Important Facts For Prelims
Buddha Purnima
- 16 May 2022
- 6 min read
Why in News?
The Prime Minister has recalled the principles of Lord Buddha and reiterated his commitment to fulfill them on the occasion of Buddha Purnima.
- He also visited Nepal during this special occasion.
What do we know about Buddha Purnima?
- It is celebrated to mark the birth of Gautam Buddha, the founder of Buddhism.
- It is also known as Vesak. In 1999, it became an UN-designated day, to acknowledge the contribution of Buddhism to society.
- It is considered a 'triple-blessed day' - as Tathagata Gautam Buddha's birth, enlightenment, and Maha Parnirvana.
- Buddha Purnima falls on a full moon night, usually between April and May, and it is a gazetted holiday in India.
- Many devotees visit Mahabodhi Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, located in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, on this occasion.
- Bodhi Temple is the location where Lord Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment.
Who was Gautam Buddha?
- He was born as Siddhartha Gautama in circa 563 BCE, in Lumbini and belonged to the Sakya clan.
- Gautam attained Bodhi (enlightenment) under a pipal tree at Bodhgaya, Bihar.
- Buddha gave his first sermon in the village of Sarnath, near Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh. This event is known as Dharma Chakra Pravartana (turning of the wheel of law).
- He died at the age of 80 in 483 BCE at Kushinagar, Uttar Pradesh. The event is known as Mahaparinibban or Mahaparinirvana.
- He is believed to be the eighth of the ten incarnations of Lord Vishnu (Dashavatar).
What is Buddhism?
- About:
- Buddhism started in India over 2,600 years ago.
- The main teachings of Buddhism are encapsulated in the basic concept of four noble truths or ariya-sachchani and eight-fold path or ashtangika marg.
- Dukkha (Sufferings) and its extinction are central to the Buddha’s doctrine.
- The essence of Buddhism is the attainment of enlightenment or nirvana which was not a place but an experience that could be attained in this life.
- There is no supreme god or deity in Buddhism.
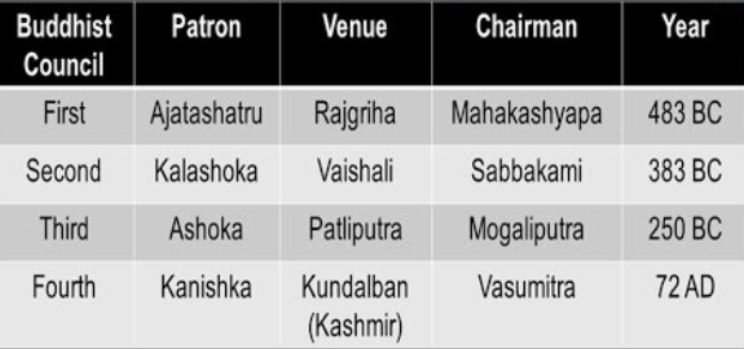
- Buddhist Councils:
- Schools of Buddhism:
- Mahayana (Idol Worship), Hinayana, Theravada, Vajrayana (Tantric Buddhism), Zen.
- Buddhism Texts (Tipitaka):
- Vinaya Pitaka (rules applicable to monastic life), Sutta Pitaka (main teaching or Dhamma of Buddha), Abhidhamma Pitaka (a philosophical analysis and systematization of the teaching).
- Contribution of Buddhism to Indian Culture:
- The concept of ahimsa was its chief contribution. Later, it became one of the cherished values of our nation.
- Its contribution to the art and architecture of India was notable. The stupas at Sanchi, Bharhut, and Gaya are wonderful pieces of architecture.
- It promoted education through residential universities like those at Taxila, Nalanda, and Vikramasila.
- The language of Pali and other local languages developed through the teachings of Buddhism.
- It had also promoted the spread of Indian culture to other parts of Asia.
- UNESCO’s Heritage Sites Related to Buddhism:
- Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara at Nalanda, Bihar
- Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi, MP
- Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya, Bihar
- Ajanta Caves Aurangabad, Maharashtra.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.With reference to the cultural history of India, which one of the following is the correct description of the term ‘paramitas’? (2020)
(a) The earliest Dharmashastra texts written in aphoristic (sutra) style
(b) Philosophical schools that did not accept the authority of Vedas
(c) Perfections whose attainment led to the Bodhisattva path
(d) Powerful merchant guilds of early medieval South India
Ans: (c)
Q. Consider the following: (2019)
- Deification of the Buddha
- Treading the path of Bodhisattvas
- Image worship and rituals
Which of the above is/are the feature/features of Mahayana Buddhism?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- The fourth Buddhist Council held at Kundalvana, Kashmir in 72 AD, presided by Vasumitra saw Buddhism divide into two branches, Hinyana and Mahayana.
- Mahayana, literally translates to ‘The Great Vehicle’, whereas supporters of Mahayana Buddhism termed the older tradition of Buddhism as Hinyana (the lesser vehicle).
- Mahayana Buddhists professed the path of the Bodhisattva to attain enlightenment and to help all sentient beings from all sufferings and pain. Hence, 2 is correct.
- This school started believing that the Buddha was the saviour and he was the one who could ensure salvation. Thus, the process of deification of Buddha started. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Besides, the worship of images of the Buddha andrituals became an important part of Buddhist school. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.