IndiaAI Mission
For Prelims: Artificial intelligence, IndiaAI Mission, Large Multimodal Models, Non-personal datasets, International Energy Agency
For Mains: IndiaAI Mission, Boosting AI innovation and startups, AI ecosystem in India
Why in News?
The Indian government's commitment to advancing artificial intelligence (AI) technology is evident with its new budgetary allocation for the IndiaAI Mission.
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has been allocated Rs 551.75 crore in the Union Budget 2024-25 to enhance AI infrastructure, including the procurement of high-performance Graphic Processing Units (GPUs).
- This move aims to support domestic AI development and reduce reliance on expensive foreign hardware.
What is the IndiaAI Mission?
- Objective: The mission aims to establish a robust AI computing infrastructure in India to support the development and testing of AI systems.
- The Mission aims to enhance data quality, and develop indigenous AI technologies. It focuses on attracting top talent, fostering industry collaboration, supporting impactful AI startups, and promoting ethical AI practices.
- Financial Support: The Union Cabinet approved the Rs 10,372 crore IndiaAI Mission in March to establish a computing capacity of over 10,000 GPUs and develop foundational models with a capacity of more than 100 billion parameters trained on datasets covering major Indian languages for priority sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Current Focus: Initial efforts will involve procuring 300 to 500 GPUs to kickstart the project.
- Importance of GPU Procurement: GPUs are critical for training and building large-scale AI models, essential for advanced AI applications.
- Data centre GPUs are crucial for parallel operations, AI, media analytics, and 3D rendering solutions, making them essential for advanced use cases like machine learning, modelling, and cloud gaming.
- The procurement will provide Indian startups with essential computing power, addressing a gap in the current market.
- Key Components of the IndiaAI Mission:
- IndiaAI Compute Capacity: Creation of a high-end AI computing ecosystem with over 10,000 Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) to support AI startups and research, along with an AI marketplace for resources.
- IndiaAI Innovation Centre: Development of indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and foundational models for various sectors. Close to Rs 2,000 crore has been earmarked for this centre
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform: A unified platform to provide seamless access to quality non-personal datasets for startups and researchers.
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative: Promotion of AI applications targeting problem statements from various governmental sectors, aiming for large-scale socio-economic transformation.
- IndiaAI FutureSkills: Expansion of AI education through undergraduate, master’s, and Ph.D. programs, as well as establishing Data and AI Labs in smaller cities.
- IndiaAI Startup Financing: Provision of streamlined funding access for deep-tech AI startups to support innovative projects.
- The Cabinet has approved government financing for deep tech startups at different growth stages, with approximately Rs 2,000 crore allocated for this purpose.
- Safe & Trusted AI: Development of guidelines and frameworks to ensure responsible AI practices, including indigenous tools for project assessment.
What are the Key Highlights of India's Artificial Intelligence Market?
- Key Trends:
-
Adoption Across Sectors: AI adoption is growing in India across different sectors due to initiatives like the National AI Strategy and the National AI Portal launched by the Government of India.
-
Sectors like healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and agriculture are rapidly integrating AI technologies.
-
- Focus on Data Analytics: Clive Humby's assertion that "data is the new oil" underscores the growing importance of AI-driven data analytics.
- Companies are leveraging AI-driven analytics to gain valuable insights, improve operations, and foster innovation, supported by initiatives like the AI for All program launched by National Association of Software and Service Companies (NASSCOM).
- Government Initiatives: Initiatives like Digital India, Make in India, and Smart Cities Mission, GI Cloud (MeghRaj) and Global INDIAai Summit hosted by India are driving AI adoption across sectors.
- Research and Development: Indian research institutions and academic organizations, such as IITs, ISI, and IISc, are actively involved in AI research and development, contributing to the global knowledge base.
-
- Clusters: AI clusters are emerging in Indian cities due to factors such as supportive policies, research institutions, and increasing demand for AI technologies. Major cities include Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Chennai, Pune, and the National Capital Region (NCR).
- Bengaluru is known as the "Silicon Valley of India" with a thriving ecosystem of multinationals, startups, and academic institutions. It has over 2,000 active startups and annual IT exports exceeding USD 50 billion. The city also has a strong presence in AI research, filing over 400 patents annually.
- Opportunities to Invest in India's AI Market:
- Using the Internet of Things (IoT) and AI-powered precision farming and crop monitoring can boost productivity.
- AI-driven fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer service automation are in demand and can collaborate with Indian banks to deploy AI solutions.
- AI offers opportunities for predictive diagnostics, personalized treatment, and drug discovery.
- AI technologies like recommendation engines and chatbots are reshaping the retail sector.
