Infographics
Indian Economy
Singareni Thermal Power Plant
For Prelims: Singareni Thermal Power Plant, Flu gas desulphurization (FGD), Central Pollution Control Board.
For Mains: Status of the Thermal Power Sector in India, Issues Associated with Thermal Power Plants.
Why in News?
Singareni Thermal Power Plant (STPP) in Telangana is set to become the first public sector coal-based power generating station in the South and first among the State PSUs in the country to have a flu gas desulphurization (FGD) plant.
- With 100% utilisation of the fly ash generated, the STPP has won the best fly ash utilisation award twice already
What are the Key Facts Related to FGD Plant?
- About:
- The FGD plant would process the sulphur and other gases (nitrogen oxides) generated in firing the coal for power generation.
- The FGD plant removes Sulphur Dioxide from the flue gas before it is released into the atmosphere and hence reduces its impact on the environment.
- The FGD plant would process the sulphur and other gases (nitrogen oxides) generated in firing the coal for power generation.
- Types of FGD Systems:
- FGD systems are characterized as either “wet” or “dry” corresponding to the phase in which the flue gas reactions take place. Four types of FGD systems:
- Wet FGD systems use a liquid absorbent.
- Spray Dry Absorbers (SDA) are semi-dry systems in which a small amount of water is mixed with the sorbent.
- Circulating Dry Scrubbers (CDS) are either dry or semi-dry systems.
- Dry Sorbent Injection (DSI) injects dry sorbent directly into the furnace or into the ductwork following the furnace.
- FGD systems are characterized as either “wet” or “dry” corresponding to the phase in which the flue gas reactions take place. Four types of FGD systems:
- Ministry Guidelines:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has set the deadline for installation of FGD plants for coal-based power plants as December-end of 2026 for non-retiring plants and as December-end of 2027 for retiring plants.
- However, it is not made compulsory for the plants that are going to retire by December-end of 2027, provided they seek exemption from the Central Pollution Control Board and Central Electricity Authority.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has set the deadline for installation of FGD plants for coal-based power plants as December-end of 2026 for non-retiring plants and as December-end of 2027 for retiring plants.
- Uses:
- The gypsum generated by the FGD plant would be used in fertiliser, cement, paper, textile and construction industries, and its sales are likely to contribute to the maintenance of the FGD plant.
What is the Status of the Thermal Power Sector in India?
- About:
- The thermal power sector has been a major source of electricity generation in India, accounting for around 75% of the country's total installed power capacity.
- As of May 2022, India has a total Thermal installed capacity of 236.1 GW of which 58.6% of the thermal power is obtained from coal and the rest from Lignite, Diesel, and Gas.
- Issues Associated with Thermal Power Plants:
- Environmental Impact: Thermal power plants emit a large amount of carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and other pollutants into the air. This leads to air pollution, which has serious health implications for people living in the vicinity of the plants.
- Thermal power plants also consume a lot of water, leading to water scarcity in some areas.
- Coal Supply: India's thermal power plants rely heavily on coal, which is mostly imported from other countries. This can lead to supply disruptions and price volatility.
- In FY22, India’ s coal import of 208.93 million tonne (MT) was worth Rs 2,28,741.8 crore.
- Financial Health: Many of India's thermal power plants are owned by government entities and are facing financial losses due to rising coal prices, low demand, and other factors.
- This has led to many plants being shut down or operating at low capacity.
- Ageing Infrastructure: Many of India's thermal power plants were built in the 1970s and 1980s and are in need of modernization.
- Upgrading these plants to meet current environmental standards can be costly.
- Renewable Energy Competition: As renewable energy becomes cheaper, thermal power plants are facing increased competition.
- This has led to a decrease in demand for thermal power and has made it harder for some plants to operate profitably.
- Environmental Impact: Thermal power plants emit a large amount of carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and other pollutants into the air. This leads to air pollution, which has serious health implications for people living in the vicinity of the plants.
Way Forward
- Implement Pollution Control Measures: As mentioned earlier, the installation of FGD plants is one of the key steps in controlling air pollution in thermal power plants.
- The government should make it mandatory for all thermal power plants to install FGD plants and other pollution control measures to reduce emissions and protect the environment.
