Indian Economy
Vostro Accounts
Prelims: Foreign Trade, Currency Depreciation & Appreciation, Global Sanctions, Balance of Payments
Mains: Internationalization of Rupee, Effect of global sanctions on economy of India, Benefits and challenges of settling trade in Rupee, Intervention of government in economy
Why in News?
20 Russian banks have opened Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVA) with partner banks in India for the settlement of payments in rupee for trade between India and Russia.
- Also, all major domestic banks have listed their nodal officers to sort out issues faced by exporters under the arrangement.
What is the Background?
- In July 2022, the RBI had unveiled a mechanism to settle international transactions in rupee to promote the growth of global trade, with emphasis on exports from India, as well as pushing rupee as an international currency.
- It is also expected to enable trade with sanction-hit nations such as Russia.
- According to the mechanism finalized by the RBI, banks of partner countries can approach authorized dealer banks in India for opening special rupee vostro accounts. The authorized dealer bank will then have to seek approval from the central bank with details of such an arrangement.
What is SRVA arrangement?
- About:
- A vostro account is an account that domestic banks hold for foreign banks in the former’s domestic currency, in this case, the rupee.
- Domestic banks use it to provide international banking services to their clients who have global banking needs.
- The SRVA is an additional arrangement to the existing system that uses Freely convertible currencies and works as a complimentary system.
- The existing systems require maintaining balances and position in such currencies like US dollar and pound to facilitate trade.
- A vostro account is an account that domestic banks hold for foreign banks in the former’s domestic currency, in this case, the rupee.
- Framework:
- Three important components namely invoicing, exchange rate and settlement are there.
- Invoicing entails that all exports and imports must be denominated and invoiced in Indian National Rupee (INR).
- The Exchange Rate between the currencies of the trading partner countries would be market-determined.
- The Final Settlement also takes place in INR.
- Three important components namely invoicing, exchange rate and settlement are there.
- Functioning:
- The authorized domestic dealer banks are required to open SRVA accounts for correspondent banks of the partner trading country.
- Domestic importers are required to make payment (in INR) into the SRVA account of the correspondent bank against the invoices for supply of goods or services from the overseas seller/supplier.
- Similarly, Domestic exporters are to be paid the export proceeds (in INR) from the balances in the designated account of the correspondent bank of the partner country.
- Indian exporters may receive advance payment against exports from overseas importers in Indian rupees through the above Rupee Payment Mechanism.
- But, it would be foremost priority of the domestic bank to ensure that the available funds are used to meet existing payment obligations i.e., already executed export orders or export payments in the pipeline.
- All reporting of cross-border transactions is to be done in accordance with the extant guidelines under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999.
- Eligibility Criteria of Banks:
- The authorized domestic bank would seek approval from the apex banking regulator providing details of the arrangement when banks from partner countries approach for opening SRVA.
- Domestic banks are responsible to ensure that the correspondent bank is not from a country mentioned in the Financial Action Task Force (FATF)’s list of High Risk & Non-Co-operative jurisdictions.
- Authorized banks can open multiple SRV accounts for different banks from the same country.
What is the Purpose of the Arrangement?
- Reduced Demand of Forex: The Economic Survey (2022-23) had argued that the framework could largely reduce the “net demand for foreign exchange, for the settlement of current account related trade flows”
- It will further arrest fall of rupee as demand for forex reduces.
- Reduced Vulnerability to External Shocks: Reduced dependence on foreign currencies, would make the country less vulnerable to external shocks.
- Rupee as International Currency: In the long-term it will promote Rupee as an international currency once the rupee settlement mechanism gains traction
- As per the Bureau for International (BIS) Settlements’ Triennial Central Bank Survey 2022, the U.S. dollar accounts for 88% of all trades. The INR accounted for 1.6%.
- Trade with Sanctioned Countries:
- Ever since sanctions were imposed on Russia, trade has been virtually at standstill with the country due to payment problems.
- As a result of the trade facilitation mechanism introduced by the RBI, we see the payment issues with Russia easing.
What is a Nostro Account?
- A Nostro account is an account held by a bank in another bank. It allows the customers to deposit money in the bank's account in another bank. It is often used if a bank has no branches in a foreign country. Nostro is a Latin word that means “ours”.
- Let's presume bank "A" does not have any branches in the Russia, but bank "B" does. Now, to receive the deposits in the Russia, "A" will open a Nostro account with "B".