What are the Challenges Anticipated for IndiaAI Mission?
- Limited GPU Capacity and Infrastructure: The mission's objective to build a high-end AI compute capacity of 10,000 GPUs is ambitious. Yet, there are concerns about the timely procurement and deployment of these GPUs to meet the growing demand for AI applications.
- High costs of GPUs, like Nvidia's A100 chip costing up to USD 10,000, pose a barrier for smaller businesses.
- Availability of GPUs is a bottleneck, and accelerating the acquisition and integration of this hardware is crucial for advancing AI capabilities.
- Data Access and Quality: Training AI models on diverse datasets, particularly for Indic languages, is crucial. However, the current datasets are inadequate for developing effective indigenous AI models.
- Limited AI Expertise and High Costs: There is a shortage of skilled AI professionals in India. Efforts are being made to address this but bridging this gap remains a challenge.
- High Implementation Costs: The cost of deploying AI solutions, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, can be prohibitively high.
- This includes capital investments for infrastructure and integration, which may hinder widespread adoption.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Effective AI deployment requires advanced cloud computing infrastructure. While efforts like AIRAWAT represent progress, India still lacks comprehensive AI and cloud computing facilities necessary for scaling AI applications.
- Ethical and Integrity Concerns: As AI algorithms increasingly influence decision-making, ensuring ethical use and avoiding biases in AI models are critical.
-
The potential for skewed results due to tampered datasets or flawed training data poses significant risks.
- Handling sensitive and personal data introduces risks related to data security and privacy.
-
- Geopolitical and Regulatory Issues: Geopolitical tensions and export control regulations can restrict access to essential AI technologies and components, impacting India’s ability to develop and deploy AI solutions effectively.
- Environmental Concerns: AI queries, especially to OpenAI’s ChatGPT, use significantly more energy than regular Google searches. Image-based AI searches consume even more energy. AI models process and sift through a larger amount of data than simple searches, requiring more electrical signals for processing, storing, and retrieving data.
-
The increased data processing generates more heat, leading to the need for powerful air-conditioning and cooling systems in data centers.
- AI tools are expected to significantly increase global energy consumption. Currently, data centres account for 1% to 1.3% of global electricity demand, projected to rise to 1.5% to 3% by 2026, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Experts view that India will soon face the significant environmental toll of AI and data centres. The increased demand for water resources for cooling data centres adds to the environmental concerns.
-
Way Forward
- Incentivize Hardware Manufacturing: The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for IT hardware, notified in 2021, and also for semiconductors offers incentives for increased investment in domestic manufacturing for eligible firms. Expanding this initiative could further stimulate growth in the sector.
- Start-up Support: Provide financial incentives, mentorship, and incubation facilities for AI startups. Establish AI-focused accelerators and incubators like T- Hub (India's largest incubation centre) of Telangana.
- Comprehensive Data Ecosystem: A National Data Platform can be developed as a centralised data repository with standardised formats and quality checks, and promote data sharing while ensuring privacy. Invest in rozation and encryption techniques, as well as data labelling and curation to improve data quality.
- Prioritise Ethical AI: Develop comprehensive AI ethics guidelines and regulations, establish independent AI ethics boards, promote transparency and explainability in AI systems, and conduct regular AI audits to identify and mitigate biases.
-
AI Applications for Societal Impact: Identify key societal challenges and develop AI-driven solutions. Prioritise AI applications in healthcare, agriculture, education, and other critical sectors. Ensure equitable access to AI benefits for all segments of society.
- Promote Sustainable AI: Support sustainable AI by investing in energy-efficient AI algorithms and hardware, promoting the use of renewable energy sources for data centres, and creating AI-powered solutions for energy optimization and resource management.
- Talent Gap: Foster partnerships for internships, research projects, and faculty exchange. Attract overseas students and employees to invest in India, increase salaries and benefits to retain AI talent.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the objectives and key components of the IndiaAI Mission. How does it aim to transform India's AI landscape? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (2022)
Q. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)
Right to Shelter as Fundamental Right
For Prelims: Supreme Court, Right to Shelter, Railway, Right to Life, Article 21, Housing, Privacy, Due Process of Law, Land Ceiling, Article 19(1)(e), Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY), National Urban Housing Fund (NUHF), National Rural Livelihood Mission, Deen Dayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM), Forest Resources, Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA), Right to Fair Compensation and Transparency in Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Resettlement Act, 2013
For Mains: Balancing Between Economic Development and Fundamental Right of Individuals.
Why in News?
The Supreme Court called for a balance between developing railway infrastructure in Haldwani, and the fundamental right to shelter for people accused of illegally occupying railway land.