- Improve Coal Quality: The quality of coal used in thermal power plants in India is relatively low, leading to higher emissions and lower efficiency.
- Therefore, the government should focus on improving the quality of coal supplied to thermal power plants by investing in technologies such as coal washing and beneficiation.
- Modernise Existing Plants: Many of India's thermal power plants are old and inefficient. The government should encourage plant owners to modernise their facilities by investing in new technologies, upgrading equipment, and adopting best practices to improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Increase Efficiency: Improving efficiency is a critical factor in reducing the cost of power generation and improving the competitiveness of the thermal power sector.
- The government should incentivize thermal power plants to adopt energy-efficient practices and technologies such as supercritical and ultra-supercritical technologies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Coal ash contains arsenic, lead and mercury.
- Coal-fired power plants release sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen into the environment.
- High ash content is observed in Indian coal.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q2. Which one among the following industries is the maximum consumer of water in India? (2013)
(a) Engineering
(b) Paper and pulp
(c) Textiles
(d) Thermal power
Ans: (d)


Governance
Draft Policy for Displaced Communities from Coastal Erosion
Prelims: NDMA, NDRF, Coastal Erosion, 15th Finance Commission’s Report.
Mains: Draft Policy for Displaced Communities from Coastal Erosion.
Why in News?
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) received the inputs from disaster management officials and researchers on the draft of India’s first national policy for the mitigation and rehabilitation of the people affected by river and Coastal Erosion.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs had directed NDMA to draft a policy based on the 15th Finance Commission’s report for 2021.
- Until now, most policies in the country only address displacement after sudden rapid-onset disasters such as floods and cyclones.
What are the Recommendations of the 15th Finance Commission Report?
- It had for the first time emphasised on rehabilitation and resettlement for people displaced by the river and coastal erosion, in view of the increasing threat due to climate change.
- It introduced mitigation measures to prevent erosion under the National Disaster Mitigation Fund (NDMF), with an allocation of Rs 1,500 crore for 2021-26.
- For the resettlement of displaced people affected by erosion, it allocates Rs 1,000 crore for the same period under the National Disaster Relief Fund (NDRF).
- It emphasized that states must follow timelines for mitigation and rehabilitation projects without delays, projects under NDRF and NDMF should be sanctioned in such a manner that they can be completed within the award period of the Commission.
What are the Key Features of Draft Policy?
- Fund Allocation:
- For both funds (NDRF and NDMF), state governments will have to avail resources on a cost-sharing basis, contributing 25% to the costs of mitigation and resettlement associated with coastal and river erosion.
- However, northeastern states have to only pool 10% of state funds.
- NDMA will coordinate the allocations and expenses under NDRF and NDMF at the national level for mitigation and rehabilitation.
- Nodal Agency:
- District Disaster Management Authorities (DDMA) would be the nodal agency to implement the measures, aided by other district agencies and a specific panchayat-level committee.
- The DDMA will prepare mitigation and rehabilitation plans and submit them to the SDMAs, from where the proposed measures will be appraised by NDMA and finally submitted to the home ministry.
- A high-level committee of the ministry will then approve the disbursal of funds.
- Detailed Hazard Assessments:
- Detailed hazard assessments carried out by central agencies such as the National Centre for Coast Research, Central Water Commission etc., and high-resolution LiDAR data available with National Remote Sensing Centre should be made available to the SDMAs.
- These should be made available in easy-to-access geographic information systems (GIS) formats by the NDMA.
- Mapping Coastal and River Erosion:
- The policy insists on mapping coastal and river erosion impacts and coming up with a database of diverse challenges confronted by the affected and vulnerable habitations.
- Impact and Vulnerability Assessments:
- The draft policy also recommends impact and vulnerability assessments of regions threatened by coastal and river erosion to be undertaken periodically, which will be spearheaded by SDMAs in coordination with the state departments and DDMAs.
What is NDMA?
- NDMA is India’s apex statutory body for disaster management.
- The NDMA was formally constituted on 27th September 2006, by the Disaster Management Act, 2005. The Prime Minister is its chairperson, and it has nine other members. One of the nine members is designated as Vice-Chairperson.
