Geography
International Migration Outlook 2023
For Prelims: International Migration Outlook 2023, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Latin America, Climate-Induced Displacement
For Mains: Similarity and interrelationship of migration to OECD countries with internal or intra-state displacement and migration in India, Demography.
Why in News?
Recently, International Migration Outlook 2023, a report on international migration patterns was released by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) to analyze the migration trends worldwide.
What are the Highlights of the Report?
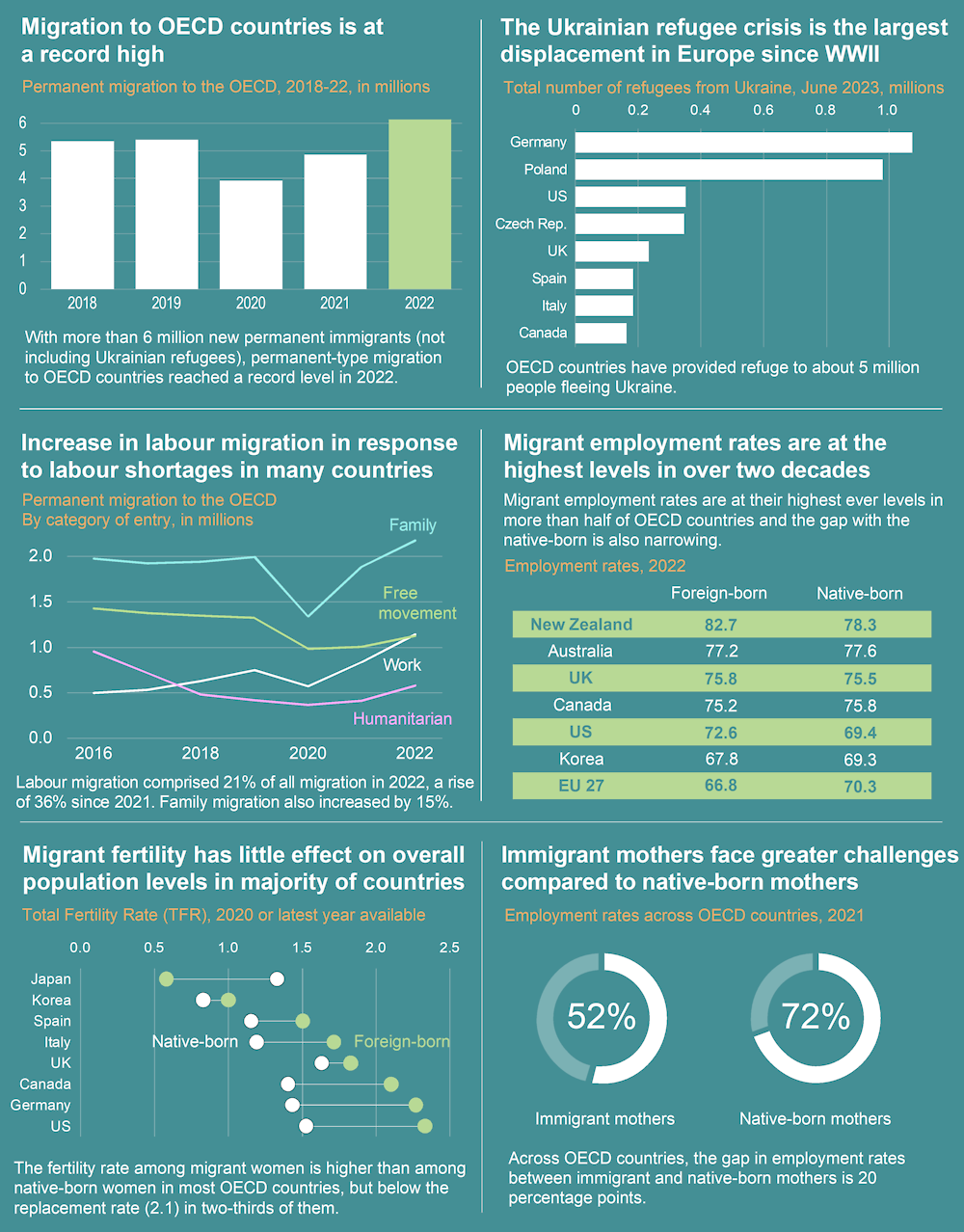
- India Leads in Migration to OECD Countries:
- In 2021 and 2022, India became the primary source of migration to OECD countries, surpassing China. India consistently topped the list with 0.41 million new migrants in both years, while China had 0.23 million new migrants, followed by Romania with approximately 200,000 new migrants.
- Climate-Induced Displacement and Policy Responses:
- The report sheds light on the increasing focus on policy responses to climate-induced displacement in recent years. Few OECD countries have explicit policies to address this issue.
- Notably, Colombia began discussing a pioneering bill in April 2023, aiming to recognize and support climate-displaced individuals, with a broad definition and provisions for housing, healthcare, education, and a national register.
- Record Refugee Inflows and Worker Migration:
- The OECD region experienced record refugee inflows due to the Russia-Ukraine war, with over 10 million people becoming internally displaced or refugees. Worker migration saw significant increases from India, Uzbekistan, and Turkey, making them prominent source countries following Ukraine.
- Recent Trends in International Migration:
- All top four destination countries (The United States, Germany, the United Kingdom and Spain) registered large year-on-year increases, between 21% and 35%. The increase was smaller in Canada (8%) the fifth destination country.
- The United States alone accounted for 1.05 million new permanent-type migrants, and the other four countries for between 440 000 and 650 000 each.
- Permanent-Type Migration by Main Categories:
- In 2022, family migration remained the primary category of entry for new permanent-type migrants, representing 40% of all permanent-type migration, a relatively stable share over time.
- The share of labour migration has increased over time. While in 2022, labour migration represented 21% of permanent-type migration, it accounted for only 16% in 2019.
- Conversely, the share of free movement migration (within the EU-EFTA and between Australia and New Zealand) has decreased since 2020. It accounted for 21% of permanent-type migration in 2022, compared with 28% in 2019.
What is OECD?
- About:
- The OECD is an intergovernmental economic organisation, founded to stimulate economic progress and world trade.
- Most OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries.
- Foundation:
- It was founded in 1961 with its Headquarters at Paris, France and total membership is 38 countries.
- The most recent countries to join the OECD were Colombia, in April 2020, and Costa Rica, in May 2021.
- India is not a member, but a key economic partner.
- Reports and Indices by OECD:
- Government at a Glance
- OECD Better Life Index.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q. “Refugees should not be turned back to the country where they would face persecution or human right violation”. Examine the statement with reference to the ethical dimension being violated by the nation claiming to be democratic with open society. (2021)
Q. Rehabilitation of human settlements is one of the important environmental impacts which always attracts controversy while planning major projects. Discuss the measures suggested for mitigation of this impact while proposing major developmental projects. (2016)
Q. Discuss the changes in the trends of labour migration within and outside India in the last four decades. (2015)
Governance
Medical College Seats and New Regulations in India
For Prelims: National Medical Commission (NMC), National Medical Commission Act, 2019,
For Mains: Medical College Seats and New Regulations in India, Government Policies & Interventions, Education
Why in News?
