Infographics
Science & Technology
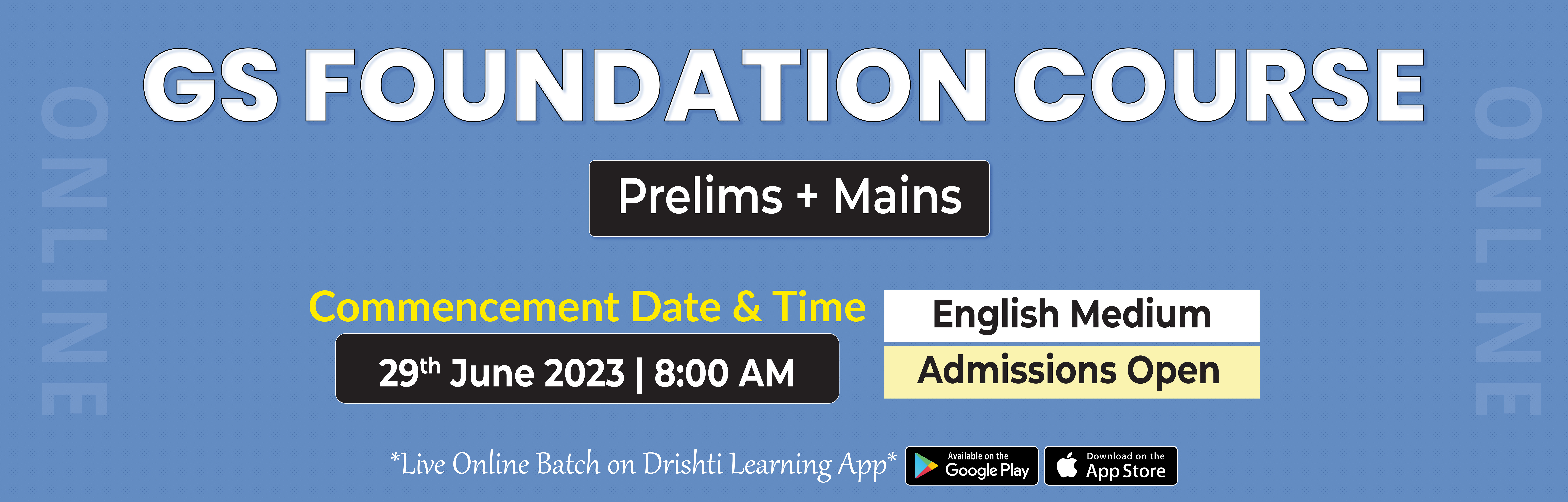
Titan Tragedy Lessons for Proposed Indian Submersible Dive
For Prelims: Matsya-6000, Titan submersible, Deep Ocean Mission, RMS Titanic, Atlantic Ocean, NOAA, UNESCO.
For Mains: Deep Ocean Mission and Its Significance for India.
Why in News?
Scientists are preparing for a Deep See Dive with the Vehicle Matsya-6000 in late 2024 similar to the Titan submersible, which recently went missing.
- The Matsya-6000 project under India’s Deep Ocean Mission, scheduled for late 2024, aims to explore the Indian Ocean at a depth of about 6,000 meters.
- In light of the recent incident of Titan Submersible, the safety systems employed for the crew will undergo reviews to ensure their effectiveness.
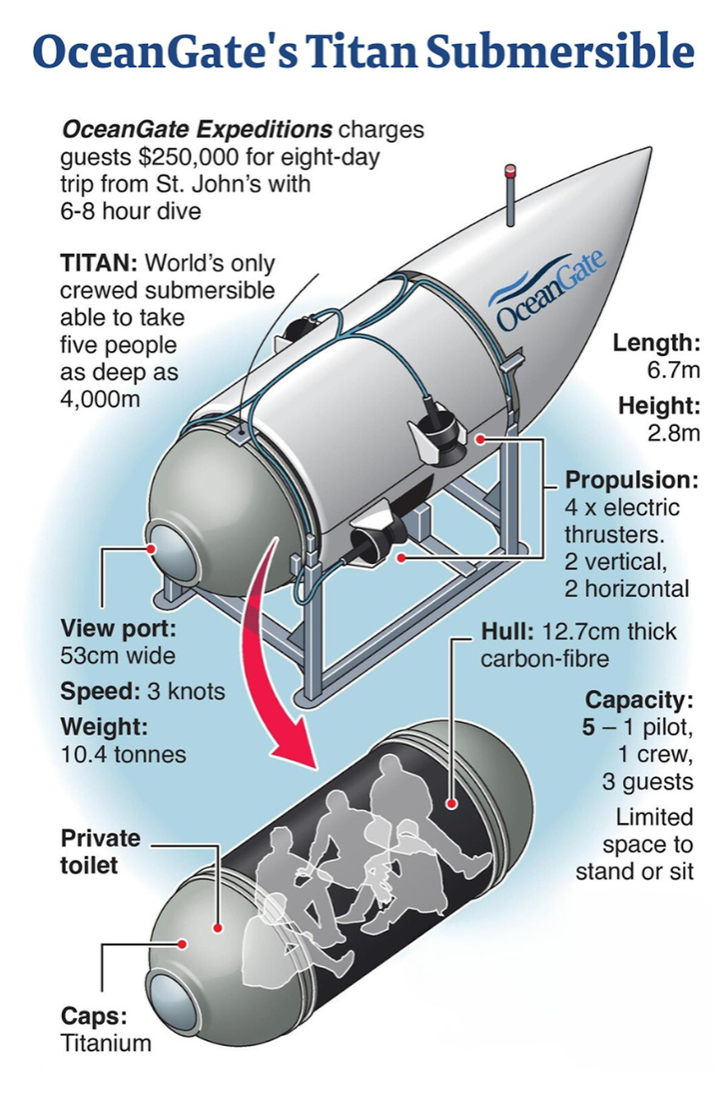
What are the Key Points of Titan Submersible?
- About:
- Titan submersible is operated by the privately owned U.S. company OceanGate that organizes underwater expeditions for both research and tourism.
