Infographics
Indian Heritage & Culture
Asian Buddhist Conference for Peace
For Prelims: 12th General Assembly of Asian Buddhist Conference for Peace, Headquarters of ABCP, India International Centre for Buddhist Culture, Four Noble Truths, Eightfold Path of Buddha, Gautam Buddha.
For Mains: Convergence of Principles of Good-Governance and Buddhist Teachings, Teachings of Buddha in Navigating Present-Day Challenges
Why in News?
Recently, the Asian Buddhist Conference for Peace (ABCP), a voluntary mass movement of Buddhists in Asia convened its 12th General Assembly in New Delhi.
What are the Major Highlights of the 12th General Assembly of ABCP?
- Theme: ABCP - The Buddhist Voice of Global South, reflects India's commitment, as demonstrated through its G20 presidency and the Voice of Global South Summit.
- India's Commitment to Buddha's Legacy: India was featured as a nation guided by the principles of Buddha.
- Proactive role of India was highlighted in developing the Buddhist circuit and establishing the India International Centre for Buddhist Culture.
- Constitutional Recognition of Buddha's Influence: Emphasis was placed on the depiction of Lord Buddha in the artwork of the Indian Constitution, specifically in Part V, where he is featured in the section on Union governance.
What is the Asian Buddhist Conference for Peace?
- About: ABCP was founded in 1970 at Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia as a voluntary movement of followers of Buddhism with both monastic (monks) and lay members.
- ABCP then emerged as a collaborative effort of Buddhist dignitaries from India, Mongolia, Japan, Malaysia, Nepal, the then USSR, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, South and North Korea.
- Headquarters: Gandanthegchenling Monastery in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia.
- The Supreme Head of Mongolian Buddhists is the current ABCP President.
- Aims of ABCP:
- Bring together efforts of Buddhists in support of consolidating universal peace, harmony and cooperation among peoples of Asia.
- Furthering their economic and social advancement and promoting respect for justice and human dignity.
- Disseminating the Buddhist culture, tradition and heritage.
How Buddhist Teachings Convergence with Principles of Good-Governance?
- Right View in Policymaking: The Buddha's emphasis on Right View, avoiding distortion and delusion, aligns with good governance principles of transparency, objectivity, and evidence-based decision-making.
- For example, Bhutan's Gross National Happiness index, inspired by Buddhist values, aims to measure public well-being beyond just economic indicators.
- Right Conduct in Leadership: The Buddha's Five Precepts - non-violence, non-stealing, non-lying, non-sexual misconduct, and non-intoxication - can be interpreted as ethical guidelines for public officials.
- Compassionate Governance: The Buddha's core teaching of compassion encourages leaders to consider the needs and suffering of all citizens, not just certain groups.
- For example, initiatives like universal healthcare or fair taxation policies reflect an attempt to govern with compassion in mind.
- Dialogue and Nonviolent Conflict Resolution: The Buddha's emphasis on Right Speech and Right Action promotes respectful communication and nonviolent solutions to conflict.
- This can be applied in international diplomacy, interfaith dialogue, and even within internal political debates.
How Teachings of Buddha Can Help in Navigating Present-Day Challenges?
- Compass for Ethical Uncertainty: In an age marked by ethical uncertainty, Buddha's teachings provide a path of sustainability, simplicity, moderation, and reverence for all life.
- The Four Noble Truths and Eightfold Path serve as a transformative roadmap, guiding individuals and nations towards inner peace, compassion, and non-violence.
- Mindfulness in a Distracted World: In an age of constant digital bombardment, the Buddha's emphasis on mindfulness is more poignant than ever.
- Practices like meditation help us navigate information overload, reduce stress, and cultivate focused attention in a scattered world.
- Compassion in a Polarised Society: With rising social and political tensions, the Buddha's teachings on compassion and understanding offer a critical antidote.
- His emphasis on recognizing the interconnectedness of all beings encourages empathetic communication and constructive conflict resolution.
