Geography
Third Consecutive La Nina Event
- 29 Aug 2022
- 11 min read
For Prelims: La Niña, El Nino, El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), India Meteorological India (IMD).
For Mains: Impacts of El Nino and La Nina on India.
Why in News?
Recently, Australia’s Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) predicted, that a third consecutive event of La Nina could be underway which could lead to unusual weather effects in various countries.
- There is an extended period of La Nina in 2022. It is the first time that this has happened since the 1950s when the event started to be recorded. The years 1973-76 and 1998-2001 were consecutive La Nina years.
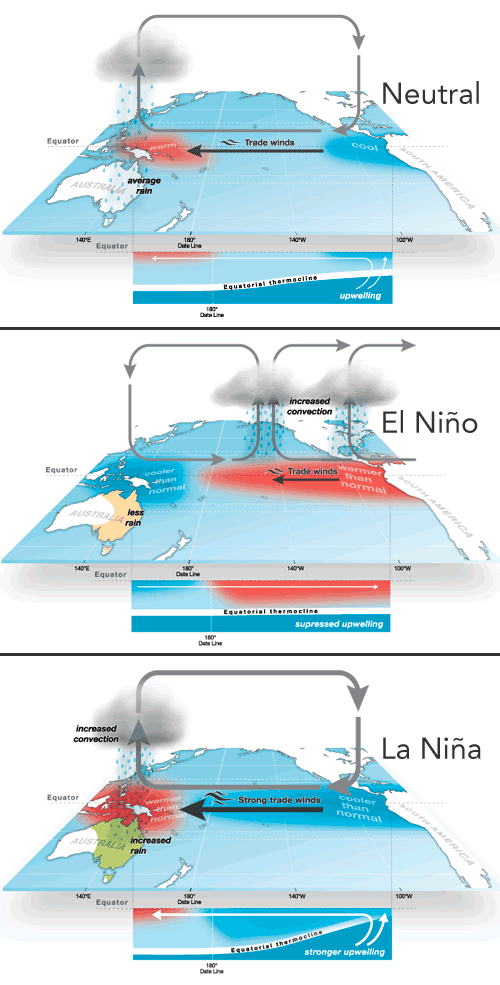
What is La Nina and El Nino?
- Normal Condition:
- In the neutral state (neither El Niño nor La Niña) trade winds blow east to west across the surface of the tropical Pacific Ocean, bringing warm moist air and warmer surface waters towards the western Pacific and keeping the central Pacific Ocean relatively cool.
- Warm sea surface temperatures in the western Pacific pump heat and moisture into the atmosphere above.
- In a process known as atmospheric convection, this warm air rises high into the atmosphere and, if the air is moist enough, causes towering cumulonimbus clouds and rain.
- The pattern of air rising in the west and falling in the east with westward moving air at the surface is referred to as the Walker Circulation.
- In the neutral state (neither El Niño nor La Niña) trade winds blow east to west across the surface of the tropical Pacific Ocean, bringing warm moist air and warmer surface waters towards the western Pacific and keeping the central Pacific Ocean relatively cool.
- La Nina:
- La Nina means the Little Girl in Spanish. It is also sometimes called El Viejo, anti-El Nino, or simply "a cold event."
- La Nina events represent periods of below-average sea surface temperatures across the east-central Equatorial Pacific.
- It is indicated by sea-surface temperature decreased by more than 0.9℉ for at least five successive three-month seasons.
- La Nina event is observed when the water temperature in the Eastern Pacific gets comparatively colder than normal, as a consequence of which, there is a strong high pressure over the eastern equatorial Pacific.
- Impacts:
- Europe: In Europe, El Nino reduces the number of autumnal hurricanes.
- La Nina tends to lead to milder winters in Northern Europe (especially UK) and colder winters in southern/western Europe leading to snow in the Mediterranean region.
- North America: It is continental North America where most of these conditions are felt. The wider effects include:
- Stronger winds along the equatorial region, especially in the Pacific.
- Favourable conditions for hurricanes in the Caribbean and central Atlantic area.
- Greater instances of tornados in various states of the US.
- South America: La Nina causes drought in the South American countries of Peru and Ecuador.
- It usually has a positive impact on the fishing industry of western South America.