- Now, if any customers in the Russia want to send money to "A", they can deposit it into A's account in "B". "B" will transfer the money to "A".
- The main difference between a deposit account and a Nostro account is that the former is held by individual depositors while foreign institutions hold the latter.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Convertibility of rupee implies (2015)
(a) being able to convert rupee notes into gold
(b) allowing the value of rupee to be fixed by market forces
(c) freely permitting the conversion of rupee to other currencies and vice versa
(d) developing an international market for currencies in India
Ans: (c)


Governance
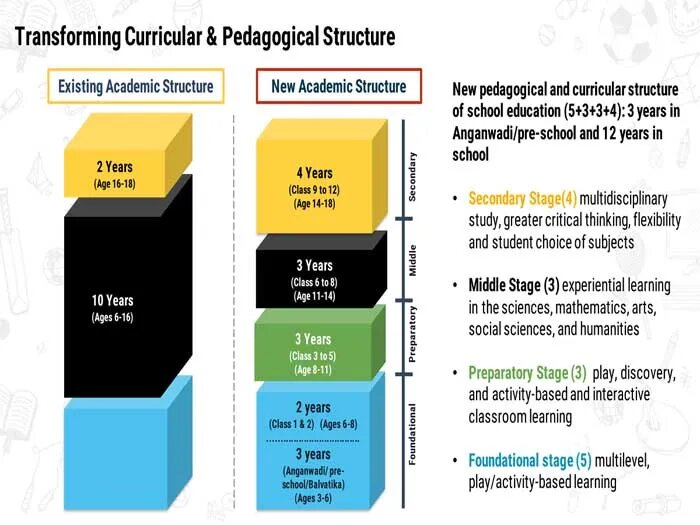
National Curriculum Framework for Foundational Stage
For Prelims: National Curriculum Framework, NEP, Right to Education
For Mains: Education System in India and related issues, NEP 2020
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Education has launched Learning - Teaching Material for the Foundational Stage under National Education Policy 2020 and Jadui Pitara was launched at the Occasion.
- In October 2022, the Ministry of Education launched the National Curriculum Framework for Foundational Stage (NCF-FS) education of children in the three to eight years age group.
What is Jadui Pitara?
- Jadui Pitara is a play-based learning-teaching material tailored for children between the age group of 3-8 years.
- It comprises playbooks, toys, puzzles, posters, flash cards, story books, worksheets as well as reflecting the local culture, social context and languages is designed to pique curiosity and accommodate the diverse needs of learners in the foundational stage.
- Jadui Pitara has been developed under the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) and is available in 13 Indian languages.
- It aims at enriching the learning-teaching environment and making it more child-centric, lively and joyful for the Amrit Generation as envisioned in the NEP 2020.
What is NCF?
- About:
- NCF is one of the key components of NEP 2020, that enables and energizes this transformation, informed by the aims, principles, and approach of NEP 2020.
- Four Sections of NCF:
- NCF for School Education
- NCF for Early Childhood Care and Education (Foundational Stage)
- NCF for Teacher Education
- NCF for Adult Education
- NCFFS:
- The NCF for the Foundational Stage (NCFFS) is developed based on the vision of the NEP 2020.
- The Foundational Stage refers to children in the age group of 3 to 8 years, across the entire range of diverse institutions in India.
- This is the first Stage in the 5+3+3+4 Curricular and Pedagogical restructuring of School Education as envisioned in NEP 2020.
- The NCFFS has been developed by NCERT through an extensive consultative process with States & UTs upto grass root level and various institutions and organisations.
- The NCF for the Foundational Stage (NCFFS) is developed based on the vision of the NEP 2020.
- Objective:
- It aims to help in positively transforming the school education system of India as envisioned in NEP 2020, through corresponding positive changes in the curriculum including pedagogy.
- It aims to realize the highest quality education for all children, consistent with realizing an equitable, inclusive, and plural society as envisaged by the Constitution of India.
What is the National Education Policy 2020?
- About:
- The NEP 2020 is a comprehensive framework for education reform in India that was approved in 2020, aiming to bring significant changes in the education system of India by providing a holistic and multidisciplinary approach to education.
- Features of the NEP 2020:
- Universalization of education from preschool to secondary level.
- Introduction of a new pedagogical and curricular structure based on cognitive and socio-emotional development of students.
- Emphasis on the development of foundational literacy and numeracy skills in primary education.