- The Middle Way in an All-or-Nothing Culture: The Buddha's concept of the Middle Way, avoiding extremes of indulgence and denial, resonates in our consumerist society.
- It encourages mindful consumption, finding balance between personal desires and responsible living.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- Sthaviravadins belong to Mahayana Buddhism.
- Lokottaravadin sect was an offshoot of Mahasanghika sect of Buddhism.
- The deification of Buddha by Mahasanghikas fostered Mahayana Buddhism.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2016)
- The concept of Bodhisattva is central to the Hinayana sect of Buddhism.
- Bodhisattva is a compassionate one on his way to Enlightenment.
- Bodhisattva delays achieving his own salvation to help all sentient beings on their path to it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Pala period is the most significant phase in the history of Buddhism in India. Enumerate. (2020)


Indian Polity
Parakram Diwas 2024
For Prelims: Parakram Diwas, Bharat Parv, Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose, Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar-2024, Vivekananda's teachings.
For Mains: Parakram Diwas 2024, Modern Indian history from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present – significant events, personalities, and issues.
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister (PM) of India has participated in Parakram Diwas (23rd January 2024) Celebrations at Red Fort to mark the birth anniversary of Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose.
- The PM has also launched Bharat Parv (organised by the Ministry of Tourism), a nine-day event to showcase India's rich diversity and exhibit different cultures.
- On the Occasion of Parakram Diwas, the Centre has announced Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar-2024, to honor the invaluable contribution rendered by individuals and organisations in the field of Disaster Management.
What is Parakram Diwas?
- Initiated in 2021, Parakram Diwas is an annual celebration in India commemorating the birth anniversary of Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose.
- The term "Parakram" translates to courage or valour in Hindi, reflecting the strong and courageous spirit of Netaji and those who fought for India's freedom.
- The celebrations typically include various events and activities that highlight the historical significance of Netaji's role in the freedom struggle.
- The comprehensive celebration is being organised by the Ministry of Culture in collaboration with its allied institutions such as the Archaeological Survey of India, National School of Drama, Sahitya Akademi, and the National Archives of India.
- As part of the program, the event will host a rich array of activities that delve into the profound legacy of Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose and the Azad Hind Fauj.
- Marking Netaji’s 125th birth anniversary, in 2022, the hologram was installed, near India Gate, where a statue of King George V had stood till its removal in 1968.
- Later the hologram of Netaji replaced by a grand statue on 8th September 2022 near India Gate in New Delhi.
- Marking Netaji’s 125th birth anniversary, in 2022, the hologram was installed, near India Gate, where a statue of King George V had stood till its removal in 1968.
What is Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar?
- Field Recognised:
- The Government of India instituted Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskaar (SCBAPP) to recognise the excellent work done by the individuals and institutions in the field of disaster management.
- Administered By:
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA was established under the Ministry of Home Affairs under the Disaster Management Act, 2005).
- Award:
- The awards are announced on the birth anniversary of Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose on 23rd January every year.
- In addition to a certificate, these awards carry a cash award of Rs. 51 lakhs for an Institution and Rs. 5 lakhs for an Individual.
- The Institution has to utilize the cash prize for Disaster Management related activities only.
- Eligibility:
- Only Indian nationals and Indian institutions can apply for the award.
- The nominated individual or institution should have worked in any area of disaster management like Prevention, Mitigation, Preparedness, Rescue, Response, Relief, Rehabilitation, Research, Innovation or early warning in India.
- SCBAPP- 2024: The 60 Parachute Field Hospital, Uttar Pradesh, has been selected for the Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar-2024 for its excellent work in disaster management, particularly in providing medical assistance during various natural calamities and crises, both nationally and internationally.