- The primary responsibility for the management of disaster rests with the State Government concerned. However, the National Policy on Disaster Management puts in place an enabling environment for all i.e., the Centre, state and district.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Discuss the recent measures initiated in disaster management by the Government of India departing from the earlier reactive approach. (2020)
Q. With reference to National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) guidelines, discuss the measures to be adopted to mitigate the impact of the recent incidents of cloudbursts in many places of Uttarakhand. (2016)
Q. Drought has been recognized as a disaster in view of its spatial expanse, temporal duration, slow onset and lasting effects on vulnerable sections. With a focus on the September 2010 guidelines from the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), discuss the mechanisms for preparedness to deal with likely El Nino and La Nina fallouts in India. (2014)


Science & Technology
James Webb Telescope spots 6 Monster Galaxies
Prelims: James Webb telescope, Big Bang, Hubble space telescope, Monster Galaxy, Big Dipper.
Mains: James Webb telescope.
Why in News?
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has discovered six Monster galaxies, formed roughly 500-700 million years after the Big Bang, according to a Study.
How were these Galaxies Found?
- Researchers spotted the six monster galaxies using the Cosmic Evolution Early 44 Release Science programme of JWST.
- The programme studies the formation of the earliest galaxies when the universe was less than 5% of its current age.
- Researchers turned the telescope to a patch of the sky close to the Big Dipper, which appears to harbor a group of stars that form a pattern in the night sky. The Hubble space telescope first observed this region in the 1990s.
- The Big Dipper is an asterism of stars, in the constellation Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear). It consists of seven bright stars, four forming a rectangular "bowl" shape and three forming a "handle". It is often used as a navigational tool, a reference point for stargazing, and as a symbol in popular culture.
What are the Findings of these Galaxies?
- Despite having the same mass as the Milky Way, one of the galaxies is 30 times smaller.
- This indicates the presence of large and mature but remarkably compact galaxies teeming with stars far sooner than scientists had considered possible.
- The telescope reveals that six large, mature galaxies are as old as the Milky Way and exist around 540-770 million years after the Big Bang.
- The universe was roughly 3 % of its current age at the time.
- These galaxies challenge our current understanding of galaxy formation as they should not have existed so early in their life.
What is JWST?
- The telescope is the result of an international collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency which was launched in December 2021.
- It is currently at a point in space known as the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point, approximately 1.5 million km beyond Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
- Lagrange Point 2 is one of the five points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system.
- Lagrange Points are positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two-body system (like the Sun and the Earth) produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion.
- It's the largest, most powerful infrared space telescope ever built.
- It's the successor to Hubble Telescope.
- It can see backwards in time to just after the Big Bang by looking for galaxies that are so far away that the light has taken many billions of years to get from those galaxies to our telescopes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Launched on 25th December, 2021, James Webb Space Telescope has been much in the news since then. What are its unique features which make it superior to its predecessor Space Telescopes? What are the key goals of this mission? What potential benefits does it hold for the human race? (2022)


Indian Economy
Blue Food
For Prelims: Blue Food, Cardiovascular Disease, Microplastics.
For Mains: Significance of Blue Food, Issues Associated with Blue Food.
Why in News?
A new study suggests that blue food sourced from aquatic environments can help reduce nutritional deficiencies and contribute to employment and export revenue in India.
What is Blue Food?
- About:
- Blue food is food derived from aquatic animals, plants or algae that are caught or cultivated in freshwater and marine environments.
- Significance:
- Key Source of Nutrient:
- Blue foods are important for the economies, livelihoods, nutritional security, and cultures of people in many countries.
- They supply protein to over 3.2 billion people, are a key source of nutrients in many coastal, rural and indigenous communities, and support the livelihoods of over 800 million people, the majority of whom work in small-scale systems.
- Low Emission and Tackle Deficiencies:
- They generate lower emissions compared to terrestrial meat.
- Aquatic foods can also be used to address B12 and omega-3 deficiencies in India.
- Over 91% of countries with vitamin B12 deficiencies also show high levels of omega-3 deficiency
- Reduce Cardiovascular Diseases:
- Promoting blue foods over red meat overconsumption could address health and environmental concerns for about 82% of the 22 countries suffering from a high cardiovascular disease risk.
- Revenue Potential for Global South:
- Blue foods can help improve nutrition, livelihoods or national revenue for the global south and indigenous communities in the global north.
