Questioning in Parliament
For Prelims: Questioning in Parliament, Lok Sabha Ethics Committee, Central Bureau of Investigation, Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, Member of Parliaments (MPs), Rajya Sabha.
For Mains: Questioning in Parliament, Parliament and State Legislatures.
Why in News?
Recently, one of the Member of Parliaments (MPs) has been questioned by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) and the Lok Sabha Ethics Committee, in her alleged involvement in ‘cash for query’ allegations.
- The member had allowed an individual to use her parliamentary login and password to post questions on her behalf in the Lok Sabha with the intention of furthering a particular agenda or receiving compensation for doing so.
- These allegations raised concerns about the ethical conduct of parliamentarians and the potential misuse of their positions for personal gain.
What is the Procedure for Raising Questions in Parliament?
- Procedure:
- Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha: The procedure for raising questions is governed by Rules 32 to 54 of the “Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha” and Directions 10 to 18 of the “Directions by the Speaker, Lok Sabha‟.
- To ask a question, an MP has to first give a notice addressed to the lower house’s Secretary-General, intimating their intention to ask a question.
- The notice usually contains the text of the question, the official designation of the Minister to whom the question is addressed, the date on which the answer is desired, and the order of preference, in case the MP tables more than one notice of questions for the same day.
- MPs can submit up to five notices of questions (both oral and written) for a single day. Notices exceeding this limit are considered for subsequent days within the same session.
- Notice Period: Typically, the notice period for a question is not less than 15 days.
- MPs can submit their notices either through an online 'Member's Portal' or by using printed forms from the Parliamentary Notice Office.
- The Speaker of Lok Sabha reviews the notices and determines their admissibility based on established rules.
- Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha: The procedure for raising questions is governed by Rules 32 to 54 of the “Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha” and Directions 10 to 18 of the “Directions by the Speaker, Lok Sabha‟.
- Conditions for Question Admissibility:
- Questions must not exceed 150 words and should avoid containing arguments, defamatory statements, or references to personal conduct, except in an official or public capacity.
- Questions that pertain to broad policy issues are not admissible due to the impracticality of addressing complex policies within a brief answer.
- Questions cannot concern matters under judicial consideration or before parliamentary committees. They should also avoid seeking information that could undermine national unity and integrity.
Note
In Rajya Sabha, the admissibility of questions is governed by Rules 47-50 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in the Council of States. Among various norms, the question “shall be pointed, specific and confined to one issue only”.
What are the Categories of Questions?
- Starred Question:
- A starred question is asked by an MP and answered orally by the Minister-in-charge. Each MP is allowed to ask one starred question per day. When a question is answered orally, supplementary questions can be asked thereon.
- UnStarred Question:
- The MP seeks a written answer, which is deemed to be laid on the table of the House by the concerned minister and supplementary questions cannot be followed.
- Short Notice Question:
- These are on an urgent matter of public importance, and an oral answer is sought. For asking such a question, a notice of less than 10 days is prescribed as the minimum period.
- Question to Private Member:
- A question can be addressed to a private member under Rule 40 of Lok Sabha’s Rules of Procedure, or under Rule 48 of Rajya Sabha’s Rules, provided that the question deals with a subject relating to some Bill, resolution or other matter for which that member is responsible.
What is the Significance of Raising Questions?
- Parliamentary Right:
- Asking questions is an inherent and unrestricted parliamentary right of MPs, serving as a tool for legislative control over executive actions.
- Functions of Questioning:
- This exercise allows MPs to acquire information on government activities, critique policies, highlight government shortcomings, and prompt ministers to take steps for the common good.
- Government's Perspective:
- For the government, questions provide insight into public sentiment regarding policies and administration. They can lead to the formation of parliamentary commissions, inquiries, or the enactment of legislation.
Way Forward
- Under Article 75 of the constitution, asking questions in parliament is a constitutional right of a member of the House. Viewed from this angle, the Question Hour in parliament stands on a different footing.
- In a way, every Question Hour is the manifestation of a direct kind of democracy in operation, in the sense that representation of the people directly questions the government on matters of governance, and the government is duty bound to answer the questions in the House.
- The concerned officials also should give a good reason on why a question should be disallowed. The reason also cannot be accessed through RTIs (Right to Information) due to privilege of the House — tough to take it to court as well.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. The Parliament of India exercises control over the functions of the Council of Ministers through (2017)
- Adjournment motion
- Question hour
- Supplementary questions
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- Adjournment motion is introduced in the Parliament to draw attention of the House to a definite matter of urgent public importance. It interrupts the normal business of the House, thereby making it a device of censure against the government. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Question Hour is a tool of “Parliamentary Oversight” over the administration or executive. During Question Hour, the government is answerable for all its acts of omission and commission to the Parliament.
- There are four types of questions: Starred Questions, Unstarred Questions, Short Notice Question and Question to Private Member. Hence, 2 is correct.