- The hospital's work during events like the Uttarakhand floods (2013), Nepal Earthquake (2015), and the Turkey and Syria earthquake (2023) is highlighted as examples of its exceptional service.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q1. In the context of Colonial India, Shah Nawaz Khan, Prem Kumar Sehgal and Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon are remembered as (2021)
(a) leaders of Swadeshi and Boycott Movement
(b) members of the Interim Government in 1946
(c) members of the Drafting Committee in the Constituent Assembly
(d) officers of the Indian National Army
Ans: (d)
- Prem Kumar Sehgal, Shah Nawaz Khan and Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon were the second-tier commanders of the Indian National Army (INA). They underwent court-martial procedure by the British at Red Fort in 1945 and were sentenced to death. However, following the widespread protests and unrest in India, they had to be released.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q2. During the Indian Freedom Struggle, who of the following raised an army called ‘Free Indian Legion’? (2008)
(a) Lala Hardayal
(b) Rashbehari Bose
(c) Subhas Chandra Bose
(d) V.D. Savarkar
Ans: (c)
- The Free Indian Legion was an infantry regiment formed by Indian volunteers. The legion was made up of Indian prisoners of wars and expatriates in Europe.
- The Indian Independence leader, Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose formed this legion with the help of German Government to fight against the British.
- The legion is also known as “Tiger Legion“.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains:
Q. Highlight the difference in the approach of Subhash Chandra Bose and Mahatma Gandhi in the struggle for freedom. (2016)


Governance
Cancellation of FCRA Registration of NGOs
For Prelims: Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, NGOs, Companies Act, 2013, Indian Trusts Act, 1882, Societies Registration Act, 1860, NGO-DARPAN Platform.
For Mains: Regulation of NGOs in India, Major Provisions of FCRA.
Why in News?
The cancellation of Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, 2010 (FCRA) registrations for two prominent non-governmental organisations (NGOs) - the Centre for Policy Research (CPR) and World Vision India (WVI) - has sparked discussions about the regulatory landscape governing foreign contributions in India.
What led to the Cancellation of the Registrations of CPR and WVI?
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) accused CPR of redirecting foreign donations to support protests and legal challenges against development projects, claiming misuse of funds to impact India's economic interests.
- The allegation includes the violation of FCRA norms through the production of current affairs programs, citing CPR's report on air pollution as an example.
- The MHA asserts that publishing such programs with foreign funds contravenes Section 3 of the FCRA.
- The allegation includes the violation of FCRA norms through the production of current affairs programs, citing CPR's report on air pollution as an example.
- Additionally, the registration of World Vision India was revoked for alleged FCRA violations spanning from 2012-13 to 2020-21.
- WVI is the recipient of the highest amount of foreign donations among all NGOs registered under the Act in 1986.
What is the FCRA?
- About: The FCRA was enacted in 1976 during the Emergency period due to concerns about foreign interference in India's affairs through financial support to independent organisations.
- It was designed to regulate foreign donations to prevent any adverse impact on internal security, ensuring alignment with the principles of a sovereign democratic republic.
- Evolution of FCRA:
- 2010 Amendment: Enacted to streamline regulations governing the acceptance and use of foreign contributions by specific individuals or associations, and to forbid such contributions for activities harmful to national interests.
- 2020 Amendment:
- Providing Aadhaar numbers of all key functionaries of NGOs, receipt of foreign contribution only through designated FCRA bank accounts with the State Bank of India
- Complete ban on domestic transfer of foreign funds
- Reduction of administrative expense limit from 50% to 20%
- Applicability: FCRA mandates registration for all associations, groups, and NGOs intending to receive foreign donations.
- Initially valid for 5 years with the possibility of renewal upon compliance with prescribed norms.
- Purposes of Foreign Contributions: Registered associations can receive foreign contributions for social, educational, religious, economic, and cultural purposes.
- Monitoring Authority: Ministry of Home Affairs
- In 2015, the MHA mandated NGOs to operate accounts in banks with core banking facilities for real-time security access.
- In 2023, the MHA amended rules for FCRA-registered NGOs, now necessitating the disclosure of assets created using foreign funds in their annual returns.
How NGOs are Regulated in India?
- About:
- As defined by the World Bank, NGOs refers to not-for-profit organisations that pursue activities to relieve suffering, promote the interests of the poor, protect the environment, provide basic social services, or undertake community development.