- Key Source of Nutrient:
- Issues Associated with Blue Food:
- Bycatch: This refers to the accidental capture of non-target species in fishing nets, which can lead to the death of these animals.
- Pollution: The presence of pollutants such as heavy metals, PCBs and microplastics in the ocean can affect the quality and safety of seafood.
- Mislabeling and Fraud: There have been instances of mislabeling of seafood products, where a cheaper fish is sold as a more expensive one.
- This can lead to consumer deception and potential health risks.
- Overexploitation: Almost 90% of global marine fish stocks are now fully exploited or overfished according to the World Bank, which is an issue with overfishing, illegal fishing, and other unsustainable aquatic food production.
Way Forward
- Increasing Awareness: Governments, NGOs, and the private sector should work together to increase awareness about the benefits of blue food and its potential to address malnutrition, poverty, and environmental degradation.
- Promoting Sustainable Fishing Practices: Fishing practices that are unsustainable, such as overfishing, destructive fishing methods, and bycatch, need to be addressed to ensure that fish stocks are not depleted and the marine ecosystem is protected.
- Encouraging Aquaculture: Aquaculture can be a sustainable way of producing blue food if it is done in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Governments can promote the development of sustainable aquaculture practices by providing technical assistance, training, and incentives.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q1. Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How have these revolutions helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? (2017)
Q2. Defining blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
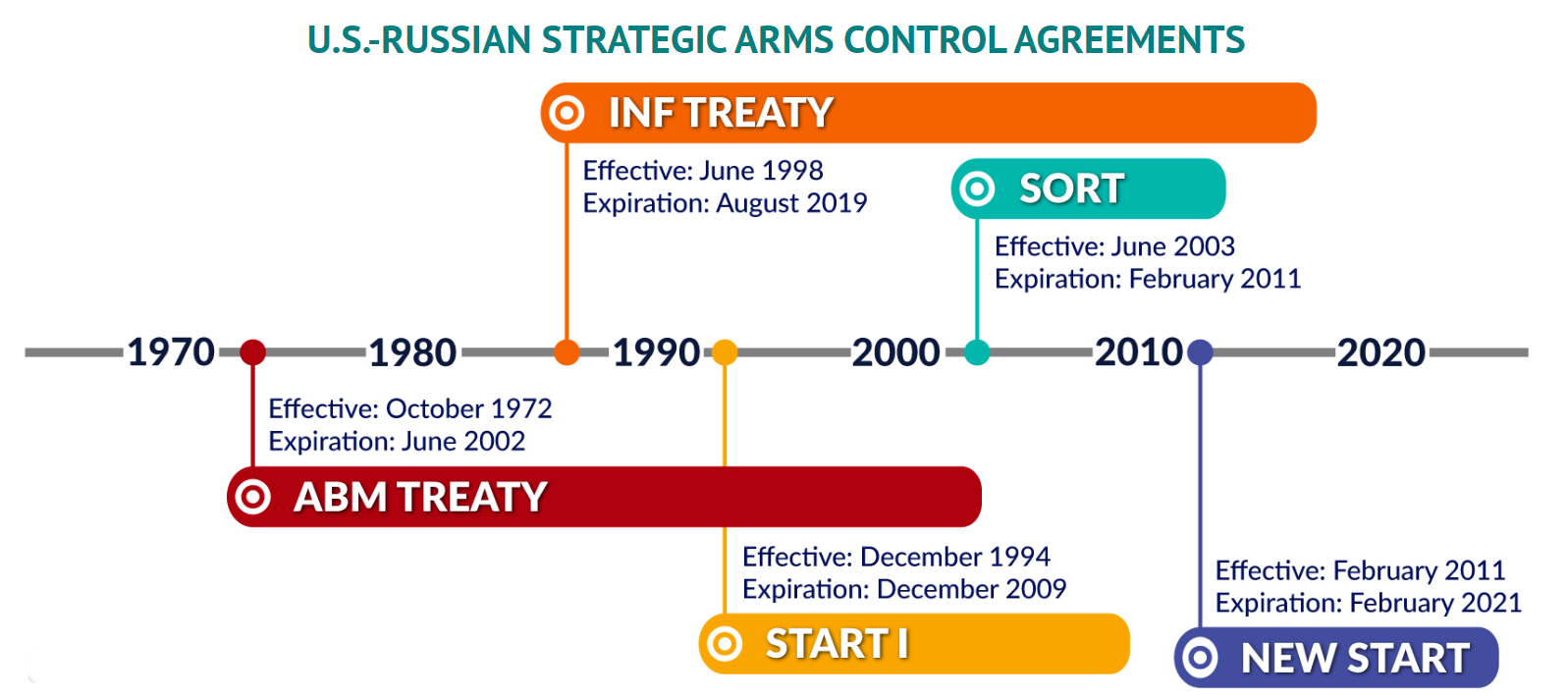
Russia Suspends New START
Why in News?