- Under the Starred Question, an oral answer is required from the minister and the members are allowed to ask the supplementary questions. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Marine Cloud Brightening
For Prelims: Marine cloud brightening, Coral bleaching, Global warming, Great Barrier Reef, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
For Mains: Mechanism of Marine Cloud Brightening and Related Challenges and Risks, Environmental Pollution & Degradation, Conservation
Why in News?
The concept of marine cloud brightening is gaining prominence recently as a tactic for addressing extreme ocean heat and as a way to reduce coral bleaching and safeguard marine ecosystems.
What is Marine Cloud Brightening?
- About:
- The concept of cloud brightening traces back to British cloud physicist John Latham, who proposed this idea in 1990 as a means to control global warming by altering the Earth's energy balance.
- Latham's calculations suggested that brightening clouds over vulnerable ocean regions could counteract the warming caused by a doubling of pre industrial atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- Mechanism of Marine Cloud Brightening:
- In clean maritime air, clouds primarily form from sulfates and sea salt crystals, which are relatively scarce, leading to larger droplets with lower light reflection.
- Marine cloud brightening (MCB) seeks to boost marine cloud reflectivity (albedo), making clouds whiter and brighter.
- It involves using water cannons or specialized vessels to release fine sea water droplets into the atmosphere.
- As these droplets evaporate, they leave behind salt particles, serving as cloud condensation nuclei that foster the formation of denser, brighter clouds.
Note
Warm clouds consist of numerous small suspended water droplets. These droplets form around tiny airborne particles known as "aerosols," which can be natural (like dust, sea salt, pollen, ash, and sulfates) or human-made (from activities like burning fossil fuels and manufacturing).
- A cloud of many small droplets is brighter than one with fewer large droplets even if both clouds contain the same amount of water overall.
- Potential Benefits:
- MCB has the potential to lower sea surface temperatures in targeted areas, potentially reducing the frequency and severity of coral bleaching events.
- This could provide a lifeline for corals, enabling their survival and recovery while the world transitions away from fossil fuels.
- Researchers are exploring the viability of MCB for the Great Barrier Reef through modeling studies and small-scale experiments.
- The Great Barrier Reef, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, has been particularly vulnerable to coral bleaching, experiencing mass bleaching events in recent years.
- MCB has the potential to lower sea surface temperatures in targeted areas, potentially reducing the frequency and severity of coral bleaching events.
Note
Surprisingly, humanity is already unintentionally engaged in cloud brightening. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change estimates humanity’s unintentional release of aerosols offsets around 30% of the warming effect due to greenhouse gases.
- Sulphates in ship exhaust are such a potent source of aerosols for droplet formation, the passage of ships leaves cloud trails called ship tracks.
- Challenges and Risks Associated with MCB:
- Technical Feasibility: MCB involves the large-scale spraying of seawater into the atmosphere at significant altitudes, which presents engineering complexities in terms of design, cost, maintenance, and operation of the spraying devices.
- Environmental Impacts: Alterations in cloud patterns and precipitation due to MCB could affect regional climate and hydrological cycles, potentially causing unintended consequences like droughts or floods.
- Ethical Issues: MCB raises ethical dilemmas about human intervention in natural processes and the governance and decision-making processes surrounding its implementation.
- Moral Hazard: MCB might lead to complacency among policymakers and the public, diminishing their commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to climate change.
What is Coral Bleaching?
- Coral bleaching is a phenomenon where corals, typically vibrant and colorful, lose their color and turn white due to stress, often caused by elevated sea temperatures.
- This occurs when the corals expel the symbiotic algae living within their tissues, which provide them with nutrients and color.
- Coral bleaching weakens the corals, making them more susceptible to disease, and can lead to their death if the stress continues.
Conclusion
MCB is still in the early stages of research and development, requiring additional studies to assess its feasibility, efficacy, impacts, risks, and governance. It is essential to recognize that MCB is not a standalone solution but a potential complementary measure to help coral reefs confront extreme heat stress in the short term. MCB should be integrated into a comprehensive approach that includes conservation, restoration, adaptation, and innovation to safeguard coral reefs from the impacts of climate change.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. 1 "Biorock technology" is talked about in which one of the following situations?
(a) Restoration of damaged coral reefs
(b) Development of building materials using plant residue
(c) Identification of areas for exploration/extraction of shale gas
(d) Providing salt licks for wild animals in forests/protected areas
Ans: (a)
Q.2 Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Most of the world’s coral reefs are in tropical waters.
- More than one-third of the world’s coral reefs are located in the territories of Australia, Indonesia and Philippines.