- It was built with “off-the-shelf” components, is lighter and more cost-efficient than other deep diving submersibles.
- Titan is made of carbon fibre and titanium and weighs 10,432 kilograms.
- It is capable of going 4,000 metres undersea and moves as fast as three knots per hour (5.56 kph).
- Objective:
- Titan Submersible was travelling to see the wreckage of RMS (Royal Mail Ship) Titanic, which is nearly four thousand metres under water in the frigid North Atlantic Ocean.
- One hour and forty-five minutes into the journey, contact with Titan was lost.
- Titan Submersible was travelling to see the wreckage of RMS (Royal Mail Ship) Titanic, which is nearly four thousand metres under water in the frigid North Atlantic Ocean.
- Concerns:
- The submersible's forward viewport was certified for 1,300 meters, but OceanGate aimed to reach 4,000 meters.
- The technology and components of the submersible may not have met rigorous safety standards. Insufficient hull testing raises the risk of failure and endangers occupants.
- The pressure vessel's combination of titanium and carbon fiber is unusual and raises concerns due to their different properties in deep diving situations.
What Happened to the Titan?
- The submersible “Titan” experienced a “catastrophic implosion,” according to the U.S. Coast Guard. The five occupants on board are presumed to have died during the implosion.
- An implosion is the opposite of an explosion. In an explosion, the force acts outwards, but in an implosion the force acts inwards. When a submersible is deep in the ocean it experiences the force on its surface due to water pressure.
- When this force becomes larger than the force hull can withstand, the vessel implodes violently.
- With every descent of 10 meters into the water, the pressure increases by approximately one atmosphere.
- One atmosphere is equivalent to the average atmospheric pressure at sea level, which is approximately 101.325 kilopascals (kPa) or 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi).
- With every descent of 10 meters into the water, the pressure increases by approximately one atmosphere.
What are Carbon Fibres and Titanium?
- Carbon Fibre: Carbon fibre is a polymer that is known to be quite strong despite being lightweight. It can be as much as five times stronger than steel and twice as stiff.
- A carbon-fibre composite, compared to titanium, is much stiffer and does not have the same kind of elasticity.
- Titanium: Titanium is as strong as steel but around 45% lighter. It is twice as strong as aluminum but only 60% heavier, according to the United States Geological Survey.
- A titanium or thick steel pressure vessel is usually a spherical shape that can withstand the crushing pressures at 3,800m – the depth at which the Titanic wreck lies.
- Titanium is elastic and can adapt to an extended range of stresses without any measurable permanent strain remaining after the return to atmospheric pressure. It shrinks to adjust to pressure forces and re-expands as these forces are alleviated.
Submarine Vs Submersible
- While the two categories can overlap, a submarine refers to an underwater vehicle that is largely independent and has power reserves to help it depart from a port or come back to the port after an expedition.
- Meanwhile, a submersible is generally smaller in size and has less power, so it needs to work with a ship in order to be launched and recovered.
- The missing submersible Titan was working with a vessel named Polar Prince.
What are the Key Points Related to Matsya-6000?
- About:
- Matsya-6000 is an indigenous deep-sea dive submersible being developed by the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) in India. It is designed to explore the depths of the Indian Ocean at a depth of about 6,000 meters.
- The mission aims to send three Indian navigators to a point approximately 1,500 km away from Kanyakumari, India.
- Objective:
- The mission's primary objective is to support India's energy requirements and explore ocean resources.
- India aims to conduct exploratory mining for Polymetallic Nodules containing valuable resources such as copper, nickel, cobalt, and manganese.
- This endeavor aligns with the Indian government's Deep Ocean Mission, which aims to develop vehicles and technology for ocean scanning and mining.
- Features of Submersible:
- The submersible features a spherical titanium hull, which is crucial for withstanding the immense pressure at great depths.
- The titanium hull is manufactured by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), as no commercial fabricators in India were capable of producing such a hull.
- Two hemispheres of titanium alloy are fused to create a single hull, which serves as the primary barrier between the crew and the surrounding water columns.
- The submersible features a spherical titanium hull, which is crucial for withstanding the immense pressure at great depths.
- Learning from Titan Incident:
- The recent incident has highlighted the need for thorough safety evaluations and repeated testing.
- The inability to locate the submersible despite multiple communication systems onboard raises questions. Future submersibles may incorporate "black box" equivalents, similar to those found in aircraft, to aid in investigating the cause of such incidents.
- The choice of titanium for the submersible's enclosure, the utilization of syntactic foam, and the implementation of acoustic communication and tracking systems should be thoroughly evaluated.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. Ilmenite and rutile, abundantly available in certain coastal tracts of India, are rich sources of which one of the following? (2023)
(a) Aluminium
(b) Copper
(c) Iron
(d) Titanium
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- India is endowed with large resources of heavy minerals which occur mainly along coastal stretches of the country.
- Heavy mineral sands comprise a group of seven minerals, viz, ilmenite, leucoxene (brown ilmenite), rutile, zircon, sillimanite, garnet and monazite. Ilmenite (FeO.TiO2) and rutile (TiO2) are the two chief mineral sources of titanium. Hence, option (d) is correct.
Governance
Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24
For Prelims: Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment, Union Budget 2023-24, Jal Jeevan Mission , Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana, Make in India, One District One Product
For Mains: Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24 Scheme, Effective Capital Expenditure
Why in News?
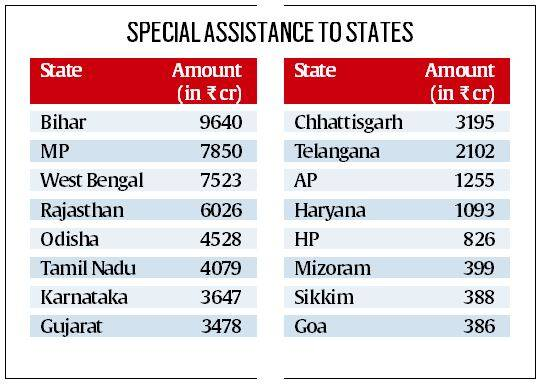
The Department of Expenditure under the Finance Ministry of India has approved capital investment proposals of Rs. 56,415 crore for 16 states in the current financial year 2023-24.