- However, the term NGO in India denotes a wide spectrum of organisations which may be non-governmental, quasi or semi governmental, voluntary or non-voluntary etc.
- As defined by the World Bank, NGOs refers to not-for-profit organisations that pursue activities to relieve suffering, promote the interests of the poor, protect the environment, provide basic social services, or undertake community development.
- Registration and Regulation: Majorly, NGOs can register as either trusts, societies, or companies under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013. Each form has its own set of rules and regulations for registration and governance.
- Trusts: Governed by the Indian Trusts Act, 1882, or equivalent state laws, requiring registration with the Charity Commissioner's office.
- Societies: Registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, or its state-specific variations, with the Registrar of Societies.
- Section 8 Companies: Registered similar to commercial companies but with non-profit objectives.
- NGO-DARPAN Platform: It provides space for interface between NGOs and Central Ministries / Departments / Government Bodies.
- This is a free facility offered by the NITI Aayog in association with National Informatics Centre to bring about greater partnership between government & voluntary sector and foster better transparency, efficiency and accountability.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Mains
Q. Can Civil Society and Non-Governmental Organisations present an alternative model of public service delivery to benefit the common citizen? Discuss the challenges of this alternative model. (2021)


Important Facts For Prelims
Madhika Language on Brink of Extinction
Why in News?
In the remote colony of Kookanam, near Karivellur grama panchayat, Kerala the Chakaliya community is grappling with the imminent loss of its unique language Madhika.
- There are only two people left, who are the last fluent speakers of Madhika. They fear that with their passing, the language will be lost to the world.
What are the Key Facts about Madhika Language and Chakaliya Community?
- About Madhika Language:
- Madhika is a language with no script and is a blend of Telugu, Tulu, Kannada, and Malayalam. Despite sounding similar to Kannada, it can bewilder listeners due to its diverse linguistic influences.
- Madhika is largely influenced by Havyaka Kannada, an old form of Kannada.
- The neglect of Madhika is attributed to the social stigma associated with the Chakaliya community. They were considered untouchables.
- Due to the lack of documentation (no script) and the passing of older speakers, there is a significant risk that Madhika may not survive beyond individuals.
- About the Chakaliya Community:
- The Chakaliya community was originally nomadic and worshippers of Thiruvenkatramana and Mariamma. They migrated from the hilly regions of Karnataka to northern Malabar centuries ago.
- Originally categorised as a Scheduled Tribe (ST), the community was subsequently reclassified into the Scheduled Caste (SC) group in Kerala.
How is the Linguistic Diversity of India?
- Indian Linguistic Space:
- India has a rich linguistic heritage, with diverse languages and writing systems.
- Writing in India dates back to the days of the Indus Valley Civilization, around four thousand years ago.
- Linguistic Survey:
- During colonial rule the first linguistic survey was conducted during 1894 to 1928 and identified 179 languages and 544 dialects.
- In 1991, the Census of India listed 1576 mother tongues’ with separate grammatical structures and 1796 speech varieties that are classified as other mother tongues’.
- As per UNESCO, any language spoken by less than 10,000 persons is considered “potentially endangered.
- Language Families of India:
- There are major language families in India, including Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Austric, Tibeto-Burman, and others.
- Threat of Extinction:
- As per People's Linguistic Survey of India (PLSI), a linguistic survey by an NGO (Bhasha Research and Publication Centre), there are around 400 languages that are at the risk of extinction in the next 50 years.
- Most of the languages at risk are spoken by marginal tribes, whose children receive little to no education. If they go to school instructions are often provided in one of India’s 22 languages recognized in the Constitution.
- Languages without scripts have greater risk of extinction like the Bhili language.
- As per People's Linguistic Survey of India (PLSI), a linguistic survey by an NGO (Bhasha Research and Publication Centre), there are around 400 languages that are at the risk of extinction in the next 50 years.
- Initiatives Taken to Conserve Threatened Languages:
What are the Constitutional Provisions Related to Languages in India?