- Coral reefs host far more number of animal phyla than those hosted by tropical rainforests.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.3 Which of the following have coral reefs? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Assess the impact of global warming on the coral life system with examples. (2019)
Supreme Court's Ruling Imposes Capital Taxation on Telecos
For Prelims: Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure, Department of Telecommunication, Telecom Licence Fee, Amortization
For Mains: Difference Between Capital and Revenue Expenditure, Mobilization of Resources
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) has held that payment of entry fee as well as variable annual license fee made by telcos will be considered capital expenditure and not revenue expenditure, and taxed accordingly.
What are the Impacts of the SC’s Ruling over Telecom Licence Fee?
- Ruling:
- The SC's judgment stipulates that the payments made by telecom companies to the Department of Telecommunication as entry fees and annual license fees under the (New Telecom) Policy of 1999 are now categorized as capital expenditures and may be amortised in accordance with Section 35ABB of the (Income Tax) Act.
- This means that instead of deducting the entire expenditure all at once, the company will need to deduct a portion of the total fee over each year for tax purposes.
- The SC's judgment stipulates that the payments made by telecom companies to the Department of Telecommunication as entry fees and annual license fees under the (New Telecom) Policy of 1999 are now categorized as capital expenditures and may be amortised in accordance with Section 35ABB of the (Income Tax) Act.
- Impact:
- Change in Accounting Treatment: Telecom companies have traditionally treated license fees as expenses, allowing them to claim deductions on a year-to-date basis for tax calculations.
- However, this ruling mandates a shift in the accounting treatment, requiring license fees to be considered as capital expenses.
- These expenses must be amortized over the license's holding period.
- Initial Impact on Cash Flow: As a direct consequence of the change in accounting treatment, telecom companies may experience a temporary reduction in cash flow.
- Higher EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) and PBT (Profit Before Tax) may result from this shift, but it is likely to be offset over the license's duration.
- Financial Strain: The ruling is expected to affect companies that have incurred substantial expenses to obtain telecom licenses, particularly those already experiencing financial losses.
- Uncertainty About Retrospective Application: The Supreme Court's order did not explicitly address whether the new accounting structure should be applied retrospectively.
- This has raised concerns within the telecom industry, as well as questions regarding tax liabilities for prior periods.
- Change in Accounting Treatment: Telecom companies have traditionally treated license fees as expenses, allowing them to claim deductions on a year-to-date basis for tax calculations.
What is Amortization?
- It is an accounting process used to spread the cost of an intangible asset or a capital expense over its useful life.
- This gradual allocation of expenses helps match the cost of the asset with the revenue it generates over time.
- In simpler terms, it means dividing a large expense into smaller portions and recognizing those portions as expenses on financial statements over a specific period.
- This practice ensures a more accurate representation of the asset's impact on a company's financial statements and tax liability over time.
What is the Difference Between Capital and Revenue Expenditure?
| Aspect | Capital Expenditure | Revenue Expenditure |
| Nature of Expenses | Expenses related to acquiring, improving, or extending long-term assets or investments expected to benefit for more than one financial year. | Day-to-day operational expenses incurred for maintaining and supporting existing assets or services. |
| Accounting Treatment | Capitalized on the balance sheet and recognized over time through amortization or depreciation. | Fully recognized as expenses in the year incurred on the income statement. |
| Tax Treatment | Subject to depreciation or amortization, leading to a delayed tax impact and often lower taxable income in the year of purchase. | Immediately deductible from taxable income, providing an immediate reduction in tax liability. |
| Impact on Profitability | Generally does not significantly impact short-term profitability as costs are spread over several years. | Has an immediate impact on profitability, as expenses are fully recognized in the year incurred. |
| Examples | Acquiring a new manufacturing facility, research and development for a new product, long-term license or franchise. | Routine machinery maintenance, employee salaries, advertising costs, utility bills. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which of the following is/are included in the capital budget of the Government of India? (2016)
- Expenditure on acquisition of assets like roads, buildings, machinery, etc.
- Loans received from foreign governments
- Loans and advances granted to the States and Union Territories
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Distinguish between Capital Budget and Revenue Budget. Explain the components of both these Budgets. (2021)
Test on Crew Escape System
For Prelims: Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Crew Escape System, Human Space Flight Mission, Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1), LVM3 Rocket, GSLV Mk III Rocket, Crew module Atmospheric Re-Entry Experiment (CARE), International Space Station (ISS).
For Mains: Impact of the recent tests of Crew Escape System on India's Gaganyaan Mission, Achievements of Indians in Science and Technology.
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) carried out the first of a series of tests of systems and procedures called the Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1) with the aim to ultimately fulfill the objectives of Gaganyaan Mission perhaps by 2025.
What is the TV-D1 Test?
- About:
- The Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1) demonstrates the performance of the Crew Escape System of the Gaganyaan project.
- The flight is the first of two abort missions to test the safety mechanisms that will allow the Gaganyaan crew to leave the spacecraft in an emergency.
- The Test Vehicle is a single-stage liquid rocket developed for this abort mission. The payloads consist of the Crew Module (CM) and Crew Escape Systems (CES) with their fast-acting solid motors, along with CM fairing (CMF) and Interface Adapters.