- Western Pacific: In the western Pacific, La Nina increases the potential for landfall in those areas most vulnerable to their effects, and especially into continental Asia and China.
- It also leads to heavy floods in Australia.
- There are increased temperatures in Western Pacific, Indian Ocean and off the Somalian coast.
- Europe: In Europe, El Nino reduces the number of autumnal hurricanes.
- EL Nino:
- El Nino is a climate pattern that describes the unusual warming of surface waters in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It is the “warm phase” of a larger phenomenon called the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
- It occurs more frequently than La Nina.
- Impacts:
- Impact on Ocean: El Nino also impacts ocean temperatures, the speed and strength of ocean currents, the health of coastal fisheries, and local weather from Australia to South America and beyond.
- Increased Rainfall: Convection above warmer surface waters brings increased precipitation.
- Rainfall increases drastically in South America, contributing to coastal flooding and erosion.
- Diseases caused by Floods and Droughts: Diseases thrive in communities devastated by natural hazards such as flood or drought.
- El Nino-related flooding is associated with increases in cholera, dengue, and malaria in some parts of the world, while drought can lead to wildfires that create respiratory problems.
- Positive impact: It can sometimes have a positive impact too, for example, El Nino reduces the instances of hurricanes in the Atlantic.
- In South America: As El Nino brings rain to South America, it brings droughts to Indonesia and Australia.
- These droughts threaten the region’s water supplies, as reservoirs dry and rivers carry less water. Agriculture, which depends on water for irrigation, is also threatened.
- In Western Pacific: These winds push warm surface water towards the western Pacific, where it borders Asia and Australia.
- Due to the warm trade winds, the sea surface is normally about 0.5 meter higher and 4-5° F warmer in Indonesia than Ecuador.
- The westward movement of warmer waters causes cooler waters to rise up towards the surface on the coasts of Ecuador, Peru, and Chile. This process is known as upwelling.
- Upwelling elevates cold, nutrient-rich water to the euphotic zone, the upper layer of the ocean.
- El Nino is a climate pattern that describes the unusual warming of surface waters in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO):
- The combined phases of La Nina and El Nino are termed El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and affect rainfall patterns, global atmospheric circulation, and atmospheric pressure across the planet.
What will be the Impacts of Third Consecutive La Nina?
- The India Meteorological India (IMD) has stated in its report that La Nina conditions currently prevail over the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Impacts on India:
- Extreme weather:
- The India Meteorological India (IMD) has predicted that some parts of India may witness heavy rains.
- The Western Ghats may receive average or below-average rain.
- Winter rainfall is less than normal in North India.
- Snowfall over Western Himalayas is less than normal.
- Winter temperatures in the plains are less than normal.
- Prolonged Winter Season over North India (extended winters).
- More rain during the second half of the Northeast Monsoon.
- Negative Impact on Agriculture:
- Farmers will be at risk of losing their standing Kharif crops if it rains during this period.
- As the harvesting of the Kharif crops begins in September-end or early October and any rain just before that would prove detrimental to the standing crops.
- Farmers will suffer a double whammy if untimely rains coincide with the harvest.
- Farmers will be at risk of losing their standing Kharif crops if it rains during this period.
- Extreme weather:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is an atmosphereocean coupled phenomenon in the tropical Indian Ocean (like the El Nino is in the tropical Pacific), characterised by a difference in Sea-Surface Temperatures (SST).
- A ‘positive IOD’ is associated with cooler than normal sea-surface temperatures in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean and warmer than normal sea-surface temperatures in the western tropical Indian Ocean.
- The opposite phenomenon is called a ‘negative IOD’ and is characterized by warmer than normal SSTs in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean and cooler than normal SSTs in the western tropical Indian Ocean.
- Also known as the Indian Nino, it is an irregular oscillation of sea-surface temperatures in the Indian Ocean in which the western Indian Ocean becomes alternately warmer and colder than the eastern part of the Indian Ocean. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
Mains
Q. Drought has been recognized as a disaster in view of its spatial expanse, temporal duration, slow onset and lasting effects on vulnerable sections. With a focus on the September 2010 guidelinesfrom the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), discuss the mechanismsfor preparednessto deal with likely El Nino and La Nina fallouts in India (2014)