Recently, the National Medical Commission (NMC) has issued guidelines putting a hold on new medical colleges and expansion of existing colleges in states with more than 100 medical education seats per million population.
- Earlier, NMC also issued new guidelines on professional conduct for doctors, which mandate them to prescribe only generic drugs instead of specific brands.
What is the Scenario of Medical Colleges in States?
- States with Excess Medical College Seats:
- At least 13 states and Union Territories in India have more than 100 seats per million population, rendering them ineligible for capacity expansion.
- Tamil Nadu has the highest number of medical college seats (11,225), followed by Karnataka (11,020), and Maharashtra (10,295).
- At least 13 states and Union Territories in India have more than 100 seats per million population, rendering them ineligible for capacity expansion.
- States with Deficient Medical College Seats:
- There is an acute shortage of medical college seats in relation to population in Meghalaya, Bihar, and Jharkhand, where the deficit is more than 75%.
- Meghalaya, with a population of approximately 33.5 lakh, has only 50 medical college seats.
- Bihar and Jharkhand, with populations of 12.7 crore and 3.9 crore, have 2,565 and 980 medical college seats, respectively.
- Uttar Pradesh, the most populous state, has 9,253 seats, with a 61% deficit.
- There is an acute shortage of medical college seats in relation to population in Meghalaya, Bihar, and Jharkhand, where the deficit is more than 75%.
What are the NMC Guidelines?
- In August 2023, the NMC issued regulations that set population-to-seats ratios for medical colleges.
- States with more than 100 medical education seats per million population are restricted from expanding their medical education capacity.
- The NMC argues that these guidelines are intended to bring down regional disparities and ensure effective quality medical education.
- The NMC's regulations will apply to new medical colleges and seat expansions starting from the 2024-25 academic session.
- The regulations do not require states with excess seats to shut down colleges or reduce existing seats.
What is the National Medical Commission (NMC) ?
- The NMC has been constituted by an act of Parliament known as National Medical Commission Act, 2019.
- The NMC acts as India's top regulator of medical education and practice.
- Committed to upholding the highest standards in healthcare education, NMC ensures the delivery of quality medical education and training across the nation.
Biodiversity & Environment
Interconnected Disaster Risks Report 2023
For Prelims: UN Interconnected Disaster Risks Report 2023, Climate change, Space debris, Wet-bulb temperature, Floods, Renewable energy sources, Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030, The Climate Risk and Early Warning Systems, Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure Society, National Disaster Management Plan
For Mains: Major Findings of the Interconnected Disaster Risks Report 2023, Major Drivers of Increasing Disaster Risks.
Why in News?
Recently, the release of the Interconnected Disaster Risks Report 2023 has thrust the world's interdependence into the spotlight, warning of impending global tipping points and underlining the critical need for immediate action to prevent potential catastrophic consequences.
What are the Major Findings of the Interconnected Disaster Risks Report 2023?
- About: The UN Interconnected Disaster Risks Report is an annual science-based report released by the United Nations University- Institute for Environment and Human Security (UNU-EHS), (first published in 2021).
- The report analyses several concrete examples of disasters each year and explains how they are inter- connected with each other and with human actions.
- The report illustrates how seemingly stable systems can gradually deteriorate until a critical threshold is crossed, resulting in catastrophic consequences.
- It introduces the concept of "risk tipping points," moments when socio ecological systems can no longer buffer risks and face a heightened risk of catastrophic impacts.
Note
The United Nations University (UNU) is the academic arm of the United Nations and acts as a global think tank. The mission of the Institute for Environment and Human Security (UNU-EHS) is to carry out cutting edge research on risks and adaptation related to environmental hazards and global change. The institute is based in Bonn, Germany.
- Tipping Points: The report highlights that the world is approaching six environmental tipping points -
- Groundwater Depletion: Groundwater stored in aquifers is vital for over 2 billion people, with 70% used for agriculture.
- However, 21 of the world's major aquifers are depleting faster than they can recharge.
- Aquifer water often took thousands of years to accumulate and is essentially non-renewable.
- Over-extraction has occurred in some areas, like Saudi Arabia, depleting over 80% of its aquifer. This forces reliance on imported crops, posing challenges for food security.
- Certain areas within the Indo-Gangetic basin in India have already crossed the critical threshold of groundwater depletion, and the entire northwestern region is expected to face severely limited groundwater availability by 2025.
- Accelerating Species Extinctions: Human activities like land use changes, overexploitation, and climate change have accelerated species extinction.
- Current extinction rates due to human influence are hundreds of times higher than normal.
- Extinction can trigger a chain reaction, causing the collapse of ecosystems.
- Mountain Glacier Melting: Glaciers are vital water sources, but they are melting at double the rate due to global warming.
- Between 2000 and 2019, glaciers lost 267 gigatons of ice per year. We are projected to lose around 50% of glaciers by 2100, even with limited warming.
- 90,000+ glaciers of the Himalayas, Karakoram and Hindu Kush mountains are at risk, and so are the nearly 870 million people that rely on them.
- Space Debris: Satellites are crucial for weather monitoring, communication, and safety, but the growing number of satellites in space is causing a space debris problem.
- Only 25% of objects in orbit are active satellites; the rest are non-functional debris.
- There are about 130 million smaller, untrackable debris pieces.
- These objects move at high speeds and pose a collision risk to operational satellites, creating a hazardous orbital environment.
- Only 25% of objects in orbit are active satellites; the rest are non-functional debris.
- Unbearable Heat: Climate change is causing more deadly heat waves. High temperatures and humidity make it hard for the body to cool down.
- When the "wet-bulb temperature" exceeds 35°C for over six hours, it can lead to organ failure and brain damage. This has already occurred in places like Jacobabad, Pakistan.
- Also, during a 2023 heatwave in India, wet-bulb temperatures went above 34°C.
- It is expected to affect over 70% of the global population by 2100.
- When the "wet-bulb temperature" exceeds 35°C for over six hours, it can lead to organ failure and brain damage. This has already occurred in places like Jacobabad, Pakistan.
- Uninsurable Future: Frequent severe weather is causing a sevenfold increase in damages since the 1970s, with USD 313 billion in losses in 2022.
- Insurance costs are rising due to climate change, making coverage unaffordable for many.
- Some insurers are leaving high-risk areas, leading to regions being labeled "uninsurable."
- For example, in Australia, about 520,940 homes may become uninsurable by 2030 due to increased flood risk.
- Groundwater Depletion: Groundwater stored in aquifers is vital for over 2 billion people, with 70% used for agriculture.
