Social Justice
ASER 2024 and Elementary Education
For Prelims: NGO, Annual Status of Education Report (ASER), Anganwadi, Digital Literacy, Elementary Education, National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, PM SHRI Schools.
For Mains: Findings of Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2024, Concerns related to elementary education and way forward.
Why in News?
The NGO Pratham Foundation released the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2024 on learning outcomes of school students in rural India.
- It is based on a 2024 survey conducted in 17,997 villages across 605 rural districts.
- It reached 649,491 children in the 3-16 years age group, and tested the reading and arithmetic skills of over 500,000 children in the 5-16 years age group.
What is ASER?
- About: ASER is a nationwide, citizen-led household survey that offers an insightful snapshot of children's schooling and learning in rural India.
- Launched in 2005, ASER tracks educational trends and challenges in rural areas, evolving in coverage, focus, and frequency.
- Focus Areas:
- Enrollment: ASER tracks school and preschool enrollment trends, highlighting improvements and challenges by state and age group.
- Learning Outcomes: It assesses basic reading and arithmetic skills, showing children’s progress at primary and secondary levels.
- Digital Literacy: ASER 2024 evaluates older children's smartphone skills, including tasks like setting alarms, browsing, and messaging.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- Pre-primary (Age Group 3-5 Years):
- Enrollment: Enrollment in pre-primary institutions (Anganwadi, government pre-primary class, or private LKG/UKG) has steadily increased since 2018.
- E.g., Enrollment of 3-year-olds rose from 68.1% in 2018 to 77.4% in 2024.
- Pre-primary Institutions: Anganwadi centres are the main provider of pre-primary education, enrolling over half of 3-4-year-olds, while one-third of 5-year-olds attend private schools or preschools.
- Enrollment: Enrollment in pre-primary institutions (Anganwadi, government pre-primary class, or private LKG/UKG) has steadily increased since 2018.
- Elementary (Age Group 6-14 Years):
- Overall Enrollment: Enrollment dropped slightly from 98.4% in 2022 to 98.1% in 2024, with government school enrollment declining from 72.9% to 66.8%.
- Reading and Arithmetic Skills: In 2024, 23.4% of Standard (Std) III children in government schools could read Std II-level text, up from 16.3% in 2022.
- In 2024, 45.8% of Std VIII students could solve basic arithmetic problems, showing slight improvement.
- Arithmetic abilities improved more than reading skills, with government schools showing faster progress than private schools.
- Older Children (Age Group 15-16 Years):
- Enrollment: The dropout rate for 15-16-year-olds decreased from 13.1% in 2018 to 7.9% in 2024, with girls at a higher rate of 8.1%.
- Smartphone Access and Usage (Digital Literacy):
- Access: Nearly 90% of 14-16-year-olds have smartphone access, with boys (85.5%) using them more than girls (79.4%).
- Ownership: 27% of 14-year-olds and 37.8% of 16-year-olds own smartphones.
- Use: 82.2% of children use smartphones, with 57% for education and 76% for social media.
- Digital Safety: 62% of children know how to block/report profiles, and 55.2% know how to make profiles private.
- School Observations:
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy (FLN): Over 80% of schools implemented FLN activities, with at least one teacher in 75% of these schools receiving FLN training.
- Attendance: Student attendance increased from 72.4% in 2018 to 75.9% in 2024, and teacher attendance increased from 85.1% to 87.5%.
- School Facilities: There were slight improvements in the availability of basic school facilities:
- Usable girls' toilets increased from 66.4% in 2018 to 72% in 2024.
- Drinking water availability rose from 74.8% to 77.7%.
- The use of non-textbook books (e.g., novels, short stories, folk tales) by students increased from 36.9% to 51.3%.
- The percentage of schools with playgrounds remained stable at around 66%.
- Difference in Outcome: There are significant state-level differences in learning outcomes and improvement since the Covid-19 pandemic.
- In Std III, reading ability lagged behind 2018 levels in over half the states, but arithmetic improved in all but six.
- In Std V and VIII, many states did not reach pre-pandemic levels, even in arithmetic.
What is Elementary Education?
- About: Elementary Education is the foundation of the entire educational system, typically beginning at the age of six.
- It marks the start of formal education, crucial for a child's physical, mental, emotional, intellectual, and social development.
- Significance:
- Foundation for Future Learning: It provides core skills (reading, writing, math, problem-solving) essential for higher education and careers.
- Development of Social Skills: Children learn teamwork, communication, and empathy through peer and teacher interactions.
- Personal and Emotional Growth: It builds self-confidence and motivation, allowing children to explore their potential and creativity.
- Promotion of Motor Skills: Activities like sports and creative expression develop fine and gross motor skills.
- Building Social Awareness: Children learn hygiene, social responsibilities, and civic duties, fostering informed future citizens.
- Long-Term Economic Impact: Investment in elementary education drives economic growth, innovation, and productivity.
- Challenges:
- Poor School Infrastructure: Of over 14.71 lakh schools in India, 1.52 lakh lack functional electricity, hindering the use of technology like computers and the internet in teaching.
- 67,000 schools, including 46,000 government-run, lack functional toilets. Only 3.37 lakh government schools (33.2%) have disabled-friendly toilets, with less than a third being functional.
- Limited Access to Technology: Only 43.5% of government schools have computers for teaching, compared to 70.9% in private, unaided schools.
- Poor Teacher Student Ratio: India has nearly lakh schools with just one teacher each.
- Social Divides: Social divides, such as caste-class, rural-urban, religious, and gender disparities, affect the quality of education.
- Language Barriers:The lack of textbooks and materials in regional languages limits education access for those not proficient in Hindi/English medium of instruction.
- Poor School Infrastructure: Of over 14.71 lakh schools in India, 1.52 lakh lack functional electricity, hindering the use of technology like computers and the internet in teaching.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to Education?
- National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan
- PRAGYATA
- Mid Day Meal Scheme
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- PM SHRI Schools
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020
Way Forward
- Early Intervention: Immediate interventions should be made to increase retention by focusing on socio-economically disadvantaged groups.
- Introduce flexible, part-time education to accommodate children who need to work or assist at home.
- Literacy for Non-Enrolled Children: Launch supplementary literacy programs for children who have dropped out or missed school.
- Improve Accountability: Establish District School Boards for local educational planning and development. Increase school inspectors to enhance oversight and education quality.
- Provision of Schools: Ensure school access within 1 km (walking distance) by establishing more schools in rural and tribal areas.
- Parental Education: Launch campaigns to educate parents on the importance of education, particularly for girls, and how education can improve their children’s future.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the state of elementary education in India? What structural and policy changes are needed to strengthen elementary education in India? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution of India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q1. Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail. (2021)
Q2. How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate on your answer. (2020)


Biodiversity & Environment
OECMs for Achieving KMGBF 2022 Targets
For Prelims: Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures (OECMs), International Union for Conservation of Nature, World Commission on Protected Areas, World Wildlife Fund, Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF), UN Environment Programme, Biodiversity, Protected Area, Savannah, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), Invasive Alien Species.
For Mains: Role of other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) in achieving Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) 2022.
Why in News?
A new report titled “Guidance on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs)” has been released by the IUCN, World Commission on Protected Areas (WCPA) and WWF.
- The guidelines, with case studies, focus on conserving land, water, and marine areas to achieve GBF Target 3 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) 2022 to conserve 30% of these areas by 2030.
