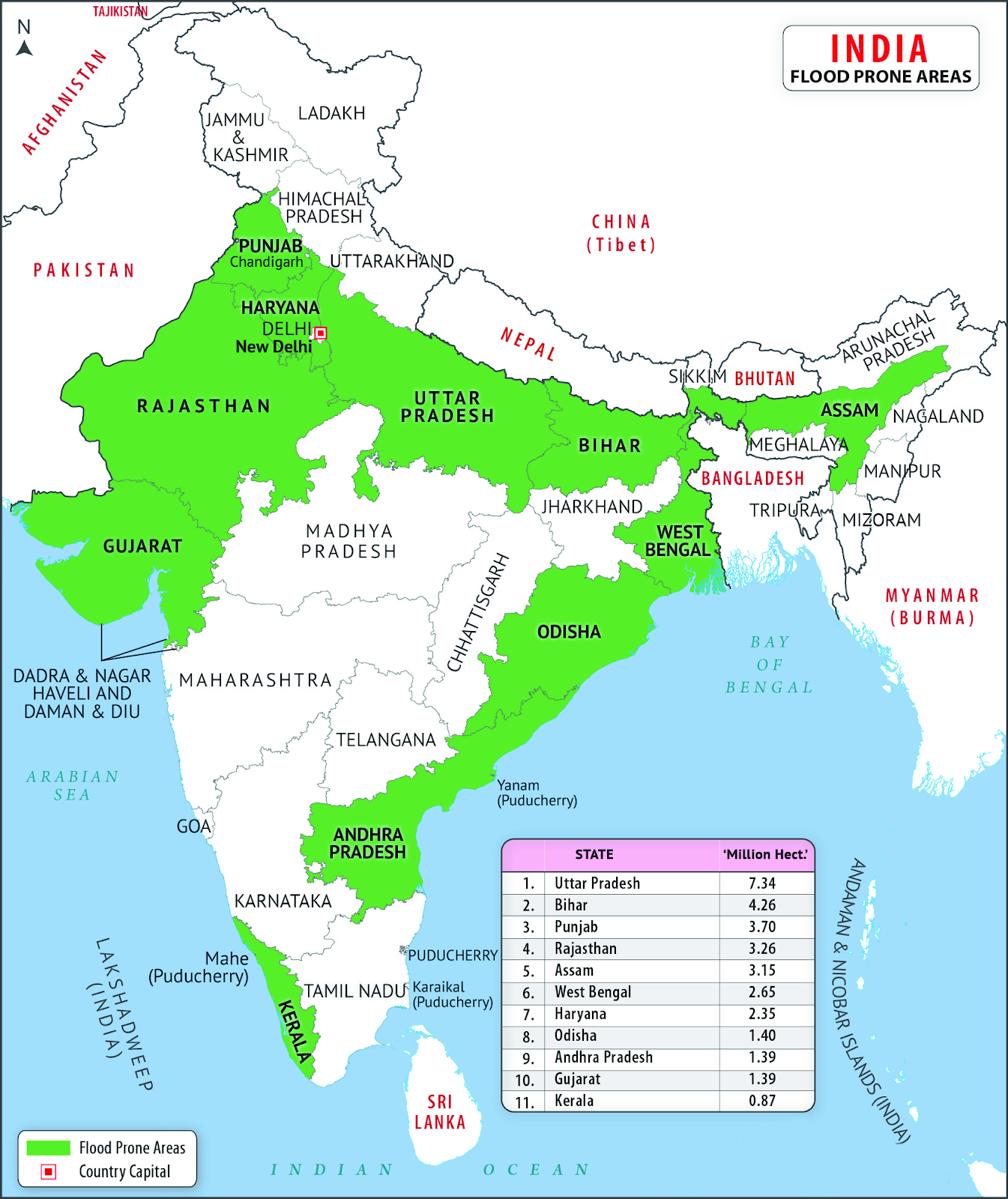
Geography
Surge in Human Settlements in Flood-Prone Areas
- 13 Oct 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Flood Zones, Climate change, World Bank Reports.
For Mains: Factors Behind Increasing Human Settlements in Flood Zones, Flood Management
Why in News?
According to a recent study conducted by the World Bank, human settlements in some of the world's riskiest flood zones have increased by a staggering 122% since 1985, contributing to the vulnerability of millions to water disasters induced by climate change. And, this growth is predominantly observed in middle- and low-income countries.
- On the other hand, the most secure regions experienced an 80% increase in growth in human settlements.
What are the Major Takeaways from the Study?
- Global Landscape of Settlement Expansion:
- Most countries, especially in East Asia, saw more settlements in regular flood zones and ultra-high flood zones than in dry areas.
- Libya, which suffered from devastating flooding in September 2023, had an 83% increase in settlement extent in the worst flood zones.
- Pakistan, experiencing catastrophic flooding both in 2022 and 2023, witnessed an 89% increase in settlements in prone areas.
- Notable Exceptions:
- Dry settlements in the United States increased by 76%, while the highest flood settlements rose by only 46%.
- Other countries with more dry settlements than ultra-wet areas include India, France, Sweden, Austria, Finland, Japan and Canada.
What are the Possible Factors Behind Increasing Human Settlements in Flood Zones?
- Rural to Urban Migration: As countries experience economic growth, urbanization near waterways becomes prevalent. Settlements often expand into flood-prone areas as cities grow.
- For Example: Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, exemplifies this issue, growing from a fishing village to over seven million people.
- Economic Factor: Low-income populations often cannot afford to live in safer, less flood-prone areas. They might be forced to live in flood-prone zones because of housing affordability constraints.
- Lack of Regulatory Enforcement: In some countries, land-use planning and zoning regulations might not be effectively enforced. This can result in settlements proliferating in flood-prone areas without adequate safeguards.
- Cultural and Historical Ties: Some communities have deep cultural or historical connections to flood-prone regions, and this can influence their decisions to remain or settle in these areas despite the risks.
- Tourism and Recreation: Coastal and riverfront areas, despite their vulnerability to flooding, continue to draw tourists and recreation enthusiasts because of their inherent appeal.
- The demand for resorts, hotels, and vacation homes can lead to settlement in these areas, even if it's only seasonal.
Note
Settlement expansion into flood zones does not negate the significance of climate change. The two issues are intertwined, compounding risks and vulnerabilities. People might prioritize immediate needs for shelter and livelihoods over long-term climate risks.
- This can lead to decisions that are more focused on short-term survival.
Way Forward
- Strict Land Use Policies: Implement and enforce stringent land use regulations that prohibit or restrict new construction in high-risk flood zones.
- Designate flood-prone areas as 'no-build' zones and enforce these restrictions consistently.
- Infrastructure Investment: There is a need to Invest in resilient infrastructure, including better flood defences, early warning systems, and floodplain mapping.
- Improve drainage systems to mitigate the impact of flooding in existing settlements.
- Government Support and Relocation Assistance: The government can offer financial incentives for residents to relocate from flood-prone areas to safer zones.
- Also, the government needs to strengthen emergency response and preparedness measures in flood-prone areas to minimize the loss of life and property during flood events.
- Public Awareness and Education: Launch public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about the risks associated with living in flood-prone areas.
- Promote community-based education programs on flood preparedness and the importance of avoiding such areas.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. The frequency of urban floods due to high intensity rainfall is increasing over the years. Discussing the reasons for urban floods, highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. (2016)
Q. Account for the huge flooding of million cities in India including the smart ones like Hyderabad and Pune. Suggest lasting remedial measures. (2020)
Q. Major cities of India are becoming vulnerable to flood conditions. Discuss. (2016)