Social Justice
World Day of Social Justice 2025
For Prelims: World Day of Social Justice, International Labour Organization (ILO), Denotified and Nomadic Tribes (DNTs), Fundamental Rights, Inequality, PM-AJAY, SRESHTA, NAMASTE, SMILE, PM-DAKSH Yojana.
For Mains: World day of social justice and its significance, Steps taken in India to ensure social justice in India.
Why in News?
The United Nations (UN) observed World Day of Social Justice (WDSJ) on 20th February 2025 advocating against poverty, exclusion, and unemployment while promoting equality and solidarity.
- The 2025 theme of WDSJ, “Empowering Inclusion: Bridging Gaps of Social Justice,” focuses on inclusive policies and social protection, while highlighting the importance of “Strengthening a Just Transition for a Sustainable Future.”
What is World Day of Social Justice?
- About: It is an initiative of the UN specifically led by the International Labour Organization (ILO) to promote social justice, equality, human rights, and fair opportunities for all.
- It was designated by the UN General Assembly on 26th November 2007.
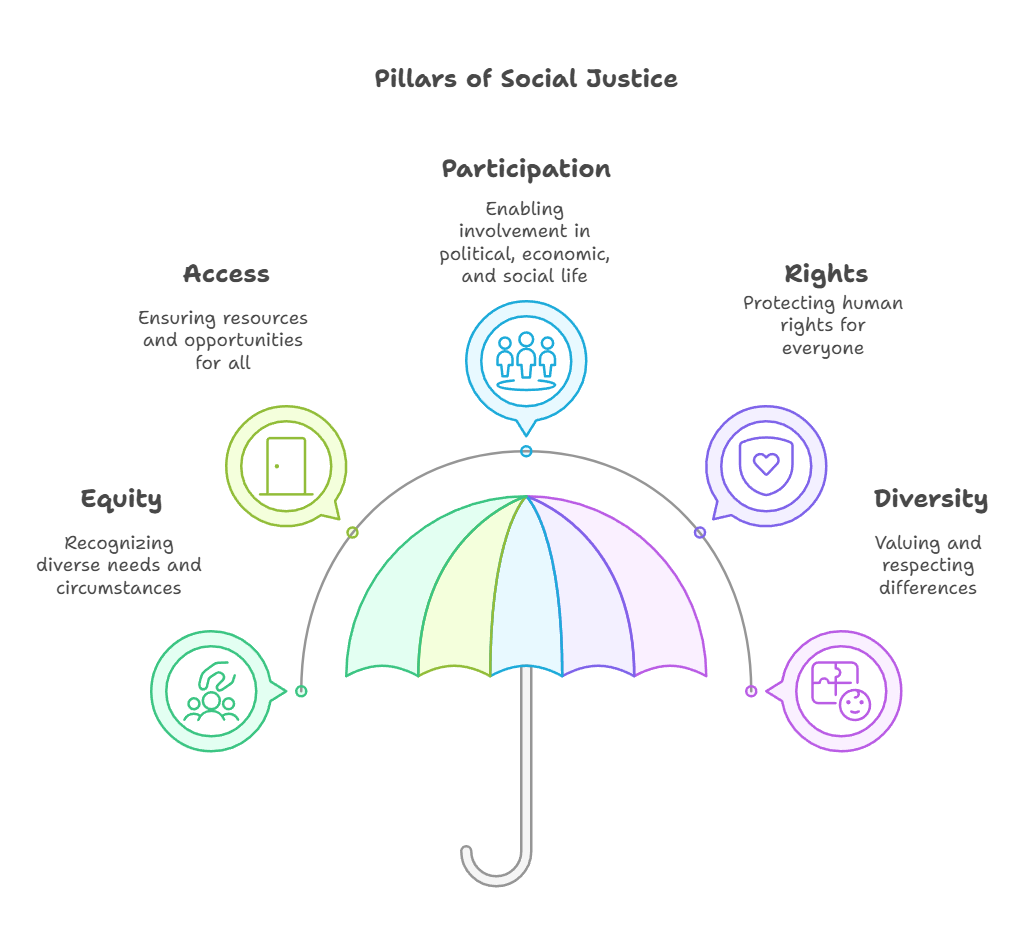
- Pillars of Social Justice:
- Role of ILO: ILO unanimously adopted the Declaration on Social Justice for a Fair Globalization on 10th June 2008 in response to the World Day of Social Justice.