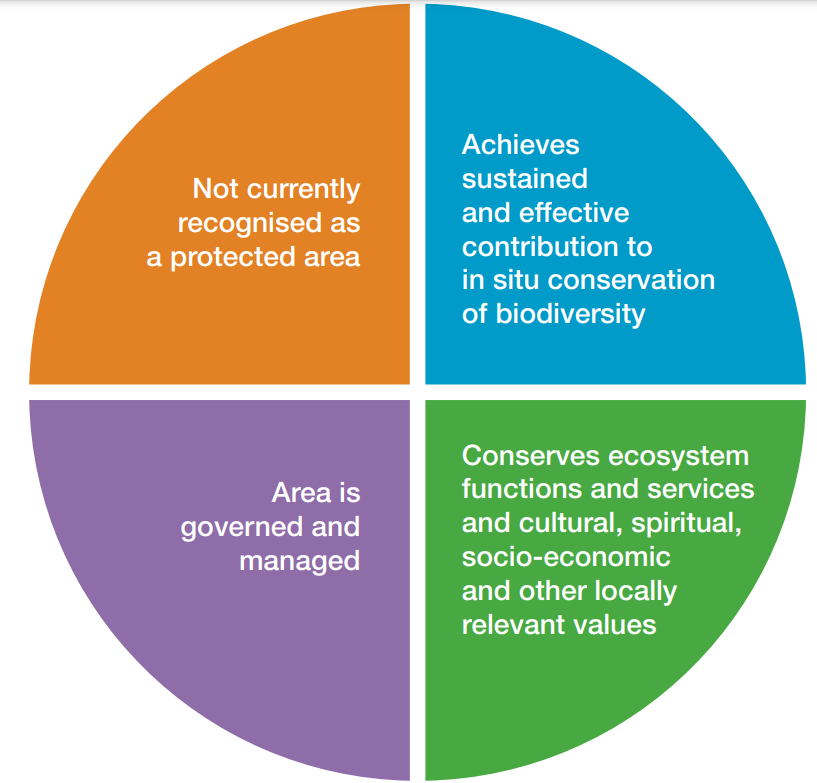
What are OECMs?
- About OECMs: An OECM is defined as a geographically defined area that is not a protected area, but is governed and managed to achieve positive, sustained, long-term outcomes for the in situ conservation of biodiversity.
- These areas conserve ecosystem functions and services, including cultural, spiritual, socio-economic, or other local values.
- e.g., Agricultural lands, forests for timber etc.
- Criteria for Identifying OECMs:
- Key Characteristics:
- Not a Protected Area: OECMs aren't formal protected areas (PAs) but contribute to biodiversity conservation.
- Governance Flexibility: OECMs can be managed by governments, private groups, Indigenous peoples, or local communities.
- Multiple Objectives: OECMs may focus on goals like water management or agriculture, with biodiversity conservation as a secondary benefit.
- Sustained Conservation: OECMs must ensure long-term in-situ biodiversity conservation through effective governance and management.
- Voluntary Identification: Identifying a site as an OECM is voluntary and requires the governing authority's agreement.
- Significance: OECMs recognize vital sites for biodiversity that aren't formally protected.
- OECMs expand the global conserved areas network, boosting biodiversity coverage without strict formalities.
- Case Studies:
- Los Amigos Conservation Area: It is located in the Los Amigos watershed, Peru and supports 12 globally threatened species, 12 primate species, and over 550 bird species.
- Wits Rural Facility: It is situated in South Africa and is mostly managed to maintain intact savannah and river habitats.
- North Tyndal Protected Water Area: It is located in Nova Scotia, Canada for biodiversity conservation by maintaining native vegetation and prohibiting harmful land uses.
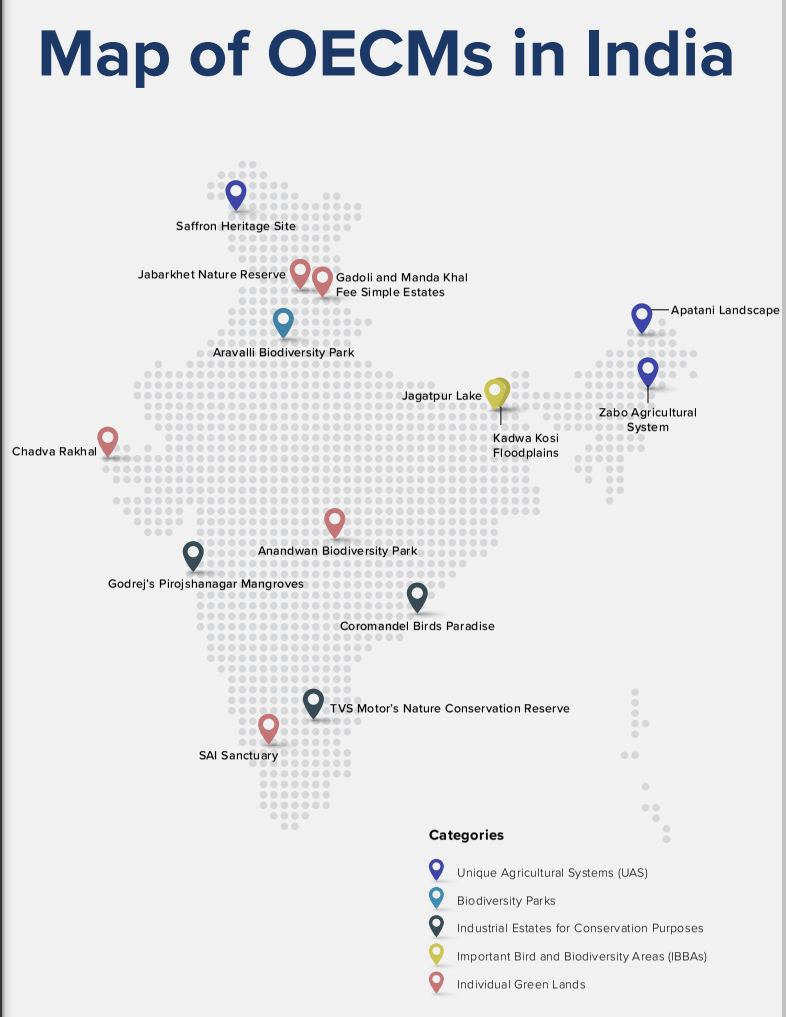
- OECMs in India:
- Difference Between OECMs from PAs:
|
Aspect |
Protected Areas (PAs) |
Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures (OECMs) |
|
Definition |
Area dedicated to long-term conservation of nature. |
Site conserving biodiversity, but not necessarily as the primary goal. |
|
Primary Objective |
Focus on biodiversity, ecosystem services, and cultural values. |
Biodiversity as a secondary or incidental outcome. |
|
Legal Recognition |
Formally recognized and legally protected. |
Voluntary, may lack formal protection. |
|
Role in Conservation Networks |
Core of conservation networks, vital for long-term protection. |
Complements PAs, enhancing ecological connectivity. |
|
Conservation Outcome |
Strict regulations for biodiversity protection. |
May support biodiversity, but not focused on conservation. |
|
Complementary Role |
Central to achieving conservation targets (e.g., 30% by 2030). |
Enhances ecological representation and connectivity. |
What are Eight Sections Containing Guidelines for OECMs?
What is KMGBF 2022?
- About: Adopted at CoP 15 (Montreal, Canada) in December 2022, it aims to halt and reverse global biodiversity loss by 2030.
- It supports the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and builds upon the achievements and lessons learned from the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011–2020.
- Objectives: It includes 23 action-oriented global targets for urgent action by 2030, aiming to restore at least 30% of degraded terrestrial, inland water, and marine ecosystems.
- This target refers to global efforts, not a requirement for each country to allocate 30% of its land and water.
- Future Outlook: The framework envisions a collective commitment to living in harmony with nature by 2050, guiding current actions and policies on biodiversity conservation and sustainable use.
Note: CBD COP-16 took place in Cali, Colombia in 2024 with the theme "Peace with Nature".
- India launched the updated National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) at COP 16 to the CBD aligning with the KMGBF.
- Cali Fund was established to ensure fair and equitable sharing of benefits from the use of digital sequence information (DSI) on genetic resources.
What is India’s Biodiversity Target Under KMGBF?
- Conservation Areas: Aim to conserve 30% of areas to enhance biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: Target a 50% reduction in invasive alien species.
- Rights and Participation: Ensure the involvement of indigenous peoples, local communities, women, and youth in conservation.
- Sustainable Consumption: Promote sustainable consumption and cut food waste by half.
- Benefit Sharing: Encourage fair sharing of benefits from genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- Pollution Reduction: Reduce pollution, halving nutrient loss and pesticide risk.
