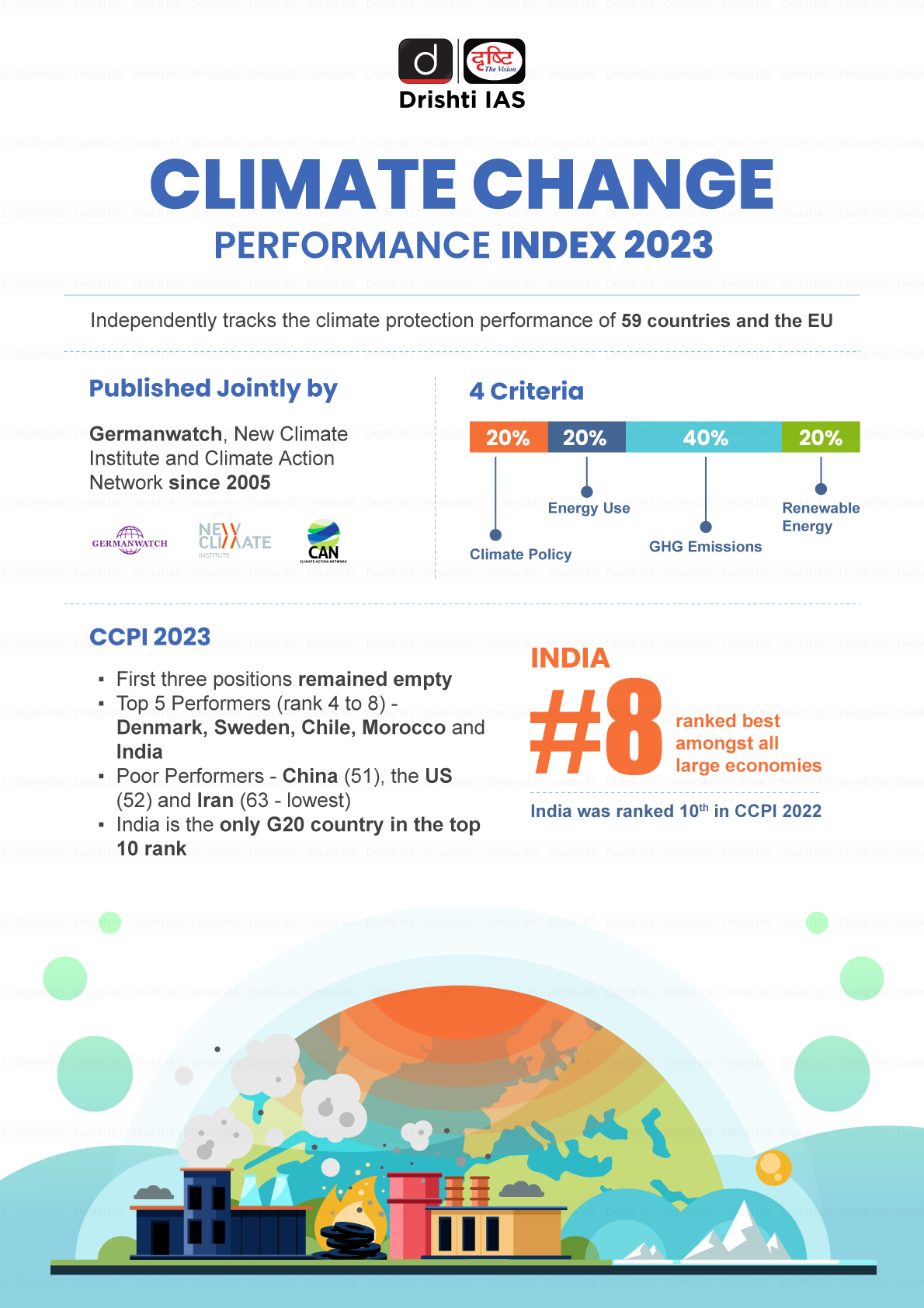
Infographics
Indian Society
Registration of Birth and Death (RBD) Act, 1969
For Prelims: National Population Register, Registrar General of India
For Mains: Population and Associated Issues, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Home Ministry proposed amendment to the Registration of Birth and Death (RBD) Act, 1969.
- The bill will be introduced in the winter session of parliament.
What are the Proposed Amendments?
- It has been proposed to make birth certificates a mandatory document for almost every sphere of life — admission in educational institutions, inclusion in the voter list, appointment in Central and State government jobs, issue of driving licence and passport.