- These loans are granted under the central scheme known as “Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24”.
- The 16 states include Arunachal Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Mizoram, Odisha, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and West Bengal.
What is the Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24 Scheme?
- Background:
- The Scheme for financial assistance to States for capital investment/expenditure, first instituted by the Ministry of Finance in 2020-21 in the wake of Covid-19 Pandemic, has given a very timely boost to capital spending by the state.
- About:
- The scheme was announced in the Union Budget 2023-24 in continuation of a similar push for capex from the last three years.
- Under the scheme, special assistance is being provided to the state governments in the form of 50-year interest free loan up to an overall sum of Rs. 1.3 lakh crore during the financial year 2023-24.
- Parts:
- The scheme has eight parts, Part-I being the largest with allocation of Rs. 1 lakh crore. This amount has been allocated amongst states in proportion to their share of central taxes and duties as per the award of the 15th Finance Commission.
- Other parts of the scheme are either linked to reforms or are for sector-specific projects.
- Part-II provides incentives to states for scrapping of old vehicles and setting up of automated vehicle testing facilities;
- Part-III and IV provide incentives to states for reforms in urban planning and urban finance;
- Part-V provides funds for increasing the housing stock for police personnel and their families within the police stations in urban areas.
- Part-VI of the scheme supports the vision of national integration, Make in India and One District One Product by promoting cultural diversity and local products through Unity Mall projects.
- Under Part-VII, Rs. 5,000 crore is provided as financial assistance to states for establishing libraries with digital infrastructure at the Panchayat and Ward level, primarily benefiting children and adolescents.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- The scheme is expected to have a higher multiplier effect on the economy by stimulating demand and creating jobs.
- The scheme also aims to enhance the pace of projects in key sectors such as Jal Jeevan Mission and Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana by providing funds for meeting the state share.
- The scheme also seeks to encourage states to undertake reforms in urban planning and urban finance to improve the quality of life and governance in cities.
What is Capital Expenditure in India?
- Capital Expenditure (Capex):
- It refers to the funds allocated by the government for the acquisition, construction, or improvement of physical assets such as infrastructure, buildings, machinery, and equipment.
- It is considered to be productive and growth enhancing as it adds to the productive capacity of the economy and generates income and employment in the future.
- The Indian government allocates capital expenditure through its annual budget, which is presented by the finance minister.
- The capital investment outlay has experienced a consecutive three-year increase, reaching Rs 10 lakh crore, which accounts for 3.3% of the GDP, marking a significant growth of 33% ( Union Budget 2023-24).
- Effective Capital Expenditure:
- The capital expenditure presented in the budget does not include the spending by the government on creating capital assets through grants-in-aid to states and other agencies.
- These grants are classified as revenue expenditure in the budget, but they also contribute to the creation of fixed assets such as roads, bridges, schools, hospitals, etc.
- Therefore, to capture the true extent of public investment by the central government, a concept of ‘effective capital expenditure’ has been introduced.
- Effective capital expenditure is defined as the sum of capital expenditure and grants for creation of capital assets.
- It is budgeted at Rs 13.7 lakh crore or 4.5% of GDP (Union Budget 2023-24).
- The capital expenditure presented in the budget does not include the spending by the government on creating capital assets through grants-in-aid to states and other agencies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following is/are included in the capital budget of the Government of India? (2016)
- Expenditure on acquisition of assets like roads, buildings, machinery, etc.
- Loans received from foreign governments
- Loans and advances granted to the States and Union Territories
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Governance
ART Regulations: Impact on Cost and Conception Opportunities
For Prelims: Assisted Reproductive Technology, fundamental right, In Vitro fertilization
For Mains: Government Policies & Interventions, Issues Related to Women
Why in News?
Recently, industry insiders have raised concerns about the restrictions imposed by the provisions of the Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) Regulations Act, 2021 introduced by the Health Ministry.
- These concerns pertain to the increased costs and limited conception opportunities faced by couples seeking ART treatments, despite the regulations aiming to enhance medical care and security for donors and patients.
What is Assisted Reproductive Technology?
- ART refers to medical procedures used to help individuals or couples conceive a child.
- It involves various techniques, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), Gamete Donation, Intrauterine Insemination, Pre-implantation Genetic Testing, Surrogacy, Altruistic Surrogacy.
- ART is often used by individuals or couples facing fertility challenges, including infertility, genetic disorders, or reproductive system abnormalities.
- ART procedures typically involve the manipulation of sperm, eggs, or embryos in a laboratory setting before transferring them to the woman's uterus.
What are the Main Features of the ART Regulations Act, 2021?
- Registration: Every ART clinic and bank must be registered under the National Registry of Banks and Clinics of India, maintaining a central database.
- Registration is valid for five years and can be renewed for another five years.
- Violations of the Act may result in cancellation or suspension of registration.
- Conditions for Sperm & Egg Donation: Registered ART banks can screen, collect, and store semen from men aged 21-55 years. Eggs can be stored from women aged 23-35 years.
- Donor Limits: Oocyte donors must be ever-married women with at least one living child of their own (minimum three years of age).
- An oocyte donor can only donate once in her lifetime, and a maximum of seven oocytes can be retrieved.
- Gamete Supply: An ART bank cannot supply gametes from a single donor to more than one commissioning couple (couple seeking services).
- Parental Rights: Children born through ART are deemed the couple's biological child, and the donor has no parental rights.
- Consent: Written informed consent is required from both the couple and the donor for ART procedures.
- Regulation of ART Processes: The National and State Boards formed under the Surrogacy Act 2021 will regulate ART services.
- Insurance Coverage: Parties seeking ART services must provide insurance coverage in favor of the oocyte donor, covering any loss, damage, or death of the donor.
- Preventing Sex Selection: Clinics are prohibited from offering to provide a child of pre-determined sex, ensuring non-discriminatory practices.
- Offences: Offences include abandonment or exploitation of children born through ART, sale or trade of embryos, and exploitation of the couple or donor.