- Article 29:
- Protects the interests of minorities, ensuring that all citizens have the right to preserve their distinct language, script, or culture.
- Eighth Schedule:
- Part XVII of the Indian Constitution deals with the official languages. The Eighth Schedule recognizes 22 official languages.
- Six languages in India currently have ‘Classical’ status.
- Part XVII of the Indian Constitution deals with the official languages. The Eighth Schedule recognizes 22 official languages.
- Article 350A:
- Provides that every state must provide primary education in the mother tongue.
- Article 350B:
- Provides for the appointment of a "Special Officer" for linguistic minorities.
- Article 351:
- Gives power to the Union government to issue a directive for the development of the Hindi language.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to India, the terms ‘HaIbi, Ho and Kui’ pertain to (2021)
(a) dance forms of Northwest India
(b) musical instruments
(c) pre-historic cave paintings
(d) tribal languages
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Odisha has a unique place in India due to its vast population of tribals residing in the state. 62 tribal communities live in Odisha which is 22.8% of the total population of Odisha.
- Odisha’s tribal language is divided into 3 main language families. They are Austro-Asiatic (Munda), Dravida and Indo-Aryan. Every tribe has its own language and language family. The languages include:
- Austro-Asiatic: Bhumij, Birhor, Rem (Bonda), Gatah (Didyai), Gutab (Gadaba), Sora(Saora), Gorum (Parenga), Khadia, Juang, Santali, Ho, Mundari, etc.
- Dravida: Gondi, Kui-Kondh, Kuvi-Kondh, Kisan, Koya, Olari, (Gadaba) Parja, Peng, Kudukh (Oraon) etc.
- Indo Aryan: Bathudi, Bhuyan, Kurmali, Sounti, Sadri, Kandhan, Aghria, Desia, Jharia, Halbi, Bhatri, Matia, Bhunjia, etc.
- Out of these languages only 7 have scripts. They are Santali (Olchiki), Saora( Sorang Sampeng), Ho (Warangchiti), Kui (Kui Script), Oraon (Kukhud Tod), Mundari (Bani Hisir), Bhumij (Bhumij Anl). Santali language has been included in the 8th Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q.2 Under which one of the following Constitution Amendment Acts, four languages were added to the languages under the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution of India, thereby raising their number to 22? (2008)
(a) Constitution (Ninetieth Amendment) Act
(b) Constitution (Ninety-first Amendment) Act
(c) Constitution (Ninety-second Amendment) Act
(d) Constitution (Ninety-third Amendment) Act
Ans: C
Mains:
Q. Are we losing our local identity for the global identity? Discuss (2017)


Important Facts For Prelims
Amrit Dharohar Capacity Building Scheme
Why in News?
The Central government is spearheading a significant transformation in the realm of wetland tourism with the 'Amrit Dharohar Capacity Building Scheme'.
- This initiative, launched in June 2023, aims to revolutionize tourism practices at ecologically-sensitive wetlands, particularly Ramsar sites like Odisha's Chilika Lake and Haryana's Sultanpur Bird Sanctuary.
What is Amrit Dharohar Capacity Building Scheme?
- About:
- The 'Amrit Dharohar Capacity Building Scheme' is a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Tourism and the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
- The scheme will be implemented over the next three years (2023 onwards) to encourage optimal use of wetlands, and enhance biodiversity, carbon stock, eco-tourism opportunities and income generation for local communities.
- The primary focus of the Scheme is to strategically transition from high-volume tourism to high-value nature tourism at ecologically-sensitive wetlands.
- Aim:
- The aim is to enhance livelihood opportunities for local communities through harnessing the nature-tourism potential of the Ramsar Sites across the country.
- Implementation:
- The scheme is being implemented in convergence with various Central Government ministries and agencies, State wetland authorities, and a network of formal and informal institutions and individuals, working together for a common cause.
- Pilot Projects and Skill Development:
- Out of 16 identified Ramsar sites, five have been selected for pilot projects under the scheme.
