China’s Global Security Initiative
For Prelims: Global Security Initiative, Quad Grouping, AUKUS Grouping, Indo-Pacific strategy
For Mains: New Cold War, Groupings & Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India's Interests, Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India's Interests
Why in News?
Recently, a new Global Security Initiative (GSI) was put forward by Chinese President. The GSI looks to counter the US Indo-Pacific strategy and the Quad (India, US, Australia, Japan grouping).
- However, China did not provide much clarity or details about the proposed global security initiative.
What is GSI, as Envisaged by China?
- Principle of Indivisible Security: With growing threats posed by unilateralism, hegemony and power politics, and increasing deficits in peace, security, trust and governance, mankind is facing more and more intractable problems and security threats.
- Thus, China held that the Global security initiative is envisaged to uphold the principle of "indivisible security”.
- The principle of "indivisible security" means that no country can strengthen its own security at the expense of others.
- Asian Security Model: GSI calls for a "common, comprehensive, cooperative and sustainable" security and building an Asian security model of mutual respect, openness and integration”.
- Opposing Sanctions: This would oppose the use of unilateral sanctions and long-arm jurisdiction, appearing to refer to Western sanctions.
- Tackling New Cold War: Indo-Pacific’ strategy to divide the region and create a ‘new Cold War’, and the use of military alliances to put together an ‘Asian version of North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
- According China, the Quad grouping was equivalent to the “Five Eyes” intelligence alliance involving Australia, New Zealand, Canada, the U.S. and U.K. and the AUKUS pact, as a key element in what he called U.S. plans to build an “Asian NATO”.
What are Reactions of Quad Members?
- Quad is not a Military Alliance: The members of the Quad have rejected the notion that it is an Asian NATO or a military alliance, and pointed to its broad-based cooperation, including on vaccines and technology.
- Double Standards of China: Chinese criticism of unilateralism, hegemony and double standards is usually aimed at the US.
- Impact of Russia-Ukraine War: China's new advances in the Pacific could be related to the stagnation of the Belt and Road Initiative, due to the Ukraine war.
What are Events Signaling a New Cold War?
- China’s Development: For several decades, China’s aggressive development under the relatively enlightened authoritarianism of Deng Xiaoping and his successors was seen positively in the United States.
- However, under Xi Jinping (President), China has evolved from a soft to a hard authoritarianism.
- There is now a president-for-life with a budding personality cult.
- US’ Counter: In order to contain rising China’s assertiveness, the US under its ‘pivot to Asia policy’ Has launched a Quad initiative & Indo pacific narrative.
- Most recently, the US proposed to expand G7 to G-11 without including China in it.
- China’s Stance on South China Sea: China’s actions in the South China Sea, first by land reclamation and then constructing artificial islands for extending extra-territorial claim, has seen sharp criticism from the US and its allies.
- Challenging Economic Hegemony: China has come out with alternative governance mechanisms to the U.S.-dominated International Monetary Fund, World Bank and World Trade Organization with its all-encompassing Belt and Road Initiative and institutions like Asia infrastructure investment bank, Contingency Reserve Agreement (CRA) of New Development Bank.
What Should be Role of India?
- India is a rising global power and citing its importance both the US and China sought to attract India in its camp. Foreign policy experts in the US argue India Is a Natural US Ally in the New Cold War.
- On the other hand, Chinese’s Ambassador in India has suggested writing “together a new chapter” with “a shared future for mankind”. In this context:
- India can promote new multilateralism under the aegis of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam- which relies on restructuring both the economic order and societal behavior for equitable sustainable development.
- India must take up intensified diplomacy with global powers so that Asian Century can be defined in terms of peaceful co-existence and global interest.
- Apart from it, India should acknowledge that national security now relies on technological superiority in Artificial Intelligence (AI), cyber and space, and not expensive capital equipment.
- Thus, India should become self-sufficient in the domain of critical technologies.
Indonesia’s Palm Oil Export Ban & Its Impact on India
For Prelims: Indonesia’s Palm Oil Export Ban & Its Impact on India, biodiesel, National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm
For Mains: Agricultural Resources, Food Security, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, Indonesia, the world’s biggest producer, exporter, and consumer of palm oil, has announced that it would be banning all exports of the commodity and its raw materials to reduce domestic shortages of cooking oil and bring down its rising prices.
- India meets half of its annual need for 8.3 million tons of palm oil from Indonesia. Thus, an export ban will affect India’s interests.