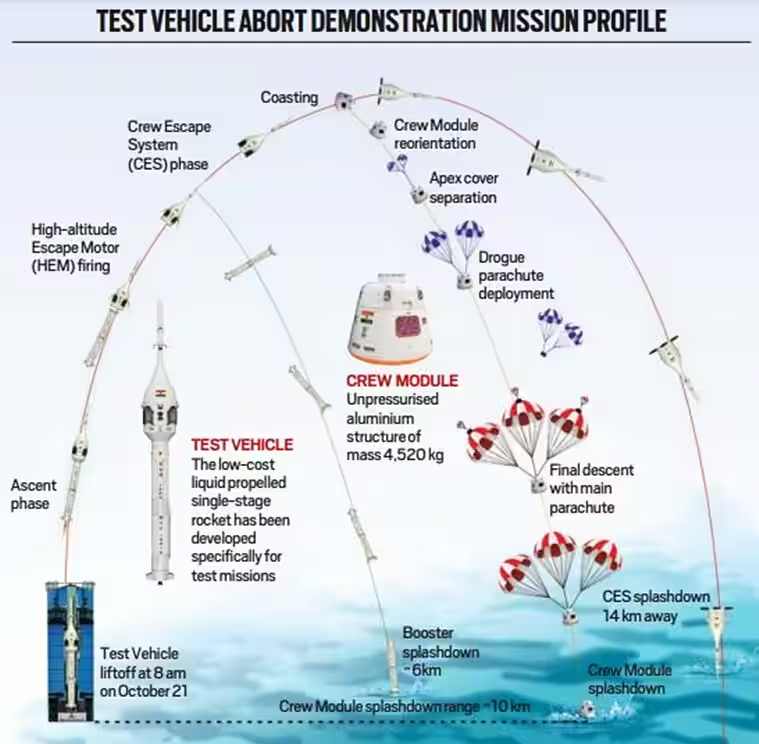
- Mechanism:
- The test exercise will see the rocket rise to an altitude of almost 17 km before an abort signal is triggered, leading to the separation of the crew module, which will descend using a parachute for a splashdown in the Bay of Bengal.
- The rocket, ISRO’s new, low-cost Test Vehicle, will reach a peak relative velocity of 363 metres/ second (about 1307 km/ hr) during the flight and the crew module will be empty for the test.
- Relevance:
- It will demonstrate a basic version of the crew module — the capsule in which the astronauts will be seated during the Gaganyaan human space flight.
- The test will check the functioning of systems for separating the crew module from the rocket in case of a mid-flight emergency (abort mission) and the escape of astronauts.
What is the New Test Vehicle To Be Used in TV-D1?
- Introduction to the New Test Vehicle:
- The ISRO plans to conduct a full-fledged crew module test flight in 2024 using the human-rated LVM3 rocket. However, for the TV-D1 mission, ISRO has developed a low-cost test vehicle specifically designed to evaluate various systems.
- Features of the Test Vehicle:
- The Test Vehicle incorporates existing liquid propulsion technology.
- Notable innovations include the throttleable and restartable L110 Vikas engine, a core component of the LVM3 rocket's second stage, which offers better control over propellant usage.
- The Test Vehicle incorporates existing liquid propulsion technology.
- Cost-Effective Alternative to GSLV Mk III:
- Previous crew module test flights, like the Crew module Atmospheric Re-Entry Experiment (CARE) in 2014, utilized expensive GSLV Mk III rockets, costing Rs 300-400 crore each. In response to cost concerns, ISRO has introduced the more economical Test Vehicle.
- Utilization of the Test Vehicle for Various Space Technologies:
- The Test Vehicle will serve as a platform for testing and developing multiple space technologies, including Scramjet engine technology for reusable space launch vehicles.
- ISRO recognizes the significance of testing the Crew Escape System of the Gaganyaan mission multiple times without incurring substantial expenses, making the Test Vehicle a valuable asset for future space endeavors.
What is the Present Crew Escape System (CES) in Gaganyaan Mission?
- Lessons From Failure of Russian Soyuz Rocket :
- In 2018, a Soyuz FG rocket failure prompted an emergency crew escape during Expedition 57 to the International Space Station( ISS) . At 50 km altitude, the crew module separated from the rocket, ensuring the safe return of astronauts. This marked the first mid-flight Soyuz rocket failure since 1975 and the initial failure of the Soyuz FG in 55 launches.
- Ensuring Crew Safety in Gaganyaan:
- ISRO prioritizes crew safety in the Gaganyaan project and seeks to extend the 2022 deadline for a secure mission. The crew module must withstand high heat and pressure conditions and feature a reliable escape system in emergencies.
- ISRO is developing life support systems and an integrated health management system to detect anomalies endangering astronauts and initiate mission aborts.