- The court further said that its orders cannot also be misinterpreted as a note of encouragement for future encroachments on public land.
What is Right to Shelter and Important Constitutional Provisions Involved?
- The Right to Shelter in India is recognised as a fundamental right under the broader ambit of the Right to Life guaranteed by Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
- This right ensures that every citizen has access to adequate housing, which is considered essential for living a life with dignity.
- It implies not just a roof over one's head but also includes adequate privacy, space, security, lighting, ventilation, basic infrastructure, and proximity to workplaces and social amenities.
- Forced evictions without proper rehabilitation and due process violate the Right to Shelter.
What are Ethical Considerations Regarding Eviction of People?
- Human Rights Violations: Every person has the right to a secure home, and evictions without adequate alternative arrangements undermine this right.
- Disproportionate Impact: Evictions disproportionately affect marginalised groups, including the poor, disabled and elderly, who may have fewer resources to relocate or adapt.
- Lack of Alternatives: Evictions are sometimes executed without offering alternative housing solutions or support services, leaving people without a place to go.
What are the Associated Judicial Verdicts Regarding Right to Shelter?
- Olga Tellis v. Bombay Municipal Corporation (1985): Slum dwellers filed a PIL arguing against eviction without alternate accommodation. The court held that eviction breached the right to livelihood, emphasising the State's duty to secure adequate means of livelihood and avoid depriving people of their rights.
- State of Maharashtra v. Basantibhai Khetan (1986): The Supreme Court upheld land ceiling laws, stating they do not violate fundamental rights. However, the State is responsible for providing rehabilitation and resettlement.
- Chameli Singh v. State of UP (1995): Justice Ramaswamy held that the right to shelter is a fundamental right under Article 21 and the right to residence [Article 19(1)(e)].
- Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation v. Ahmed Singh and Gulab Singh (1996): Similar to Olga Tellis case, the court allowed the eviction of pavement dwellers on the condition that they were provided with alternate accommodation.
- Sudama Singh and others v. State of Delhi and others (2010): Petitioners sought relocation from slum clusters. The Delhi High Court ruled that any eviction must include adequate compensation or alternate accommodation.
What are Government Initiatives to Provide Shelter to People?
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY): It is a credit-linked subsidy scheme by the government of India to facilitate access to affordable housing for the low and moderate-income residents of the country.
- National Urban Housing Fund (NUHF): It provides financial assistance to states and Union Territories for the implementation of housing schemes.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission: It aims to reduce poverty by enabling the poor households to access gainful self-employment and skilled wage employment opportunities, resulting in appreciable improvement in their livelihoods on a sustainable basis.
- Deen Dayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM): It focuses on providing shelter equipped with essential services to the urban homeless.
- Slum Rehabilitation Authority (SRA) Scheme: Particularly active in Maharashtra, this scheme focuses on rehabilitating slum dwellers by providing them with housing.
What Laws are Made to Support the Right to Shelter in India?
- Slum Areas (Improvement and Clearance) Act, 1956:
- It authorises the government to clear slum areas that are unfit for habitation due to health and safety risks.
- In such cases, redevelopment plans are formulated to replace substandard housing with better, more durable structures.
- The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006:
- It provides the right to hold and live in forest land under individual or common occupation for habitation or self-cultivation for livelihood.
- It also recognizes the rights of forest communities to use and manage forest resources.
- Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA):
- It regulates the real estate sector to ensure transparency, accountability, and timely delivery of housing projects.
- It protects homebuyers by mandating registration of projects and providing a grievance redressal mechanism.
- Right to Fair Compensation and Transparency in Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Resettlement Act, 2013:
- It includes detailed provisions for resettlement and rehabilitation of those affected by land acquisition.
- This ensures that displaced families receive support to relocate and rebuild their lives, including housing.
- Model Tenancy Act, 2021:
- It seeks to establish a speedy adjudication mechanism for dispute resolution, regulate renting of premises, and protect interests of landlords and tenants.
How Balance between Development Projects and Right to Shelter can be Maintained?
- Alternative Housing Solutions: Provide adequate alternative housing options for those displaced by development projects.
- Legal Protections and Fair Procedures: Ensure that evictions, if necessary, are conducted in a lawful and just manner, with appropriate compensation and support.
- Community Development and Integration: Incorporate community development programs into the project to enhance local infrastructure, services, and economic opportunities.