- It expands upon the Philadelphia Declaration 1944 and the Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work 1998.
- In 2009, ILO launched Social Protection Floors that ensure basic social security to prevent or reduce poverty.
- Social Justice in India: In India, MoSJE is the nodal agency for uplifting vulnerable communities, including:
- Scheduled Castes, Other Backward Classes, and Senior Citizens
- Victims of Alcoholism and Substance Abuse
- Transgender Persons, and Denotified and Nomadic Tribes (DNTs),
- Economically Backward Classes (EBCs), and the Economically Weaker Section (EWS).
- Significance:
- Globalization: The declaration redefined the ILO’s role in globalization, ensuring social justice remains central to economic policies.
- Alignment with UN Goals: It supports the UN’s vision of decent work, fair globalization, fundamental rights, social protections, and productive social dialogue.
- Global Stability: Social justice is essential for global peace and security which remains threatened by labor insecurity, inequality, and social contract breakdowns.
- Social Justice: Achieving social justice requires fundamental freedoms, human rights, and economic stability.
- Challenges: Persistent issues such as financial crises, insecurity, poverty, exclusion, and inequality continue to hinder social justice on a global scale.
What are India’s Constitutional Provisions on Social Justice?
- Preamble: It ensures social, economic, and political justice, guarantees equality of status and opportunity, and promotes fraternity to uphold individual dignity and national unity.
- Fundamental Rights:
- Article 23: It prohibits human trafficking and forced labour, making such practices punishable by law.
- Article 24: It bans child labour in hazardous occupations, protecting children’s rights to safety and education.
- Directive Principles of State Policy:
- Article 38: It directs the State to reduce social and economic inequalities.
- Article 39: It ensures equal livelihood, fair wages, and protection from exploitation.
- Article 39A: It guarantees free legal aid for disadvantaged people.
- Article 46: It mandates special educational and economic promotion for SCs, STs, and weaker sections to prevent discrimination.
What are Initiatives for Ensuring Social Justice in India?
- PM-AJAY: Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY) supports Scheduled Caste (SC) communities through skill development, income generation, and village infrastructure.
- It has three components i.e., Adarsh Gram development, Grants-in-Aid for socio-economic projects, and hostel construction in higher education institutions.
- SRESHTA: Scheme for Residential Education for Students in High Schools in Targeted Areas (SRESHTA) funds top CBSE/State Board schools for SC students in classes 9-12 and supports NGOs to run residential and non-residential schools and hostels.
- Purple Fests (Festival of Inclusion): It fosters inclusion, dignity, and equal opportunities for persons with disabilities (Divyangjan) promoting solidarity and mutual respect.
- NAMASTE: National Action for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) is a central sector scheme to ensure the safety, dignity, and sustainable livelihood of sanitation workers in urban India.
- It was expanded to include waste pickers as a target group from FY 2024-25.
- SMILE: Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE) scheme is aimed at the rehabilitation of transgender individuals and persons engaged in begging to create Begging-free India.
- It is currently implemented in 81 cities and as of November, 2024, 7,660 beggars were identified, and 970 rehabilitated.
- PM-DAKSH Yojana: Pradhan Mantri Dakshta Aur Kushalta Sampann Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) yojana provides free skill training to SCs, OBCs, EBCs, DNTs, and Safai Karamcharis for economic empowerment.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA): It aims for a drug-free India by targeting 272 high-risk districts through supply control (Narcotics Control Bureau), awareness and demand reduction (MoSJE), and treatment (Ministry of Health).
- Since its launch (15th August 2020), NMBA has reached 13.57 crore people, including 4.42 crore youth, with 3.85 lakh educational institutions participating.
Conclusion
India’s efforts towards social justice are rooted in constitutional provisions and targeted schemes addressing socio-economic disparities. By promoting inclusive policies, skill development, and rehabilitation programs, the government aims to uplift marginalized communities, ensuring dignity, equity, and sustainable livelihoods, aligning with global commitments to social justice and empowerment.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How do constitutional provisions in India support social justice? Discuss with examples of key government initiatives. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Other than the Fundamental Rights, which of the following parts of the Constitution of India reflect/reflects the principles and provisions of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)? (2020)
- Preamble
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Fundamental Duties
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.‘Economic Justice’ as one of the objectives of the Indian Constitution has been provided in (2013)
(a) the Preamble and the Fundamental Rights
(b) the Preamble and the Directive Principles of State Policy
(c) the Fundamental Rights and the Directive Principles of State Policy
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Does the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 ensure effective mechanisms for empowerment and inclusion of the intended beneficiaries in the society? Discuss. (2017)


Geography
Inland Waterways in India
For Prelims: PM Gati Shakti, National Waterway, Inland Waterways Authority of India, Multi-Modal Logistics Park, PM MITRA parks, Mega Food Parks
For Mains: Role of Inland Waterways in India’s transportation network, Infrastructure & Development
Why in News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has lauded the inauguration of the Inland Waterways Transport (IWT) Terminal at Jogighopa in Assam, highlighting India's vast inland waterways' (about 14,500 km of navigable waterways) potential for freight transport.