- It shall be mandatory for hospitals and medical institutions to provide a copy of all death certificates, stating the cause of death, to the local registrar apart from the relative of the deceased.
- According to the Civil Registration System (CRS) report, the registration level of births for the country increased to 92.7% in 2019 from 82.0% in 2010 and that of registered deaths increased from 66.9% in 2010 to 92.0 % in 2019.
- CRS is an online system for registration of births and deaths under the operational control of the RGI.
What is the Need for the Amendments?
- The draft amendments would enable the Registrar General of India (RGI) under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) to “maintain a database of registered birth and deaths at the national level”.
- The birth and death database at the national level that will be available with the RGI may be used to update the Population Register, the Electoral Register, and the Aadhar, ration card, passport and driving licence databases.
- If the amendments are implemented, the Centre could use the data to update the National Population Register (NPR) that was first prepared in 2010 and revised through door-to-door enumeration in 2015.
- The NPR already has a database of 119 crore residents and under the Citizenship Rules, 2003, it is the first step towards the creation of a National Register of Citizens (NRC).
What is Registration of Birth and Death (RBD) Act, 1969?
- Registration of Births and Deaths in India is mandatory with the enactment of RBD, Act 1969 and is done as per the place of occurrence of the event.
- Under the RBD Act, it is the responsibility of the States to register births and deaths.
- State governments have set up facilities for registering births and deaths and keeping records.
- A Chief Registrar appointed in every State is the executive authority for implementation of the Act.
- A hierarchy of officials at the district and lower levels do the work.
- The RGI, appointed under this Act, is responsible for coordinating and unifying the implementation of the RBD Act.


Geography
Rare Earth Metals
For Prelims: Confederation of Indian Industry, India Rare Earths Mission, Deep Ocean Mission
For Mains: Rare Earth Metals and the need to develop capabilities to increase its production in India
Why in News?
Amid India's reliance on China for rare earth minerals imports, the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) has urged the government to encourage private mining in the sector and diversify supply sources.
- Though India has 6% of the world’s rare earth reserves, it only produces 1% of global output, and meets most of its requirements of such minerals from China.
- In 2018-19, for instance, 92% of rare earth metal imports by value and 97% by quantity were sourced from China.
What are the Suggestions of CII?
- CII suggested that an 'India Rare Earths Mission' be set up manned by professionals, similar to the India Semiconductor Mission, as a critical component of the Deep Ocean Mission.
- The industry group has also mooted making rare earth minerals a part of the ‘Make In India’ campaign, citing China’s ‘Made in China 2025’ initiative that focuses on new materials, including permanent magnets that are made using rare earth minerals.
What are Rare Earth Metals?
- They are a set of seventeen metallic elements. These include the fifteen lanthanides on the periodic table in addition to scandium and yttrium that show similar physical and chemical properties to the lanthanides.
- The 17 Rare Earths are cerium (Ce), dysprosium (Dy), erbium (Er), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), holmium (Ho), lanthanum (La), lutetium (Lu), neodymium (Nd), praseodymium (Pr), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), scandium (Sc), terbium (Tb), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), and yttrium (Y).
- These minerals have unique magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties and thus are used in many modern technologies, including consumer electronics, computers and networks, communications, health care, national defense, clean energy technologies etc.
- Even futuristic technologies need these REEs.
- For example, high-temperature superconductivity, safe storage and transport of hydrogen for a post-hydrocarbon economy etc.
- They are called 'rare earth' because earlier it was difficult to extract them from their oxides forms technologically.
- They occur in many minerals but typically in low concentrations to be refined in an economical manner.
How China Monopolised Rare Earths?
- China has over time acquired global domination of rare earths, even at one point, it produced 90% of the rare earths the world needs.
- Today, however, it has come down to 60% and the remaining is produced by other countries, including the Quad (Australia, India, Japan and United States).
- Since 2010, when China curbed shipments of Rare Earths to Japan, the US, and Europe, production units have come up in Australia, and the US along with smaller units in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
- Even so, the dominant share of processed Rare Earths lies with China.
What is India's Current Policy on Rare Earths?
- Exploration in India has been conducted by the Bureau of Mines and the Department of Atomic Energy. Mining and processing has been performed by some minor private players in the past, but is today concentrated in the hands of IREL (India) Limited (formerly Indian Rare Earths Limited), a Public Sector Undertaking under the Department of Atomic Energy.