- Biodiversity Planning: Manage areas to prevent loss of high biodiversity regions.
IUCN
- Created in 1948, IUCN is the world’s largest and most diverse environmental network.
- IUCN is a membership union composed of over 1,400 organizations, including both government and civil society groups.
- IUCN is a leading provider of conservation data, assessments, and analysis, offering tools and knowledge to support global environmental efforts.
- It prepares the IUCN Red Data Book (now known as the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species) in which species are classified into categories based on their risk of extinction e.g., Critically Endangered, Endangered etc.
IUCN World Commission on Protected Areas (WCPA)
- It is the world’s leading network of expertise on protected and conserved areas, with over 2,500 members across 140 countries.
- It offers strategic advice to policymakers on establishing, managing, and strengthening protected areas.
WWF
- WWF, founded in 1961, is an international NGO focused on environmental conservation and protecting vulnerable species and ecosystems.
- Its mission is to halt environmental degradation and create a future where humans live in harmony with nature.
Conclusion
The release of the OECM guidelines by IUCN and WWF supports the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, aiming to conserve 30% of land, waters, and marine areas by 2030. India's biodiversity targets align with global goals to enhance conservation, reduce invasive species, and promote sustainable consumption.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures (OECMs). How are they different from Protected Areas? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. “Momentum for Change: Climate Neutral Now” is an initiative launched by (2018)
(a) The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
(b) The UNEP Secretariat
(c) The UNFCCC Secretariat
(d) The World Meteorological Organisation
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Define the concept of carrying capacity of an ecosystem as relevant to an environment. Explain how understanding this concept is vital while planning for sustainable development of a region. (2019)


Social Issues
Impact of Early Smartphone Use on Adolescents
For Prelims: Anxiety, PRAGYATA guidelines, E-PG Pathshala, Metaverse, Virtual Reality, National Human Rights Commission, CHILDLINE 1098, Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing, National Educational Alliance for Technology
For Mains: Digital platforms and its impact on children, Cyber Security and Privacy, Technology and Society.
Why in News?
A study by Sapien Labs, titled “The Youth Mind: Rising Aggression and Anger”, highlights the troubling link between early smartphone use and deteriorating mental well-being in adolescents aged 13-17 in India and the US.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
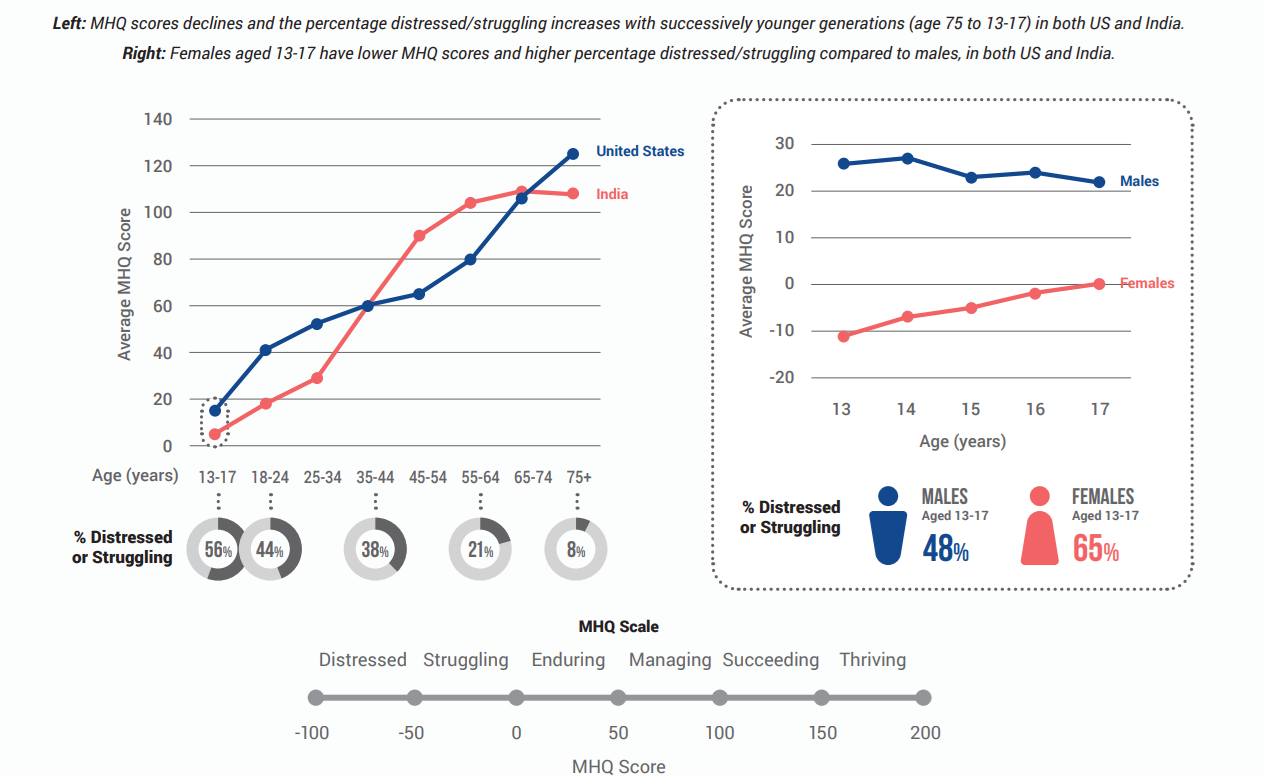
- Smartphone Use and Mental Health: The study based on Mind Health Quotient (MHQ) of adolescents reveals a significant correlation between the early initiation of smartphone use and the decline in mental health among adolescents, with symptoms such as aggression, anger, irritability, and hallucinations becoming more prevalent.
- Adolescents who start using smartphones at a younger age show more pronounced mental health issues.
- In addition to sadness and anxiety, new symptoms like intrusive thoughts and detachment from reality were observed, indicating a deeper mental health crisis.
- Online Exposure Risks: Early smartphone access exposes young people to inappropriate content, disrupts sleep, and reduces in-person interactions, which are vital for developing social skills and coping with conflict.
- Gender Differences: The study points out that females are particularly vulnerable, with rising aggression and anger being observed more frequently among girls.
- Notably, 65% of adolescent girls reported distress, significantly higher than boys.
- Cultural Differences: The decline in mental well-being is slower in India compared to the US.
- The decline in mental well-being is evident in both males and females in the US, but only females in India show a decline, with some aspects improving in males.
- Educational Technology as a Solution: The study suggests using educational technology and restricted access to smartphones with parental controls as potential solutions to mitigate the mental health impact.
Mind Health Quotient (MHQ)
- About: The MHQ is a comprehensive assessment of 47 aspects of mental function, measured across six dimensions (Mood and Outlook, Adaptability and Resilience, Social Self, Drive and Motivation, Cognition, and Mind-Body Connection).
- The aggregate MHQ score correlates with functional productivity, with higher scores linked to more productive days.
- Unlike "mental wellbeing," which focuses on emotional states, "mind health" encompasses both emotional and functional aspects, emphasizing the ability to navigate life's challenges and maintain productivity.
- MHQ Vs IQ and EQ: MHQ differs from Intelligence Quotient (IQ ) (measures cognitive abilities) and Emotional Quotient (EQ) (measures emotional intelligence (EI)).
- MHQ encompasses a broader range of mental functions, including mood, resilience, and mind-body connection.
What is the Impact of Early Digital Access to Children?
- The proliferation of the internet and social media has been a double-edged sword for children. While on one hand it has democratized learning for millions, on the other it has exposed children to harmful and toxic behaviours.
- Positive Impacts:
- Enhanced Learning Opportunities: Digital access offers a wealth of educational resources, and India’s initiatives like tablet sets pre-loaded with educational content, and PRAGYATA guidelines ensure that students focus on learning while limiting distractions.
- E-PG Pathshala provides access to online courses and collaborative learning, especially for students in remote areas.