- These pilot sites include Sultanpur National Park (Haryana), Bhitarkanika Mangroves (Odisha), Chilika Lake (Odisha), Sirpur (Madhya Pradesh), and Yashwant Sagar (Madhya Pradesh).
- Training programs for participants are carried under the Alternative Livelihood Programme (ALP) (a 30 hours/15 days training programme) and Paryatan Navik Certificate (boatman certification for tourism).
- Out of 16 identified Ramsar sites, five have been selected for pilot projects under the scheme.
Note
- High-value travellers as those who are likely to spend more, stay longer, and disperse beyond tourist hotspots.
- Nature tourism is based on the natural attractions of an area like birdwatching, photography, stargazing, camping, hiking, hunting, fishing, and visiting parks.
- Nature tourists are experiential tourists who are interested in a diversity of natural and cultural resources.
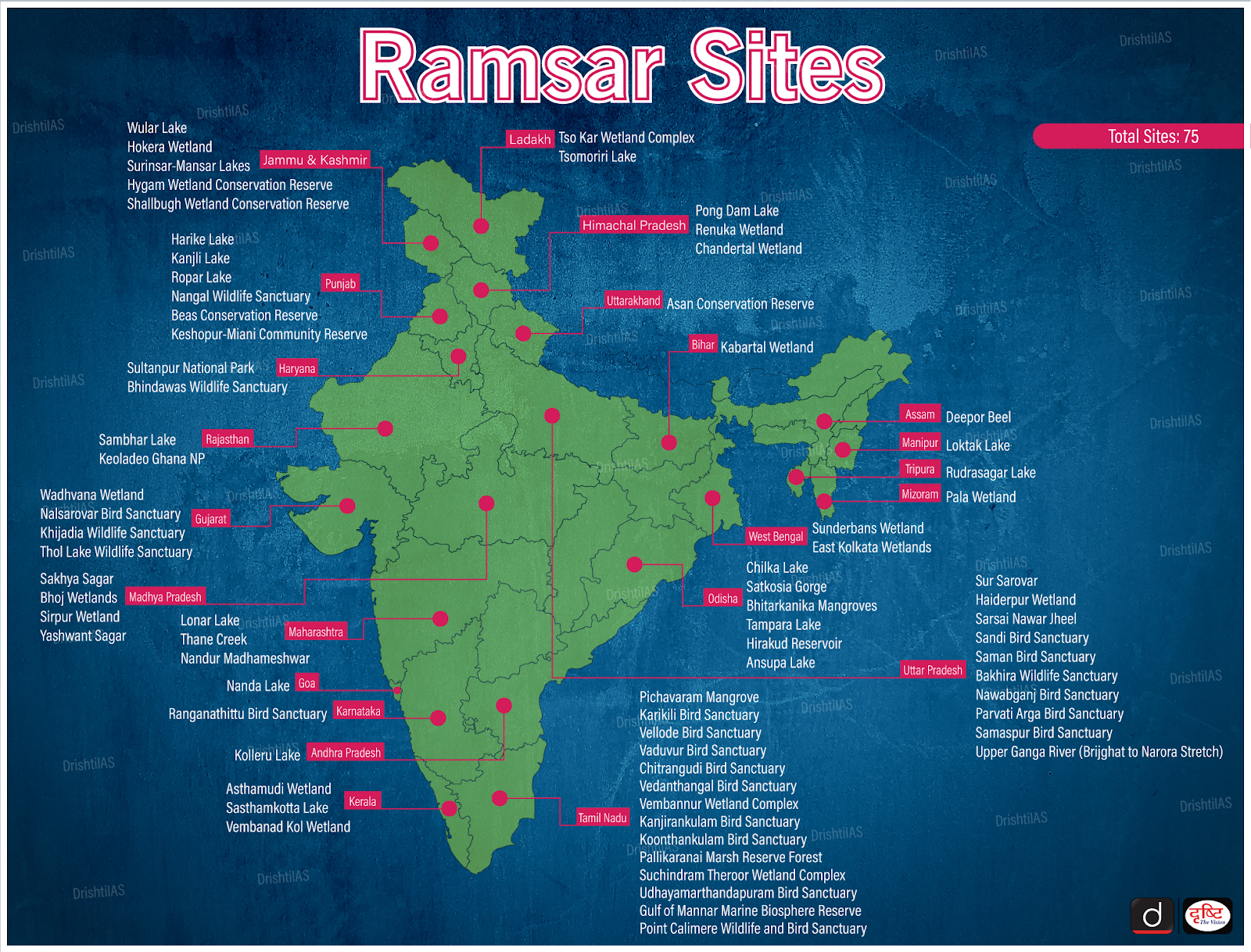
What is a Ramsar Site?