What are the Key Facts About Inland Waterways Transport Terminal at Jogighopa?
- IWT Terminal: Located in Assam, on the Brahmaputra River (National Waterway-2 (NW-2)).
- The Bangladesh Border (Dhubri) to Sadiya stretch of the Brahmaputra River (891 km) in Assam was declared NW-2 under the National Waterway Act, 1988.
- Significance: The Jogighopa IWT Terminal supports PM Gati Shakti, enhancing inland waterways for economic growth.
- It serves as an international port of call for Bhutan and Bangladesh, linking to the Multi-Modal Logistics Park (MMLP) at Jogighopa, boosting cargo movement and logistics in Assam and the Northeast.
- It boosts trade and commerce with neighboring countries. Reduces transportation costs and transit time.
- Strengthens India’s Act East Policy. Improves multi-modal connectivity by integrating road, rail, and waterways. Provides direct waterway access for Bhutan, reducing reliance on road networks.
What is Inland Waterways Transport?
- About: It refers to the movement of people and goods on navigable waterways such as rivers, canals, lakes, and other inland water bodies.
- Legislative Framework:
- Inland Waterways Authority of India Act, 1985: Led to the formation of Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) in 1986.
- IWAI is an autonomous organization responsible for the development, maintenance, and regulation of NWs.
- National Waterways Act, 2016: Declared 111 inland waterways as NWs for enhanced shipping and navigation.
- Inland Vessels Act, 2021: Replaced the Inland Vessels Act, 1917, introduced uniform regulations for inland vessels, ensuring safety, navigation, and compliance across India.
- Inland Waterways Authority of India Act, 1985: Led to the formation of Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) in 1986.
- Criteria to be as a National Waterway: A waterway qualifies as a National Waterway if it is navigable by propelled vessels, and 50 km long (except for urban areas and intra-port traffic).
- It should serve multiple states or connect a prosperous hinterland or major ports or support strategic navigation for national security or link unserved areas lacking other transport modes.
- Growth of Inland Waterways in India: 767% increase in operational National Waterways since 2014, and 635% rise in cargo handled.
- Cargo traffic grew from 18 to 133 million tonnes (FY 2023-24) at a 22% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR).
- Government Initiatives: Maritime India Vision 2030, Sagarmala Programme, and National Perspective Plan for interlinking rivers.
- Major National Waterways in India:
|
National Waterway (NW) No. |
Location(s) |
|
NW-1: Ganga-Bhagirathi-Hooghly River System (Haldia - Allahabad) |
Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal |
|
NW-3: West Coast Canal (Kottapuram - Kollam), Champakara and Udyogmandal Canals |
Kerala |
|
NW-4: Krishna River (Muktiyala - Vijayawada) |
Andhra Pradesh |
|
NW-10: Amba River |
Maharashtra |
|
NW-68: Mandovi River (Usgaon Bridge to Arabian Sea) |
Goa |
|
NW-73: Narmada River |
Gujarat, Maharashtra |
|
NW-100: Tapi River |
Gujarat, Maharashtra |
|
NW-97: Sunderbans Waterways (Namkhana to AtharaBanki Khal) |
West Bengal (through Indo-Bangladesh Protocol Route) |
What are the Benefits and Challenges in Developing IWT in India?