- Interconnectedness: Climate change, driven by increased greenhouse gas emissions, acts as a common driver of tipping points. This includes glacier melting, extreme weather events, and shifts in the insurance risk landscape.
- These interconnected environmental issues can trigger feedback loops, such as rising sea levels from glacier melt, intensifying coastal flooding and elevating the demand for disaster insurance.
- Ultimately, these tipping points have significant socioeconomic consequences.
What are the Major Drivers of Increasing Disaster Risks?
- Urbanisation: Rapid Urbanization often occurs without adequate planning and infrastructure development.
- As cities grow, more people and property become exposed to hazards like floods and earthquakes, increasing disaster vulnerability.
- Environmental Degradation: Deforestation, soil erosion, and pollution weaken natural ecosystems and reduce their ability to act as buffers against disasters. Environmental degradation amplifies the impacts of hazards.
- Inadequate and Inefficient Infrastructure: Insufficiently built or maintained infrastructure, such as bridges, buildings, and roads, can crumble during disasters, leading to significant economic and social losses.
- Poor Land Use Planning: Inadequate land use planning can result in communities settling in high-risk areas like floodplains or wildfire-prone regions. This contributes to increased exposure to disasters.
- Water Management Issues: Mismanagement of water resources can lead to droughts, water scarcity, and flooding.
- These issues can have far-reaching consequences for food security, economies, and communities.
- Global Interconnectedness: As the world becomes more interconnected, disruptions in one area can have cascading effects globally.
- This interconnectedness can propagate the economic and social impact of disasters.
What does the Report Recommend as Solutions to Mitigate Disaster Risk?
- UN Interconnected Disaster Risks Report 2023 uses the four-category framework to classify and prioritize solutions for addressing disaster risks.
- Avoid-Delay: These are actions that aim to prevent disasters by slowing them down using current methods.
- For example, implementing strict building codes and land-use regulations to prevent major damage from disasters.
- Avoid-Transform: These actions focus on preventing disasters by making significant changes in how things are done.
- For example, transitioning from fossil fuel-based energy production to renewable energy sources (like solar and wind) to avoid the risks associated with climate change
- Adapt-Delay: These actions prepare us to handle disasters by buying more time to respond.
- For example, developing advanced early warning systems for tsunamis to buy time for people to evacuate and prepare for the disaster.
- Adapt-Transform: These actions involve making big changes to how we do things to adapt to disasters.
- For example, implementing coastal zoning policies and restoring natural barrier ecosystems (like mangroves) to adapt to rising sea levels and transform coastal protection strategies.
- Avoid-Delay: These are actions that aim to prevent disasters by slowing them down using current methods.
What are the Initiatives for Disaster Risk Reduction?
- Global:
- Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030
- The Climate Risk and Early Warning Systems (CREWS)
- International Day for Disaster Risk Reduction - 13th October
- Green Climate Fund’s Sectoral Guide on Climate Information & Early Warning Systems
- India’s Initiatives:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q. Discuss the recent measures initiated in disaster management by the Government of India departing from the earlier reactive approach. (2020)
Q. Vulnerability is an essential element for defining disaster impacts and its threat to people. How and in what ways can vulnerability to disasters be characterized? Discuss different types of vulnerability with reference to disasters. (2019)
Q. Describe various measures taken in India for Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) before and after signing ‘Sendai Framework for DRR (2015-30)’. How is this framework different from ‘Hyogo Framework for Action, 2005’? (2018)
Indian Economy
India's Food Export Rejections in the United States
For Prelims: India’s Major Food Exports to US, Salmonella, World Trade Organization, Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Agreement, Food Safety and Standards Authority of India , Codex Alimentarius
For Mains: Major Provisions of SPS Agreement, Measures to Improve Food Safety and Quality Standards in India, Agricultural Marketing.
Why in News?
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently disclosed data on food imports over the past four years. Among the nations engaged in food exports to the US, India, Mexico, and China have experienced the highest incidence of refusals.
- The data highlights the hurdles faced by Indian food exporters in the American market. High refusal rates continue to be a pressing issue.
What are the Key Aspects Related to India's Food Export Rejections in the United States?
- Refusal Statistics: India, Mexico, and China:
- Between October 2019 and September 2023, India, Mexico, and China experienced significant refusals of food export shipments to America.
- India's refusal rate, which measures the percentage of shipments refused out of all food export shipments, was 0.15%.
- In comparison, China's refusal rate was 0.022%, and Mexico's was 0.025%.
- India's rate is substantially higher, signaling a higher incidence of refusal relative to the total exports.
- Majors Factors Behind Refusals:
- The products consisted in whole or in part of a filthy, putrid, or decomposed substance or be otherwise unfit for food.
- The products contained Salmonella, a bacteria that causes severe stomach infections.
- The products used an unapproved new drug, an unsafe food additive, or a prohibited substance.
- The products were misbranded in terms of nutritional labels, ingredients information, or health claims.
- Long-Term Trends in India's Refusals:
- In the last decade, India's food export refusals have seen a downward trend in absolute terms. From a peak of 1,591 refusals in 2015, it decreased to 1,033 refusals in 2023.
- Despite these refusals, India's food exports to the US stood at USD 1.45 billion in FY23, representing a 16% increase from the previous fiscal year. Key exports included basmati rice, natural honey, guar gum, and cereal preparations etc.
- In the last decade, India's food export refusals have seen a downward trend in absolute terms. From a peak of 1,591 refusals in 2015, it decreased to 1,033 refusals in 2023.
What is the International Measure Backing the Food Import Refusal By the United States?
- About:
- The World Trade Organization (WTO)'s Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Agreement ensures that traded products between WTO members do not spread pests and diseases, and that food products do not contain harmful substances or pathogens.
- The "SPS Agreement" entered into force with the establishment of the WTO on 1 January 1995.
- WTO has 164 member nations (including India and the United States).
- Major Provisions:
- Members have the right to implement sanitary and phytosanitary measures for the protection of human, animal, or plant life and health, provided such measures align with this Agreement.
- Measures should be based on scientific principles and supported by scientific evidence, except as provided in Article 5(7) of the Agreement.
- Measures should also not discriminate unfairly between Members and should not serve as a disguised restriction on international trade.
- Members must accept equivalent sanitary and phytosanitary measures from other Members, even if they differ.
- The exporting Member must prove that its measures meet the importing Member's required level of protection.
- Access for inspection and testing should be provided upon request.
What are the Impacts of Frequent Food Export Rejections on India?
- Increased Regulatory Compliance Costs: Continuous refusals result in escalated compliance costs for Indian exporters. To meet the stringent standards of the US market, investments to fit with compliance measures become essential, adding financial strain.
- Trade Loss and Market Reputation: Rejected shipments impact revenue and diminish trust among foreign buyers, potentially reducing future trade opportunities.
- Sectors contributing to major exports could be disproportionately affected, impacting the livelihoods of farmers and businesses reliant on these exports.