- India has granted government corporations such as IREL a monopoly over the primary mineral that contains REEs: monazite beach sand, found in many coastal states.
- IREL produces rare earth oxides (low-cost, low-reward “upstream processes”), selling these to foreign firms that extract the metals and manufacture end products (high-cost, high-reward “downstream processes”) elsewhere.
- IREL’s focus is to provide thorium — extracted from monazite — to the Department of Atomic Energy.
What are the Related Steps taken?
- Globally:
- The Multilateral Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) was announced in June 2022, with the goal of bringing together countries to build robust critical minerals supply chains needed for climate objectives.
- Involved in this partnership are the United States (US), Canada, Australia, Republic of Korea, Japan, and various European countries.
- India is not included in the partnership.
- By India:
- Ministry of Mines has amended Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957 through the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2021 for giving boost to mineral production, improving ease of doing business in the country and increasing contribution of mineral production to Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- The amendment act provides that no mine will be reserved for particular end-use.
Way Forward
- India must take lessons from other advanced economies on how they are planning to secure their mineral needs and attempt to join multinational fora on assuring critical mineral supply chains – or use existing partnerships, such as Quad and BIMSTEC, to foster such dialogues.
- There must also be top-level decision making within the government to strategize on how to create vertically integrated supply chains of green technologies manufacturing, or we may be in serious danger of missing out on our climate change mitigation targets.
- India needs to create a new Department for Rare Earths (DRE), which would play the role of a regulator and enabler for businesses in this space.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Recently, there has been a concern over the short supply of a group of elements called ‘rare earth metals’. Why? (2012)
- China, which is the largest producer of these elements, has imposed some restrictions on their export.
- Other than China, Australia, Canada and Chile, these elements are not found in any country.
- Rare earth metals are essential for the manufacture of various kinds of electronic items and there is a growing demand for these elements.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


International Relations
Meeting of China-Indian Ocean Region Forum
For Prelims: Indian Ocean region, Indian Ocean Rim Association, SAGAR, IONA, Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure.
For Mains: Implications of Increasing Chinese Influence in Indian Ocean Region.
Why in News?
Recently, the China International Development Cooperation Agency (CIDCA), held a meeting of the China-Indian Ocean Region Forum in which 19 countries took part but not India.
What are the Key Highlights of the Meet?
- Theme: Shared Development: Theory and Practice from the Perspective of the Blue Economy.
- Participating Countries:
- Indonesia, Pakistan, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Maldives, Nepal, Afghanistan, Iran, Oman, South Africa, Kenya, Mozambique, Tanzania, Seychelles, Madagascar, Mauritius, Djibouti, Australia and representatives of 3 international organisations were present.
- India was reportedly not invited.
- Marine Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Cooperation Mechanism:
- China proposed to establish a marine disaster prevention and mitigation cooperation mechanism between China and countries in the Indian Ocean region.
- China expressed its willingness to provide necessary financial, material, and technical support to countries in need.
What does China Seek from the Meet?
- China is contending for influence in the strategic Indian Ocean region with substantial investments in ports and infrastructure in several countries.
- China has made substantial investments in ports and infrastructure investments in several countries, including Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- China has acquired Sri Lanka’s Hambantota port on a 99-year lease besides building the port at Pakistan’s Gwadar in the Arabian Sea opposite India’s western coast and infrastructure investments in the Maldives.
What are the Concerns?
- China has often been accused of engaging in “debt diplomacy” in these countries under its Belt and Road Initiative allegedly in the name of infrastructure development.
- Since 2008, China has regularly deployed a contingent of naval warships in the Gulf of Aden and established its first foreign military base in Djibouti in 2017.
- At the same time India's absence is seen as an attempt to challenge India’s traditional presence in the region amid apprehensions of politicization of the Indian Ocean region. Moreover, the Chinese Foreign Ministry refused to disclose who the participants were from other countries.
- India has been a traditional partner and supporter of Indian Ocean Region (IOR) countries.
How is India's Presence in IORA?
- In addition, to act as a first responder during major crises in the littoral countries, India regularly engages with the Indian Ocean littoral countries through such mechanisms as the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) and Indian Ocean Navies Symposium (IONS) under the vision of Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR).
- India has strong influence in the Indian Ocean region where India-backed organisations like the IORA have taken strong roots.
- India continues to promote its official policy of “coordination, cooperation and partnership” in the regional maritime domain.