Recently, Russia has announced to suspend its participation in the New START, the last remaining major military agreement with the United States.
What is the New START?
- Background:
- The name START comes from the original “Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty”, known as START-I, which was signed between the US and the erstwhile USSR in 1991, and came into force in 1994.
- START-I, which capped the numbers of nuclear warheads and intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) that each side could deploy at 6,000 and 1,600 respectively, lapsed in 2009, and was replaced first by the SORT, also known as the Treaty of Moscow), and then by the New START treaty.
- New START:
- The New START, the “Treaty between the United States of America and the Russian Federation on Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms”, entered into force on 5th February 2011, and placed new verifiable limits on intercontinental-range nuclear weapons.
- The two countries had to meet the treaty’s central limits on strategic offensive arms by February 2018, and to then stay within those limits for the period the treaty remained in force. The US and Russia Federation subsequently agreed to extend the treaty through February 2026.
What are the Implications of the Suspension?
- A suspension of the treaty may mean that it will be harder for the US to monitor compliance.
- Since Russia has already suspended mutual inspections of nuclear weapons sites and participation in a bilateral consultative commission, it would be a serious blow if Putin went further and stopped routine reporting and data exchange on nuclear weapon movements and other related developments.
- The move is” entirely symbolic” and most probably Russia made the announcement to pressure US into approaching Russia about ending the war, so Russia can dictate the terms under which that would happen.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. The “New START” treaty was in the news. What is this treaty? (2011)
(a) It is a bilateral strategic nuclear arms reduction treaty between the USA and the Russian Federation.
(b) It is multilateral energy security cooperation treaty among the members of the East Asia Summit.
(c) It is a treaty between the Russian Federation and the European Union for the energy security cooperation.
(d) It is a multilateral cooperation treaty among the BRICS counries for the promotion of trade
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Mad Cow Disease
Why in News?
Recently, Brazil has halted its beef exports to China after a case of Mad Cow Disease was confirmed in the northern state of Para.
What is Mad Cow Disease?
- About:
- Also known as Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) is degenerative, transmissible, slowly progressive, and a fatal infection that affects the central nervous system of adult cattle.
- Causes:
- BSE is caused by a protein called a prion normally found on cell surfaces, the normal prion protein changes into an abnormal prion protein that is harmful.
- After getting altered, these proteins destroy the nervous system tissue- the brain and spinal cord.
- The body of a sick cow does not even know the abnormal prion is there. Without knowing it is there, the cow’s body cannot fight off the disease.
- BSE is caused by a protein called a prion normally found on cell surfaces, the normal prion protein changes into an abnormal prion protein that is harmful.
- Transmission:
- A cow gets BSE by eating feed contaminated with parts that came from another cow that was sick with BSE.
- Symptoms:
- A common sign of BSE in cows is incoordination. A sick cow has trouble walking and getting up and may also act very nervous or violent.
- It usually takes four to six years from the time a cow is infected with the abnormal prion to when it first shows symptoms of BSE. This is called the incubation period. During the incubation period, there is no way to tell that a cow has BSE by looking at it.
- Once a cow starts to show symptoms, it gets sicker and sicker until it dies, usually within two weeks to six months.
- Treatment:
- There is no treatment for BSE and no vaccine to prevent it.


Important Facts For Prelims
18th UIC World Security Congress
Why in News?
The 18th UIC World Security Congress, organised by the Railway Protection Force (RPF) and the International Union of Railways (UIC), ended with the adoption of the Jaipur Declaration.
What are the Major Highlights of the Jaipur Declaration?