- Diplomatic and Global Image Consequences: Repeated refusals can strain India-US trade relations. Constant rejection may lead to discussions on trade barriers, potentially creating diplomatic tensions between the two nations.
- Continuous refusals might negatively impact India's global image as a reliable food exporter, affecting not only the US market but also influencing perceptions in other international markets.
How India can Improve its Food Safety and Quality Standards?
- Strict Inspection and Quality Control: Strengthening the role and capacity of the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), the apex food regulator in the country, to monitor, inspect, and certify food products for domestic and export markets.
- Enhanced Testing Protocols: Developing and enforcing comprehensive testing protocols for food products to identify contaminants, pathogens, and adulterants.
- Investing in advanced laboratory equipment for more accurate and rapid testing.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Utilizing blockchain technology to create transparent and traceable supply chains, enabling rapid identification of the source of contamination or quality issues.
- Global Standards Adherence: Adopting international best practices and standards for food safety and quality management, such as Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), Good Hygienic Practices (GHP), and Codex Alimentarius.
Biodiversity & Environment
Impact of Disasters on Agriculture and Food Security: FAO
For Prelims: Impact of Disasters on Agriculture and Food Security, Food and Agriculture Organization, Extreme Disaster, Climate Change, Food Security, Rain-Fed agriculture.
For Mains: Impact of Disasters on Agriculture and Food Security, Poverty and developmental issues, Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
Why in News?
Recently, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has released a report titled 'The Impact of Disaster on Agriculture and Food Security' stating that the frequency of Extreme Disaster events has risen significantly over the past 50 years.
- The report estimated losses caused by disasters on agricultural production over the past three decades and delves into the diverse threats and impacts affecting the crops, livestock, forestry, and fisheries and aquaculture subsectors.
- It analyzed the complex interplay of underlying risks, such as Climate Change, Pandemics, Epidemics and Armed conflicts, and how they drive disaster risk in agriculture and Agrifood systems at large.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Magnitude of Agricultural Losses:
- Over the last 30 years, an estimated USD 3.8 trillion worth of crops and livestock production has been lost due to disaster events.
- This translates to an average annual loss of USD 123 billion, which is approximately 5% of the global agricultural Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Agriculture is one of the most highly exposed and vulnerable sectors in the context of disaster risk, given its profound dependence on natural resources and climate conditions.
- Recurrent disasters have the potential to erode gains in food security and undermine the sustainability of agrifood systems.
- Impact on Different Countries:
- Disasters have the highest relative impact on lower and lower middle-income countries, where they can cause losses of up to 15 % of their total agricultural GDP.
- Small Island Developing States (SIDS) also experience significant losses, amounting to nearly 7% of their agricultural GDP.
- Losses by Product Groups:
- There are increasing trends in losses related to major agricultural products.
- Cereals are the most affected, followed by fruits and vegetables and sugar crops, with average losses of millions of tonnes each year.
- Meats, dairy products, and eggs also show substantial losses.
- Regional Differences:
- Asia experiences the largest share of total economic losses, followed by Africa, Europe, and the Americas.
- However, in Asia, these losses account for a smaller percentage of agricultural added value compared to Africa.
- Increasing Frequency of Disasters:
- Disaster events have been on the rise, increasing from 100 per year in the 1970s to around 400 events per year worldwide in the past two decades.
- These events are becoming more frequent, intense, and complex, with expected worsening impacts due to climate-induced disasters.
- Impact on Vulnerable Groups:
- Small-scale farmers, particularly those practicing Rain-Fed agriculture, are the most vulnerable to disaster impacts.
- Supporting the adoption of farm-level disaster risk reduction practices can help reduce losses and enhance resilience.
- Investment in farm-level disaster risk reduction good practices can perform on average 2.2 times better than previously applied practices.
What are the Recommendations?
- Proactive and timely interventions, such as anticipatory actions in response to forecasted hazards, can significantly reduce disaster risks in agriculture.
- For every USD 1 invested in anticipatory action, rural families can gain up to USD 7 in benefits and avoided agricultural losses.
- The report outlines three key priorities for addressing the impact of disasters on agriculture:
- Improving data and information on disaster impacts, developing multi-sectoral and multi-hazard disaster risk reduction approaches, and enhancing investments in resilience to reduce disaster risk in agriculture and improve livelihoods.
What is the Food and Agriculture Organization?
- About:
- FAO is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
- World Food Day is celebrated every year around the world on 16th October. The day is celebrated to mark the anniversary of the founding of the FAO in 1945.
- It is one of the UN food aid organisations based in Rome (Italy). Its sister bodies are the World Food Programme and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD).
- FAO is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
- Initiatives Taken:
- Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS).
- Monitors the Desert Locust situation throughout the world.
- The Codex Alimentarius Commission or CAC is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture was adopted by the Thirty-First Session of the Conference of the FAO in 2001.
- Flagship Publications:
- The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA).
- The State of the World's Forests (SOFO).
- The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI).
- The State of Food and Agriculture (SOFA).
- The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets (SOCO).
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The FAO accords the status of ‘Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS)’ to traditional agricultural systems. What is the overall goal of this initiative? (2016)
- To provide modern technology, training in modern farming methods and financial support to local communities of identified GIAHS so as to greatly enhance their agricultural productivity.
- To identify and safeguard eco-friendly traditional farm practices and their associated landscapes, agricultural biodiversity and knowledge systems of the local communities.
- To provide Geographical Indication status to all the varieties of agricultural produce in such identified GIAHS.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Important Facts For Prelims
DNA and Face Matching Systems At Police Stations
Why in News?
Over a year after Parliament passed the Criminal Procedure Identification Act (CrPI), 2022; the Centre is preparing to introduce 'DNA and Face Matching' systems in 1,300 police stations nationwide, despite the Act's provisions not yet being fully implemented.
What is the Context of ‘DNA and Face Matching Systems’ Under CrPI Act, 2022 ?
- Introduction to the Act and Rules:
- In 2022, the Indian Parliament passed CrPI Act that grants police and central investigating agencies the authority to collect, store, and analyze physical and biological samples, which even include retina and iris scans, of arrested individuals.
- This legislative move aimed to enhance law enforcement capabilities and ushered in a new era in criminal identification and data management.
- Rollout of the Act and Rules:
- The responsibility for implementing the Act and establishing the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the measurement collection process was entrusted to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), a central organization.
- The NCRB played a pivotal role in guiding police officials on the proper protocol for recording these measurements.
- Expanding Measures and Committees for Implementation:
- The Act and rules did not directly mention DNA sample collection and face matching procedures, but the NCRB conveyed plans to implement these measures in discussions with State police officials.
- Additionally, the Ministry of Home Affairs formed a Domain Committee comprising State police and central law enforcement representatives for recording DNA data.