What is Palm Oil & Its Use?
- Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms.
- It is used as cooking oil, and in everything from cosmetics, processed foods, cakes, chocolates, spreads, soaps, shampoo, and cleaning products to biofuel.
- The use of crude palm oil in making biodiesel is being branded as ‘green diesel’.
- Indonesia and Malaysia together account for almost 90% of the global palm oil production, with Indonesia producing the largest quantity at over 45 million tonnes in 2021.
- The oil palm industry has come under criticism for what are reportedly unsustainable production practices leading to deforestation, and exploitative labor practices carried forward from the colonial era.
- However, palm oil is preferred by many as it is inexpensive, oil palms produce more oil per hectare than some other vegetable oil plants like soybean.
How Important is Palm Oil for Global Supply Chains?
- Palm oil is the world’s most widely used vegetable oil with its global production in the year 2020 being over 73 Million Tones (MT), according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
- It is estimated to be 77 MT for the current year FY 2022-23.
- According to Reuters, palm oil makes up 40% of the global supply of the four most widely used edible oils: palm, soybean, rapeseed (canola), and sunflower oil.
- Indonesia is responsible for 60% of the global supply of palm oil.
Why are the Prices of Edible Oils Rising?
- India is the biggest importer of palm oil. The prices of palm oil rose this year as demand increased because of the short supply of alternative vegetable oils.
- The production of soybean oil, the second most-produced oil, is expected to take a hit this year due to a poor soybean season in major producer Argentina.
- The production of canola oil was hit in Canada last year due to drought, and supplies of sunflower oil, 80-90% of which is produced by Russia and Ukraine, has been badly hit by the ongoing conflict.
- Due to pandemic-induced labor shortage, and the global food inflation linked to the pandemic and the Ukraine crisis, the global prices of edible oil have risen significantly since the end of last year.
How Will It Impact India?
- India is the biggest importer of palm oil, which makes up 40% of its vegetable oil consumption.
- India meets half of its annual need for 8.3 MT of palm oil from Indonesia.
- This would lead to a rise in those already grappling with record-high wholesale inflation.
- It is important that, last year, the Centre also unveiled National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm to boost India’s domestic palm oil production.
Way Forward
- Increasing Domestic Yield: Given advantages pertaining to Palm oil for India’s cooking requirements, the Indian farmers should be incentivized to intensify efforts for area expansion under oil palm to enhance palm oil production in the country.
- For this, the National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm is a step in the right direction.
- Diversification: India should diversity its procurement as well requirements.
- Firstly, India should look to procure more palm oil from other countries.
- Secondly, Tree Borne Oilseeds (TBOs), like sal, mahua, olive, jatropha, neem, jojoba, wild apricot, walnut, tung etc. can be explored as an alternative.
Issue of Petrol and Diesel Pricing in India
For Prelims: VAT, Excise Duty , crude oil prices
For Mains: Issue of Petrol and Diesel Pricing in India, Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India's Interests
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister urged several Opposition-ruled states to cut taxes on petrol and diesel in order to reduce the economic burden on citizens and work as a team in this time of global crisis following the spirit of cooperative federalism”.
- Maharashtra, West Bengal, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Jharkhand have not reduced Value-added tax (VAT) on Petrol and Diesel.
- VAT is consumption tax which is added to a product at every point of the supply chain where value is added to it.
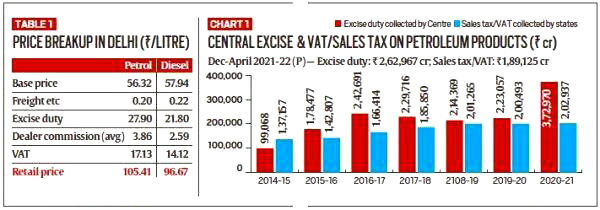
What are the Components of Retail Prices of Fuel?
- Retail prices of petrol and diesel are made up of mainly 3 components:
- Base price (reflecting cost of international oil)
- Central Excise Duty
- State Tax (VAT)
- Central and state taxes form a major chunk of the price of petrol and diesel in India.
- Excise duty is constant for all over India, state taxes (sales tax and value added tax) vary depending upon the rates levied by different state governments.
- These taxes make fuel even more costly for consumers.
- In November 2021, the Centre had reduced excise duties on both petrol and diesel to bring some relief to end-use customers.
- Exercise duty was reduced by Rs 5 per liter on petrol and Rs 10 per liter on diesel.