- Safe and Secure Rail Network:
- The declaration highlighted the commitment of UIC to work towards providing a more safe and secure rail network across the globe, by also fully activating the Asia-Pacific, Latin America and African regional assemblies by 2025.
- Adoption of New Technologies and Role of RPF:
- It called for the adoption of new technologies such as Artificial Intelligence 5G, IoT among others to develop comprehensive solutions for Railway Security.
What is Union International Des Chemins?
- The UIC (Union International Des Chemins) or International Union of Railways established in 1922 is headquartered in Paris.
- It is the worldwide professional association representing the railway sector for research, development & promotion of rail transport.
What is the Railway Protection Force?
- About:
- RPF is the prime security and law- enforcement organisation in the field of Railway Security in India.
- Constituted as a federal Force in the year 1957, RPF is responsible for security of railway property, passenger and passenger zones.
- RPF personnel serve the Nation and go the extra mile in their line of duty embodying its tagline “Sewa hi Sankalp- A promise to serve”.
- Role Played by Railway Protection Force:
- RPF has played exceptional role towards enhancing passenger security in india through various initiatives such as Operation Nanhe Farishte for rescue of children and Operation AAHT for rescuing women and children from the clutches of traffickers.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Amazon to Join ONDC
Amazon has announced that it will join the Indian government’s ONDC (Open Network for Digital Commerce) platform. In 2022, Microsoft became the first big technology company to join the network with an intention of introducing group buying in the Indian market through social e-commerce.
ONDC is an open e-commerce protocol set up by the Ministry of Commerce’s Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT). Under ONDC, it is envisaged that a buyer registered on one participating e-commerce site may purchase goods from a seller on another participating e-commerce site (for example, Flipkart).
Presently, buyers and sellers have to be on the same app for a transaction which happens through the same platform.
Read More: Open Network for Digital Platform (ONDC), E-Commerce
Great Backyard Bird Count (GBBC) 2023
During the Great Backyard Bird Count (GBBC) 2023 across 35 States and Union Territories, West Bengal reported the highest number of species (498) followed by Uttarakhand and Arunachal Pradesh.
As per the Bird Count India (BCI), Kerala recorded the highest number of checklists of birds. Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu were placed second and third.
BCI is an informal partnership of organisations and groups working together to increase collective knowledge about bird distributions and populations.
India was among 190 countries that participated in GBBC 2023, an annual event that brings bird enthusiasts, students and nature enthusiasts together for counting birds they see around the places where they live, work or study. The GBBC was launched in 1998. Bird Count India organises the GBBC in the country. A remarkable increase in participation across the country helped India upload the second-highest number of checklists after the United States of America and the third-highest species of any country.
Read More: State of the World’s Birds
Garcinia Pedunculata
Garcinia pedunculata, a medicinal plant commonly called 'Borthekera' in the Assamese language, traditionally forbidden for raw consumption, has been found to protect from heart diseases.
The dried pulp of the ripe fruit of the medicinal plant reduced cardiac hypertrophy indicators and oxidative stress and heart inflammation brought on by International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Multiple studies have reported that it is a rich source of antioxidants. However, the cardioprotective potential has yet to be explored earlier.
ISO is an independent, non-governmental international organization with a membership of 167 national standards bodies.
To reduce the cases of cardiovascular and other non-communicable diseases, the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) is being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM).
Read More: Non-Communicable Diseases
eShram Portal
The eShram portal has experienced unprecedented success from the unorganised/migrant workers of the country and as on 24th February 2023, over 28.60 crore workers have registered on the eShram portal.
The eShram portal was launched in 2021 by the Ministry of Labour & Employment to create a National Database of unorganised/migrant workers and to provide them with a Universal Account Number (UAN).
The objective of the eShram portal is to extend the benefits of social security and welfare schemes to unorganised workers especially migrant workers and to identify workers who are deprived of the various benefits of the welfare schemes due to a lack of awareness or otherwise. With this objective, the Ministry of Labour & Employment initiated the matching the eShram beneficiaries’ data with the Ration Card (National Food Security Act (NFSA) data available from the Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD). This initiative will ensure that Ration Card benefits under NFSA are made available to all eligible workers registered on eShram.
Read More: Formalising the Informal Sector, e-Shram Portal & Informal Economy in India



.png)