- Challenges and Controversies Surrounding the Act:
- Critics decried the legislation as "unconstitutional" and an intrusion on privacy.
- In addition to the controversy, practical challenges emerged, including the need for training and resources in various states, with concerns over funding and operating costs.
- Moreover, the NCRB emphasized the importance of technologically, legally, and forensically sound tools and systems, along with robust safeguards to prevent misuse of the collected data. This context underscores the complexity and significance of the Act and its associated rules.
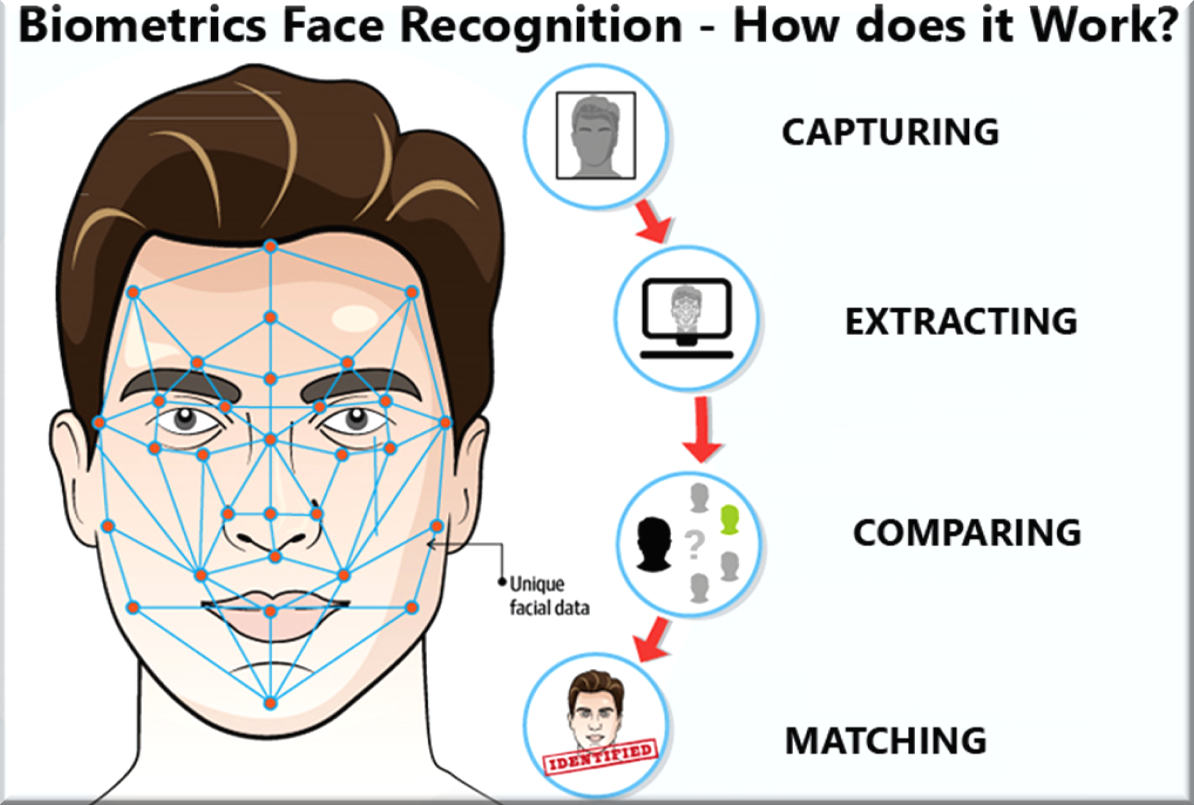
What is the ‘DNA and Face Matching Systems’ Technology?
- Face Matching System:
- Face Matching System is an algorithm-based technology which creates a digital map of the face by identifying and mapping an individual’s facial features, which it then matches against the database to which it has access.
- In the Automated Facial Recognition System (AFRS), the large database (containing photos and videos of peoples’ faces) is used to match and identify the person.
- Image of an unidentified person, taken from CCTV footage, is compared to the existing database using Artificial Intelligence technology, for pattern-finding and matching.
- DNA Matching Systems:
- DNA matching systems, also known as DNA profiling or DNA fingerprinting, are techniques used to compare and identify individuals based on their unique genetic characteristics.
- These systems analyze specific regions of an individual's DNA, which are highly variable among people, to create a unique genetic profile for each individual.
- DNA matching is commonly used in criminal investigations to link suspects to crime scenes or victims. DNA evidence found at a crime scene, such as blood, hair, or bodily fluids, can be compared to the DNA profiles of potential suspects.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The identity platform ‘Aadhaar’ provides open “Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)”. What does it imply? (2018)
- It can be integrated into any electronic device.
- Online authentication using iris is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q. In addition to fingerprint scanning, which of the following can be used in the biometric identification of a person? (2014)
- Iris scanning
- Retinal scanning
- Voice recognition
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Important Facts For Prelims
Dengue
Why in news?
Recently, Dengue cases have surged significantly in some states like Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Tamil Nadu.
What is Dengue?
- About:
- Dengue is a self-limiting febrile illness with symptoms ranging from asymptomatic to severe.
- Dengue is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus (Genus Flavivirus), transmitted by several species of female mosquito within the genus Aedes, principally Aedes aegypti.
- This mosquito also transmits chikungunya and Zika infection.
- Serotypes of Dengue:
- There are 4 distinct, but closely related, serotypes (separate groups within a species of microorganisms that all share a similar characteristic) of the virus that cause dengue (DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3 and DEN-4).
- Symptoms:
- Sudden high fever, severe headaches, pain behind the eyes, severe bone, joint, and muscle pain, etc.
- Dengue Vaccine:
- The dengue vaccine CYD-TDV or Dengvaxia was approved by the US Food & Drug Administration in 2019, the first dengue vaccine to get the regulatory nod in the US.
- Dengvaxia is basically a live, attenuated dengue virus which has to be administered in people of ages 9 to 16 who have laboratory-confirmed previous dengue infection and who live in endemic areas.
- Researchers at India’s National Centre for Biological Sciences, in collaboration with nine other institutions in India, Africa, and the US, have developed India’s first and only DNA vaccine candidate for dengue fever.
- In preliminary trials on mice, the candidate generated a robust immune response and improved survival rates after exposure to the disease.
- The dengue vaccine CYD-TDV or Dengvaxia was approved by the US Food & Drug Administration in 2019, the first dengue vaccine to get the regulatory nod in the US.
- Controlling Dengue Using Bacteria:
- Researchers from the World Mosquito Program have used mosquitoes infected with Wolbachia bacteria to successfully control dengue, leading to a 77% reduction in incidence in Indonesia.
What is DNA Vaccine?
- A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a small piece of DNA that codes for a specific antigen (a molecule that triggers an immune response) from a pathogen, such as a virus or bacterium, to stimulate an immune response.
- The DNA is injected directly into the body's cells, where it instructs the cells to produce the antigen.