- As coordinator to the priority area on disaster risk management, India has published guidelines for IORA. It has also urged partners to join the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure launched at the UN in September 2019.
- India has been trying to emerge as the net provider of information in the IOR and in that direction it created the Information Fusion Centre located in Gurugram to assist member countries of IOR with real-time crisis information. Bangladesh, Mauritius, Maldives, Sri Lanka and Seychelles have been part of the information support structure of India.
What is the Indian Ocean Rim Association?
- It was established in 1997 and is a regional forum that seeks to build and expand understanding and mutually beneficial cooperation through a consensus-based, evolutionary and non-intrusive approach.
- IORA has 23 member states and 9 Dialogue Partners.
- Members: Australia, Bangladesh, the Comoros, France, India, Indonesia, Iran, Kenya, Madagascar, Malaysia, Maldives, Mauritius, Mozambique, Oman, Seychelles, Singapore, Somalia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Thailand, the United Arab Emirates and Yemen.
- China is a dialogue partner in the IORA.
- The IORA Secretariat is based in Mauritius.
- The association gains importance by the fact that the Indian Ocean carries half of the world’s container ships, one-third of the world’s bulk cargo traffic and two-thirds of the world’s oil shipments.
- It is a lifeline of international trade and transport and the Indian ocean region is woven together by trade routes and commands control of major sea-lanes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)


Science & Technology
PSLV-C54
For Prelims: Launch Vehicles, SRO, PSLV, EOS, INS-2B, India-Bhutan Satellite, Astrocast, Anand.
For Mains: Space Technology, INS-2B, EOS-6 and Significance.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully launched the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) C54 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
- This was the 56th flight of PSLV, which marks the final mission for the year for PSLV-C54 rocket.
What are the Satellites Launched?
- Nano Satellite-2 for Bhutan (INS-2B):
- About:
- INS-2B satellite is a collaborative mission between India and Bhutan with two payloads.
- NanoMx, a multispectral optical imaging payload developed by Space Applications Centre (SAC)
- APRS-Digipeater which is jointly developed by DITT-Bhutan and URSC was successfully deployed.
- INS-2B satellite is a collaborative mission between India and Bhutan with two payloads.
- Significance of INS-2B:
- It will provide high-resolution images to Bhutan for the management of the country’s natural resources.
- The launch of the new satellite is part of India’s efforts to back Bhutanese King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck’s plans to use advanced technology, including ICT and space technology, for the development of Bhutan.
- The collaboration also fits in with India’s “neighbourhood first” policy.
- About:
- Anand:
- The Anand three axis stabilized Nano satellite is a technology demonstrator for miniaturized electro-optical payload and all other sub-systems like TTC, power, onboard computer and ADCS from Pixxel, India was also placed in the orbit successfully.
- Astrocast:
- Astrocast, a 3U spacecraft, is a technology demonstrator satellite for the Internet of Things (IoT) as the payload. There are 4 nos. of Astrocast Satellites in this mission. These spacecrafts are housed within an ISISpace QuadPack dispenser.
- The dispenser protects the satellite from contamination.
- Thymbolt Satellites:
- The Thybolt is a 0.5U spacecraft bus that includes a communication payload to enable rapid technology demonstration and constellation development for multiple users from Dhruva Space using their own Orbital Deployer with a minimum lifetime of 1 year.
- EOS-6:
- Earth Observation Satellite-06 (EOS-06) is the Oceansat series’ 3rd-generation satellite envisaged to observe ocean colour data, sea surface temperature and wind vector data to use in oceanography, climatic and meteorological applications.
- The satellite also supports value added products such as potential fishing zones using chlorophyll, Sea Surface Temperature (SST) and wind speed and land based geophysical parameters.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)
Q2. With reference to ‘Astrosat’, the astronomical observatory launched by India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- Other than USA and Russia, India is the only country to have launched a similar observatory into space.
- Astrosat is a 2000 kg satellite placed in an orbit at 1650 km above the surface or the Earth.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q.3 Consider the following statements: (2010)
The satellite Oceansat-2 launched by India helps in
- estimating the water vapour content in the atmosphere
- predicting the onset of monsoons.
- monitoring the pollution of coastal waters.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Dhamma Dipa International Buddhist University
For Prelims: Dhamma Dipa International Buddhist University (DDIBU), Buddhism, Schools of Buddhism, Buddhist Texts
For Mains: Significance of Buddhist Councils, Contribution of Buddhism in Indian Culture, Buddhism as way of Soft Diplomacy, Initiatives taken to Promote Buddhism in India
Why in News?