- Fuel prices remained constant after the Centre's exercise duty reduction.
- However, a recent surge in global crude oil prices owing to the war between Russia and Ukraine led to corresponding hikes in the price of petrol and diesel in India too.
- The price reduction varied across states due to differences in VAT rates.
- States with higher VAT witnessed slightly higher reduction in pump prices.
- Retail rates of petrol and diesel are governed by international prices as India depends on imports for meeting 85% of its oil needs.
What are the Government Earnings from Fuel Prices?
- Exercise duty and VAT on fuel constitute an important source of revenue for both the Centre and the states.
- As per the Budgets 2020-21, Excise duty on fuel makes up about 18.4% of the Centre’s gross tax revenues.
- Petroleum and alcohol, on average, account for 25-35% of states’ own tax revenue.
- Of the revenue receipts of states, central tax transfers comprise 25-29%, and own tax revenues 45-50%.
- Petroleum and alcohol, on average, account for 25-35% of states’ own tax revenue.
- During April-December 2021, taxes on crude oil and petroleum products had yielded Rs 3.10 lakh crore to the central exchequer, including Rs 2.63 lakh crore as excise duty, and Rs 11,661 crore as cess on crude oil.
- For the same period, Rs 2.07 lakh crore accrued to the state’s exchequer, of which Rs 1.89 lakh crore was through VAT.
What are the Constraints of States in Lowering Fuel Taxes?
- Major Source of Revenue:
- Petroleum and liquor account for roughly a third of states’ own tax revenue, making it difficult for states to forgo a part of it.
- Impact of Pandemic:
- The economic downturn and the pandemic had led to higher spending needs and reduced revenues.
- States’ consolidated fiscal deficit had jumped from 2.6% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in FY20 to 4.7% in FY21.
- The economic downturn and the pandemic had led to higher spending needs and reduced revenues.
What are the Options to Cool Inflation?
- As India is heavily dependent on imports for crude, there is no way of cooling energy price inflation other than by lowering taxes on the finished product or by re-introducing subsidies.
- Subsidies enable state-owned fuel retailers to sell at a lower price, while private refiners who do not get subsidy from the government are forced to incur losses.
- Given that higher fuel prices are getting transmitted to prices of other items as transportation becomes costlier, it is believed that monetary tightening would be the right solution.
Way Forward
- India has been experimenting with diversifying its source of oil and gas imports, creating strategic oil reserves, blending ethanol with auto fuel and an ambitious electric mobility plan.
- However, these measures are yet to achieve a critical mass to have a positive impact on energy prices in the face of a massive surge in global prices of crude oil, gas, petrol, and diesel.
- The easiest way that the government can stop fuel prices from rising is by cutting taxes on them, and by taking less dividends from oil Public sector undertakings.
- The government should restrict the export of fuel and other Petro-products.
- This will force refineries to sell their output in the domestic market, removing one reason for giving them assured trade-parity prices.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In the context of global oil prices, “Brent crude oil” is frequently referred to in the news. What does this term imply? (2011)
- It is a major classification of crude oil.
- It is sourced from North Sea.
- It does not contain sulphur.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 2 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Brent crude oil is one of the major classifications of crude oil done on the basis of geographical location of the source.
Cyber Security
For Prelims: Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative, Cyber Swachhta Kendra, Online cybercrime reporting portal,
For Mains: Issue of Cyber Security, Steps that needs to be taken.
Why in News?
Recently, CERT-In has asked all government and private agencies to mandatorily report cyber security breach incidents to it within six hours of noticing them.
- CERT-In is empowered under Section 70B of the Information Technology Act to collect, analyse and disseminate information on cyber security incidents.
What is CERT-IN?
- Computer Emergency Response Team - India is an organisation of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology with the objective of securing Indian cyberspace.
- It is the nodal agency which deals with cybersecurity threats like hacking and phishing.
- It collects, analyses and disseminates information on cyber incidents, and also issues alert on cybersecurity incidents.
- CERT-IN provides Incident Prevention and Response Services as well as Security Quality Management Services.
What are the Mandates of the CERT-In?
- Mandatorily Enable Logs:
- It mandates all service providers, intermediaries, data centres, corporates and government organisations to mandatorily enable logs of all their ICT (Information and Communication Technology) systems.
- The service providers has to maintain the logs securely for a rolling period of 180 days, and the same shall be maintained within the Indian jurisdiction.
