Agriculture
Electronic Soil
- 30 Dec 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Electronic Soil, Hydroponics, Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO).
For Mains: Electronic Soil, e-technology in the aid of farmers.
Why in News?
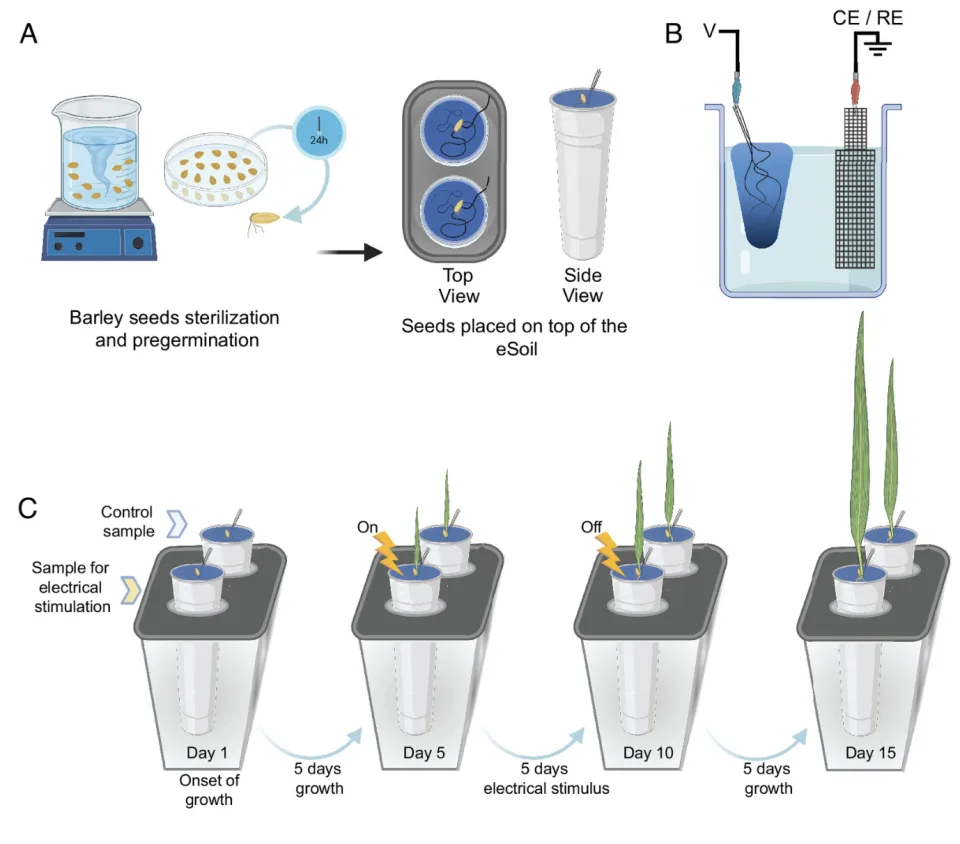
Recently, researchers from Linköping University in Sweden have developed ‘Electronic Soil’ that can speed up the growth of plants in Hydroponic spaces.
What is Electronic Soil?
- About:
- The electronic soil (eSoil) developed is a novel conductive cultivation substrate tailored specifically for hydroponic systems.
- Unlike traditional substrates like mineral wool, which are non-biodegradable and manufactured using energy-intensive processes, eSoil is composed of cellulose, a biopolymer, blended with a conductive polymer known as PEDOT (Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)).
- This innovative blend of materials allows for the stimulation of root systems in plants through low-power electrical currents.
- Significance:
- eSoil offers the advantage of significantly lower energy consumption and eliminates the risk associated with high-voltage systems.
- The significance of eSoil lies in its ability to enhance the growth of plants, as evidenced by a study showing a 50% increase in the growth rate of barley seedlings cultivated in hydroponic systems using this technology.
- Hydroponics coupled with eSoil can be potentially helpful in addressing global food demands, especially in urban settings where arable land is limited.
What is Hydroponics?
- Hydroponics:
- Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in a water based, nutrient rich solution in a soilless media.
- It does not use soil, instead the root system is supported using an inert medium such as perlite, rockwool, clay pellets, peat moss, or vermiculite.
- The fundamental is to allow the plants roots to come in direct contact with the nutrient solution, while also having access to oxygen, which is essential for proper growth.
- Advantages:
- Land and Water Efficient: The hydroponic farming technology with closed water loop systems is a viable option for farmers with limited access to land and water.
- Suitable for Urban Areas: The significance of soilless systems increases many folds when it comes to urban and peri-urban areas where the arable land is polluted.
- Lower Resource Consumption: Lower and more efficient resource consumption allows this alternative farming technique to be adopted by a variety of stakeholders.
- Higher Yield: According to the Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO), the vegetable yield of soilless systems is 20-25% higher than in traditional systems as the number of plants per square metre is higher.
- Drawbacks:
- Much Time and Attention Required: The water needs to be replaced at regular intervals as standing or recirculating water makes it easier for plant disease to spread if pathogens enter the water supply.
- Water and Electricity Intensive: Water and electricity are the two major factors in Hydroponic farming, in absence of adequate water supply or stable electricity, the Hydroponic system won’t thrive well.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. What is the use of biochar in farming? (2020)
- Biochar can be used as a part of the growing medium in vertical farming.
- When biochar is a part of the growing medium, it promotes the growth of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms.
- When biochar is a part of the growing medium, it enables the growing medium to retain water for longer time.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- Biochar is a porous carbonaceous solid produced by heating various biomass feedstocks under high temperatures in an oxygen-limited environment.
- As biochar migrates vertically through the soil profile, therefore can be used as a part of the growing medium in vertical farming. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Due to its adsorption ability, some biochars have the potential to immobilise heavy metals, pesticides, herbicides, and hormones; prevent nitrate leaching and faecal bacteria into waterways; and reduce N2O and CH4 emissions from soils. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Biochar can help retain water and nutrients in the soil for the plants to take up as they grow. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.