- Personalised Learning: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence -based platforms adapt to students' learning styles, providing customized educational experiences.
- Digital tools like games, simulations, and interactive platforms can make learning more engaging, helping children develop skills in various subjects, such as math, language, and science.
- Skills Development: Exposure to digital technology can help children develop important skills like problem-solving, coding, and digital literacy, which are vital in today’s technology-driven world.
- In recent years, "Kidfluencers" have driven a booming social media advertising industry, with children earning significant amounts through sponsored content.
- Social Connection: Helps reduce loneliness by keeping kids connected with family and friends.
- Access to Support: Provides easy access to mental health resources and coping strategies.
- Enhanced Learning Opportunities: Digital access offers a wealth of educational resources, and India’s initiatives like tablet sets pre-loaded with educational content, and PRAGYATA guidelines ensure that students focus on learning while limiting distractions.
- Negative Impacts:
- Physical Inactivity: Adolescence is crucial for developing emotional habits, with factors like sleep, physical activity, coping skills, and supportive relationships promoting well-being.
- However, early digital access to children leads to sedentary behavior, affecting both physical and mental health.
- Screen Addiction can cause anxiety, depression, and sleep problems and brain rot, leading to mental stagnation and reduced cognitive function.
- Privacy: Violations by tech companies, hackers, or advertisers can lead to identity theft, fraud, manipulation, and exposure to harmful content.
- Cyberbullying: Increases vulnerability to online harassment, impacting self-esteem.
- Children can fall victim to extortion or online exploitation by predators who manipulate or threaten them using personal information or explicit content.
- The internet exposes children to the risk of encountering pornography, as unfiltered content can lead to accidental exposure or targeted exploitation, raising serious legal, psychological, and safety concerns.
- In the realm of the Metaverse and Virtual Reality, virtual predators exploit children through scams, harassment, and discrimination, fostering an environment ripe for cyberbullying.
- FOMO: Social media often presents an idealised life, causing young people to feel like they're missing out (Fear of Missing Out (FOMO), leading to anxiety, stress, and inadequacy.
- Reduced Social Interaction: Excessive phone use can decrease face-to-face interactions, hindering social skills.
- Violence: Exposure to online violence, including violent games and graphic content, can desensitize children, normalize aggression, and lead to increased fear and emotional distress.
- Young internet users are vulnerable to recruitment by extremist and terrorist groups.
- Physical Inactivity: Adolescence is crucial for developing emotional habits, with factors like sleep, physical activity, coping skills, and supportive relationships promoting well-being.
Online Child Safety Statistics
- Mental Health: According to the World Health Organization (WHO) globally, 1 in 7 adolescents faces a mental disorder, contributing to 15% of the disease burden, with depression, anxiety, and behavioral disorders as leading causes, and early digital access being a key contributor.
- Neglecting adolescent mental health can lead to lasting physical and mental health issues, limiting opportunities for a fulfilling adult life.
- Cyberbullying: Over a third of young people in 30 countries report being cyberbullied, with 1 in 5 skipping school because of it.
- Online Sexual Exploitation: 80% of children in 25 countries report feeling in danger of online sexual abuse or exploitation.
- Children in India are at high risk of exposure to child sexual abuse material (CSAM) due to the rapid increase in internet usage and the availability of harmful content.
- According to the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), India accounted for 5.6 million reports of CSAM out of 32 million globally in 2022, highlighting a significant problem.
What are India's initiatives to Protect Children Online and Productive Digital Access?
- Protect Children Online:
- POSCO Act (Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act), 2012: The POSCO Act has provisions to protect children from online sexual offences, including mandatory reporting and child-friendly procedures.
- CHILDLINE 1098: It is a National, 24 Hour, Emergency toll free phone service for children in need of care and protection. It is a project of The Ministry of Woman and Child Development.
- Digital Literacy Programs: The Ministry of Education and CBSE have incorporated cyber safety in school curricula to educate children on safe internet use.
- Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000: Section 67B of the IT Act, imposes stringent punishments for publishing or viewing CSAM online.
- Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children (CCPWC): The CCPWC is a Nirbhaya Fund project that raises awareness, strengthens law enforcement capacity, and enhances cyber forensic facilities.
- Productive Digital Access:
Way Forward
- Child Online Safety Toolkit: Install the Child Online Safety Toolkit on children's devices, this toolkit provides a hands-on, comprehensive approach to safeguarding young users online.
- It aligns with international frameworks like the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC), addressing key issues such as cyberbullying, emotional intelligence, and mental health.
- Delay Smartphone Ownership: Delaying smartphone ownership (until at least 8th grade) could help reduce aggression, anxiety, and suicide rates among adolescents, urging action from parents, schools, and governments.
- Stronger Regulations: Some countries, like Australia, have already taken steps to protect children by banning social media use for those under the age of 16.
- Implement the draft Data Protection Rules, 2025, through which India has introduced requirements for age verification and parental consent for children under 18 to access social media.
- Awareness: Promote digital literacy programs that teach children about the potential dangers of online spaces and equip them with skills to identify harmful content, cyberbullying, and online predators.
- Mental Health Support: Invest in accessible mental health resources like National Tele Mental Health Programme, Kiran Helpline, and MANAS Mobile App for children and adolescents, offering counseling and coping strategies for those impacted by excessive screen time and online exploitation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How can early smartphone use impact the mental health of adolescents? Discuss the implications and possible measures to mitigate these effects. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. In order to enhance the prospects of social development, sound and adequate health care policies are needed particularly in the fields of geriatric and maternal health care.Discuss. (2020)
Q. What are the different elements of cyber security ? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)


Economy
UNCTAD Global Investment Trends Monitor Report
For Prelims: Foreign Direct Investment, United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), Global Investment Trends Monitor for 2024, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
For Mains: Global FDI Trends, India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), FDI’s role in the development.
Why in News?
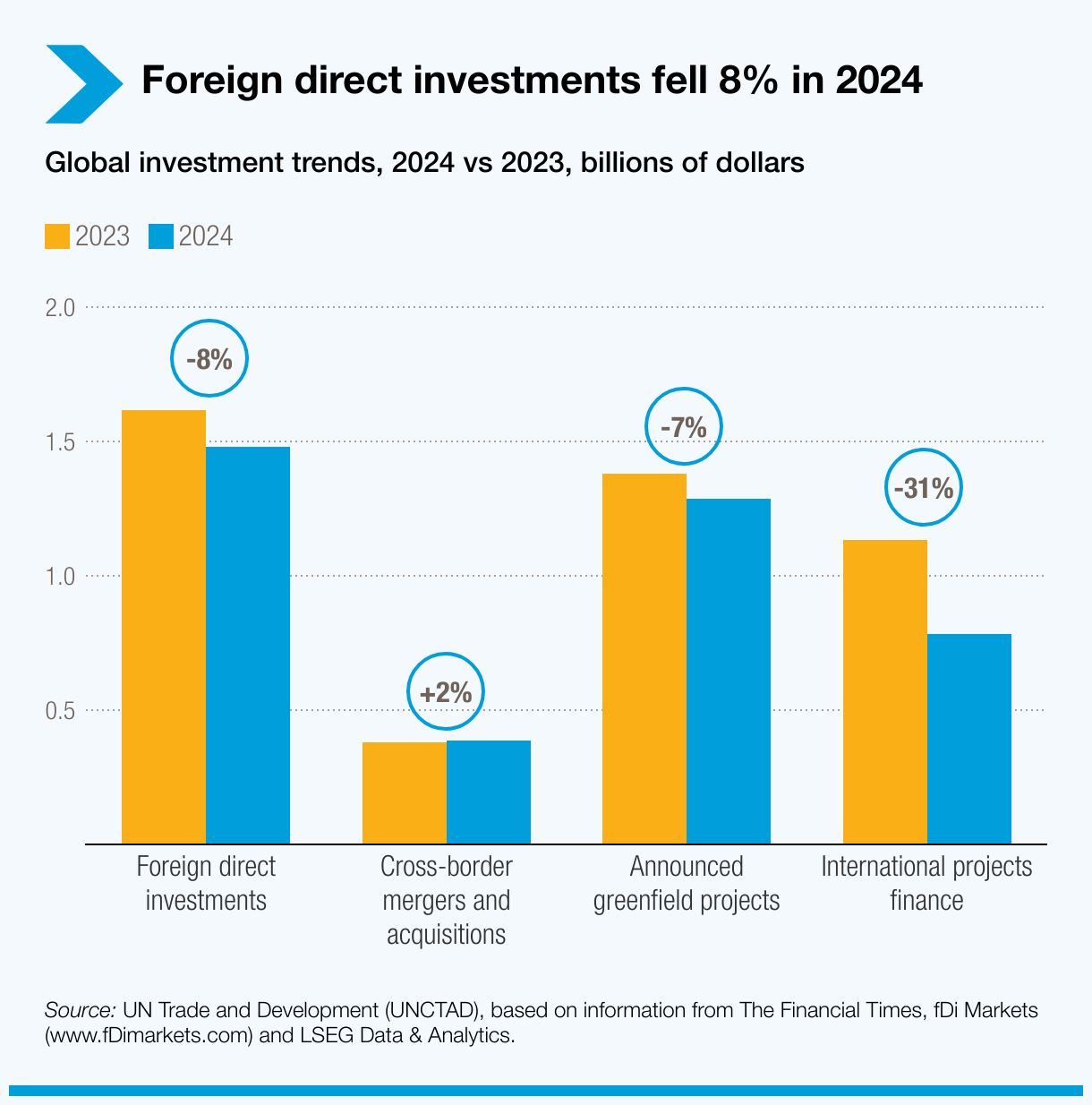
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has released its Global Investment Trends Monitor for 2024, reporting an 8% decline in global Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- This threatens funding for critical sectors like infrastructure and renewable energy which are essential for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- About:
- It is the leading institution of the UN established in 1964, that is focused on trade and development of developing countries.