- The log should be provided to CERT-In along with reporting of any incident or when directed by the computer emergency response team.
- The service providers has to maintain the logs securely for a rolling period of 180 days, and the same shall be maintained within the Indian jurisdiction.
- It mandates all service providers, intermediaries, data centres, corporates and government organisations to mandatorily enable logs of all their ICT (Information and Communication Technology) systems.
- Connect and Synchronize all ICT systems:
- To ensure the chain of events is accurately reflected in the time frame, service providers have been asked to connect and synchronize all their ICT systems clocks to the Network Time Protocol (NTP) Server of the National Informatics Centre (NIC) or National Physical Laboratory (NPL).
- NTP is a protocol used for reliably transmitting and receiving accurate time sources over TCP/IP-based networks.
- It is used for synchronizing the internal clock of computers to a common time source.
- To ensure the chain of events is accurately reflected in the time frame, service providers have been asked to connect and synchronize all their ICT systems clocks to the Network Time Protocol (NTP) Server of the National Informatics Centre (NIC) or National Physical Laboratory (NPL).
- Requires Maintaining Records:
- It also require virtual asset, exchange, and custodian wallet providers to maintain records on KYC and financial transactions for a period of five years.
- Companies providing cloud, virtual private network (VPN) will also have to register validated names, emails, and IP addresses of subscribers.
- It also require virtual asset, exchange, and custodian wallet providers to maintain records on KYC and financial transactions for a period of five years.
What is the Need of Such Initiative?
- Address the issue Hindrance:
- It will address the issue of hindrance in the analysis of breach incidents in handling cyber incidents.
- Streamline the Date Records:
- There have been cases in the past where cases of non-storage or availability of data and proper records with intermediaries and service providers have been identified.
- These guidelines will streamline the date records to be maintained and proper reporting of security incidents to CERT-In.
- There have been cases in the past where cases of non-storage or availability of data and proper records with intermediaries and service providers have been identified.
- Address the Users Right to Know:
- End-user has the right to know if their data is loaded so that an individual can protect himself from fraud transactions, fake loans, ID misuse etc.
- Government should also force companies to inform their users within 24 hours of the incident.
- Many users are still unaware if their KYC (Know Your Customer) and financial data is safe or not.
- End-user has the right to know if their data is loaded so that an individual can protect himself from fraud transactions, fake loans, ID misuse etc.
What are Government Initiatives for Cyber Security?
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Online cybercrime reporting portal
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Information Technology Act, 2000
- National Cyber Security Strategy 2020
Way Forward
- India is the one of the fastest digital adapters among 17 of the most-digital economies globally, and rapid digitisation does require forward-looking measures to boost cybersecurity.
- It is important for the corporates or the respective government departments to find the gaps in their organisations and address those gaps and create a layered security system, wherein security threat intelligence sharing is happening between different layers.
- There is a need for an apex body to ensure operational coordination amongst various agencies and ministries.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- According to section 70B of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act), the Union Government by notification should appoint an agency named Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERTIn) to serve as the national agency for incident response.
- The Union Government under section 70B of the IT Act, 2000 established and notified rules of CERT-In in 2014. According to Rule 12(1)(a), it is mandatory for service providers, intermediaries, data centers and corporate bodies to report cyber security incidences to CERT-In within a reasonable time of occurrence of the incident. Hence, 1, 2 and 3 are correct. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Amendment in Civil Registration System
For Prelims: Civil Registration System, National Population Register, Registrar General of India
For Mains: Population and Associated Issues, Government Policies & Interventions, Need and Significance of Amendment in Civil Registration System
Why in News?
According to the 2020-21 annual report of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), the Central government is planning to revamp the Civil Registration System (CRS) to enable the registration of birth and death in real-time with minimum human interface that will be independent of location.
- The RGI (Registrar General of India) is empowered under Section 3(3) of the Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD) Act, 1969 to take steps to coordinate and unify the activities of Chief Registrars of Births and Deaths of all States
What is the Civil Registration System?
- Civil Registration System (CRS) in India is the unified process of continuous, permanent, compulsory and universal recording of the vital events (births, deaths, stillbirths) and characteristics thereof.
- The data generated through a complete and up-to-date CRS is essential for socio-economic planning.
What are the Proposed Amendments?
- Updating for New Changes due to Birth and Death:
- There is a need to update the NPR (National Population Register) again, first collated in 2010 and updated in 2015 with Aadhaar, mobile and ration card numbers “to incorporate the changes due to birth, death and migration.