- The immune system then recognizes the antigen as foreign and mounts an immune response against it, which helps to develop immunity to the pathogen.
- DNA vaccines are third-generation vaccines.
- The ZyCoV-D is the world's first and India's indigenously developed DNA based vaccine for Covid-19.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q.1 Consider the following statements: (2017)
- In tropical regions, Zika virus disease is transmitted by the same mosquito that transmits dengue.
- Sexual transmission of Zika virus disease is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q.2 ‘Wolbachia method’ is sometimes talked about with reference to which one of the following? (2023)
(a) Controlling the viral diseases spread by mosquitoes
(b) Converting crop residues into packing material
(c) Producing biodegradable plastics
(d) Producing biochar from thermo-chemical conversion of biomass
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
Avian Influenza
Why in News?
A recent study has shed light on significant shifts in the ecology and evolution of highly pathogenic avian H5 influenza viruses, revealing a change in their global distribution.
- These viruses have been of growing concern due to their potential impact on both avian and mammalian populations, including humans.
What are the Major Findings of the Study?
- While the epicenter of these viruses was originally confined to Asia, the study's findings suggest that this epicenter has now expanded to include new regions in Africa and Europe.
- The two H5 strains originating from African and European bird populations were found to have evolved through genetic reassortment with low pathogenic viral variants as they spread.
- This genetic reassortment is a critical factor driving the evolution and diversification of these viruses.
- The study underlined that the increasing persistence of avian influenza in wild bird populations is a catalyst for the evolution and spread of new viral strains.
- Wild birds play a crucial role in transmitting and amplifying these viruses, contributing to their ongoing evolution.
What is Genetic Reassortment?
- Genetic reassortment is a type of genetic recombination that occurs when genes from two organisms are mixed to create a new genetic sequence. This new sequence is called a recombinant.
- It can increase genetic diversity during the evolution of seasonal viruses. It can also lead to novel and potentially deadly viruses.
What is Avian Influenza?
- About:
- Avian influenza, often referred to as bird flu, is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects birds, particularly wild birds and domestic poultry.
- In 1996, highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus was first identified in domestic waterfowl in Southern China. The virus is named A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996.
- Transmission to Humans and Related Symptoms:
- Human cases of H5N1 avian influenza occur occasionally, but it is difficult to transmit the infection from person to person. As per World Health Organisation(WHO), when people do become infected, the mortality rate is about 60%.
- It can range from mild flu-like symptoms, including fever, cough, and muscle aches, to severe respiratory issues like pneumonia, difficulty breathing, and even cognitive problems such as altered mental status and seizures.
- Human cases of H5N1 avian influenza occur occasionally, but it is difficult to transmit the infection from person to person. As per World Health Organisation(WHO), when people do become infected, the mortality rate is about 60%.
- Avian Influenza and India:
- Initial Outbreak:
- The initial outbreak of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) H5N1 in India occurred in 2006 in Navapur, Maharashtra, and was followed by annual outbreaks.
- H5N8 was first observed in India in November 2016, mainly affecting wild birds across five states, with Kerala reporting the most cases.
- The disease has been reported in 24 states and union territories, resulting in the culling of over 9 million birds to control its spread.
- Related Initiative:
- India's approach to controlling Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) follows a "detect and cull" policy as outlined in the National Action Plan for Prevention, Control, and Containment of Avian Influenza (revised - 2021)
- Initial Outbreak:
- Treatment:
- Antivirals have demonstrated effectiveness in the treatment of avian influenza virus infections in humans, lowering severity and the risk of death.
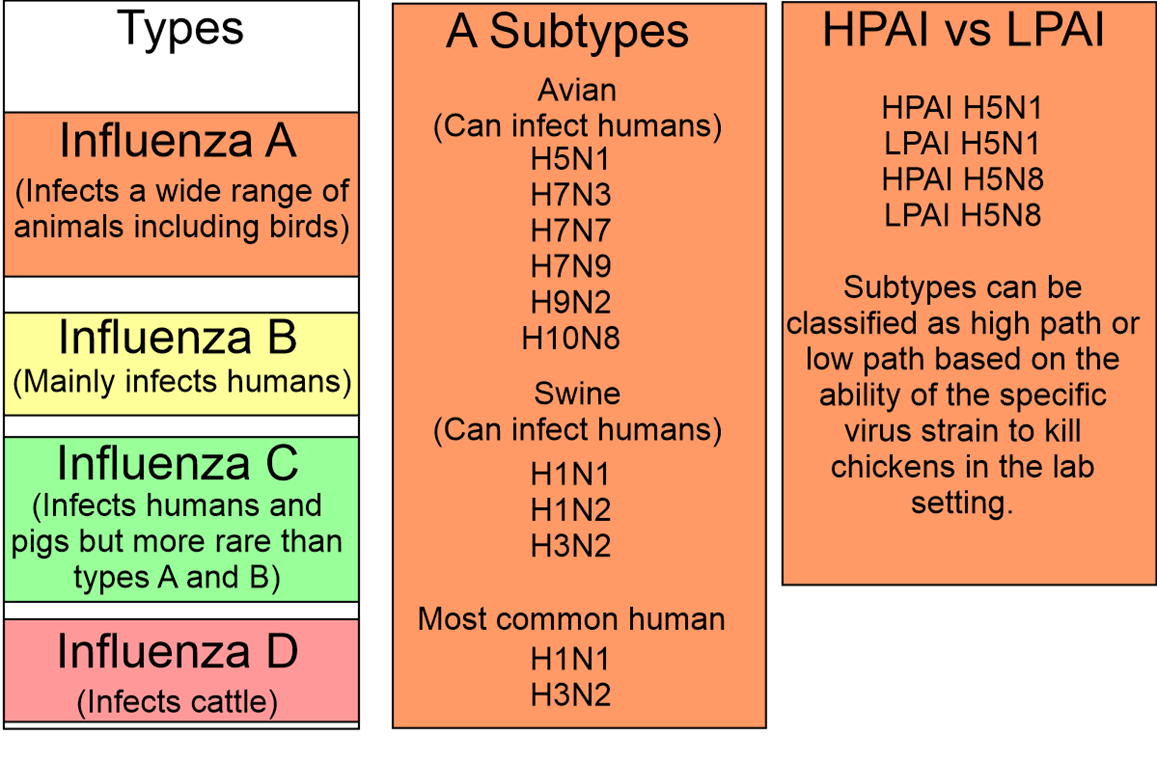
What are the Types of Influenza Virus?
Note
HPAI stands for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza and LPAI stands for Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. H1N1 virus is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to which one of the following diseases? (2015)
(a) AIDS
(b) Bird flu
(c) Dengue
(d) Swine flu
Ans: (d)
Important Facts For Prelims
New Made-In-India EV Charging Standard
Why in News?