- Long-Term Planning: Develop long-term strategies for urban planning and housing that integrate development goals with the need for affordable and accessible housing.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court has linked the right to shelter with the right to life, emphasising its fundamental nature and its recognition as a human right by the United Nations. While the State is duty-bound to work towards providing affordable housing, this does not mean it must construct all housing or prevent all displacement. The right to shelter, distinct from the right to land, highlights the need for clear understanding and realistic expectations. By recognizing its true essence, individuals can better advocate for their rights and seek judicial redress when necessary.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Development and fundamental rights of individuals are often in conflict with each other. Do you agree? Give examples. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Discuss the various social problems which originated out of the speedy process of urbanisation in India. (2013)
Q. The basis of providing urban amenities in rural areas (PURA) is rooted in establishing connectivity. Comment (2013)
India's First Offshore Mineral Auctions
For Prelims: critical minerals, Atmanirbhar Bharat, Exclusive Economic Zone , National Critical Minerals Mission, Nuclear energy, Geological Survey of India, Indian Bureau of Mines
For Mains: Critical Minerals, Significance of Critical Minerals for India, Mineral Distribution in India.
Why in News?
India is set to launch its first offshore mineral auctions, marking a significant step in resource management. This initiative, part of the proposed National Critical Minerals Mission (NCCM), aims to enhance the supply chain for critical minerals.
- Union Minister of Mines announced the identification of 10 blocks, marking a pivotal moment in the nation’s quest for self-reliance in mineral resources, in line with the vision of an Atmanirbhar Bharat.
What are the Key Details of the Offshore Mineral Auctions?
- Mineral Blocks Identified: Exploration reports of 10 blocks located in India’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) are available for auction for grant of composite license. Of these, 7 blocks of poly-metallic nodules and crusts are located in Andaman Sea, 3 blocks of lime-mud are located off the Gujarat coast.
- Types of Minerals: The mineral blocks which contain critical minerals like Cobalt and Nickel which are key to manufacturing low-carbon technologies to generate, store and transmit clean energy and steel manufacturing.
- Regulatory Framework: The auctions will be conducted under the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act (OAMDR), 2002.
-
Composite licenses will be issued for mineral resource determination, exploration, and commercial production.
-
Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002
- The Ministry of Mines administers the OAMDR Act, 2002, which provides for development and regulation of mineral resources in the territorial waters, continental shelf, exclusive economic zone and other maritime zones of India and to provide for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The recent amendment in 2023 introduced a transparent auction process for operating rights, establish a trust for mining-affected persons, increase exploration, and provide relief in case of disasters.
- The amendment removed discretionary renewals, established a standard lease period of fifty years, introduced composite license, set area limits for operating rights, and facilitated easy transfer of composite license and production lease.
What is the National Critical Mineral Mission?
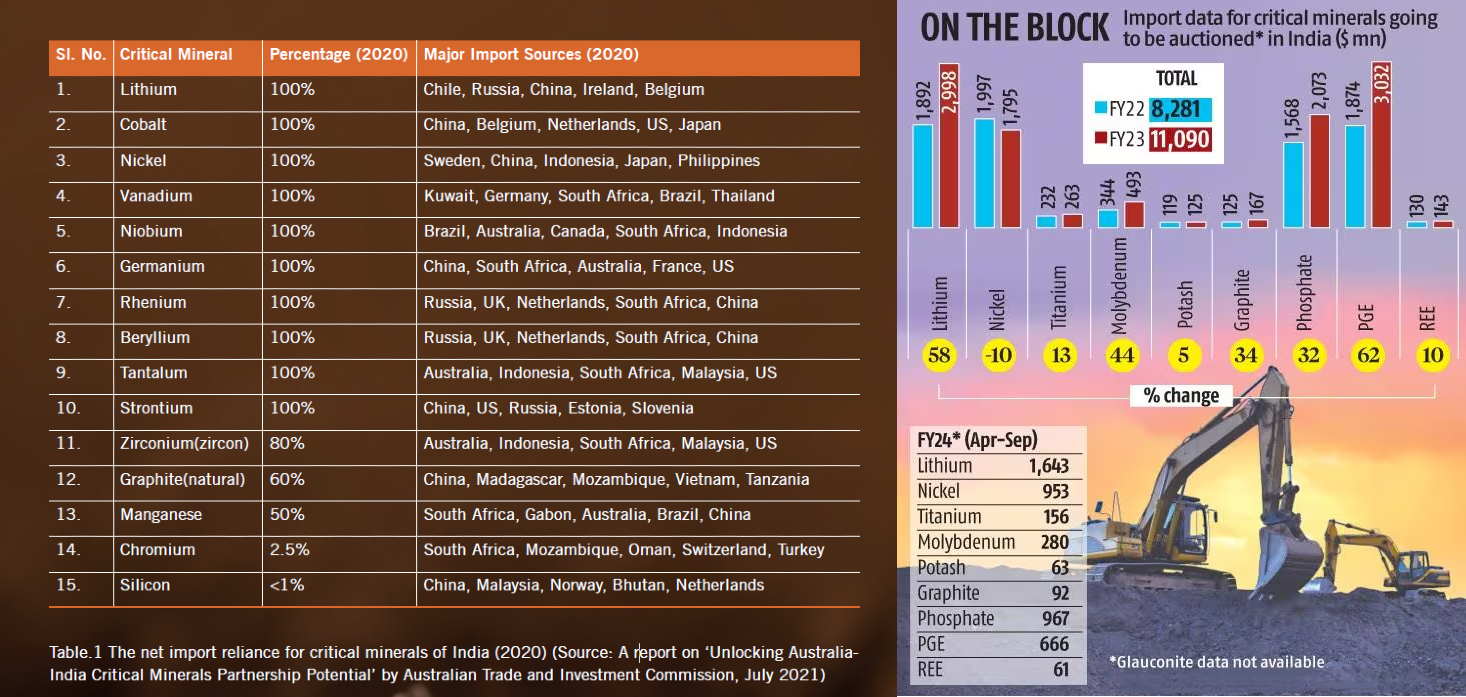
- Need: Increasing demand for electronic gadgets and clean energy technologies has led to India's heavy reliance on importing critical minerals, primarily from China.