- It provides expertise and policy advice on issues related to trade, investment, finance, and technology transfer to promote sustainable development.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Structure: It is a part of the UN Secretariat, reports to the General Assembly and Economic and Social Council; has its own membership, leadership, and budget.
- Flagship Reports:
- Trade and Development Report
- World Investment Report
- Digital Economy Report
- Technology and Innovation Report
What are the Key Highlights of the Global Investment Trends Monitor for 2024 Report?
- Global FDI Trends:
- Global FDI: Global Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows increased by 11% reaching about USD 1.4 trillion in 2024. However, when excluding flows through European conduit economies, FDI decreased by around 8%.
- Conduit economies are countries that allow financial flows to be diverted to other countries for tax avoidance. Eg: Ireland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Switzerland and the UK.
- Developed Economies: FDI into developed economies surged by 43%, driven primarily by multinational transactions passing through conduit economies.
- However, excluding these transactions, FDI into developed economies fell by 15%.
- Developing Economies: FDI flows to developing economies declined by 2% in 2024, following a 6% drop in 2023.
- Global FDI: Global Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows increased by 11% reaching about USD 1.4 trillion in 2024. However, when excluding flows through European conduit economies, FDI decreased by around 8%.
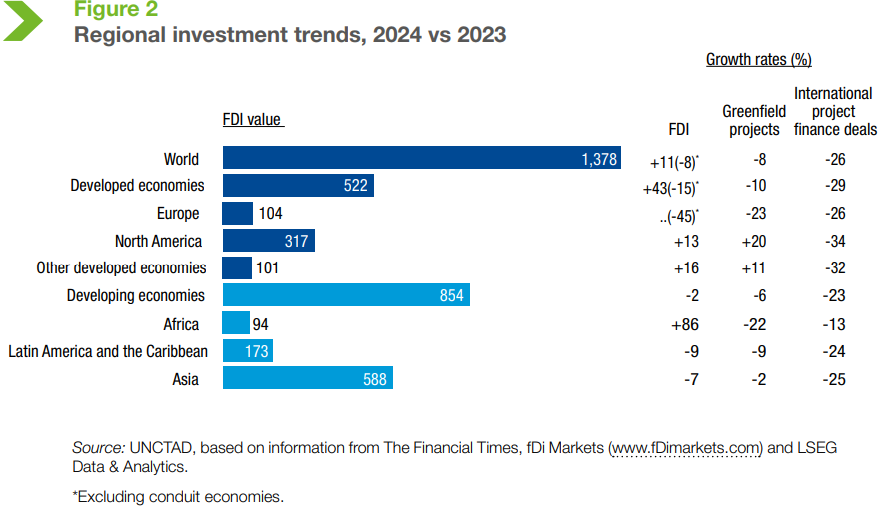
- Regional Investment Trends:
- Developed Economies:
- FDI in Europe dropped 45% (excluding conduit economies) but North America saw a 13% rise.
- Greenfield project announcements in developed economies fell by 10%, but the value of greenfield projects rose by 15%, mainly due to semiconductor megaprojects.
- Developing Economies:
- Greenfield investment announcements decreased by 6% in number.
- Africa and Asia saw the largest declines in greenfield project numbers, with nearly 200 fewer projects in Africa and 150 fewer in Asia.
- It also declined in Latin America and the Caribbean.
- FDI in Africa surged by 84% to USD 94 billion, mainly driven by a large project in Egypt.
- FDI in Central America has increased.
- FDI flows to developing Asia decreased by 7%, with China experiencing a 29% decline, while ASEAN saw a 2% increase and India saw a 13% rise.
- India experienced growth in greenfield projects. The international project finance in India dropped by 23% in number and 33% in value.
- Greenfield investment announcements decreased by 6% in number.
- Developed Economies:
- SDG-Related Investments:
- Investments in sectors related to the SDGs, including infrastructure, agrifood systems, and water and sanitation, decreased by 11% in 2024.
- This drop could impact critical sectors such as affordable and clean energy (SDG 7), industry and infrastructure (SDG 9), and water and sanitation (SDG 6).
- Renewable energy project finance slowed, with international deals down 16%, and domestic finance down 60%.
What are the Prospects for Global FDI in 2025 as per UNCTAD Report?
- Global FDI Outlook:
- Global FDI is expected to grow moderately, with the US and EU seeing stronger growth.
- US investment abroad has declined as focus shifts to domestic projects, while Chinese investment abroad has increased.
- ASEAN, Eastern Europe, West Asia, North Africa, and Central America may benefit from global supply chain shifts.
- For India, moderate FDI growth is expected in 2025, driven by improved financing conditions, increased mergers and acquisitions (M&A), and ongoing reforms.
- Global FDI is expected to grow moderately, with the US and EU seeing stronger growth.
- Key Influencing Factors:
- FDI growth will depend on GDP, trade, inflation, market volatility, geopolitical dynamics, technology advancements, and policy changes.
- Private equity and sovereign investors will also play a significant role.
- Economic Growth:
- Stable GDP growth is expected with improved projections for capital formation and trade, benefiting global investments.
- Lower interest rates could reduce borrowing costs, boosting cross-border investments, especially in infrastructure.
- Technology & Sector Trends:
- Investments in sectors like AI, cloud computing, cybersecurity, and renewable energy (green hydrogen, electric vehicles) are expected to rise.
What is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
- About:
- Types of FDI:
- Greenfield Investment: Creating new business operations from the ground up, offering high control and customization.
- Brownfield Investment: Expanding through mergers, acquisitions, or joint ventures by utilizing existing facilities.
- While control may be lower than in Greenfield investments, it still allows significant influence over operations.
- FDI in India:
- Regulation: FDI in India is governed by the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, and is administered by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- FDI Prohibition in India: FDI is strictly prohibited in sectors like atomic energy generation, gambling and betting, lotteries, chit funds, real estate, and the tobacco industry.
- Latest Data Related to FDI: FDI inflows into India crossed USD 1 trillion between April 2000 and September 2024, totaling USD 1,033.40 billion.
- From 2014 to 2024, India attracted USD 667.4 billion in cumulative FDI, a 119% increase from the 2004-2014 period.