|
Category |
Benefits |
Challenges |
|
Cost & Efficiency |
Cost-effective and fuel-efficient transport mode |
High siltation and shoal formation increase maintenance costs |
|
Environmental Impact |
Lower carbon emissions and eco-friendly transport |
Seasonal depth fluctuations (many rivers have shallow depths) and dredging impact riverbeds, aquatic life, and lead to community resistance due to ecological concerns. |
|
Traffic Reduction |
Reduces congestion on roads and railways |
Lack of adequate navigational aids and waterways transport terminals |
|
Trade & Connectivity |
Enhances domestic and cross-border trade (e.g., Indo-Bangladesh Protocol route) |
Inconsistent water flow, as major portion is diverted for irrigation and industrial use |
|
Regional Development |
Boosts economic growth in remote areas |
Infrastructure gaps, including inadequate jetties and ports |
|
Tourism Potential |
Promotes river tourism and cruise industry |
Bridges and vertical clearance issues for large vessels |
|
Private Investment |
Encourages multi-modal transport integration |
Limited private sector participation and investment |
Way Forward
- Cargo and Passenger Movement: Integrate inland waterways with economic zones like PM MITRA parks and Mega Food Parks to boost cargo movement. Develop cruise tourism to enhance passenger transport via the Cruise Bharat Mission.
- Boost cargo movement under the Jalvahak Scheme with incentives and fixed scheduled services on key National Waterways.
- Financial & Policy Support: Create Inland Waterways Development Funds, enhance waterway-related infrastructure, preserve traditional navigation practices through the Riverine Community Development Scheme.
- Public-Private Partnership: Attract private investment in terminal development, vessel manufacturing, and cargo handling by providing financial incentives and tax benefits.
- Sustainable Development: Adopt green vessels, and sustainable dredging techniques are crucial for eco-friendly inland waterway development.
- These measures will reduce pollution, protect aquatic ecosystems, and ensure long-term navigability while maintaining environmental balance.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How can Inland Waterways contribute to India's multi-modal transport network |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Enumerate the problems and prospects of inland water transport in India. (2016)


Biodiversity & Environment
Climate Risk Index 2025
For Prelims: Climate Change, Climate Risk Index 2025, Floods, Drought, Cyclones
For Mains: Key Findings of the Climate Risk Index 2025, Impact of Climate Change, Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Why in News?
The international environmental think tank ‘Germanwatch’ has released the Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2025.
What is Climate Risk Index 2025 and its Key Findings?
- Climate Risk Index:
- About: CRI ranks countries based on their vulnerability to extreme weather events, assessing human and economic losses caused by climate-induced disasters.
- Frequency: Released annually since 2006, covering data from the past 30 years.
- Methodology & Criteria: CRI assesses the impacts of extreme weather events on countries across six key indicators: economic losses, fatalities, and affected people, both in absolute and relative terms.
- Findings of Climate Risk Index 2025:
- Between 1993 and 2022, over 765,000 lives were lost, resulting in economic losses of USD 4.2 trillion.
- The floods, droughts, and storms were the leading causes of global displacement.
- In 1993-2022, Dominica, China, and Honduras were the top-3 countries affected by extreme weather events.
- Myanmar, Italy, and India were among the other highly impacted countries.
- Pakistan, Belize, and Italy were the top-3 affected in 2022.
- 7 of the 10 worst-affected countries are low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
- Between 1993 and 2022, over 765,000 lives were lost, resulting in economic losses of USD 4.2 trillion.
- Impact on India: India ranked 6th most affected country (1993-2022), accounting for 80,000 fatalities (10% of global) due to extreme weather events and 4.3% of global economic losses (USD 180 billion).
- India has faced severe floods (1993, 2013, 2019), intense heat waves (~50°C in 1998, 2002, 2003, 2015), and destructive cyclones like Gujarat (1998), Odisha (1999), Hudhud (2014), and Amphan (2020).
Note: The Asia-Pacific (APAC) Climate Report 2024, by the Asian Development Bank projects that India may face a 24.7% GDP loss by 2070 due to climate change, driven by rising sea levels and declining labour productivity.
What are the Key Challenges Related to Climate Change Mitigation Strategies as per the Report?
- Historical Responsibility vs. Future Emissions: High-income nations, despite their historical emissions, demand greater climate responsibility from emerging economies like India and China, leading to tensions over burden-sharing and climate finance commitments.
- Global Temperature Breach: The 1.5°C threshold was breached for a full year in 2024, exposing inadequate mitigation efforts.
- Without higher ambition, including nationally determined contributions (NDCs), the world is on track for a temperature increase of 2.6–3.1°C by 2100.
- Weak Climate Commitments: Many countries are not updating their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), creating a gap between promises and action. Poor policy implementation further weakens mitigation efforts.