- This import dependency has negative economic impacts, contributing to the current account deficit and affecting domestic production.
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 has highlighted strategic concerns regarding India's dependence on China for critical minerals.
- Objective: Ensure a sufficient supply of critical minerals, including copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt and rare earth elements. These minerals are essential components in almost all electronic gadgets ranging from laptops to electric cars.
- Applications:
- Electronics: Essential for manufacturing laptops, electric cars, and other electronic gadgets.
- Clean Energy Technologies: Vital for wind turbines and other renewable energy sources.
- High-Priority Sectors: Nuclear energy, renewable energy, space, defense, telecommunications, and high-tech electronics.
- Legislative and Budgetary Measures to Support NCCM:
- Mines and Minerals (Development & Regulation) Amendment Bill 2023: Allows awarding of exploration licenses for 30 deep-seated and critical minerals, including antimony, beryllium, lithium, and more.
- Budgetary Support:
- The Union Budget 2024-2025 proposed increased allocations for the Geological Survey of India (GSI), Indian Bureau of Mines (IBM), and National Mineral Exploration Trust (NMET).
- Rs.1,300 crore for GSI to improve geoscience data and strategic planning.
- Rs.135 crore for IBM to enhance regulatory efficiency and environmental protection.
- Rs. 400 crore for NMET to accelerate mineral exploration and support startups in the sector.
- The Union Budget 2024-2025 proposed increased allocations for the Geological Survey of India (GSI), Indian Bureau of Mines (IBM), and National Mineral Exploration Trust (NMET).
- Waiver of Customs Duty: The Union Budget 2024-2025 proposed the elimination of customs duties on 25 critical minerals and reductions for two others.
-
This move aims to lower costs for industries reliant on these minerals, attract investments in processing and refining, and foster the growth of downstream industries.
-
Zero import duty on blister copper will stabilize the supply chain for copper refiners, crucial for electronics and construction industries.
-
How Does Offshore Mineral Auctions Align with the Proposed National Critical Minerals Mission?
- Expanding Capabilities: Tapping into offshore mineral resources will significantly enhance India's capabilities in sectors like clean energy and steel manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Approach: The proposed NCCM will oversee the entire supply chain of critical minerals, from domestic production to recycling.
- It will also shield the country from elevated levels of import reliance and supply risks owing to global geo-political turbulence.
- Focus on Research and Development: The mission will address trade and market access, scientific research, and technology development in the critical minerals value chain.
- Encouraging Recycling Initiatives: The initiative aims to incentivise the Indian industry to develop recycling capacities for critical minerals, reducing reliance on primary sources.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Evaluate the potential impact of the National Critical Minerals Mission (NCCM) on India's industrial and technological sectors. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Recently, there has been a concern over the short supply of a group of elements called ‘rare earth metals’. Why? (2012)
- China, which is the largest producer of these elements, has imposed some restrictions on their export.
- Other than China, Australia, Canada and Chile, these elements are not found in any country.
- Rare earth metals are essential for the manufacture of various kinds of electronic items and there is a growing demand for these elements.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. Despite India being one of the countries of Gondwanaland, its mining industry contributes much less to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in percentage. Discuss. (2021)
Q. “In spite of adverse environmental impact, coal mining is still inevitable for development”. Discuss. (2017)
ADCs Raise Demand to Pass 125th Constitutional Amendment Bill
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief Executive Magistrates (CEMs) of 10 Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) from northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya and Mizoram and Tripura met the Union Home Minister, putting forward the demand of passing of the 125th Constitutional Amendment Bill.