- Increased focus on research and development in education.
What are the Other Government Initiatives Related to Educational Reforms?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- As per the Right to Education (RTE) Act, to be eligible for appointment as a teacher in a State, a person would be required to possess the minimum qualification laid down by the concerned State Council of Teacher Education.
- As per the RTE Act, for teaching primary classes, a candidate is required to pass a Teacher Eligibility Test conducted in accordance with the National Council of Teacher Education guidelines.
- In India, more than 90% of teacher education institutions are directly under the State Governments.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (2020)


Biodiversity & Environment
Gross Domestic Climate Risk Ranking
Prelims: Gross domestic climate risk ranking, RCP8.5,
Mains: Climate risks, Adaptation and Mitigation
Why in News?
According to Gross Domestic Climate Risk ranking by Cross Dependency Initiative (XDI), India has nine states in the 50 high risk states including Punjab, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Kerala and Assam.
- XDI is a global organisation specialising in climate risk analysis for regions, banks and companies.
What is this Report About?
- The index calculated the ‘Physical climate risk’ to built environments such as buildings and properties across 2,600 States and provinces globally in 2050.
- The index assigned an Aggregated Damage Ratio (ADR) to each region, which signifies the total amount of damage a region’s built environment would sustain in 2050. A high ADR signifies more peril.
What are the Findings?
- Vulnerabilities:
- Risk originates from 8 climate change Hazards: Riverine and surface flooding, coastal inundation (coastal flooding), extreme heat, forest fire, soil movement (drought-related), extreme wind and freeze thaw.
- Most damage posed to built infrastructure globally is caused by “riverine and surface flooding or flooding combined with coastal inundation.
- Global Findings:
- According to report the vast majority (80%) of 50 provinces facing the highest climate risk to their physical infrastructure by 2050 are in China, the US, and India.
- Two of China’s largest sub-national economies – Jiangsu and Shandong – top the global ranking; followed by the U.S. which has 18 regions in the top 100 list.
- Asia dominates the list with 114 of the top 200 regions falling in the continent, including Pakistan, Indonesia and most South East Asian countries.
- Devastating flooding in 2022 affected 30% of the area of Pakistan and has partially or fully damaged more than 9 lac houses in Sindh province.
- India Specific Findings:
- Under high emissions scenarios such as the Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) 8.5 , high risk provinces will witness an average of 110% increase in damage risk by 2050.
- Currently, with 0.8 degrees rise in temperature, India’s 27 states and more than three-quarters of its districts are extreme event hotspots accounting for a 5% loss in GDP.
- If global warming is not limited to 2-degree thresholds, climate-vulnerable states in India will lose more than 10% of their gross state domestic product (GSDP).
- Bihar, Assam, and Tamil Nadu had the highest ADR among other Indian States. Assam, in particular, would witness the maximum increase of climate risk: rising up to 330% by 2050.
- Assam has witnessed an experienced exponential increase in flood events since 2011, and it had 15 of India’s 25 districts most vulnerable to climate change.
- 11 of the 36 districts in Maharashtra were found to be “highly vulnerable” to extreme weather events, droughts and dwindling water security.
- Under high emissions scenarios such as the Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) 8.5 , high risk provinces will witness an average of 110% increase in damage risk by 2050.
What is the Significance of the Report?
- The ranking data can also be significant for investors, as extensive built-up areas overlap with high levels of economic activity and property wealth.
- It can inform climate resilient investment, in conjunction with adaptation measures and infrastructure planning undertaken by state and provincial governments
- The finance industry can directly compare global industrial hubs like Mumbai, New York and Berlin using a like-for-like methodology to check vulnerability of global supply chains.
What are the Steps Taken by India regarding Climate Change?
- Global Leadership:
- India has already established its global thought leadership by founding institutions like International solar alliance (ISA) and Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI). Also, India gave stronger climate targets for 2030 in revised Nationally determined contributions (NDCs).
- It seeks to make India the climate solutions hub for the world by fostering systemic, technological, and financial innovations from the margins to the mainstream.
- Reforms in Transport Sector:
- India is accelerating its e-mobility transition with the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles Scheme.
- A voluntary vehicle scrapping policy to phase out old and unfit vehicles complements the existing schemes.
- India's Support to EVs:
- India is among a handful of countries that support the global EV30@30 campaign, which aims for at least 30% new vehicle sales to be electric by 2030.