The foundation stone for the Dhamma Dipa International Buddhist University (DDIBU) at Manu Bankul in Sabroom of South Tripura district will be laid on 29th November 2022.
- DDIBU is expected to become the first Buddhist-run university in India to offer Buddhist education along with courses in other disciplines of modern education as well.
What is Buddhism?
- About:
- Buddhism started in India over 2,600 years ago.
- The religion is based upon the teachings, life experiences of its founder Siddhartha Gautam.
- The main teachings of Buddhism are encapsulated in the basic concept of four noble truths or ariya-sachchani and eight-fold path or ashtangika marg.
- Four noble truths:
- Suffering (dukkha) is the essence of the world.
- Every suffering has a cause – Samudya.
- Suffering could be extinguished – Nirodha.
- It can be achieved by following the Atthanga Magga (Eight-Fold Path).
- Eight-Fold Paths: It consists of various interconnected activities related to knowledge, conduct, and meditative practices.
- Right view
- Right intention
- Right speech
- Right action
- Right livelihood
- Right mindfulness
- Right effort
- Right concentration
- Four noble truths:
- The essence of Buddhism is the attainment of enlightenment or nirvana which was not a place but an experience that could be attained in this life.
- There is no supreme god or deity in Buddhism.
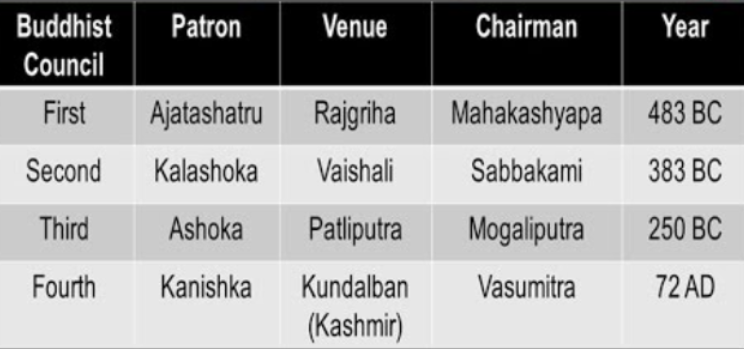
- Buddhist Councils:
- Schools of Buddhism:
- Mahayana (Idol Worship), Hinayana, Theravada, Vajrayana (Tantric Buddhism), Zen.
- Buddhist Texts (Tipitaka):
- Vinaya Pitaka (rules applicable to monastic life), Sutta Pitaka (main teaching or Dhamma of Buddha), Abhidhamma Pitaka (a philosophical analysis and systematization of the teaching).
- Contribution of Buddhism to Indian Culture:
- The concept of ahimsa was its chief contribution. Later, it became one of the cherished values of our nation.
- Its contribution to the art and architecture of India was notable. The stupas at Sanchi, Bharhut, and Gaya are wonderful pieces of architecture.
- It promoted education through residential universities like those at Taxila, Nalanda, and Vikramasila.
- The language of Pali and other local languages developed through the teachings of Buddhism.
- It had also promoted the spread of Indian culture to other parts of Asia.
- UNESCO’s Heritage Sites Related to Buddhism:
- Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara at Nalanda, Bihar
- Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi, MP
- Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya, Bihar
- Ajanta Caves Aurangabad, Maharashtra.
- The Buddhist chanting of Ladakh was included in the UNESCO’s Representative List of Humanity's Intangible Cultural Heritage in 2012.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to Indian history, consider the following texts: (2021)
- Nettipakarana
- Parishishtaparvan
- Avadanashataka
- Trishashtilakshana Mahapurana
Which of the above are Jaina texts?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Nettipakarana is a mythological Buddhist scripture, sometimes included in the Khuddaka Nikaya of Theravada Buddhism's Pali Canon.
- Parishishtaparvan is a 12th-century Sanskrit mahakavya by Hemachandra which details the histories of the earliest Jain teachers.
- Avadanasataka is an anthology in Sanskrit of one hundred Buddhist legends, approximately dating to the same time.
- Trishashthilkshana Mahapurana is a major Jain text composed largely by Acharya Jinasena during the rule of Rashtrakuta.
- Hence, option B is correct.