- Insufficient Climate Finance: The USD 300 billion annual funding for developing nations is inadequate, and delays in operationalizing the Loss and Damage Fund hinder support for climate-vulnerable countries.
Read More:
What are the Key Suggestions to Combat Climate Change as per the Report?
- Enhanced Climate Finance: Greater financial and technical support is needed for vulnerable countries to adapt and manage climate-induced losses and damages.
- Strengthening Mitigation Efforts: Nations must scale up their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to restrict global warming to 1.5°C or lower.
- Accountability of High-Income-High-Emission Countries: Developed nations must expedite mitigation actions to curb rising human and economic costs.
- Call for Urgent Climate Action: Timely action in adaptation & mitigation is needed to avoid escalating climate-related losses in the future.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the economic impacts of climate change and their influence on the global geoeconomic landscape. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of India’s preparation for Climate-Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements: (2021)
- The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is a part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research programme.
- The project of CCAFS is carried out under Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centres.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2 Which of the following best describes/describe the aim of ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India? (2016)
- Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’.
- Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future.
- Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q.3 With reference to ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- It is an initiative of the European Union.
- It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets.
- It is coordinated by World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (2021)
Q.2 ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How will India be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India be affected by climate change? (2017)


Important Facts For Prelims
Detection of Most Energetic Neutrino
Scientists detected the highest-energy neutrino using the KM3NeT (Cubic Kilometre Neutrino Telescope) observatory in the Mediterranean Sea.
- It was 30 times more energetic than any previously observed, 1015 times more energetic than photons, and 10,000 times more powerful than particles from the Large Hadron Collider, the world's largest particle accelerator.
Cubic Kilometre Neutrino Telescope (KM3NeT): KM3NeT is an under construction European research facility in the Mediterranean Sea that studies neutrinos.
- It's designed to detect neutrinos from distant sources and from Earth's atmosphere.
Note: India's Neutrino Observatory project is proposed to be set up at Pottipuram village in Theni (Tamil Nadu) in a 1,200-metre-deep cave.
What are Neutrinos?
- About: Neutrinos, often called "ghost particles", are electrically neutral, nearly massless subatomic particles that rarely interact with matter.
- This allows them to travel vast distances through stars, planets, and galaxies without being deflected by magnetic fields, making them reliable "cosmic messengers."
- Sources of Neutrinos:
- Natural Sources: Sun (solar neutrinos), Nuclear reactions in stars, supernovae, and cosmic rays.
- Artificial Sources: Nuclear reactors, radioactive decay and particle accelerators.
- Big Bang Neutrinos: Remnants from the early universe, contributing to cosmological studies.
- Types/Flavors of Neutrinos:
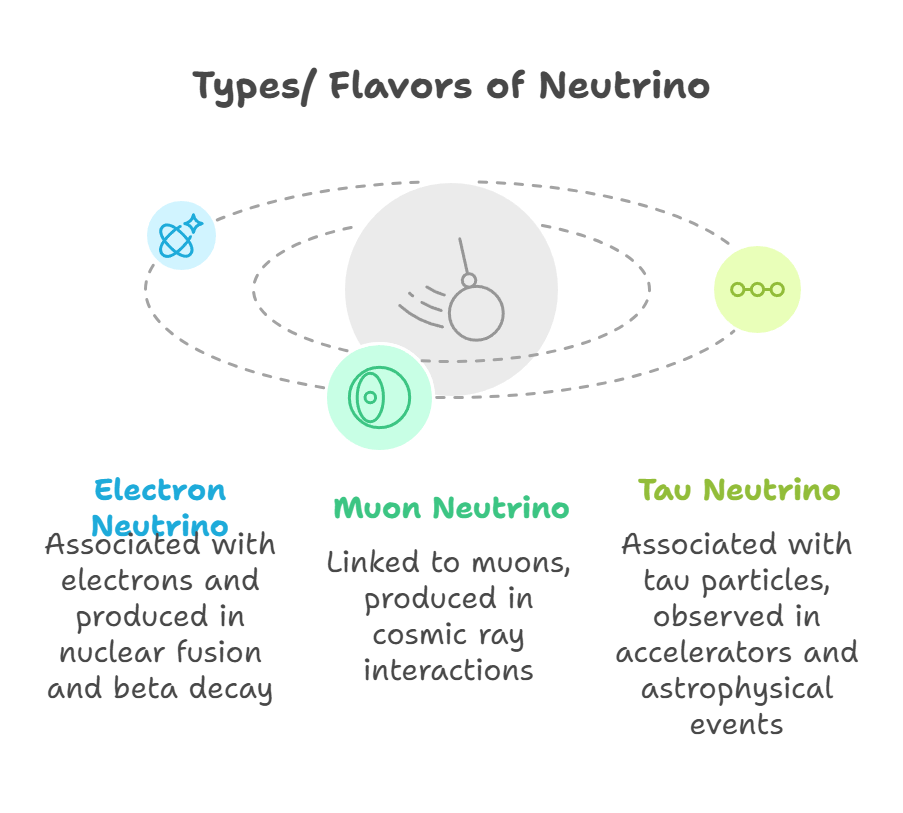
- Neutrinos undergo oscillation (change from one flavour to another) while traveling due to quantum mixing.