- In this context, the Union government decided to form a committee headed by the Minister of State for Home Affairs to resolve the issues related to the Bill.
What are the Proposed Amendments in the 125th Constitutional Amendment Bill?
- The Bill aims to grant more financial, executive and administrative powers to tribal autonomous councils under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution.
-
Village and Municipal Councils:
- The proposal includes the creation of Village and Municipal Councils alongside the existing District and Regional Councils.
- Village Councils will be set up for individual villages or clusters of villages in rural areas, while Municipal Councils will be established in urban areas within each district.
- District Councils will have the authority to enact laws regarding:
- The number and composition of Village and Municipal Councils.
- The delimitation of constituencies for elections to these councils.
- The powers and functions of the Village and Municipal Councils.
- Rules for Devolution of Powers: The Governor will have the authority to create rules for the devolution of powers and responsibilities to Village and Municipal Councils.
-
These rules may cover:
- The preparation of economic development plans.
- The implementation of land reforms.
- Urban and town planning.
- Regulation of land use, among other responsibilities.
- The Bill proposes that the Governor may also establish rules for the disqualification of council members based on defection.
-
- State Finance Commission: The Bill provides for the appointment of a Finance Commission in these states to assess the financial status of District, Village, and Municipal Councils. The Commission will make recommendations on:
- The distribution of taxes between states and District Councils.
- Grants-in-aid to District, Village, and Municipal Councils from the state’s Consolidated Fund.
- Elections to Councils: Elections for District Councils, Regional Councils, Village Councils, and Municipal Councils will be overseen by the State Election Commission, which is appointed by the Governor for these four states.
-
Current Status of the Bill:
- The Constitution (125th Amendment) Bill 2019, was introduced in the Rajya Sabha and was subsequently referred to the Departmental-Related Standing Committee on Home Affairs.
- The committee raised several concerns about the Bill in its 2020 report, and it has remained pending since then.
What is the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution?
- Scope: Provides for governance of tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram to protect tribal rights.
- Constitutional Basis: Article 244 (2) (provisions of the Sixth Schedule shall apply to the administration of the tribal areas in the States of Assam Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram) and Article 275 (1) (it guarantees grants-in-aid from the Consolidated Fund of India).
- Autonomy: Provides for governance through Autonomous District Councils (ADCs), which can legislate on land, forest, cultivation, inheritance, customs, and taxes.
- Governance: ADCs function like miniature states with legislative, executive, and judicial powers.
What are Autonomous District Councils (ADCs)?
- About: ADCs are constitutional devices created under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution (Article 244) in Northeast India. Their purpose is to protect cultural identities and preservation of natural resources of the tribal people.
- Governor’s Authority: Can organise, reorganise, and modify autonomous districts, including their areas and boundaries.
- Tribal Distribution: If multiple tribes are present, the governor can create autonomous regions within the district.
- Composition:
- District Council: Each district has a council of 30 members (4 nominated by the governor, 26 elected), serving a five-year term.
- Regional Council: Each autonomous region has its own council.
- Administration: District and regional councils manage their jurisdictions and may establish village councils or courts for tribal disputes. Appeals are heard as specified by the Governor.
- As of now, 10 autonomous councils exist - three each in Assam, Meghalaya, and Mizoram, and one in Tripura.
Read more: Indepth- 6th Schedule & ILP
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Under which Schedule of the Constitution of India can the transfer of tribal land to private parties for mining be declared null and void? (2019)
(a) Third Schedule
(b) Fifth Schedule
(c) Ninth Schedule
(d) Twelfth Schedule
Ans: (b)
Gulf Stream and Climate Sensitivity
Why in News?
A recent study, published in Nature, has revealed that the Gulf Stream was significantly stronger during the last ice age (about 20,000 years ago) due to more powerful winds across the subtropical North Atlantic.
- This finding suggests that the Gulf Stream's strength is sensitive to changes in wind patterns, which could impact future climate if these winds weaken due to climate change.
Note:
- The Gulf Stream is a powerful ocean current that brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico up the eastern coast of North America.
- It then crosses the Atlantic Ocean, influencing the climate of Western Europe by making it warmer than it would otherwise be.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Research Methodology: Analysis of fossil foraminifera from sediment cores off North Carolina and Florida was used to gauge the prehistoric Gulf Stream's strength.