- A Ramsar site is a wetland designated to be of international importance under an environmental treaty signed in February 1971 at Ramsar, Iran under the auspices of UNESCO.
- Ramsar provides for national action and international cooperation regarding the conservation of wetlands, and wise sustainable use of their resources.
- India has 75 Ramsar sites.
 |
 |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. "If rainforests and tropical forests are the lungs of the Earth, then surely wetlands function as its kidneys." Which one of the following functions of wetlands best reflects the above statement? (2022)
(a) The water cycle in wetlands involves surface runoff subsoil percolation and evaporation.
(b) Algae form the nutrient base upon which fish, crustaceans, molluscs, birds, reptiles and mammals thrive.
(c) Wetlands play vital role in maintaining sedimentation balance and soil stabilization.
(d) Aquatic plants absorb heavy metals and excess nutrients.
Ans: (c)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Under Ramsar Convention, it is mandatory on the part of the Government of India to protect and conserve all the wetlands in the territory of India.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 were framed by the Government of India based on the recommendations of Ramsar Convention.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 also encompass the drainage area or catchment regions of the wetlands as determined by the authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


Rapid Fire
Indian Stock Market is Fourth-largest Globally
Recently, the Indian stock market has surpassed Hong Kong to claim the position of the fourth-largest stock market globally.
- Despite a 1.5% dip in domestic indices, the combined value of listed shares on Indian exchanges reached USD 4.33 trillion, exceeding Hong Kong's USD 4.29 trillion, as reported by Bloomberg.
- Factors contributing to India's stock market growth include a strong GDP growth forecast, manageable inflation, political stability, and foreign portfolio investors' inflow.
- The US, China and Japan are the top stock markets in the world.
Read more: Stock Market Regulation


Rapid Fire
Exercise Desert Knight
Recently, the Indian Air Force (IAF) joined forces with the French Air and Space Force (FASF) and United Arab Emirates (UAE) Air Force in Exercise Desert Knight, showcasing collaborative air operations and strengthening diplomatic ties.
- Exercise Desert Knight is a joint military exercise between India, France, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- The exercise took place over the Arabian Sea, with the IAF operating from bases in India.
- The exercise's main goal was to improve cooperation and interoperability between the three air forces.
Read more: Indo-French Joint Exercise Desert Knight-21


Rapid Fire
Rabbit r1
Rabbit Inc. has developed a platform supported by an artificial intelligence model, capable of replicating human smartphone actions and executing them upon request. This device essentially enhances the functionalities of existing voice assistants.
- The r1, the company's first device, is a palm-sized standalone gadget driven primarily by natural language for completing tasks.
- It utilizes a biased-for-action AI model called a large action model (LAM) within the Rabbit OS, leveraging neuro-symbolic programming to enable direct learning from user interactions and task execution, bypassing the translation of text-based requests into Application Programming Interface(APIs), resulting in a more nuanced human-to-machine interaction focused on routine and minimalistic tasks.
- It aims to surpass the constraints of traditional chatbots by mitigating reliance on text-based AI models (large language models) that heavily rely on annotated data, allowing it to perform actionable tasks beyond generating plans.
- The r1 can manage various tasks, such as arranging an Uber ride or organizing an entire vacation, including booking flights and hotels.
Read more: Artificial Intelligence