- India’s advocacy of five elements for climate change “Panchamrit”, at the UNFCCC COP26 in Glasgow is a commitment to the same.
- Role of Government Schemes:
- The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana has helped 88 million households to shift from coal-based cooking fuels to LPG connections.
- Role of Industries in Low-Carbon Transition:
- The public and private sectors in India are already playing a key role in meeting the climate challenge, helped by growing customer and investor awareness, as well as increasing regulatory and disclosure requirements.
- Hydrogen Energy Mission:
- Focus on generation of hydrogen from green power resources.
- Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT):
- It is a market-based mechanism to further accelerate as well as incentivize energy efficiency in the large energy-intensive industries.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Which of the following best describes/describe the aim of ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India? (2016)
- Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’.
- Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future.
- Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- National Mission for a Green India, also known as Green India Mission (GIM), is one of the eight missions outlined under India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change. It was launched in February 2014.
- To increase forest/tree cover to the extent of 5 million hectares (mha) and improve quality of forest/tree cover on another 5 mha of forest/non forest lands. Separate sub-targets existing for different forest types and ecosystems (eg., wetland, grassland, dense forest, etc.). Hence, statement 3 is correct.
Q2. The scientific view is that the increase in global temperature should not exceed 2°C above pre industrial level. If the global temperature increases beyond 3°C above the pre-industrial level, what can be its possible impact/impacts on the world? (2014)
- Terrestrial biosphere tends toward a net carbon source.
- Widespread coral mortality will occur.
- All the global wetlands will permanently disappear.
- Cultivation of cereals will not be possible anywhere in the world.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Examine the status of forest resources of India and its resultant impact on climate change. (2020)
Q. “Policy contradictions among various competing sectors and stakeholders have resulted in inadequate ‘protection and prevention of degradation’ to environment.” Comment with relevant illustrations. (2018)


Governance
International Mother Language Day
For Prelims: International Mother Language Day, UNESCO, United Nations (UN), Bhasha Sangam, Namath Basai, National Education Policy 2020.
For Mains: India's Initiatives to Protect Indigenous Languages.
Why in News?
On International Mother Language Day, which was celebrated on February 21, 2023, it was revealed that India is losing many of its languages due to modernisation and globalisation, particularly because of the lack of education.
- The theme of 2023 is “Multilingual education – a necessity to transform education”.
What is International Mother Language Day?
- About:
- UNESCO declared 21st February as International Mother Language Day in 1999 and the World has been celebrating the same since 2000.
- The day also commemorates a long struggle by Bangladesh to protect its mother language Bangla.
- The resolution to mark 21st February as the International Mother Language Day was suggested by Rafiqul Islam, a Bangladeshi living in Canada.
- Aim:
- UNESCO has emphasised the importance of mother-tongue-based education for the preservation of linguistic heritage, and the International Decade of Indigenous Languages has been initiated to safeguard cultural diversity.
- Concern:
- According to the United Nations (UN), every two weeks, a language disappears and the world loses an entire cultural and intellectual heritage.
- In India, this is especially affecting tribal areas where children struggle to learn in schools that do not offer instruction in their native tongues.
- Only 6 tribal languages in the state of Odisha have a written script, leaving many without access to literature and learning materials.
What are Global Efforts for Protection of Languages?
- The UN has designated the period between 2022 and 2032 as the International Decade of Indigenous Languages.
- Earlier, the United Nations General Assembly had proclaimed 2019 as the International Year of Indigenous Languages (IYIL).
- The Yuelu Proclamation, made by UNESCO at Changsha (China) in 2018, plays a central role in guiding the efforts of countries and regions around the world to protect linguistic resources and diversity.
What are India's Initiatives to Protect Indigenous Languages?
- Bhasha Sangam: The government has launched the "Bhasha Sangam" program, which encourages students to learn and appreciate different languages, including their mother tongues.
- The program also aims to promote multilingualism and cultural diversity.
- Central Institute of Indian Languages: The government has also established the Central Institute of Indian Languages, which is dedicated to the research and development of Indian languages.
- Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT): The CSTT is providing publication grants towards the publications of University Level Books in regional languages.
- It was established in 1961 to evolve technical terminology in all Indian Languages.
- State-level Initiatives: There are also several state-level initiatives to protect mother tongues. For example, the Odisha government has launched the "Ama Ghara" program, which provides education in tribal languages to tribal children.