- Findings showed the Gulf Stream was twice as deep and fast during the last ice age.
- Impact on Climate: Despite the strength of the Gulf Stream, the global climate was much colder than at present.
- A weakened Gulf Stream in the future could limit tropical heat reaching Europe, potentially cooling the continent and raising sea levels in North America.
- Role of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC): The Gulf Stream is part of the AMOC, which involves both deep water formation and wind patterns.
- Climate change-induced disruptions, such as melting glacial water from Greenland, could weaken the AMOC.
- A weakened AMOC could significantly cool Europe by 10 to 15 degrees Celsius, disrupt agriculture, and alter weather patterns.
- AMOC Loops and Climate Impact:
- The AMOC should be viewed as interconnected loops (subtropical and subpolar) rather than a simple conveyor belt.
- Different parts of the AMOC may respond uniquely to climate change, affecting climate impacts.
- The AMOC should be viewed as interconnected loops (subtropical and subpolar) rather than a simple conveyor belt.
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
- About: AMOC is a major system of ocean currents that forms part of the global ocean conveyor belt or ThermoHaline Circulation (THC), distributing heat and nutrients across the world's oceans.
- Working of AMOC: AMOC transports warm surface waters from the tropics to the Northern Hemisphere, where the water cools and sinks. It then returns as a bottom current through the South Atlantic, eventually being spread to all ocean basins by the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), the only current circulating the globe.
- Implications of Decline of AMOC: A weakened AMOC, including the Gulf Stream, could cause Europe to become very cold, reduce rainfall, and potentially influence El Nino and shift monsoons in South America and Africa.
- Causes of Decline: Predictions suggest global warming may weaken major ocean systems. Melting Greenland ice and the "Last Ice Area" contribute freshwater that lowers water salinity and density, impeding the AMOC flow. Increased precipitation and river runoff in the Indian Ocean may also impact AMOC.
- Importance: AMOC is crucial for redistributing heat and regulating global weather patterns.
Read more: Ocean currents
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. What could be the main reason/reasons for the formation of African and Eurasian desert belt? (2011)
- It is located in the sub-tropical high pressure cells.
- It is under the influence of warm ocean currents.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct in this context?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q. Consider the following factors: (2012)
- Rotation of the Earth
- Air pressure and wind
- Density of ocean water
- Revolution of Earth
Which of the above factors influence the ocean currents?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
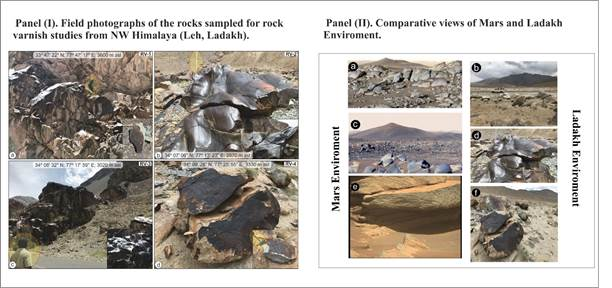
Ladakh's Rock Varnish
Why in News?
Recently, Magnetofossils, fossilised magnetic particles from magnetotactic bacteria, have been discovered in rock varnish layers in Ladakh.
- Rock varnish is a dark brown to black coating that covers stable, subaerially exposed rock surfaces in arid and semiarid regions.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Findings:
- The analysis of the rock varnish samples from Ladakh revealed higher concentrations of oxidized manganese (Mn4+) and carboxylic acid functionality, indicating organic signatures.
- These findings suggest that the rock varnish in Ladakh, a potential Martian analogue site, contains enriched concentrations of magnetic minerals likely derived from biotic sources.
- Magnetic minerals are those that preserve a record of the Earth's magnetic field from when they formed and can be found in rocks, sediments, and soils.
- Significance:
- The study offers valuable insights for astrobiology by demonstrating how life can thrive in extreme environments, such as Ladakh, the "cold desert of India."
- The findings are crucial for planning future space missions by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and other space agencies, including Mars exploration, where identifying habitable environments is a primary goal.
- Identifying biotic signatures in rock varnish helps scientists target potential biosignatures on Mars and other planets, supporting the search for extraterrestrial life
- A biosignature is any characteristic, element, molecule, substance, or feature that can be used as evidence for past or present life.
- Identifying biotic signatures in rock varnish helps scientists target potential biosignatures on Mars and other planets, supporting the search for extraterrestrial life
Magentofossils
- About:
- Magnetofossils refer to fossilised remains of magnetotactic bacteria that contain magnetic minerals.
- Magnetotactic bacteria leave fossilised magnetic particles in geological records.
- Magnetofossils refer to fossilised remains of magnetotactic bacteria that contain magnetic minerals.