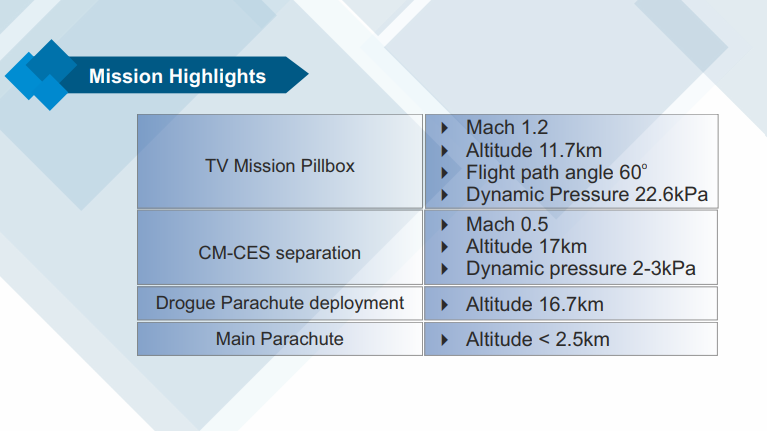
- TV-D1 Mission Stages:
- In the TV-D1 flight, the Crew Escape System separates from the Test Vehicle around 11.7 km altitude. After approximately 90 seconds, the crew module detaches, deploys parachutes, and descends slowly over seven minutes.
- The Indian Navy will recover the crew module from the Bay of Bengal, marking a crucial milestone in the Gaganyaan program's development.
- Gaganyaan Mission Status:
- The Gaganyaan mission's timeframe is currently 2024 or later, emphasizing safety over haste. An unmanned mission is planned for the beginning of the following year, with abort missions in the same year.
- The manned mission is expected by late 2024 or early 2025, depending on various scenarios.
- ISRO has already achieved human rating for critical rocket components, and Crew Escape System design is obliged to ensure the safeguard mechanism for astronauts over deadline.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Line of Duty Compensation for Agniveer
For Prelims: Compensation to Agniveer, Agnipath scheme, Seva Nidhi, Three services (Army, Navy and Airforce), Armed Forces Battle Casualty Fund.
For Mains: Compensation to Agniveer after Death in Line of Duty, Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes.
Why in News?
Recently, an Agniveer passed away on duty at the Siachen glacier, which sparked a controversy regarding the entitlement of pensions and Compensation for the families of Agniveers.
- In 2022, the government unveiled the Agnipath Scheme for recruiting soldiers (Agniveers) across the Three services (Army, Navy and Airforce).
What Compensation is Promised After the Demise of an Agniveer?
- Seva Nidhi:
- An Agniveer's family is entitled to several forms of compensation, including a non-contributory insurance sum of Rs 48 lakh, Rs 44 lakh as compensation, and 30% of Seva Nidhi contributed by the Agniveer, with an equal matching contribution by the government.
- Additionally, interest accrues on these amounts.
- Armed Forces Battle Casualty Fund:
- The family also receives pay for the remaining tenure from the date of death, amounting to over Rs 13 lakh, as well as a contribution of Rs 8 lakh from the Armed Forces Battle Casualty Fund.
- Army Wives Welfare Association:
- To provide immediate financial assistance, the Army Wives Welfare Association offers Rs 30,000 to the next of kin.
What is the Agnipath Scheme?
- About:
- It allows patriotic and motivated youth to serve in the Armed Forces for a period of four years. Youth will be able to be recruited into the army for a short duration.
- Under the new scheme, around 45,000 to 50,000 soldiers will be recruited annually, and most will leave the service in just four years.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- It is only for personnel below officer ranks (those who do not join the forces as commissioned officers).
- Commissioned officers are the army's highest ranked officers.
- Commissioned officers hold an exclusive rank in the Indian armed forces. They often hold a commission under the president's sovereign power and are officially instructed to protect the country.
- Aspirants between the ages of 17.5 years and 21 years will be eligible to apply.
- It is only for personnel below officer ranks (those who do not join the forces as commissioned officers).
- Objectives:
- It aims at providing an opportunity to the patriotic and motivated youth with the ‘Josh’ and ‘Jazba’ to join the Armed Forces.
- It is expected to bring down the average age profile of the Indian Armed Forces by about 4 to 5 years.
- The scheme envisions that the average age in the forces is 32 years today, which will go down to 26 in six to seven years.
- Benefits for Agniveers:
- Upon the completion of the 4-years of service, a one-time ‘Seva Nidhi’ package of Rs 11.71 lakhs will be paid to the Agniveers that will include their accrued interest thereon.
- They will also get a Rs 48 lakh life insurance cover for the four years.
- In case of death, the payout will be over Rs 1 crore, including pay for the unserved tenure.
- The government will help rehabilitate soldiers who leave the services after four years.
What are the Concerns Related to Agniveers?