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has recently approved a groundbreaking charging connector standard for Light Electric Vehicles (LEVs), including scooters, bikes, and rickshaws.
What is India's New EV Charging Standard?
- About:
- Named ISI7017 (Part 2/Sec 7): 2023, this standard is a result of collaboration among NITI Aayog, the Department of Science and Technology, Ather Energy (a private firm), and other stakeholders.
- Unique Features of India's New EV Charging Standard:
- Remarkable feature of India's new EV charging standard is its ability to combine alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) charging for LEVs.
- This approach, akin to globally established standards for electric cars, enhances interoperability and compatibility among various EV models and charging infrastructure providers.
- Consequences of Diverse Charging Standards:
- India's EV manufacturers, unlike those in some other countries, are not obligated to adhere to a specific charging standard. This results in different charging standards for EVs from different companies, paralleling the past situation of Apple and Android smartphones.
- For example, Ola Electric, Ather Energy, and Ultraviolette Automotive all employ distinct charging standards for their EVs.
- India's EV manufacturers, unlike those in some other countries, are not obligated to adhere to a specific charging standard. This results in different charging standards for EVs from different companies, paralleling the past situation of Apple and Android smartphones.
What are Different Charging Standards Worldwide?
- China:
- China uses a national standard for EV charging connectors that is called GB/T, effectively addressing range anxiety with a dense network of charging stations.
- United States:
- While there isn't a national standard, collaboration between EV manufacturers like Ford and General Motors aims to establish common standards.
- Europe:
- The Combined Charging System (CCS) standard dominates in Europe, backed by the European Union, promoting uniformity.
- Japan:
- Japan employs the CHAdeMO standard, though it's being phased out in North America in favor of more common standards.
What are Some Government Initiatives to Promote EV Adoption?
- The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME)scheme II
- The National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP)
- The National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery Storage
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme
- The Vehicle Scrappage Policy
- Go Electric campaign
- Global EV30@30 campaign
- The Ministry of Power, in its revised guidelines on charging infrastructure (MoP Guidelines), has prescribed that at least one charging station should be present in a grid of 3 km and at every 25 kms on both sides of the highways.
- The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs has also amended the Model Building Bye-laws, 2016 (MBBL) to mandate setting aside 20% of the parking space for EV charging facilities in residential and commercial buildings.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017.
- The Agreement aims to limit greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2ºC or even 1.5ºC above pre-industrial levels.
- Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $ 1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. How is efficient and affordable urban mass transport key to the rapid economic development in India? (2019)
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Indian Army Gets Vertical Wind Tunnel
Indian Army's Special Forces Training School (SFTS) in Himachal Pradesh has acquired the Army's first Vertical Wind Tunnel (VWT), enhancing the training infrastructure for special forces and combat free-fallers.
- The VWT is designed to improve the Combat Free Fall (CFF) skills of armed forces personnel, creating a controlled environment to simulate real-life freefall conditions.The VWT functions by generating specific air velocities, replicating different CFF conditions.
- It assists both beginners and seasoned free-fallers and CFF instructors by simulating a wide range of freefall scenarios, thereby aiding in assessing individual reactions in an airborne operating environment.
Read More: Defense Research and Development Organisation, Indian Navy
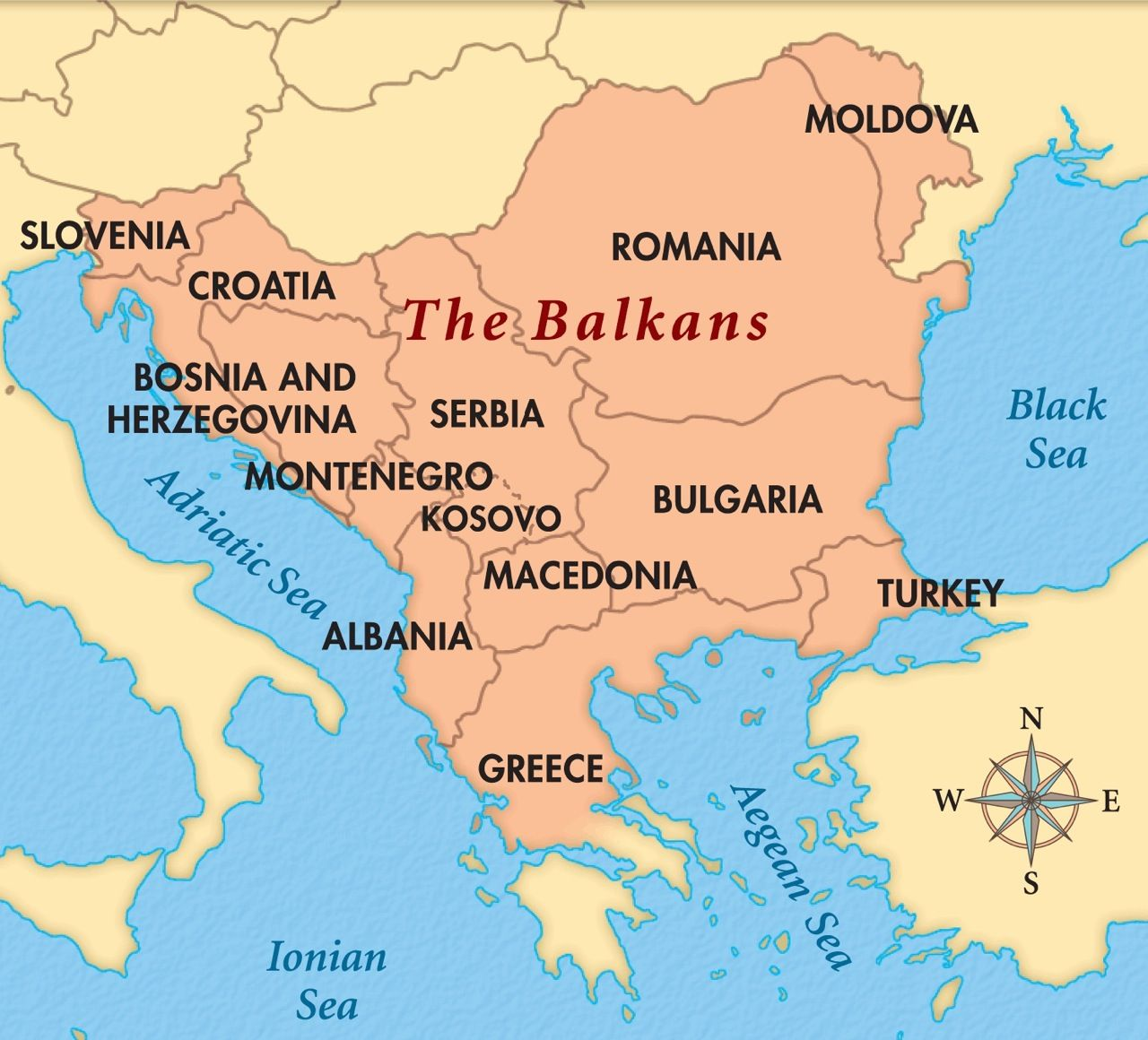
Soaring Tensions Between Kosovo And Serbia
The European Union (EU) and the US along with diplomats from Germany, France, and Italy are calling on Kosovo and Serbia to restart their dialogue in an effort to reduce the escalating tensions between the two nations.