What are the Opportunities and Challenges Related to FDI in India?
- Opportunities for FDI in India:
- Large Market Size and Growth: India’s 1.4 billion population drives high demand for both affordable and high value goods.
- India is one of the fastest growing economies and its GDP is projected to grow at 6.5% in 2025 and 2026 as per IMF.
- Favorable Demographics: A young workforce (over 65% below 35 years) provides a relatively skilled and cheap labour pool.
- Government Initiatives: Policies like "Make in India," "Atmanirbhar Bharat," and ease of doing business reforms streamlined requirements and made favourable destinations to attract FDI.
- Strategic Location: India's location acts as a gateway to the emerging markets of South Asia, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia.
- Large Market Size and Growth: India’s 1.4 billion population drives high demand for both affordable and high value goods.
- Challenges in Attracting FDI:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Complex tax systems, inconsistent policies (retrospective taxation), and bureaucratic delays hinder business operations.
- Infrastructure Challenges: Poor infrastructure, particularly in rural and suburban areas, limits ease of doing business.
- Labor Laws: Rigid labor laws and low labor market flexibility create challenges for businesses.
- Expectations from Investors:
- Technology Transfer: India seeks foreign expertise and technology in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and renewable energy.
- Job Creation: Investors are expected to create employment opportunities for India's growing workforce.
- Sustainable Investments: India encourages green and sustainable investments to meet its climate goals (e.g., National Action Plan on Climate Change).
Conclusion
India’s large market, economic growth, and favorable demographics offer significant opportunities for FDI. While government initiatives like “Make in India” create a favorable environment, challenges such as regulatory hurdles and infrastructure gaps remain. India expects investors to contribute to technology transfer, job creation, and sustainable growth, which will support both economic and social development goals.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the role of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in enhancing India’s competitiveness and innovation ecosystem. How do improvements in global competitiveness influence FDI inflows? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Foreign Direct Investment in India, which one of the following is considered its major characteristic? (2020)
(a) It is the investment through capital instruments essentially in a listed company.
(b) It is a largely non-debt creating capital flow.
(c) It is the investment which involves debt-servicing.
(d) It is the investment made by foreign institutional investors in Government securities.
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following: (2021)
- Foreign currency convertible bonds
- Foreign institutional investment with certain conditions
- Global depository receipts
- Non-resident external deposits
Which of the above can be included in Foreign Direct Investments?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 4
(d) 1 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Justify the need for FDI for the development of the Indian economy. Why is there a gap between MOUs signed and actual FDIs? Suggest remedial steps to be taken for increasing actual FDIs in India. (2016)


Important Facts For Prelims
Achievements Under National Health Mission
Why in News?
The Central Government recently presented a 2021-24 assessment report on the National Health Mission (NHM), highlighting its achievements in improving healthcare accessibility and addressing key health challenges, including Covid-19.
What are the Key Achievements of the NHM (2021-24)?
- Human Resource Expansion:
- Between FY 2021-24, NHM engaged over 12 lakh additional healthcare workers, including medical officers, nurses, specialists, community health officers (CHOs), and AYUSH doctors.
- 1.56 lakh Ni-kshay Mitra volunteers supported over 9.4 lakh TB patients under the Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, improving healthcare delivery in rural areas.
- Reduction in Mortality Rate:
- Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) declined by 83% since 1990 (exceeding the global decline of 45%).
- The Under-5 Mortality Rate (U5MR) reduced by 75% (outperforming the global reduction of 60%).
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) decreased from 39 (2014) to 28 (2020).
- Total Fertility Rate (TFR) dropped from 2.3 (2015) to 2.0 (2020).
- Disease Control and Elimination
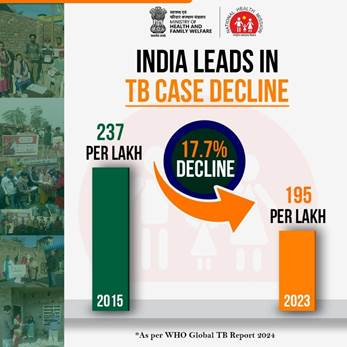
- Tuberculosis: TB incidence reduced by 17.7% (2015-2023) and mortality decreased by 21.4% under National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP).
- Malaria: Malaria cases initially declined by 13.28% in 2021, but rose by 9.13% in 2022 and 28.91% in 2023.
- Deaths fell by 3.22% in 2021, dropped by 7.77% in 2022, despite the rise in cases.
- Kala-azar: Kala-azar elimination was successful, with 100% of endemic blocks achieving the target of less than one case per 10,000 population by 2023.
- Tuberculosis: TB incidence reduced by 17.7% (2015-2023) and mortality decreased by 21.4% under National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP).
- Vaccination and Immunization Campaigns:
- The Measles-Rubella Elimination Campaign, under the Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI) 5.0, vaccinated over 34.77 crore children, achieving an impressive 97.98% coverage.
- During Covid-19 pandemic over 220 crore vaccine doses (Jan 2021–Mar 2024) were administered.
- Implementation of the India Covid-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Package (ECRP).
- The U-WIN platform launched in January 2023, tracked vaccination events in real-time and expanded to 65 districts by FY 2023-24.
- Healthcare Infrastructure Expansion:
- By March 2024, 7,998 public health facilities were certified under National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS), with 4,200 receiving national certification.
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs: Operational centers increased to 1.72 lakh, ensuring essential healthcare services for millions.
- Specialized Health Initiatives:
- Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme (PMNDP): PMNDP delivered 62.35 lakh hemodialysis sessions in FY 2023-24, benefiting 4.53 lakh patients.
- National Sickle Cell Anemia Elimination Mission (NSCAEM): NSCAE Mission screened 2.61 crore individuals, focusing on tribal regions, aiming for disease elimination by 2047.
What is the National Health Mission?
- About:
- The NHM, launched in 2013, aims to provide accessible, affordable, and quality healthcare, focusing on vulnerable and underserved populations.
- It integrates the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) and the National Urban Health Mission (NUHM).
- Initiatives:
- Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child, and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A), including Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK).
- Communicable Diseases Control: Focusing on Tuberculosis (TB), malaria, leprosy, and HIV/AIDS under initiatives such as the National Vector-Borne Disease Control Programme and Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme.
- Non-Communicable Diseases: For diabetes, hypertension, and cancer under the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke.
- Other Initiatives:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent Covid-19 pandemic, consider the following statements:
- The Serum Institute of India produced Covid-19 vaccine named Covishield using mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using vector based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
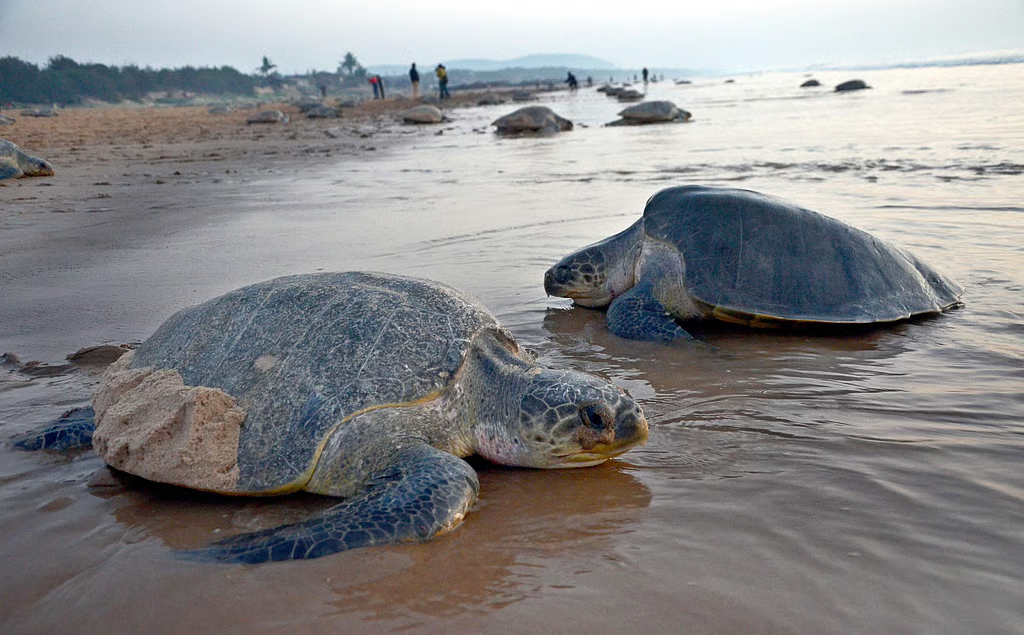
Mass Nesting of Olive Ridley Turtles
Why in News?