- Punishment includes imprisonment of 8-12 years and a fine of Rs 10-20 lakhs.
- Clinics and banks are prohibited from advertising or offering sex-selective ART.
- Offences carry imprisonment of 5-10 years and a fine of Rs 10-25 lakhs.
What are the Challenges and Concerns Regarding ART Regulations, 2021?
- Increased Cost: The regulations may lead to higher treatment costs due to additional requirements such as insurance, testing, and registration fees.
- Reduced Availability: Limitations on the number of donors and cycles per donor may result in a shortage of suitable donors, making it harder for couples to find matching gametes.
- Fertility rates are declining in India and worldwide, making the limited availability of donors a significant challenge.
- Challenges in Finding Suitable Donors: The restrictions may pose challenges for doctors and couples in finding donors that meet specific requirements or preferences.
- Discouragement for Potential Donors: Concerns over legal and social repercussions, as well as lack of incentives, may discourage potential donors from participating in the ART process.
Way Forward
- Enhance affordability through subsidies and partnerships.
- Expand the donor pool through awareness campaigns and community support.
- Streamline donor matching with a centralized platform and advanced technology.
- Encourage research and innovation for cost-effective treatments.
- Develop a supportive legal framework protecting rights and addressing ethical concerns.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q. In the context of recent advances in human reproductive technology, “Pronuclear Transfer” is used for (2020)
(a) fertilization of egg in vitro by the donor sperm
(b) genetic modification of sperm producing cells
(c) development of stem cells into functional embryos
(d) prevention of mitochondrial diseases in offspring
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Pronuclear transfer involves the transfer of pronuclei from one zygote to another. This technique first requires fertilisation of healthy donated eggs (provided by the mitochondrial donor) with the intended male parent sperm. Simultaneously, the intending mother’s affected oocytes are fertilised with the intending father’s sperm.
- By using a technique, called ‘Maternal Spindle transfer’, the maternal DNA is put into the egg of a donor woman, which is then fertilized using the father’s sperm. The procedure was developed to help existing In-vitro-Fertilization (IVF) treatments in which mothers have mitochondrial diseases.
- Mutations in maternal DNA are a cause of mitochondrial disease, a heterogeneous group of diseases that can lead to premature death, sometimes in infancy or childhood. Most mitochondrial diseases lack specific treatments, and women who carry the causative mutations are at high risk of transmitting the diseases to their offspring. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.


Geography
Indian Ocean Dipole
For Prelims: Indian Ocean Dipole, El Nino, IMD, Monsoon, ENSO, Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean.
For Mains: Indian Ocean Dipole and its impact on El Nino.
Why in News?
The Indian Monsoon is expected to be influenced by the El Nino phenomenon in 2023, there are also anticipations of a positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) developing, which could potentially offset the impact of El Nino.
- According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), there is about 80% probability for positive IOD conditions and 15% of a neutral IOD during June-August 2023 season.
- While the El Nino is already firmly established in the Pacific Ocean in 2023, the IOD is still in the neutral phase and may develop in the coming months.
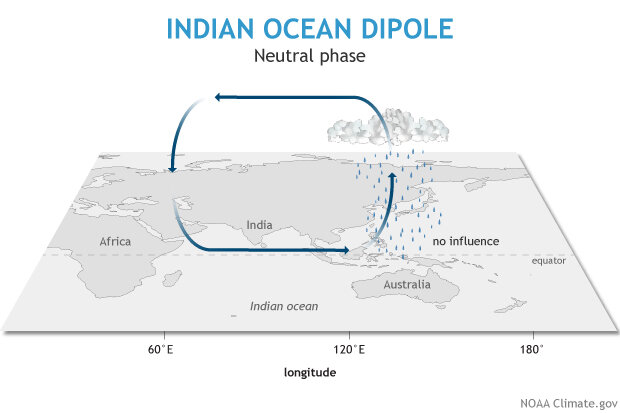
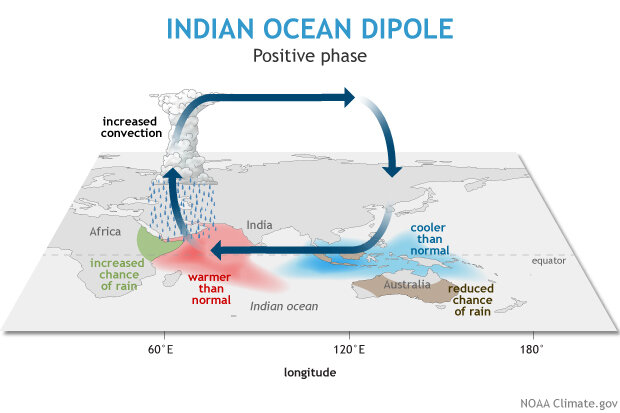
What is the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)?
- IOD or Indian Nino:
- IOD, sometimes referred to as the Indian Nino, is similar to the El Nino phenomenon, occurring in the relatively smaller area of the Indian Ocean between the Indonesian and Malaysian coastline in the east and the African coastline near Somalia in the west.
- The El Nino is the warmer-than-normal phase of the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon, during which there are generally warmer temperatures and less rainfall than normal in many regions of the world, including India.
- One side of the ocean, along the equator, gets warmer than the other.
- IOD is said to be positive when the western side of the Indian Ocean, near the Somalia coast, becomes warmer than the eastern Indian Ocean.
- It is negative when the western Indian Ocean is cooler.
- IOD, sometimes referred to as the Indian Nino, is similar to the El Nino phenomenon, occurring in the relatively smaller area of the Indian Ocean between the Indonesian and Malaysian coastline in the east and the African coastline near Somalia in the west.