Q2. With reference to Indian history, consider the following pairs: (2021)
| Historical person | Known as | |
| 1. | Aryadeva | Jaina scholar |
| 2. | Dignaga | Buddhist scholar |
| 3. | Nathamuni | Vaishnava scholar |
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) None of the pairs
(b) Only one pair
(c) Only two pairs
(d) All three pairs
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Aryadeva was a Mahayana Buddhist monk, a disciple of Nagarjuna and a Madhyamaka philosopher. Dignaga was an Indian Buddhist scholar and one of the Buddhist founders of Indian logic. Sri Ranganathamuni, popularly known as Sriman Nathamuni (823 CE–951 CE), was a Vaishnava theologian who collected and compiled the Nalayira Divya Prabandham. Hence, only pairs 2 and 3 are correctly matched. First pair is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option C is correct.
Q3. With reference to the cultural history of India, which one of the following is the correct description of the term ‘paramitas’? (2020)
(a) The earliest Dharmashastra texts written in aphoristic (sutra) style
(b) Philosophical schools that did not accept the authority of Vedas
(c) Perfections whose attainment led to the Bodhisattva path
(d) Powerful merchant guilds of early medieval South India
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Paramita or parami (in Sanskrit and Pali respectively) is a Buddhist term often translated as “perfection”.
- In Mahayana Buddhism, the bodhisattva practices the six paramitas, or transcendent perfections which are generosity, discipline, patience, diligence, meditative concentration, and wisdom.
- Parmitas are described in Buddhist commentaries as noble character qualities generally associated with enlightened beings.
- Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Q4. Consider the following: (2019)
- Deification of the Buddha
- Treading the path of Bodhisattvas
- Image worship and rituals
Which of the above is/are the feature/features of Mahayana Buddhism?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The fourth Buddhist Council held at Kundalvana, Kashmir in 72 AD, presided by Vasumitra saw Buddhism divide into two branches, Hinyana and Mahayana.
- Mahayana, literally translates to ‘The Great Vehicle’, whereas supporters of Mahayana Buddhism termed the older tradition of Buddhism as Hinyana (the lesser vehicle).
- Mahayana Buddhists professed the path of the Bodhisattva to attain enlightenment and to help all sentient beings from all sufferings and pain. Hence, 2 is correct.
- This school started believing that the Buddha was the saviour and he was the one who could ensure salvation. Thus, the process of deification of Buddha started. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Besides, the worship of images of the Buddha and rituals became an important part of Buddhist school. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1. Pala period is the most significant phase in the history of Buddhism in India. Enumerate. (2020)
Q2. Early Buddhist Stupa-art, while depicting folk motifs and narrative successfully expounds Buddhist ideals. Elucidate (2016)


Important Facts For Prelims
Bluebugging
Why in News?
Several smartphones have their Bluetooth settings on discovery mode as it is a default setting, making it vulnerable to bluebugging.
What is Bluebugging?
- About:
- It is a form of hacking that lets attackers access a device through its discoverable Bluetooth connection.
- A hacker can gain unauthorized access to these apps and devices and control them as per their wish through bluebugging.
- Any Bluetooth-enabled device including True Wireless Stereo (TWS) devices or earbuds are susceptible to bluebugging.
- Once a device or phone is bluebugged, a hacker can listen to the calls, read and send messages and steal and modify contacts.
- Even the most secure smartphones like iPhones are vulnerable to such attacks.
- Preventive Measures:
- Turning off Bluetooth and disconnecting paired Bluetooth devices when not in use.
- Making Bluetooth devices undiscoverable from Bluetooth settings.
- Updating the device’s system software to the latest version.
- Limited use of public Wi-Fi.
- Watch out for suspicious activities on your device.
- Monitoring of sudden spikes in data usage.
- Usage of modern anti-virus software.
What are the Related Government Initiatives?
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Online Cybercrime Reporting Portal
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Information Technology Act, 2000
- National Cyber Security Strategy 2020
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- According to section 70B of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act), the Union Government by notification should appoint an agency named Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERTIn) to serve as the national agency for incident response.
- The Union Government under section 70B of the IT Act, 2000 established and notified rules of CERT-In in 2014. According to Rule 12(1)(a), it is mandatory for service providers, intermediaries, data centers and corporate bodies to report cyber security incidences to CERT-In within a reasonable time of occurrence of the incident. Hence, 1, 2 and 3 are correct.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Sangeet Natak Akademi Awards
Why in News?