- Also, Namath Basai by Kerala State Government has proved to be very beneficial in educating children from tribal areas by adopting vernacular languages as medium of instruction.
Way Forward
- Despite the current grim situation, there is hope for India's mother tongues as the National Education Policy 2020 advocates for mother tongue-based education from the early stages of education to higher education. This could help these languages survive in the long-term, but it is important to address the question of linguistic justice and ensure that language is not a barrier to education.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2021)
- 21st February is declared to be the International Mother Language Day by UNICEF.
- The demand that Bangla has to be one of the national languages was raised in the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
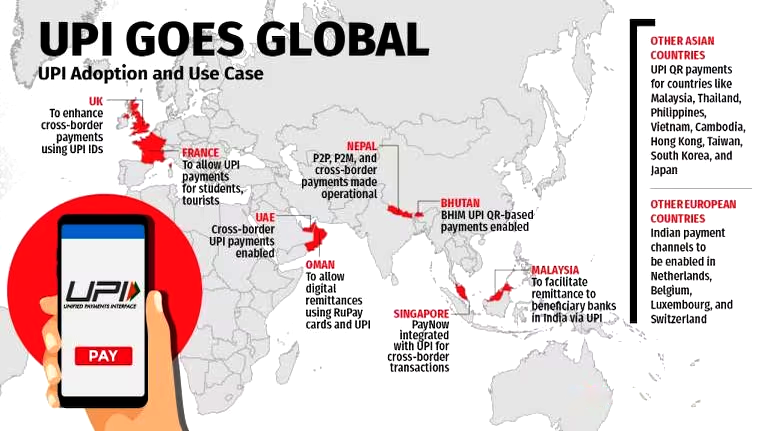
UPI-PayNow Integration
Why in News?
Recently, India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and Singapore’s PayNow have been integrated to enable faster Remittances between the two countries.
- Singapore has become the first country with which cross-border Person to Person (P2P) payment facilities have been launched.
- The UPI-PayNow partnership marks the world’s first to feature cloud-based infrastructure and participation by non-bank financial institutions.
What is UPI and PayNow?
- UPI:
- UPI is India’s mobile-based fast payment system, which facilitates customers to make round-the-clock payments instantly, using a Virtual Payment Address (VPA) created by the customer.
- VPA is a unique identifier assigned to an individual to facilitate the transfer of funds through a digital payments system. It is a user-created identifier that can be used instead of providing sensitive bank account details while making payments.
- It eliminates the risk of sharing bank account details by the remitter. UPI supports both Person-to-Person (P2P) and Person-to-Merchant (P2M) payments and it also enables a user to send or receive money.
- UPI is India’s mobile-based fast payment system, which facilitates customers to make round-the-clock payments instantly, using a Virtual Payment Address (VPA) created by the customer.
- PayNow:
- PayNow is a fast payment system in Singapore. It enables peer-to-peer funds transfer service, available to retail customers through participating banks and Non-Bank Financial Institutions (NFIs) in Singapore.
- It allows users to send and receive instant funds from one bank or e-wallet account to another in Singapore by using just their mobile number, Singapore National Registration Identity Card (NRIC)/Foreign Identification Number (FIN), or VPA.
- Linkage:
- With this facility, funds held in bank accounts or e-wallets can be transferred to /from India using just the UPI ID, mobile number, or VPA.
- This facility will eliminate the need for entering the details of beneficiaries, such as bank account numbers, bank codes etc.
What is the Significance of the Move?
- The project is expected to greatly benefit the Indian diaspora, especially migrant workers and students, in Singapore as it allows faster and cost-efficient funds transfer across both countries without the mandate of getting onboard the other payment system.
- As per the ministry of external affairs (MEA) document Population of Overseas Indians (2022), there are approximately 6.5 lakh Indians, including non-resident Indians and persons of Indian origin, currently residing in Singapore.
- Of the total inward remittances to India in 2020-21, the share of Singapore stood at 5.7%, according to the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) Remittance Survey, 2021.
- Integration of the system will bring down the cost of sending remittances by as much as 10%.
- By reducing the cost and inefficiencies of remittances between Singapore and India, the PayNow-UPI linkage will directly benefit individuals and businesses in Singapore and India that greatly rely on this mode of payment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements: (2018)
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following is a most likely consequence of implementing the ‘Unified Payments Interface (UPI)’? (2017)
(a) Mobile wallets will not be necessary for online payments.
(b) Digital currency will totally replace the physical currency in about two decades.