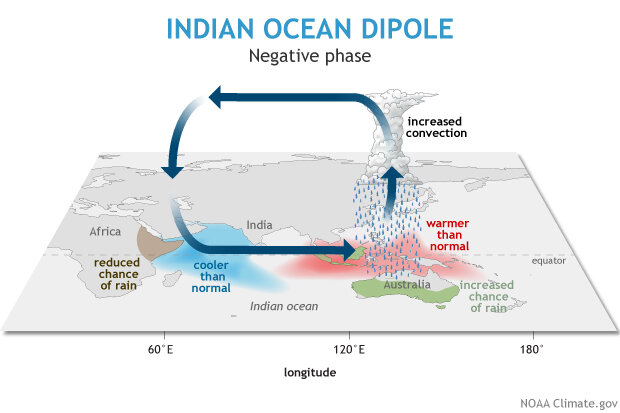
- Mechanism:
- Negative IOD:
- The air circulation in the Indian Ocean basin moves from west to east, that is from the African coast towards the Indonesian islands, near the surface, and in the opposite direction at the upper levels. That means the surface waters in the Indian Ocean get pushed from west to east.
- In a normal year, warmer waters in the western Pacific near Indonesia cross over into the Indian Ocean and make that part of the Indian Ocean slightly warmer. That causes the air to rise and helps the prevailing air circulation.
- In the years when the air circulation becomes stronger, more warm surface waters from the African coast are pushed towards the Indonesian islands, making that region warmer than usual. This causes hotter air to rise, and the cycle reinforces itself.
- This is the state of negative IOD.
- Positive IOD:
- Air circulation becomes slightly weaker than normal. In some rare cases, the air circulation even reverses direction. The consequence is that the African coast becomes warmer while the Indonesian coastline gets cooler.
- A positive IOD event is often seen developing at times of an El Nino, while a negative IOD is sometimes associated with La Nina.
- During El Nino, the Pacific side of Indonesia is cooler than normal because of which the Indian Ocean side also gets cooler. That helps the development of a positive IOD.
- Air circulation becomes slightly weaker than normal. In some rare cases, the air circulation even reverses direction. The consequence is that the African coast becomes warmer while the Indonesian coastline gets cooler.
- Impact of IOD:
- In the Indian Ocean, IOD exhibits an ocean-atmosphere interaction that closely resembles the fluctuations observed during El Niño events in the Pacific Ocean. However, the IOD is considerably less powerful compared to El Niño, resulting in relatively minimal impacts.
- A positive IOD helps rainfall along the African coastline and also over the Indian sub-continent while suppressing rainfall over Indonesia, southeast Asia and Australia. The impacts are opposite during a negative IOD event.
- Past Events:
- In 2019 the IOD event developed during the late monsoon but was so strong that it compensated for the deficit rainfall during the first month of the monsoon season (June had 30% deficiency that year).
- The deficit in June that year was also attributed to a developing El Nino but that fizzled out later.
- In 2019 the IOD event developed during the late monsoon but was so strong that it compensated for the deficit rainfall during the first month of the monsoon season (June had 30% deficiency that year).
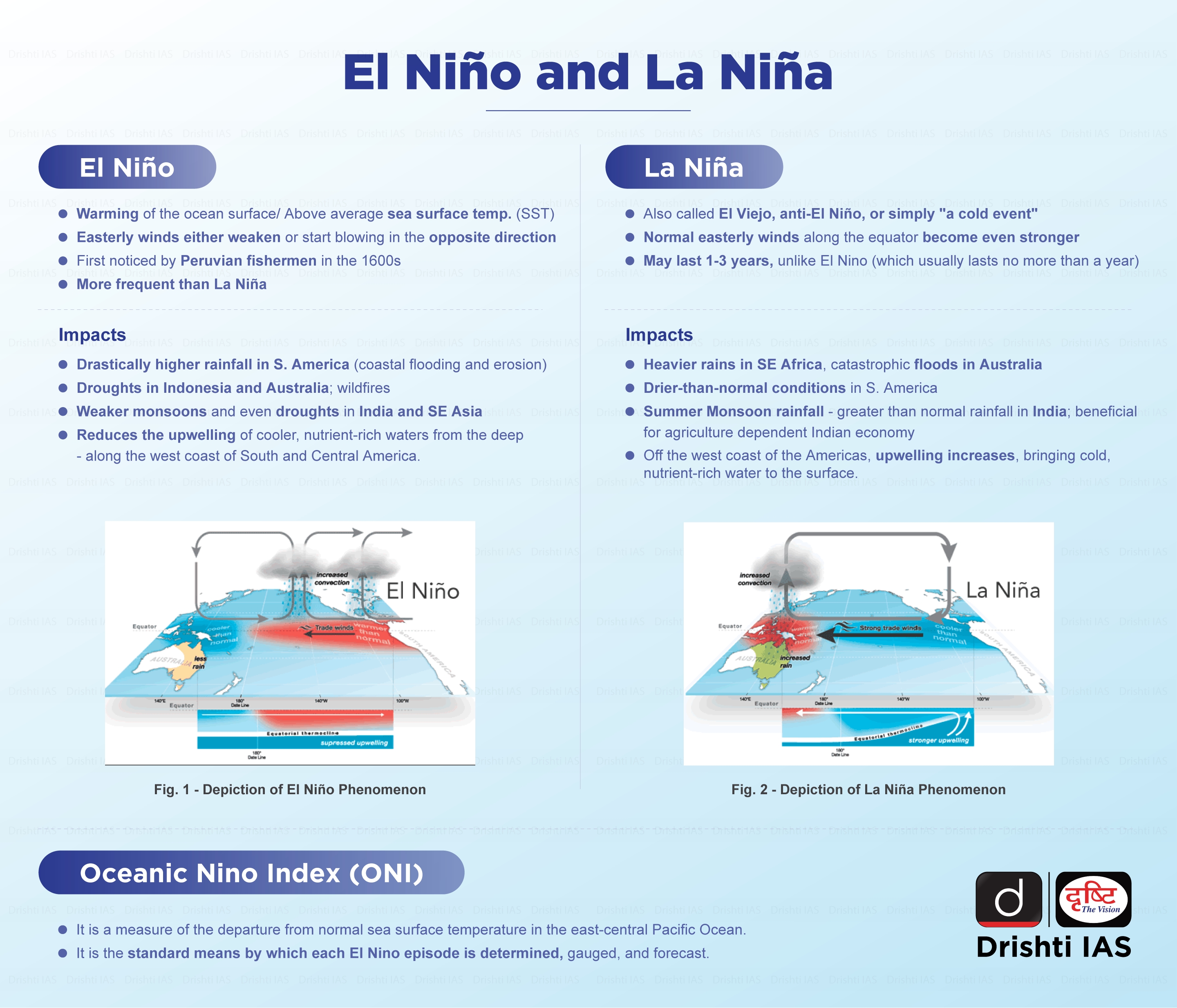
What is ENSO?