- Difficult to Find Another Job:
- The 'Agnipath' initiative paves the path for the enlistment of approximately 45,000 personnel into the Army, Navy, and Air Force in its inaugural year.
- However, these recruits will serve on a temporary four-year contract. Upon the fulfillment of their contract, 25% of them will be retained, while the remaining will exit the armed forces.
- No Pension Benefit:
- Those hired under the 'Agnipath' scheme will be given a one-time lump sum of a little more than Rs 11 lakh when they end their four-year tenure.
- However, they do not receive any pension benefits. For most, seeking a second job is essential to support themselves and their families.
- Training May Remain Unutilized:
- Forces will lose experienced soldiers.
- The jawans joining the Army, Navy and Air Force will be given technical training so that they are able to support the ongoing operations.
- Women are yet to be inducted under this scheme.
Way Forward
- Government should consider relaxation in mandatory licensing regulations for Agniveers to attract more of them to invest in starting up a business unit.
- It will act as a double benefit move of providing entrepreneurial opportunity and growth in the economy.
- Attractive interest rates on deposits for Agniveers would stimulate savings and benefit banks.
- For those Agniveers who want to pursue higher education, a relaxation in the admission criteria (relaxation in cut off etc) will prove to be a major attraction.
- Highly qualified and disciplined Agniveers will have the ability to take up ample opportunities available to them.
India’s Position in Global Economic Growth
For Prelims: International Monetary Fund (IMF), Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Headline Inflation, MGNREGA, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Fiscal Deficit
For Mains: Issues and concerns in achieving its potential growth while achieving the fiscal deficit targets.
Why in News?
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), India’s contribution to global economic growth is expected to rise by 2%, as 16% contribution will grow to 18% in the next five years due to India growing faster.
What are the Factors Contributing to India’s Projected Growth?
- Monsoon:
- While the overall rainfall was 6% below the expected during the monsoon season (due to 36% deficit rains in August), the spatial distribution is quite even. Out of 36 states/UTs, 29 received normal/above-normal rains.
- The SBI Monsoon Impact Index, which considers the spatial distribution, has a value of 89.5, faring much better than the full season index value of 60.2 in 2022.
- Continuous Thrust on Capital Expenditure:
- During the first five months of the current year (2023), the capital expenditure of the states as a percentage of the budgeted target is at 25%, while the Centre’s is at 37%, which is higher than the previous years and reflecting renewed capital generation.
- New Company Registrations:
- The robust new companies’ registration depicts strong growth intentions. Around 93,000 companies were registered in the first half of 2023-24 as compared to 59,000 five years back.
- It is interesting to note that the average daily registration of new companies increased to 622 in 2023-24 (an increase of 58%) from 395 in 2018-19.
- The robust new companies’ registration depicts strong growth intentions. Around 93,000 companies were registered in the first half of 2023-24 as compared to 59,000 five years back.
- Credit Growth:
- All scheduled commercial banks' (SCBs) credit growth (year-on-year) has been accelerating since early 2022. Aggregate deposits grew by 13.2% and credit by 20% till September. In the coming months, the Government expects credit demand to remain robust due to the festive season.
- Formalization of the Economy:
- The growth in credit is attributed to the formalization of the Indian economy over the past decade. People with no previous credit history are increasingly becoming integrated with the banking system.
- Approximately 40% of new credit accounts added in the last nine years are from individuals who had no prior credit history. This group contributes to at least 10% of the incremental credit growth.
What are the Challenges Faced by India in Achieving its Projected Growth?
- Weak Demand:
- The demand for goods and services in India has been stagnant or declining due to various factors, such as low income growth, high inflation, unemployment, and the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- This has affected the consumption and investment levels in the economy, and reduced the tax revenue for the government.
- Unemployment:
- Despite rapid economic growth, unemployment remains a serious issue in both rural and urban areas. The Covid-19 pandemic has worsened the situation, as many businesses have shut down or reduced their operations, leading to job losses.
- According to the National Statistical Office’s (NSO) Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) report for the year 2021-22, the unemployment rate for 2021-22 was 4.1%.
- Despite rapid economic growth, unemployment remains a serious issue in both rural and urban areas. The Covid-19 pandemic has worsened the situation, as many businesses have shut down or reduced their operations, leading to job losses.
- Poor Infrastructure:
- India lacks adequate infrastructure, such as roads, railways, ports, power, water, and sanitation, which hampers its economic development and competitiveness.
- According to the World Bank, India’s infrastructure gap is estimated to be around $1.5 trillion. Poor infrastructure also affects the quality of life and health of the people, especially in rural areas.
- Balance of Payments Deterioration:
- India has been running a persistent current account deficit, which means that its imports exceed its exports. This reflects its dependence on foreign goods and services, especially oil and gold, and its low export competitiveness.
- India’s exports and imports decreased by 6.59% and 3.63%, respectively, in 2022 over 2021. Given this pace, It will be difficult to achieve the USD 2 trillion export target by 2030.