(c) FDI inflows will drastically increase.
(d) Direct transfer of subsidies to poor people will become very effective.
Ans: (a)
Q3. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) helps in promoting the financial inclusion in the country.
- NPCI has launched RuPay, a card payment scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
Moon Dust as a Solar Shield
Why in News?
Recently, a team of Researchers have published a study titled- “Dust as a Solar Shield”, proposing that launching Moon Dust into the stratosphere can slow down Global-Warming.
What was the Proposal?
- Solar Radiation Management:
- They proposed the regular transport of moon dust to a gravity point (Lagrange Point) between Earth and Sun to temper the ravages of global warming.
- They called it Solar Radiation Management (SRM) or Stratospheric Aerosol Injection, because by spraying aerosols in the stratosphere, it controls the Radiation of Sunlight reaching the Earth.
- Ideas for filtering solar radiation to keep Earth from overheating have been kicking around for decades, ranging from giant space-based screens to churning out reflective white clouds.
- Analogy with Volcanic Spew and Moon Dust:
- Artificially spraying Moon Dust into the stratosphere has been motivated from the fact that a sufficiently powerful Volcanic Eruption can spew sulphates and other aerosols into the stratosphere and thus cool the air there.
- Aerosols in the stratosphere, especially radiation-scattering ones such as sulphates, do have a cooling effect.
- Dimming of the amount of incoming sunlight with stratospheric aerosols will have similar outcomes as compared to the Moon Dust.
- When Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines blew its top in 1991, it lowered temperatures in the northern hemisphere by about 0.5C for nearly a year.
- Artificially spraying Moon Dust into the stratosphere has been motivated from the fact that a sufficiently powerful Volcanic Eruption can spew sulphates and other aerosols into the stratosphere and thus cool the air there.
- Efficacy:
- Blocking 1 or 2 % of the Sun's rays is all it would take to lower Earth's surface by a degree or two Celsius - roughly the amount it has warmed over the last century.
What can be the Consequences of this Technique?
- Spraying dust in the Stratosphere may cool summer but can lead to widespread Drought across the earth, sending crop yields plummeting, leading to disease and starvation.
- Any projections related to changes in rainfall, as a result of throwing dust into the atmosphere or in space to block sunlight, will be highly uncertain.
- Other climate mitigation strategies, such as the use of Renewable Energy, emissions reductions schemes, Carbon-Capture Technologies, and bioenergy, are not expected to have any dangerous unintended consequences. On the other hand, spraying aerosols even in a small pocket of the stratosphere will have global consequences that can’t fully be quantified at present.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Brain-Inspired Image Sensor can Detect Miniscule Objects
Why in News?
A new study at Indian Institue of science (IISc) has shown that a brain-inspired image sensor can go beyond the diffraction limit of light to detect miniscule objects such as cellular components or nanoparticles invisible to current microscopes.
What is this Technology?
- The technique combines optical microscopy with a neuromorphic camera and machine learning algorithms and presents a major step forward in pinpointing objects smaller than 50 nanometers in size.
- The diffraction limit prevents optical microscopes from distinguishing between two objects smaller than a certain size (typically 200-300 nanometers).
- The neuromorphic camera mimics the way the human retina converts light into electrical impulses.
- In neuromorphic cameras, each pixel operates independently, generating sparse and lower amount of data. The process is similar to how the human retina works.
- It allows the camera to “sample” the environment with much higher temporal resolution.
- In conventional cameras, each pixel captures the intensity of light falling on it and these pixels are pooled together to reconstruct an image of the object.
- In neuromorphic cameras, each pixel operates independently, generating sparse and lower amount of data. The process is similar to how the human retina works.
- The experiment used the neuromorphic camera to pinpoint individual fluorescent beads smaller than the limit of diffraction, by shining laser pulses at both high and low intensities, and measuring the variation in the fluorescence levels.
- As the intensity increases, the camera captures the signal as an “ON” event, while an “OFF” event is reported when the light intensity decreases.
- The data from these events were pooled together to reconstruct frames.
What is the Significance of this Technique?
- This approach can have widespread applications in precisely tracking and understanding stochastic processes in biology, chemistry and physics.
- It will help understand the thumb rules of biological processes like self-organisation.
- The team was also able to closely track the movement of a fluorescent bead moving freely in an aqueous solution using this technique.
What is a Stochastic process?
- It is a process involving the operation of chance and is also known as Random process.