- In a normal year, the eastern side of the Pacific Ocean, near the northwestern coast of South America, is cooler than the western side near the islands of Philippines and Indonesia.
- This happens because the prevailing wind systems that move from east to west sweep the warmer surface waters towards the Indonesian coast.
- The relatively cooler waters from below come up to replace the displaced water.
- An El Nino event is the result of a weakening of wind systems that leads to lesser displacement of warmer waters.
- This results in the eastern side of the Pacific becoming warmer than usual. During La Nina, the opposite happens.
- Both these conditions, together called El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO), affect weather events across the world.
- Over India, the El Nino has the impact of suppressing monsoon rainfall.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Question: How far do you agree that the behaviour of the Indian monsoon has been changing due to humanizing landscape? Discuss. (2015)


Governance
CSR Guidelines for Empowering Ports
For Prelims: Corporate Social Responsibility , Sagar Samajik Sahayyog, Ports, Major Port Authorities Act, 2021.
For Mains: Significance of Corporate Social Responsibility
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways has launched 'Sagar Samajik Sahayyog,' its new guidelines for Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), aiming to empower ports to address local community issues in a more cooperative and swift manner.
What are the Key Highlights of the Guidelines?
- CSR Funding:
- Ports in India will allocate a specific percentage of their net annual profit towards CSR activities. The CSR budget for ports will be based on their respective turnover for the year, the division will be as follows:
- Ports with an annual turnover of less than Rs 100 crores will spend 3-5% on CSR.
- Ports with a turnover between Rs 100 to 500 crores will spend 2-3%.
- Ports with a turnover exceeding Rs 500 crores will spend 0.5-2%.
- 2% of the total CSR expenses will be dedicated to project monitoring by the ports to ensure effective implementation and monitoring of the respective CSR projects.
- Ports in India will allocate a specific percentage of their net annual profit towards CSR activities. The CSR budget for ports will be based on their respective turnover for the year, the division will be as follows:
- CSR Committee:
- Each Major Port will establish a corporate social responsibility committee, headed by a deputy chairperson of major port to plan and implement CSR initiatives.
- The committee will consist of two other members. CSR projects must be implemented into the business plans of major ports, addressing social and environmental concerns related to their operations.
- A CSR plan will also need to be prepared for each financial year.
- Allocation and Focus Areas:
- The CSR projects and programmes will focus on activities specified in Section 70 of the Major Port Authorities Act, 2021.
- According to Section 70 of the Act, the organization may use its funds for providing social benefits including development of infrastructure in areas of education, health, housing, skill development, training and recreational activities for its own employees, customers etc.
- 20% of the CSR expenses must be earmarked for the Sainik Kalyan Board at the district level, the National Maritime Heritage Complex, and the National Youth Development Fund.
- Additionally, 78% of the funds should be directed towards social and environmental welfare initiatives benefiting the community.
- These include projects related to drinking water, education, vocational training, non-conventional and renewable energy sources for electricity, health and family welfare, livelihood promotion for Economically Weaker Sections (EWS), community centers, and hostels.
- 2 % of the total CSR expense is allocated for project monitoring under the CSR programs by the ports.
- The CSR projects and programmes will focus on activities specified in Section 70 of the Major Port Authorities Act, 2021.
What is the Significance of the Guidelines?
- The guidelines enable ports to directly undertake CSR activities, fostering community welfare and development.
- By embracing a framework that includes local communities as partners, CSR has the potential to drive positive change and become a significant catalyst for progress.
- The guidelines aim to make CSR a potent force for positive transformation. This initiative reflects the government's commitment to maximum governance and community-centric development.
What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
- About:
- The concept of CSR is the idea that companies should assess and take responsibility for their effects on the environment and on social welfare, and to promote positive social and environmental change.
- The four main types of corporate social responsibility are:
- Environmental Responsibility
- Ethical Responsibility
- Philanthropic Responsibility
- Economic Responsibility
- The Corporate Social Responsibility provisions within Companies Act 2013 is applicable to companies with an annual turnover of 1,000 crore and more, or a net worth of Rs. 500 crore and more, or a net profit of Rs. 5 crore and more.
- The Act requires companies to set up a CSR committee which shall recommend a Corporate Social Responsibility Policy to the Board of Directors and also monitor the same from time to time.
- Activities under CSR:
- Specified under Schedule VII of the Companies Act 2013, some major activities include:
- Eradicating hunger, poverty and malnutrition and promotion of education, gender equality.
- Fighting Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome(AIDS), Human Immunodeficiency Virus, and other disorders
- Ensuring Environmental Sustainability
- Protection of National Heritage, Art and Culture including restoration of buildings and sites of historical importance and works of art.
- Measures for the benefit of armed forces veterans, war widows and their dependents.
- Training to promote rural sports, nationally recognized sports, paralympic sports and Olympic sports
- Contribution to the PM's National Relief Fund or any other fund set up by the Central Government for socio-economic development and relief.
- Specified under Schedule VII of the Companies Act 2013, some major activities include:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. Corporate social responsibility makes companies more profitable and sustainable. Analyse. (2017)


Important Facts For Prelims
Uttar Pradesh's 7 Products Receive GI Tags
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh, known for its rich cultural heritage and traditional crafts, has recently seen seven of its distinctive products being granted Geographical Indication (GI) tags by the Geographical Indications Registry in Chennai.
Which Seven Products from Uttar Pradesh have Received the GI Tag?
- Amroha Dholak: A Musical Marvel
- The Amroha Dholak is a musical instrument crafted from natural wood.