- Kosovo and Serbia both aspire to join the EU, but they have been told to resolve their differences first. Western powers are pushing for the implementation of a 10-point plan proposed by the EU to resolve political crises.
- A key point of contention is the establishment of the Association of Serb-Majority Municipalities (ASM) in Kosovo, which has faced legal challenges.
- Conflict between two countries dates back to 2008 when Kosovo unilaterally declared independence from Serbia. Kosovo's independence has been recognized by a significant number of countries but Serbia does not recognize Kosovo's sovereignty which led to border disputes.
Read More: Kosovo-Serbia Conflict, North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
RISUG: Reversible Male Contraceptive
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has concluded a seven-year study on the male contraceptive Reversible Inhibition of Sperm Under Guidance (RISUG), finding it to be safe and effective.
- RISUG is a non-hormonal injectable contraceptive that provides long-lasting sterility with complete reversibility.
- RISUG works by injecting a polymer gel made of styrene maleic anhydride (SMA). It can be reversed by injecting a solvent called dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) into the vas deferens, which dissolves the polymer gel and flushes it out of the body.
Indian Economy to Surpass Japan by 2030: S&P Global
According to S&P Global Market Intelligence, the Indian economy is set to surpass Japan and Germany by 2030, GDP (Gross Domestic Product) increasing from USD 3.5 trillion in 2022 to USD 7.3 trillion by 2030.
- At present, India is ranked 5th in terms of the size of its economy at USD 3.7 trillion in 2023-24.
- This rapid growth is expected to make India the Second-Largest economy in the Asia-Pacific region, surpassing Japan.
- India is poised to grow in such a manner due to its favorable long-term growth prospects, driven by its youthful demographic profile and rising urban household incomes.
- The middle class, coupled with the rapidly growing domestic consumer market and industrial sector, makes India an appealing investment destination for multinational companies.
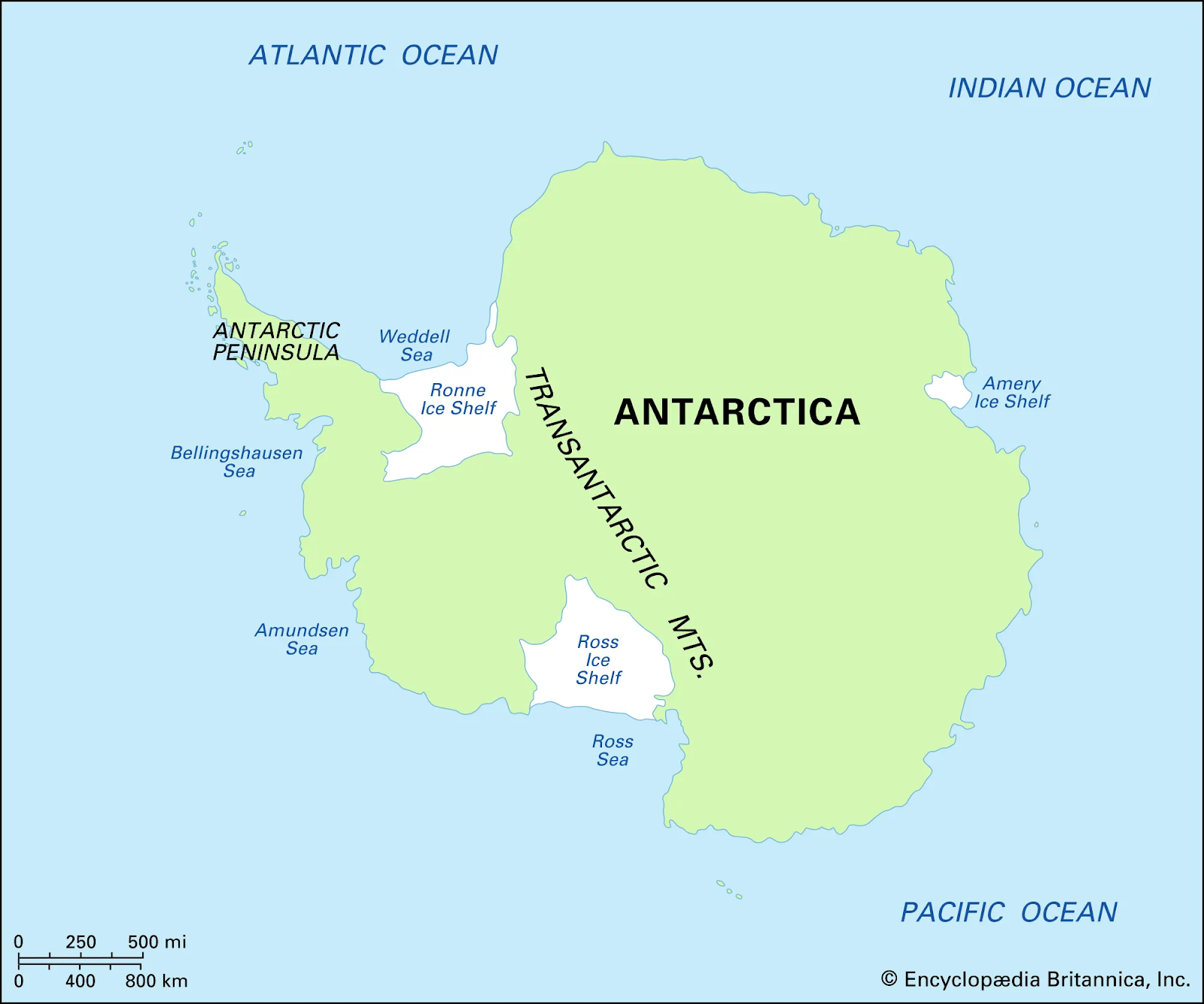
Antarctica's Ancient Landscape Revealed
Recently, scientists have unearthed a remarkable find beneath the icy expanse of Antarctica, shedding light on a time when the continent was far from its current icy desolation.
- In East Antarctica's Wilkes Land region, a vast ancient landscape has been discovered, featuring valleys and ridges sculpted by ancient rivers.
- It hints at a bygone era when Antarctica's climate was considerably warmer, possibly supporting a diverse array of wildlife.
- Antarctica was once part of the Gondwana supercontinent before splitting off due to plate tectonics.
- The landscape and flora of Antarctica likely resembled today's cold temperate rainforests before it entered a deep freeze.
- Antarctica was once part of the Gondwana supercontinent before splitting off due to plate tectonics.
Read more: Rapidly Melting Antarctic Ice