- For example, in radioactive decay every atom is subject to a fixed probability of breaking down in any given time interval.
What is Diffraction Limit?
- The diffraction limit is a fundamental physical limit on the ability of an optical system to resolve or distinguish between two closely spaced objects.
- The smallest resolvable distance between two-point sources of light is determined by the size of the aperture or lens used to observe the objects, as well as the wavelength of the light being observed.
- In practical terms, this means that even with a perfect lens or telescope, there is a limit to how much detail can be resolved in an image.
- Objects that are closer together than the diffraction limit will appear blurred or indistinguishable in the image.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Announcement of Opportunity (AO)
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has made an Announcement of Opportunity (AO) to allow scientists and researchers to analyse data from the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission, AstroSat.
The space agency has made the AO soliciting proposals for 13th AO cycle observations from AstroSat. This AO soliciting proposal for the Thirteenth AO cycle is for Indian as well as international proposers as Principal Investigators (PIs) to utilise AstroSat observatory time. The observations will be carried out between October 2023 to September 2024.
This announcement is open to Indian scientists, researchers residing and working at institutes, universities and colleges in India for 55% of observing time and to non-Indian scientists, researchers, Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), working at space agencies, institutes, universities and colleges around the globe for 20% of observing time.
AstroSat is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray and UV spectral bands simultaneously, providing a space astronomy observatory operated by ISRO. AstroSat was launched in 2015 and completed seven years in orbit at the end of September 2022.
Read More: AstroSat, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
Live Transcription of Courtroom Proceedings
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) started a first-of-its-kind project to transcribe its proceedings live using Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The SC transcription is using Teres, which is a platform used often for transcribing arbitration proceedings. The transcript will also be shared with lawyers who argued cases for verification and is likely to be uploaded on the SC website every evening.
It is the second major decision towards making the court more transparent after the SC’s decision to livestream its proceedings before Constitution Benches.
In 2022, the Chief Justice of India (CJI) launched the digital platform FASTER (Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records) to communicate interim orders, stay orders, bail orders, etc, of the Supreme Court to authorities concerned through a secured electronic communication channel. The Supreme Court has also launched other programmes involving technology like AI based portal ‘SUPACE’ in the judicial system aimed at assisting judges with legal research.
In the United States, court transcripts are available to litigants and the public. The US’s SC provides audio and text transcripts of the proceedings. In the United Kingdom, a litigant can ask for a transcript of the court proceedings for a fee if the hearing is recorded.
Read More: Artificial Intelligence, Live-Streaming of the Supreme Court's Proceedings
World Day of Social Justice
Every year, February 20 marks the World Day of Social Justice across the globe.
The General Assembly determined that in 2007, February 20 will be observed annually as World Day of Social Justice. In 2008, the International Labour Organisation (ILO) endorsed the ILO Declaration on Social Justice for Equitable Globalization. This is the ILO's third major declaration of principles and policy since the ILO's Constitution of 1919.
This day promotes awareness of social injustice and breaking down barriers based on gender, age, race, ethnicity, religion, culture, or handicap. Several schools, colleges, and universities hold numerous activities and events on this particular day. So that people across the world understand the need to uphold social justice values.
The theme for this year focuses on the recommendations available on the common agenda prepared to strengthen global solidarity and to rebuild trust in government by "Overcoming Barriers and Unleashing Opportunities for Social Justice".
Read More: International Labour Organisation (ILO)
"Where justice is denied, where poverty is enforced, where ignorance prevails, and where any one class is made to feel that society is an organized conspiracy to oppress, rob and degrade them, neither persons nor property will be safe." -Frederick Douglas
Anubhuti Inclusive Park
Recently, the Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways laid the Foundation Stone of the world's largest and unique Divyang Park - Anubhuti Inclusive Park in Nagpur, Maharashtra.
This is the world's first inclusive disabled park that is made by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. Various projects have been conceptualized for the disabled as well as for the general public and senior citizens. The park will have adapted facilities for all 21 types of disabilities, it will have facilities like a touch and smell garden, hydrotherapy unit, water therapy, and independent room for mentally challenged children, and mothers.
In 2016, the central government passed the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act for the rights of persons with disabilities. This law is to give the disabled the right to live with dignity. Taking initiative under this, the Central Government has created some Divyang Parks in South India and Madhya Pradesh.
Read More: Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, Initiatives for the Empowerment of Disables