- Preferred wood choices include mango, jackfruit, and teakwood.
- Animal skin, usually goatskin, is meticulously fitted to create the drum's surface.
- The Amroha Dholak is a musical instrument crafted from natural wood.
- Baghpat Home Furnishings:
- Baghpat and Meerut are renowned for their exclusive handloom home furnishing products.
- The weaving process involves cotton yarn and is predominantly done on frame looms.
- Barabanki Handloom Product:
- Barabanki and its surrounding areas are home to around 50,000 weavers and 20,000 looms.
- The annual turnover of the Barabanki cluster is estimated to be ₹150 crore.
- Barabanki and its surrounding areas are home to around 50,000 weavers and 20,000 looms.
- Kalpi Handmade Paper:
- Kalpi is recognized for handmade paper manufacturing.
- Munnalal 'Khaddari,' a Gandhian, introduced the craft in the 1940s, although its roots in Kalpi's history may extend further.
- Kalpi is recognized for handmade paper manufacturing.
- Mahoba Gaura Patthar Hastashlip:
- Mahoba Gaura Patthar Hastashlip represents the unique stone craft of Mahoba.
- The stone used, scientifically known as the 'Pyro Flight Stone,' is a soft and radiant white-coloured stone predominantly found in the region.
- Mainpuri Tarkashi:
- Sambhal Horn Craft:
- Sambhal Horn Craft utilises raw materials procured from deceased animals and this craft form is entirely handmade.
What is a GI Tag?
- About:
- A geographical indication (GI) tag is a name or sign used on certain products that correspond to a specific geographical location or origin.
- For example, Darjeeling Tea, Kanchipuram Silk, etc.
- The GI tag ensures that only the authorised users or those residing in the geographical territory are allowed to use the popular product name.
- It also protects the product from being copied or imitated by others.
- A registered GI is valid for 10 years.
- A geographical indication (GI) tag is a name or sign used on certain products that correspond to a specific geographical location or origin.
- Legal Framework and Obligations:
- The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 seeks to provide for the registration and better protection of geographical indications relating to goods in India.
- It is governed and directed by the WTO Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS).
- Furthermore, the significance of protecting industrial property and geographical indications as integral components of intellectual property is acknowledged and emphasised in Articles 1(2) and 10 of the Paris Convention.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which of the following has/have been accorded ‘Geographical Indication’ status? (2015)
- Banaras Brocades and Sarees
- Rajasthani Daal-Bati-Churma
- Tirupathi Laddu
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q2. India enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 in order to comply with the obligations to (2018)
(a) ILO
(b) IMF
(c) UNCTAD
(d) WTO
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
QS World Ranking 2024
Why in News?
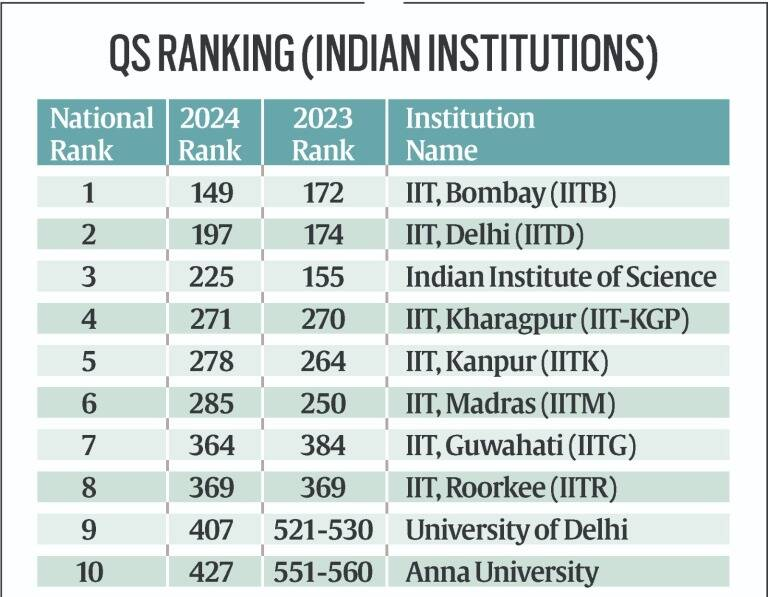
Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay has achieved a significant milestone by breaking into the world's top 150 universities in the latest edition of the Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) World University Ranking. This remarkable leap comes after eight years since the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore achieved a similar feat.
- However, the ranking list has witnessed fluctuations, with IISc falling 70 positions. These changes are attributed to the revised ranking parameters introduced by Quacquarelli Symonds, the UK-based ranking agency.
What are the Key Insights from QS World University Ranking?
- Global Rankings Overview:
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) tops the World University Ranking for the twelfth consecutive time.
- National University of Singapore becomes the first Asian university to enter the top 10.
- Indian Universities in QS World Rankings:
- India is the seventh most represented country globally, with 45 universities ranked.
- IIT Bombay achieves its highest rank ever, securing the 149th position globally in the QS World University Ranking.
- IIT Bombay demonstrates excellence in employment reputation and citation per faculty. Notable improvement in citation per faculty, rising from 55.1 to 73.1.
- University of Delhi and Anna University make their debut in the top 500 universities.
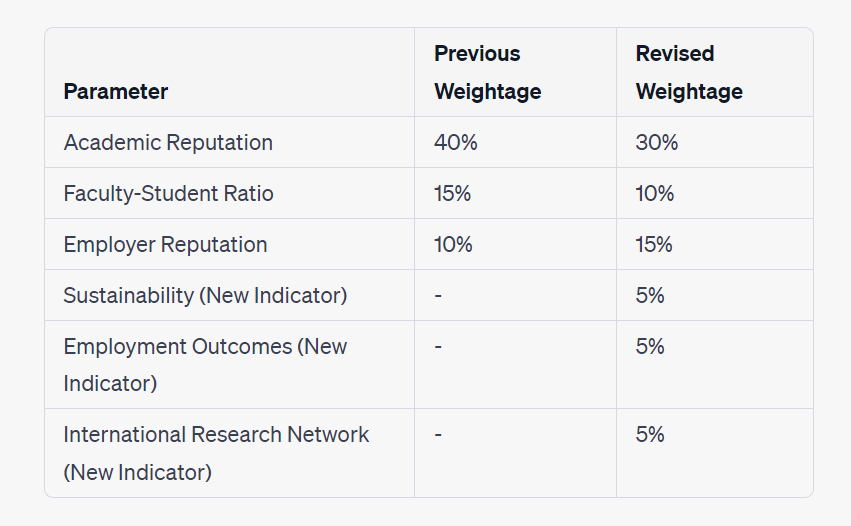
What are the Revised Ranking Parameters in QS?