- Geopolitical Tensions: India's geopolitical relationships, including border disputes, can impact regional stability and potentially affect economic prospects.
- India is increasingly vulnerable to global economic uncertainties, including ongoing wars and conflicts that may lead to crude oil inflation and supply shortages.
- Trade Imbalances: India faces trade imbalances with some of its major trading partners, which can impact its economic growth and stability.
- India is increasingly vulnerable to global economic uncertainties, including ongoing wars and conflicts that may lead to crude oil inflation and supply shortages.
Way Forward
- Boosting Private Investment: Private investment is a key driver of economic growth, as it increases productivity, innovation and competitiveness. The government has taken several initiatives to improve the ease of doing business, reduce corporate tax, provide credit guarantees, and attract foreign direct investment.
- However, more reforms are needed in areas such as land, labour and logistics to reduce the cost and risk of doing business in India.
- Increasing Competitiveness: India needs to enhance its competitiveness in the global market by diversifying its exports, improving its infrastructure, promoting innovation and digitalization, and integrating with regional and global value chains.
- The government has announced several schemes to support manufacturing, such as Production Linked Incentive (PLI), Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP), and Make in India.
- However, these schemes need to be complemented by trade liberalization and regulatory simplification to ensure a level playing field for domestic and foreign firms.
- Promoting Green Growth: India has committed to reduce its carbon intensity and increase its renewable energy capacity as part of its climate change goals. The government has also introduced green bonds to finance green infrastructure projects.
- However, more efforts are needed to address the environmental challenges such as air pollution, water scarcity, waste management and biodiversity loss that pose a threat to India’s growth and well-being.
- Maintain Stability in the Economy: India could maintain a stable and low inflation rate, which can foster confidence and investment. India could also ensure adequate liquidity and credit availability for productive sectors, especially for small and medium enterprises. India could also develop its financial markets and institutions to facilitate savings and investment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q 1. A decrease in tax to GDP ratio of a country indicates which of the following? (2015)
- Slowing economic growth rate
- Less equitable distribution of national income
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q 2. Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments. (2019)
Q 3. Do you agree that the Indian economy has recently experienced V-shaped recovery? Give reasons in support of your answer. (2021)
Large Language Models
For Prelims: ChatGPT, Artificial Intelligence, Large Language Models (LLMs), Principal Scientific Advisor, Deep Tech, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT)
For Mains: Benefits and the prospects of Large Language Models ( LLMs) on India’s scientific and technological prowess.
Why in News?
As per Principal Scientific Advisor, India will set up a “high powered committee” to explore the development of Large Language Models (LLMs), tools that harness Artificial Intelligence to create applications that can understand and process human language.
What are Large Language Models ?
- About:
- LLMs : LLMs are a specific class of generative AI models that are trained to understand and generate human-like text.
- These models are built using deep learning techniques, particularly using neural networks.
- They can generate coherent and contextually relevant text given a prompt or input.
- One of the most well-known examples of LLMs is OpenAI's GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer).
- LLMs : LLMs are a specific class of generative AI models that are trained to understand and generate human-like text.
- Generative AI:
- Generative AI refers to the subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating systems capable of generating content that is similar to what a human might produce.
- These systems learn from patterns in existing data and then use that knowledge to produce new, original content.
- This content can take various forms, such as text, images, music, and more.
- US-India Collaboration:
- India and the U.S. have a great relationship now, which is perfect for deep tech cooperation. India’s draft policy on deep tech says that Startup India’s database lists over 10,000 startups in different deep tech areas, which aligns well with the U.S.-India partnership.
What is Deep Tech?
- About:
- Deep tech or deep technology refers to a class of startup businesses that develop new offerings based on tangible engineering innovation or scientific discoveries and advances.
- Usually, such startups operate on, but are not limited to, agriculture, life sciences, chemistry, aerospace and green energy.
- Deep tech fields like Artificial Intelligence, advanced materials, blockchain, biotechnology, robotics, drones, photonics, and quantum computing are moving more and more quickly from early research to market applications.
- Characteristics of Deep Tech:
- Impact: The deep tech innovations are very radical and disrupt an existing market or develop a new one. Innovations based on deep tech often change lives, economies, and societies.
- Time & Scale: The time required for deep technology to develop the technology and reach the market-ready maturity is way more than shallow technology development (like mobile apps and websites). It took decades for artificial intelligence to develop and it is still not perfect.
- Capital: Deep tech often requires a lot of early-stage funding for research and development, prototyping, validating hypotheses, and technology development.
- Challenges Faced by Deep Tech:
- For deep-tech startups, funding is one of the biggest challenges. Less than 20% of startups receive financing. Government funds are underutilized, and domestic capital is lacking for such startups.
- Talent and market access, research guidance, investors’ understanding of deep-tech, customer acquisition and cost for talent are the major challenges faced by them.