- CRS facing various Challenges:
- The CRS system is facing challenges in terms of timelines, efficiency and uniformity, leading to delayed and under-coverage of birth and death.
- To address the challenges faced by the system in providing prompt service delivery to the public, the Government of India has decided to introduce transformational changes in the Civil Registration System of the country through an IT [information technology] enabled backbone leading to registration of birth and death on a real-time basis with minimum human interface.
- Automation and Time Bound System:
- The changes would be in terms of automating the process delivery points so that the service delivery was time-bound, uniform and free from discretion.
- The changes would be sustainable, scalable and independent of the location.
- Amendments to RBD Act:
- It also proposed amendments to the Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD) Act , 1969 that will enable it to “maintain the database of registered birth and deaths at the national level.
- According to the proposed amendments, the database may be used to update the Population Register, Electoral Register, Aadhar, Ration Card, Passport and Driving License databases.
- The registration of birth and death is mandatory under the RBD Act and the Chief Registrar is mandated to publish a statistical report on the registered births and deaths during the year.
Way Forward
- A very techno-utopian idea of governance is needed, where citizens don’t have to ask for anything and the government will provide it before one demand it.
- To achieve this techno-utopian reality, a unified population database needs to be created which can be effectively used to track people in real-time.
Museums Grant Scheme
Why in News?
The Ministry of Culture and Tourism has granted Rs 3.75 crore under the ‘Upgradation of Museums Scheme’ as part of Museums Grant Scheme for the Rs 5-crore project in Eluru town, Andhra Pradesh.
What is the Museums Grant Scheme?
- About:
- The scheme was launched in 2013.
- The Ministry of Culture provides financial assistance under the Scheme to the State Governments and Societies, Autonomous bodies, Local Bodies and Trusts registered under the Societies Act 1860, for setting up new Museums.
- It aims to strengthen and modernize the existing museums at the Regional, State and District level.
- The scheme also aims to develop at least 1 Central / State Government Museum located in the State Capital each year.
- Components:
- Establishment and Development of District and Regional Museums:
- Under this component museums have been classified into two categories:
- Category-I: Government-owned State level Museums and renowned Museums with exquisite collection.
- Category-II: all other Museums.
- The maximum amount of financial assistance provided under this Component is limited to Rs.10 crore.
- Under this component museums have been classified into two categories:
- Development of Museums in State Capitals:
- Financial assistance under this component is provided to existing renowned museums of the Central or State Government located in the Capital cities.
- The maximum financial assistance under this component is limited to Rs. 15 Crore per museum.
- Establishment and Development of Large-Scale Museums in Public Private Partnership Mode:
- Under this component, it is proposed to establish large scale museums as joint ventures with State Governments and the civil society in Public Private Partnership Mode.
- The maximum financial assistance provided under this component is 40% of the project cost subject to a maximum of Rs. 20 Crore per museum.
- Establishment and Development of District and Regional Museums:
What is a Museum?
- A museum is an institution in which objects of historical, scientific, artistic, or cultural interest are stored and exhibited.
- ICOM (International Council of Museums) defines museum as “A museum is a non-profit, permanent institution in the service of society and its development, open to the public, which acquires, conserves, researches, communicates and exhibits the tangible and intangible heritage of humanity and its environment for the purposes of education, study and enjoyment”
- ICOM is a non-governmental organization dedicated to museums, maintaining formal relations with UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) and having a consultative status with the United Nations Economic and Social Council.
What are the other Schemes Related to Museums?
- The National Portal and Digital Repository for Indian Museums (under the Ministry of Culture) have been launched for digitization of the collections of the Museums.
- JATAN: Virtual Museum Software: JATAN is a virtual museum builder software, that enables creation of digital collection management system for Indian museums and is deployed in several national museums across India.