Recently, the Sangeet Natak Akademi announced the list of 10 Akademi fellows and 128 artists who will receive the prestigious Sangeet Natak Akademi Awards (Akademi Puraskar) for 2019, 2020, and 2021.
- Apart from this, the Akademi announced the names of 102 young artistes for the Ustad Bismillah Khan Yuva Puraskar for the years 2019, 2020 and 2021.
What is Sangeet Natak Akademi?
- The Sangeet Natak Akademi is India's national academy for music, dance and drama.
- It was created by a resolution of the (then) Ministry of Education, Government of India, in 1952 with Dr P.V. Rajamannar as its first Chairman.
- It is presently an Autonomous Body of the Ministry of Culture, Government of India and is fully funded by the Government for implementation of its schemes and programmes.
- The Akademi establishes and looks after institutions and projects of national importance in the field of the performing arts. Few important ones are:
- National School of Drama, New Delhi was set up in 1959
- Jawaharlal Nehru Manipur Dance Academy in Imphal- 1954
- Kathak Kendra (National Institute of Kathak Dance) in New Delhi- 1964
- National Projects of Support to Kutiyattam (Sanskrit theatre of Kerala), Chhau dances of eastern India, Sattriya traditions of Assam, etc.
What is Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship (Akademi Ratna) and Award?
- Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship:
- The Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship is the highest honour conferred by Sangeet Natak Akademi without distinction of nationality, race, caste, religion, creed, or sex.
- The Fellowship of the Akademi is the most prestigious and rare honour, which is restricted to 40 numbers at any given time.
- The Akademi Fellowship carries purse money of Rs. 3.00 lakhs, a Tamrapatra and an Angavastram.
- Sangeet Natak Akademi Awards:
- The awards are given to the artists from the field of Music, Dance, Theatre, Traditional/Folk/Tribal Music/Dance/Theatre, Puppetry and Overall contribution/scholarship in the Performing Arts etc.
- The Akademi Awards carries purse money of Rs. 1.00 lakh, a Tamrapatra and an Angavastram.
What is “Ustad Bismillah Khan Yuva Puraskar”?
- Sangeet Natak Akademi has decided to institute “Ustad Bismillah Khan Yuva Puraskar” from the year 2006 to be awarded to artists who have shown / demonstrated conspicuous talent in the fields of music, dance and drama.
- Young outstanding practitioners upto the age of 40 years will be eligible to be considered for Yuva Puraskar every year. Age as on the date of nomination received will be reckoned from 1st April of that year.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2009)
- The National School of Drama was set up by Sangeet Natak Akademi in 1959.
- The highest honour conferred by the Sahitya Akademi on a writer is by electing him its Fellow.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards
Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation 2022 has been announced which included four winners from India.
Award-Winning Countries: What’s the Scenario?
- Global Performance:
- Thirteen projects from six countries that have been acknowledged for awards were:
- Afghanistan, China, India, Iran, Nepal and Thailand.
- Thirteen projects from six countries that have been acknowledged for awards were:
- India’s Performance:
- Award of Excellence: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya, Mumbai
- Award of Distinction: Stepwells of Golconda, Hyderabad
- Award of Merit: Domakonda Fort, Telangana, and Byculla Station, Mumbai
- Significance of Heritage Sites:
- There is a nature and culture linkage that heritage sites demonstrate. They can address climate change with net-zero water requirements.
- The restoration of wells shows how conservation of heritage sites can have multiple objectives.
What is UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation?
- Since 2000, the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation programme has recognised the efforts of private individuals and organisations in restoring, conserving and transforming structures and buildings of heritage value in the region.
- It encourages other property owners to undertake conservation projects within their communities, either independently or by public-private partnerships.
- The awards give people a sense of pride and sense of ownership of their own heritage.
Note
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya, Mumbai:
- The museum is a part of the Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai's world heritage property.
- It was established as the Prince of Wales Museum of Western India in 1922.
- The museum is a part of the Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai's world heritage property.
- Byculla Station, Mumbai:
- The station was built in 1853. The first train of the country passed through Byculla station almost one-and-a-half centuries ago. It has been restored to its original Gothic, heritage, architectural glory.
- Domakonda Fort, Telangana:
- The Domakonda Fort is private property and was built in the 18th century with an amalgam of styles including stucco work, arched pillars, flat ceiling, and a courtyard with a water garden pond.