What is the Draft National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP), 2023?
- About:
- The policy seeks to bolster research and development in deep tech start-ups, which work on fundamental and technical problems, unlike firms that monetise technology with distinguished business models.
- The policy also seeks to find approaches to provide financing to deep tech start-ups at critical moments, such as before they go to market with their products or ideas.
- Facilitate Startups:
- The policy seeks to simplify the intellectual property regime for such start-ups, ease regulatory requirements, and proposes a slew of measures to promote these firms.
- NDTSP suggests that an Export Promotion Board be created to ease barriers of entry for Indian deep tech start-ups into foreign markets, and that clauses to ease such market access be included in foreign trade agreements.
- Recommendations:
- Policy suggests the creation of an “Inter Ministerial Deep Tech Committee” to regularly review the requirements of enabling the deep tech ecosystem to function better.
- The policy restates the government’s disappointment with international agreements that it argues have left India on the backfoot in terms of manufacturing and development power.
- The need of the hour is a coordinated, comprehensive push to optimally engage with international partners and multilateral institutions to push the Indian Deep Tech Ecosystem.
Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India
- India has had a Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) since 1999. Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam was the first PSA from 1999-2001.
- The PSA’s office aims to provide pragmatic and objective advice to the Prime Minister and the cabinet in matters of Science and Technology. The Office of PSA was placed under the Cabinet Secretariat in 2018.
- The Prime Minister's Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC) is an overarching Council that facilitates the PSA’s Office to assess the status in specific science and technology domains, comprehend challenges in hand, formulate specific interventions, develop a futuristic roadmap and advise the Prime Minister accordingly.
- The Office of PSA, supported by the project management team at Invest India, is facilitating the delivery and progress of all Nine national missions under PM-STIAC. Four of the nine missions, Deep Ocean Mission, Natural Language Translation mission, AI mission, and Quantum Frontier mission have been approved.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q 2. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Exercise MILAN 2024
The Mid Planning Conference (MPC) of MILAN 24 (Multilateral Naval Exercise - 2024), to be hosted by the Indian Navy at Visakhapatnam during Feb 2024, was conducted by the Eastern Naval Command (ENC).
- MILAN is a biennial multilateral naval exercise incepted by Indian Navy in 1995 at Andaman and Nicobar Command.
- Starting with the participation of only four countries, viz Indonesia, Singapore, Sri Lanka and Thailand, in the 1995 edition, the exercise has since transitioned leaps and bounds in terms of number of participants and complexity of exercises.
- Originally conceived in consonance with India’s ‘Look East Policy’, MILAN expanded in ensuing years with India’s ‘Act East policy’ and SAGAR Initiative, to include participation from island nations in the Western IOR (Indian Ocean Region) as also IOR littorals.
Read More: Andaman and Nicobar Command
UN's 78th Anniversary
Recently, the World has celebrated the 78th anniversary of the United Nations (UN) on 24th October 2023.
- United Nations Day is an annual event that commemorates the anniversary of the entry into force of the UN Charter in 1945. It is celebrated on 24th October to promote awareness and understanding of the UN's goals and achievements.
- The forerunner of the United Nations was the League of Nations, an organization conceived in circumstances of the First World War, and established in 1919 under the Treaty of Versailles "to promote international cooperation and to achieve peace and security."
- The UN has 6 components which were established in 1945 such as the General Assembly, Security Council, Economic and Social Council, Trusteeship Council, International Court of Justice, UN Secretariat.
Read More: Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), International Maritime Organization (IMO)
Exercise Harimau Shakti 2023
The joint bilateral training exercise between India and Malaysia, "Exercise Harimau Shakti 2023," commenced at Umroi Cantonment, featuring a Battalion of the Rajput Regiment from the Indian contingent and Malaysian Army's 5th Royal Battalion.
- This exercise, involves establishing a Joint Command Post, integrated surveillance grid, and Joint Surveillance Centre, emphasizing joint force deployment in various environments, intelligence operations, the use of drones and helicopters, casualty management, and logistics.
- The exercise underscores the strengthening of defense cooperation between the Indian and Malaysian armies, further fostering bilateral relations between the two nations.
Read more: India-Malaysia Defence Cooperation
National Cooperative Exports Limited
The National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL), established as an umbrella organization for cooperative sector exports, has made substantial progress, receiving orders valued at Rs 7,000 crore.
- The Union Minister of Cooperation emphasized that a significant portion of export profits, approximately 50%, will directly benefit farmers through the NCEL.
- The NCEL, an umbrella body for cooperative sector exports registered under the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act, 2002.
- NCEL is launched in the cooperative sector with 6 objectives of increasing exports, prospering the farmer, changing the crop pattern, providing a global market for organic products, gaining a place for India in the global market for biofuel and strengthening the cooperative sector.
Read more: Promoting Cooperatives in India