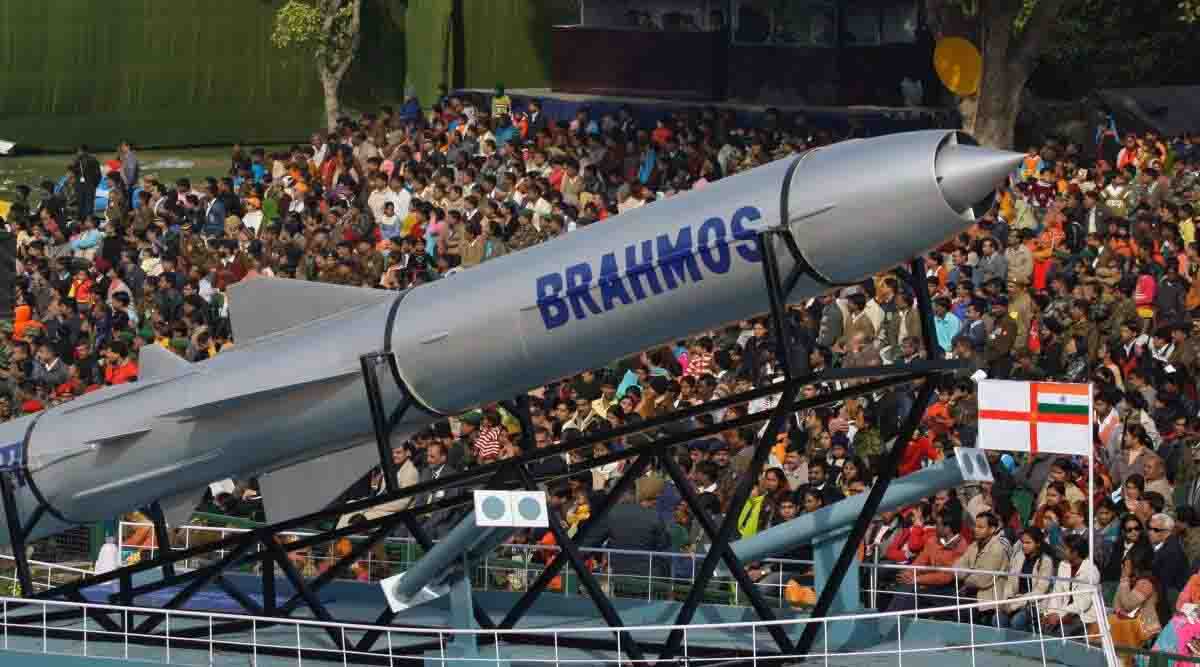
Anti-Ship Version of Brahmos Missile
Why in News?
Recently, an anti-ship version of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile was successfully test-fired jointly by the Indian Navy and the Andaman and Nicobar Command.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Command is the only tri-services command of the Indian armed forces.
What is BrahMos?
- BrahMos is a joint venture between the Defence Research and Development Organisation of India (DRDO) and the NPOM of Russia.
- BrahMos is named on the rivers Brahmaputra and Moskva.
- It is a two-stage (solid propellant engine in the first stage and liquid ramjet in second) missile.
- It is a multiplatform missile i.e it can be launched from land, air, and sea and multi capability missile with pinpoint accuracy that works in both day and night irrespective of the weather conditions.
- It operates on the "Fire and Forgets" principle i.e., it does not require further guidance after launch.
- Brahmos is one of the fastest cruise missiles currently operationally deployed with speed of Mach 2.8, which is nearly 3 times more than the speed of sound.
- Earlier, the Indian Air Force (IAF) successfully test-fired the BrahMos missile from a Sukhoi fighter jet.
- Recently, the Indian Navy also successfully test-fired an advanced version of the Brahmos missile from a stealth destroyer in the Indian Ocean.
- Following India’s entry into the MTCR (Missile Technology Control Regime) club in June 2016, the range is planned to be extended to 450 km and to 600km at a later stage.
- The BrahMos missile was initially developed with a range capped at 290 km.
What Defense Equipment does India procure From Russia?
- Submarines: Six Air Independent Propulsion (AIP-powered) conventional submarines under the P75-I project.
- Negotiations for leasing two nuclear-ballistic submarines.
- Frigates & Guided-missile Destroyers: Four of the Navy’s 10 guided-missile destroyers are Russian Kashin class, and 6 of its 17 frigates are Russian Talwar class.
- Aircraft Carrier: The only aircraft carrier in service with India, INS Vikramaditya is a Soviet-made Kiev-class vessel that came into service for the Indian Navy in 2013.
- Fighter Aircraft: Russia has also been one of main exporters of fighter aircraft to India, including hundreds of Sukhoi and MiG jets.
- All six of the service’s air tankers are Russian-made Il-78s.
- Tanks: Indian Army’s main battle tank force is composed predominantly of Russian T-72M1 (66%) and T-90S (30%).
- Missile Defense System: S-400 anti-missile system.