- Significance in Astrophysics:
- Neutrinos, unlike cosmic rays, travel undisturbed, making them crucial for tracing high-energy astrophysical events.
- Scientists detect neutrinos using deep-sea or ice observatories that capture Cherenkov radiation (a detectable flash of light) from rare interactions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of modern scientific research, consider the following statements about ‘IceCube’, a particle detector located at South Pole, which was recently in the news: (2015)
- It is the world’s largest neutrino detector, encompassing a cubic kilometre of ice.
- It is a powerful telescope to search for dark matter.
- It is buried deep in the ice.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
Parambikulam Tiger Reserve
A faunal survey at the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve (TR) in Kerala highlighted key species present in the reserve.
- Important species:
- Birds: Rufus-bellied hawk-eagle, Indian grey hornbill, Great Indian hornbill, Ceylon frogmouth etc.
- Butterfly: Five-bar swordtail, Spot swordtail, Southern birdwing (India’s second largest butterfly species), Nilgiri tiger etc.
- Others: Leopards, Lion-tailed macaques, Smooth-coated otters.
- About Parambikulam TR: It is located in the Palakkad and Thrissur districts of Kerala and declared a Tiger Reserve in 2009 under Project Tiger.
- It is a well-preserved ecological area within the Nelliampathy-Anamalai landscape of the Southern Western Ghats in India.
- It is home to the world's first scientifically managed teak plantation and boasts the largest and oldest teak tree, named Kannimara.
- The Parambikulam, Sholayar, and Thekkady rivers flow through the reserve.
Read More: Early Migration of Butterflies


Rapid Fire
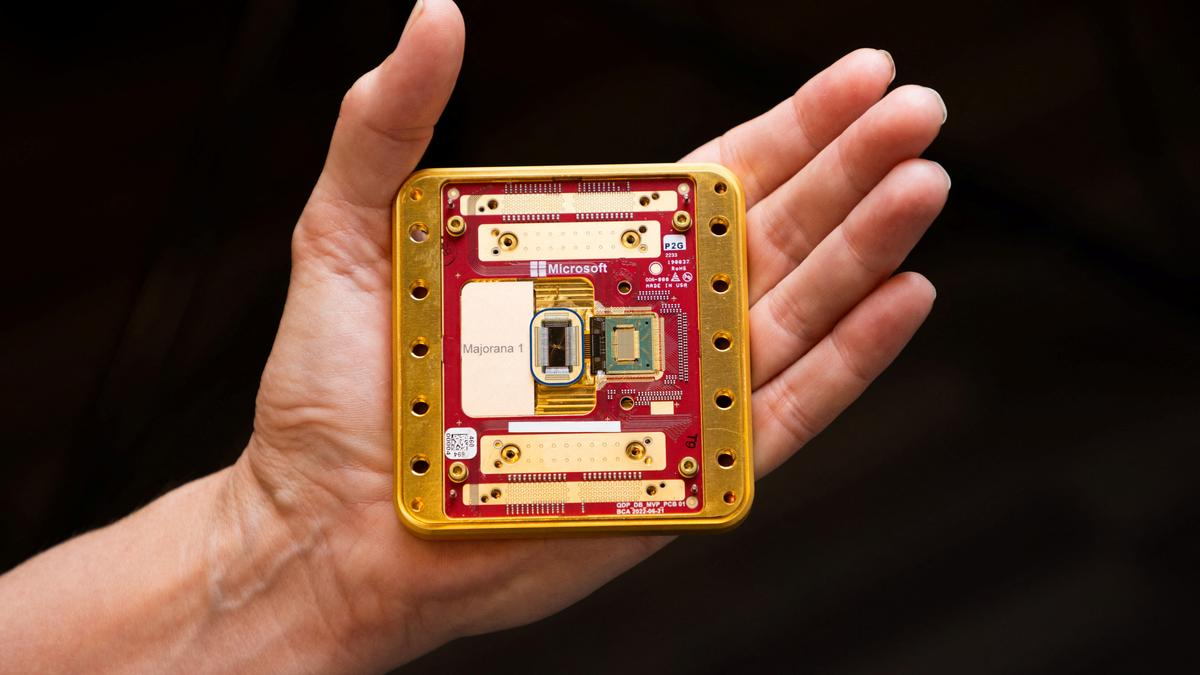
Majorana 1
Microsoft has introduced Majorana 1, the world's first quantum chip powered by a Topological Core architecture, which aims to revolutionize quantum computing.