The Olive Ridley turtles are expected to return in large numbers to the Rushikulya River mouth in Odisha for their mass nesting, a vital occurrence for the conservation of this species.
What are Key Facts About Olive Ridley Turtles?
- Scientific Classification:
- Scientific Name: Lepidochelys olivacea
- Class: Reptilia
- Family: Cheloniidae
- Appearance: Olive ridley turtles are an olive or grayish-green with a heart-shaped carapace (top shell).
- They closely resemble Kemp’s ridleys (primarily found in the Gulf of Mexico) and are the smallest sea turtles. Their size and shape vary by region, with the largest found in West Africa.
- Habitat and Distribution: Found in the tropical regions of the Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic Oceans. Inhabits both pelagic (open ocean) and coastal waters.
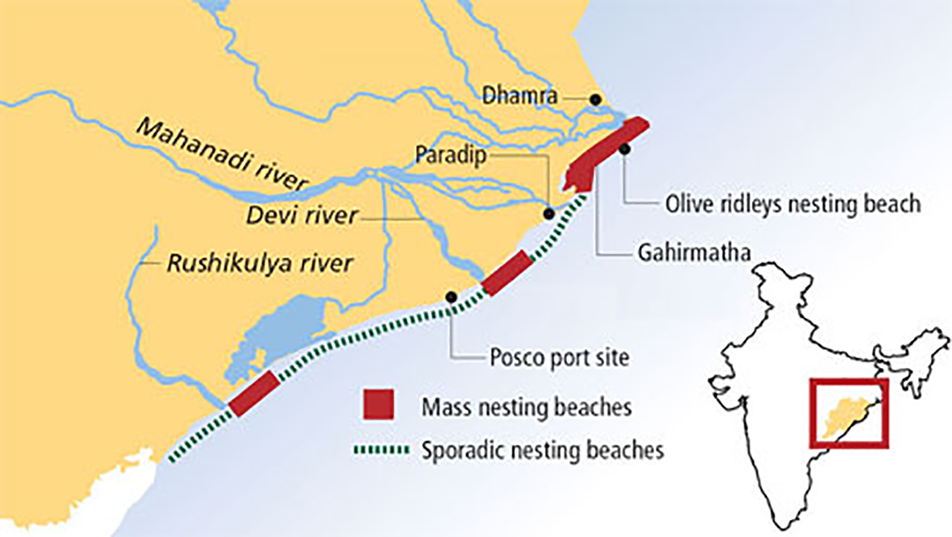
- Major nesting sites in India: Rushikulya, Gahirmatha, Devi River mouth in Odisha, and the Andaman Islands.
- Gahirmatha marine sanctuary is recognised as the largest known mass nesting rookery for Olive Ridley sea turtles in the world.
- Major nesting sites in India: Rushikulya, Gahirmatha, Devi River mouth in Odisha, and the Andaman Islands.
- Reproduction: Olive ridley turtles are famous for arribada (Spanish for "arrival"), a unique mass nesting behavior where thousands of females nest simultaneously.
- From September, they travel 9,000 km from the Pacific to the Indian seas. After mating, males retreat, and females nest from December to March.
- Females nest 1-3 times per season, laying around 100 eggs per clutch.
- The sex of hatchlings is determined by nest temperature.
- From September, they travel 9,000 km from the Pacific to the Indian seas. After mating, males retreat, and females nest from December to March.
- Diet and Behavior: Like all sea turtle species, except the herbivorous Green Turtle, the Olive Ridley is an omnivore, eating jellyfish, snails, crabs, prawns, algae, and small fish.
- Migrate long distances between feeding and nesting sites.
- Protection Status:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule 1
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Threats: Bycatch in fishing gear (trawls, gillnets, longlines).
- Poaching and egg harvesting for human consumption.
- Habitat loss from coastal development, plastic ingestion, and marine pollution, along with rising temperatures and sea levels, threaten olive ridley turtles by disrupting nesting sites and food sources.
- Conservation Initiatives:
- Operation Olivia: Indian Coast Guard initiative (since the 1980s) to protect nesting turtles and prevent illegal trawling.
- Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs): Odisha mandates TEDs in trawls(cone-shaped net) to prevent accidental deaths.
- Tagging: Olive Ridley turtles are tagged with non-corrosive metal tags to track their movements and safeguard their habitats.
Note:
Indian biologist Shailendra Singh has been honored with the Behler Turtle Conservation Award (considered as the the “Nobel Prize” of turtle conservation) for saving three critically endangered turtle species (Northern River Terrapin, Red-crowned Roofed Turtle, Black Softshell Turtle) from extinction.
Rushikulya River
- The Rushikulya River originates from the Rushyamala hills in the Eastern Ghats, Kandhamal district, Odisha and flows southeast into the Bay of Bengal.
- Its prominent tributaries include Padma, Boringanalla, Joro, Badanadi, Baghua, Dhanei, and Ghodhado. The river has no delta at its mouth.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following is the national aquatic animal of India? (2015)
(a) Saltwater crocodile
(b) Olive ridley turtle
(c) Gangetic dolphin
(d) Gharial
Ans: C
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Some species of turtles are herbivores.
- Some species of fish are herbivores.
- Some species of marine mammals are herbivores.
- Some species of snakes are viviparous.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
Kailash Mansarovar Yatra
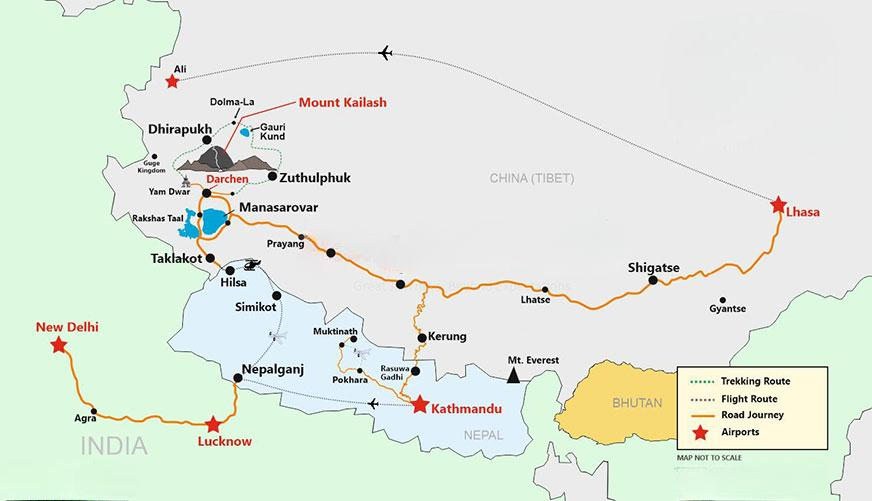
India and China agreed to revive the annual Kailash Mansarovar Yatra (KMY).
- Mount Kailash is a diamond-shaped peak made of black rock, located in Tibet.
- India organizes the KMY annually between June and September through the Lipulekh Pass (since 1981) in Uttarakhand and the Nathu La Pass (since 2015) in Sikkim.
- Mount Kailash stands at 6,638 meters and is considered a sacred peak by Hindus, Buddhists, Jains, and Bons (indigenous religion of Tibet).
- For Tibetans Buddhists, Kailash is the cosmic axis, or Mount Meru, connecting heaven and earth.
- In Hinduism, it is the abode of Lord Shiva and Goddess Parvati.