- QS introduced three new indicators: sustainability, employment outcomes, and international research network, each with a weightage of 5%.
- Adjustments were made to existing parameters: academic reputation, faculty-student ratio, and employer reputation.
- Decreased weightage for faculty-student ratio.
- Impact on Indian Institutions:
- Reduction in faculty-student ratio weightage benefits Indian institutions overall.
- However, research-focused institutions like IISc face challenges due to decreased weightage.
- Employability outcomes indicator benefits several Indian institutions.
What is QS World University Rankings?
- QS World University Rankings are released annually by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS).
- The rankings evaluate the performance and quality of universities worldwide.
- The methodology considers indicators such as academic reputation, faculty-student ratio, employer reputation, sustainability, employment outcomes, international research network, citations per faculty, international faculty ratio, and international student ratio.
- They provide rankings by subject, region, student city, business school, and sustainability.


Important Facts For Prelims
Rani Durgavati
Why in News?
Recently, the Madhya Pradesh government launched a six-day rally called the Rani Durgavati Gaurav Yatra to commemorate the life and legacy of the 16th-century queen, Rani Durgavati, who fought against the Mughals.
Who was Rani Durgavati?
- About:
- Rani Durgavati, born in 1524 in Mahoba's Chandela dynasty (present-day Uttar Pradesh, near the border with Madhya Pradesh), was a symbol of India's self-determination.
- Chandelas were known for building the famous Khajuraho temples in the 11th century.
- She married Dalpat Shah, the son of Gond King Sangram Shah, and ruled the kingdom of Garha-Katanga after the death of her husband in 1550 with great vigor and courage.
- The Kingdom of Garha-Katanga included the regions of Narmada Valley and parts of Northern Madhya Pradesh.
- Gond tribe is a prominent tribe in central India known for their rich cultural heritage and resilience.
- As per the government’s documentation, the queen and her generals managed the affairs of the kingdom for 16 years.
- Rani Durgavati, born in 1524 in Mahoba's Chandela dynasty (present-day Uttar Pradesh, near the border with Madhya Pradesh), was a symbol of India's self-determination.
- The Mughal Attack on Garha-Katanga:
- Rani Durgavati, the brave queen of Garha-Katanga, opposed the Mughal Empire's expansion in the mid-16th century.
- Rani Durgavati displayed strong leadership while fighting against Akbar's commander Asaf Khan and the neighboring Malwa Sultan Baz Bahadur. She initially triumphed in the battle against Asaf Khan's attack on her kingdom.
- However, the Mughals regrouped and overwhelmed her forces. Rather than surrendering, Rani Durgavati chose to sacrifice her life.
- Legacy and Recognition:
- Revered as a patriotic ruler who symbolized India's self-determination.
- Described as a combination of beauty, grace, courage, and bravery by Abul Fazl, the court historian of Akbar.
- Remembered for her sacrifices and as a defender of her culture.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Helen Keller Day
Optimism is the faith that leads to achievement, nothing can be done without hope.” - Helen Keller. The Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities under Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, in India observed Helen Keller's Day on June 27, 2023, commemorating the remarkable life and achievements of Helen Keller, who overcame her deafness and blindness to become an inspiration to millions.
Despite her disabilities, Keller's determination and perseverance led her to become a renowned writer, founder of the "American Foundation for the Blind," and a passionate advocate for people with disabilities. Her autobiography, "The Story of My Life," published in 1903, remains one of her most famous works. Other notable publications include "Optimism," "The World I Live In," and "My Religion."
Read more: Person with Disabilities in India
National Exit Test (NExT)
The National Medical Commission recently announced the National Exit Test (NExT), which will serve as the two-step medical licentiate exam and replace the Foreign Medical Graduates Exam (FMGE) and the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test – Postgraduate (NEET-PG). Students admitted to the MBBS course in 2019 will be the first batch to take the National Exit Test (NExT).
The National Medical Commission is a statutory body in India that was established in 2019 by the government to replace the Medical Council of India (MCI).
Read more: National Medical Commission, National Exit Test.
President Honors Armed Forces with Prestigious Service Awards
Recently, President of India bestowed Distinguished Service Awards upon 84 serving and retired personnel of the armed forces and the Indian Coast Guard in New Delhi. The awards included 52 Ati Vishisht Seva Medals (AVSMs), 3 Uttam Yudh Seva Medals (UYSMs), and 28 Param Vishisht Seva Medals (PVSMs).
AVSMs are awarded for exceptionally distinguished service in the armed forces. A Bar is added to AVSMs for multiple instances of outstanding service. UYSMs recognize exceptional operational service during a war or specific military operations. PVSMs recognize distinguished service of the highest order in the armed forces, honoring individuals who have displayed exceptional commitment and dedication to their duties.
Read more: Gallantry Awards
Aadhaar Authentication for Birth and Death Registrations
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has allowed the Registrar General and Census Commissioner to utilize Aadhaar authentication for birth and death registrations, following authorization from the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY). The Registrar, appointed under the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, will now have the option to voluntarily verify the Aadhaar numbers provided in the reporting forms for births and deaths. This authentication process aims to establish the identity of individuals such as children, parents, informants, and spouses.
The Registrar General and Census Commissioner is a government office responsible for overseeing the registration of vital events such as births, deaths, and marriages. They play a crucial role in maintaining accurate demographic data and conducting national censuses.
Read more: Safeguarding Aadhaar Data