid waste (MSW) and other waste materials into electricity, heat, or fuel through various technologies like
- Incineration: Waste is burned at high temperatures to produce steam, which drives a turbine to generate electricity.
- Gasification: Converts waste into syngas (a mixture of CO, H₂, and CH₄), a raw material for fuel.
- Pyrolysis: Organic waste is decomposed at high temperatures without oxygen, producing bio-oil, syngas, and biochar as usable fuels.
- Wind Energy: It involves the use of wind power by placing windmills to generate electricity.
- India, the world's 4th largest wind power producer, generates 50 Gigawatts (GW) of electricity across nine windy states.
- Solar Energy: It involves setting up solar panels on houses, buildings or large-scale solar farms that absorb sunlight and convert light into electricity.
- India is the world's 3rd largest solar power generator after China (1st) and USA (2nd).
- Hydropower: It involves blocking part of a river by a dam and then water is released to generate electric power.
- The top five dams across India together generate as much as 50 GW of hydroelectric energy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the reasons/factors for exposure to benzene pollution? (2020)
- Automobile exhaust
- Tobacco smoke
- Wood burning
- Using varnished wooden furniture
- Using products made of polyurethane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. In the context of solving pollution problems, what is/are the advantage/advantages of bioremediation technique? (2017)
- It is a technique for cleaning up pollution by enhancing the same biodegradation process that occurs in nature.
- Any contaminant with heavy metals such as cadmium and lead can be readily and completely treated by bioremediation using microorganisms.
- Genetic engineering can be used to create microorganisms specifically designed for bioremediation.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)