- In Jainism, Kailash is Ashtapada, where Rishabhanatha attained enlightenment.
- Mount Kailash is considered the spiritual center of the Earth, with the Sutlej, Brahmaputra, Kamali, and Indus rivers originating from it.
- Lake Mansarovar is located at the base of the mountain.
- Mount Kailash, though lower in height than Mount Everest (8,849 meters), remains unclimbed as its ascent is prohibited due to its sacred significance.
Read More: Kailash Manasarovar Yatra


Rapid Fire
Aroma Mission
The Ministry of Science & Technology said that the Northeast region as well as Jammu & Kashmir (J&K) have been on the priority list of the Aroma Mission.
- About Aroma Mission: It was started in J&K and aims to boost India’s aroma industry by enhancing the cultivation of aromatic crops and production of essential oils. It is popularly known as the Lavender Revolution.
- Aromatic crops (like rose, peppermint) are plants grown for their fragrant oils, used in industries like cosmetics, aromatherapy, and food flavoring.
- Focus: It focuses on the cultivation of high-value aroma crops such as lemongrass, lavender, vetiver, palmarosa, and others.
- Related Initiatives: The Incubation & Innovation Complex (IICON) at CSIR-North-East Institute of Science and Technology (CSIR-NEIST), Jorhat was inaugurated to provide farmers with advanced technologies and facilities.
- CSIR-NEIST introduced aromatic crops across 5,000+ hectares in the Northeast and set up 39 essential oil distillation units.
- Potential Impact: Targeted production of over 2000 tonnes of high-quality essential oils worth more than Rs. 300 crores annually.
- Expected to generate 60 lakh man-days of rural employment, and increase farmers' income by Rs. 60,000 to 70,000 per hectare annually.
- Nodal Agency: The nodal agency is CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CSIR-CIMAP), Lucknow.
Read More: Aroma Mission & Floriculture Mission


Rapid Fire
Namdapha Tiger Reserve
NamdaphaTiger Reserve (NTR) in Arunachal Pradesh has recorded the first sighting of an adult male elephant in 12 years.
- Elephants traditionally migrated between Namsai (Arunachal Pradesh) and Myanmar via NTR, however, encroachments since 1996 have blocked migration corridors, confining them in northern areas.
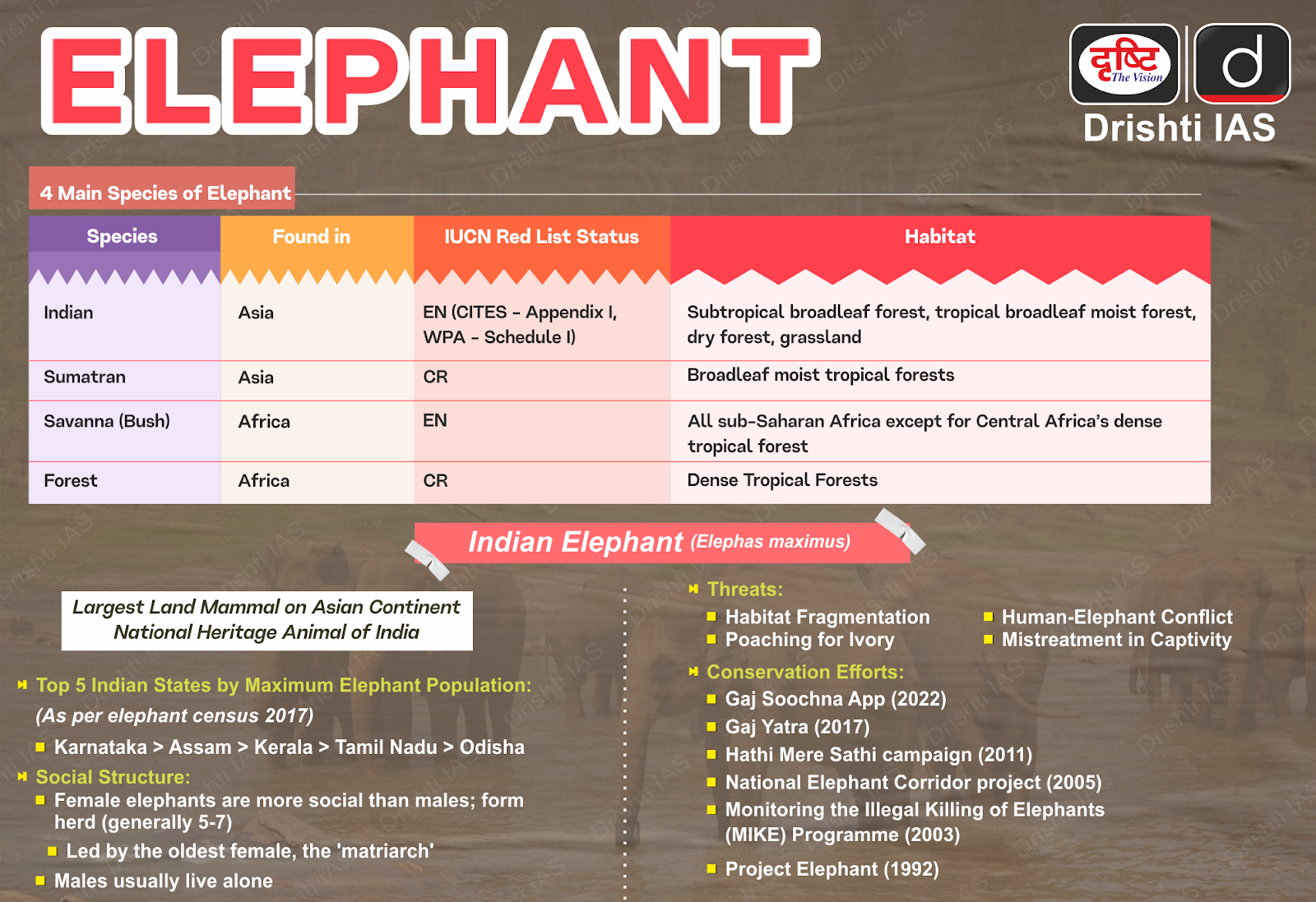
About Elephants:
- India hosts about 60% of the world's Asian elephant population, with an estimated 27,312 elephants (2017 census) and 138 elephant corridors.
- Asian elephants have a 22-month gestation period and are classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
Namdapha Tiger Reserve
- Location: Changlang District (Arunachal Pradesh)
- Recognition: Declared as Wildlife Sanctuary in 1972, National Park and Tiger Reserve in 1983.
- Vegetation: Northern Tropical Evergreen Forest, Moist Deciduous Forests, and Alpine Scrub Forests.
- River: Namdapha River
Other Protected Areas in Arunachal Pradesh
- Pakke Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Mouling National Park
- Kamlang Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Itanagar Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Eagle Nest Wildlife Sanctuary.
Read More: Namdapha Flying Squirrel


Rapid Fire
Aadhaar for Chinar Trees
The Jammu & Kashmir (J&K) government has initiated the “Tree Aadhaar” mission to conserve the region's iconic chinar trees (Platanus orientalis var. cashmeriana) by geo-tagging and mapping trees, giving each tree a unique ID through a detailed census.
- Chinar Tree:
- Type: Deciduous tree from the Platanaceae family.
- Characteristics: It is native to cool, water-rich regions of the Eastern Himalayas, can grow up to 30 meters tall with a girth of 10-15 meters.
- It takes 30-50 years to mature and up to 150 years to reach full size.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN: Data Deficient
- Significance: The tree, named during the Mughal era (Jahangir), is the state tree of J&K, and is a major tourist attraction, particularly in autumn.
- It holds cultural significance in local art, literature, and crafts such as paper-mâché and carpets.
Tree Aadhaar Mission:
- Launched in 2021, the mission tracks Chinar trees to prevent unauthorized cutting.
- Over 28,560 trees have been geo-tagged with unique Tree Aadhaar numbers.
- Each tree features a QR code, using GIS technology, providing details on its location, height, girth, health, and ecological threats.
Read More: IUCN’s First Global Tree Assessment




.png)