- Magnetotactic Bacteria:
- Magnetotactic bacteria are mostly prokaryotic organisms that arrange themselves along the earth’s magnetic field. It was discovered by Salvatore Bellini in 1963.
- These organisms follow the magnetic field to reach places that had optimal oxygen concentration. This process is facilitated by the presence of iron-rich crystals within their cells.
- Magnetotactic bacteria create tiny crystals of magnetite or greigite within their cells to navigate changing oxygen levels and sediment saturation in water bodies.
- Crystals within magnetotactic bacteria are arranged in a chain configuration through magnetotaxis.
- Rare giant magneto fossils are less common than conventional magnetic fossils, these are likely produced by eukaryotes rather than bacteria.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following: (2021)
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Virus
Which of the above can be cultured in an artificial/synthetic medium?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Earth’s magnetic field has reversed every few hundred thousand years.
- When the Earth was created more than 4000 million years ago, there was 54% oxygen and no carbon dioxide.
- When living organisms originated, they modified the early atmosphere of the Earth.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Subvention Scheme
Recently, the Supreme Court has provided relief to homebuyers in the National Capital Region (NCR) under the Subvention scheme.
- The Supreme Court has instructed banks not to take coercive action against individuals who have not received possession of their flats.
- Subvention Scheme:
- In real estate, subvention schemes involve a tripartite agreement between the buyer, banker, and developer.
- The buyer pays 5-20% upfront, while the bank loans the rest to the developer.
- The developer pays the loan interest until the buyer takes possession, after which the buyer's EMI starts.
- This scheme boosts sales for developers and delays EMI payments for buyers.
- However, in the present case many builders have defaulted on these payments.
- Subsidy:
- Subsidy is direct financial assistance provided by the government or another entity to reduce the cost of a product or service for the consumer.
- This leads to a decrease in the price of the product or service for the consumer. For example, government subsidies on food grains, fertilizers, or fuel.
Read More: Interest Subvention Scheme
New Pension Scheme ‘Vatsalya’
The Union Budget 2024-25, introduced the National Pension Scheme (NPS) Vatsalya, a groundbreaking pension scheme aimed at minors.
- This scheme allows parents or guardians to initiate a NPS account for their children, thereby laying the groundwork for responsible financial management from an early age.
- It is a contributory pension scheme, and will have contributions by parents and guardians.
- Upon reaching adulthood (18 years), the NPS Vatsalya accounts seamlessly convert into regular NPS accounts, promoting consistent saving habits.
- The NPS is a voluntary pension system for all citizens, including both residents and Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) between the ages of 18 and 70 years.
- It is a market-linked contribution scheme that allows Indian citizens to systematically save for their retirement and also derive tax benefits out of it.
Read more: National Pension System, Union Budget 2024-25
Typhoon Gaemi
Recently, Typhoon Gaemi has brought torrential rains that have caused widespread destruction and fatalities across Eastern China, Taiwan and the Philippines.
- Typhoon Gaemi made landfall in Taiwan the strongest in eight years, causing severe flooding in the island's second-largest city, Taichung.
- In the Philippines, it exacerbated seasonal rains, triggering floods and landslides and caused severe flooding in Zhejiang province and led to the highest warning for rainstorms in Wenzhou city in China.
- Typhoons are a kind of storm. The storms, depending on where they occur, may be called hurricanes, typhoons or cyclones.
- The scientific name for all these kinds of storms is tropical cyclones.
- Tropical cyclones are intense circular storms that originate over the warm tropical oceans with speed more than 119 km/hr and heavy rains.
- Tropical cyclones rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere.
| Type | Location |
| Typhoon | China Sea and Pacific Ocean |
| Hurricane | West Indian islands, Caribbean Sea, Atlantic Ocean |
| Tornado | Guinea lands of West Africa, southern USA |
| Willy-willies | North-western Australia |
| Tropical Cyclone | Indian Ocean Region |
Read more: Cyclone
The Indian Newspaper Society (INS) Towers
Recently, the Prime Minister of India inaugurated the Indian Newspaper Society (INS) Towers on his visit to the Indian Newspaper Society (INS) Secretariat in Mumbai. It would serve as the nerve center for the newspaper industry.
- The Society's origins date back to 1927, with the establishment of a group initially known as The India, Burma & Ceylon Newspapers’ London Committee.
- It was renamed as Indian & Eastern Newspaper Society (IENS) in 1935, and headquartered in London.
- It served as the official representative body for newspapers, magazines, reviews, and journals published across India, Burma, Ceylon, and other Asian countries.
Read more: Press Council of India


.png)