- Key Facts About Majorana 1: It is the first quantum chip to utilize a Topoconductor (Topological Superconductor), creating a new state of matter beyond solids, liquids, or gases, but a topological state.
- It is composed of indium arsenide (a semiconductor) and aluminum (a superconductor), enabling enhanced quantum stability and performance.
- The chip relies on Majorana fermions that act as their own antiparticles.
- It features eight qubits, but its Topological Core architecture enables error-resistant scaling to one million qubits, ensuring stable quantum computations.
- Unlike classical computers using binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use qubits, which exist in multiple states simultaneously, enabling exponentially faster computations.
- Applications: Could help in breaking down microplastics, creating self-healing materials, improving healthcare solutions, and solving complex chemistry and materials science problems.
Read more: Quantum Technology


Rapid Fire
Dinesh Khara Committee
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has formed a 7 member committee, chaired by Dinesh Khara to review the Insurance Act, 1938.
- It aligns with the proposed Insurance Amendment Bill, which seeks to increase the FDI limit from 74% to 100%.
- Currently, Insurance Act, 1938 provides a broad legal framework to regulate the insurance sector.
- Key reforms under consideration:
- Composite licence (life, health, and general insurance), Captive licence,
- Differential capital (Adjusting capital needs based on risk profiles),
- Reduction in solvency norms, Change in investment regulations
- One-time registration for intermediaries etc.
- IRDAI is the statutory body established under the IRDA Act, 1999 and is responsible for regulating and promoting the insurance industry in India.
Read More: Insurance Sector in India


Rapid Fire
First BioBank in a Zoo
- India’s first wildlife bio-bank at Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (Darjeeling Zoo) is fully operational.
- Since its establishment in July 2024, it has collected DNA and tissue samples from 60 animals of 23 species, prioritizing endangered species.
- Biobank: The biobank (frozen zoo) preserves genetic material from animals for conservation and research.
- This includes cells, tissues, and reproductive samples of endangered and deceased animals.
- The samples are stored in cryogenic conditions (-196°C in liquid nitrogen) to maintain genetic diversity.
- It is part of a national conservation plan, in collaboration with the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB), under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- In future, biobanks are planned to be set up at Delhi National Zoo and Nandankanan Zoo (Odisha).
- Species like the American black-footed ferret and northern one-horned rhino have been revived using preserved DNA and captive breeding.
Darjeeling Zoo:
- It is India’s largest high-altitude zoo, specializing in captive breeding of alpine species like snow leopards, Himalayan wolves, and red pandas.
- It houses endangered fauna, including gorals, Siberian tigers, and rare birds.
Read More: Darjeeling Zoo’s Conservation Breeding Programme for Snow Leopards


Rapid Fire
Digital Brand Identity Manual
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has launched the Digital Brand Identity Manual (DBIM) to establish a standardized and seamless digital presence across all government platforms.
- DBIM: It standardizes color palettes, typography, and iconography across government websites, mobile apps, and social media while introducing Gov.In CMS, a centralized content management system for seamless updates.
- It ensures common UI/UX (user interface/user experience) principles for better accessibility and user experience of all government websites.
- The Central Content Publishing System (CCPS) of DBIM enables consistent updates of official announcements, policies, and schemes.
- Significance: DBIM enhances "Minimum Government, Maximum Governance" by ensuring a cohesive digital identity, improving accessibility, streamlining policy access and strengthening India’s e-governance leadership.
Read more: Navigating India's Digital Growth